Why does stye appear?
Barley is formed at the moment of an explosion in the number of Staphylococcus aureus, which lives on the body of every person. The impetus for the growth of its numbers is weakening of the immune system and hypothermia. The risk of stye formation is greater in children than in adults, since their immune system is not yet fully developed. However, the reasons for its occurrence vary somewhat depending on age.
Causes of eyelid inflammation in adults
Most often, barley appears in adults due to external factors. Thus, the reasons for its formation are:
- Decreased immunity during the cold season, leading to the appearance of colds.
- Metabolic slowdown as a result of hypothermia.
- Blockage of the sebaceous glands and the formation of abscesses due to non-compliance with personal hygiene rules.
- Lack of vitamins in spring.
- Decreased immunity due to lack of nutrients caused by gastrointestinal disease.
- Blockage of the sebaceous glands and hair follicles due to furunculosis.
Sometimes the stye goes away, but then appears again. An example would be this case:
This may indicate problems with the immune system. In this case, you need to contact an immunologist.
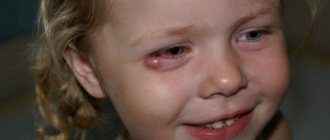
Why do children suffer from stye?
Children's immunity is formed by the age of 7. Until this point, their risk of developing barley is higher. The main reasons for its formation are the same as in adults. At the same time, the following are added to the list of factors that provoke inflammation of the eyelid:
- Hormonal imbalances during adolescence.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Neglect of hygiene rules when wearing contact lenses.
- Infection in premises where many people live.
The development of the inflammatory process can also provoke diseases of the visual organs.
Treatment
At the first sign of stye in a child, you should immediately contact a pediatric ophthalmologist. In an uncomplicated course, barley in a child responds well to treatment and usually goes away in 7-10 days. In most cases, local conservative therapy is carried out for barley in a child. At the beginning of the development of the inflammatory process, cleansing and daily disinfection of the eyelids is performed: treatment with a decoction of chamomile, calendula, extinguishing the infiltrate with 70% ethyl alcohol, 1% brilliant green solution. Before the head of the stye breaks through, the child is prescribed thermal procedures to the site of inflammation (dry heat, ultraviolet irradiation, UHF), which increase blood flow and natural drainage. Eye drops containing antiseptics (sodium sulfacyl solution), antibiotics (chloramphenicol, ciprofloxacin solution), and glucocorticosteroids (dexamethasone solution) are instilled into the conjunctival sac. Ointment applications of erythromycin and tetracycline ointments under the eyelid continue even after the opening of the child’s stye. To prevent the infection from spreading deeper when opening a stye, it is necessary to ensure that the child does not rub his eyes with his hands. In case of development of general symptoms (fever, malaise), the use of antipyretic, sulfonamide or antibacterial drugs is indicated. Surgical treatment is required for large external and internal barley that is not amenable to conservative treatment. Under local anesthesia, the child's stye is opened, followed by daily postoperative treatment of the purulent wound and antibacterial therapy. When barley recurs, the child is prescribed vitamins, immunomodulators, and autohemotherapy.
Characteristic symptoms
First of all, with excessive activity of staphylococcus, the eyelid becomes swollen and inflamed. A compaction with an abscess forms on it. The affected area turns red. In this case, discomfort such as itching, pain and a feeling of the presence of a foreign body in the eye appears. A severe inflammatory process can provoke the following phenomena:
- Temperature increase.
- Attacks of nausea.
- Decreased appetite.
- Headache.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
Styes cause tearing. Sometimes during inflammation, swelling occurs, making it difficult to open the eye.
Symptoms of the disease
Barley is a white or yellowish purulent head, which is located on the swollen red eyelid. But in some cases the head does not form, and the eyelid swells significantly.
Here we can talk about internal barley, which is also called meibomitis (an inflammatory process in the meibovian glands).
So, what are the symptoms of the disease? This:
- swelling in the eyelid area;
- painful sensations when touching the eyelid;
- redness, conjunctiva;
- Pain in the eyes;
- headache;
- slight increase in temperature;
- feeling of weakness.
Remember: with a mild form of the disease, complete recovery can occur within 4 days.
Classification
Barley varies in type and location. According to this classification, the following types of inflammation are distinguished:
- External. The infection develops in the ciliary bulb or sebaceous gland of Zeiss. Because of this, inflammation forms at the edge of the eyelid.
- Internal. Bacteria collect in the passage of the meibomian glands, leading to their irritation. In this case, barley forms on the eyelid from the inside.
- Hot. Short-term inflammation that resolves within a week. In this case, barley forms in the eyelash pocket.
- Cold. Characterized by damage to the passage of the meibomian glands. Inflammation develops over several months and involves the cartilage of the eyelid. The subcutaneous seal is large in size and resembles a bone.
Another name for cold stye is chalazion. If it puts pressure on the eyeball, it must be removed. Under more favorable circumstances, the chalazion may resolve on its own.
What types of barley are there?
The abscess can be located on the edges of the upper or lower eyelid so that it is visible from the outside - this type of stye is characterized as external. But it can also be internal, forming under the eyelid on the mucous membrane, and is called meibomite. This is a purulent inflammation of the meibomian glands. In the external form, the purulent formation usually opens and goes away without consequences (with proper treatment of barley), while the internal one is more dangerous. It causes great inconvenience: it rubs against the eyeball and feels like a foreign body, causing discomfort.
If it ruptures, pus will enter the surrounding tissues of the eye, which can cause the development of chalazion and conjunctivitis, as well as lead to the development of chronic meibomitis. Therefore, in this case, it is recommended to immediately go to the hospital, and not wait until the stye on the eye bursts inside on its own. If pus gets into the bloodstream, it can lead, for example, to sepsis.
First aid
To diagnose barley, a visual examination is sufficient. If it is possible to detect its signs in time, then it is possible to begin treating the inflammation in the first hours of its development and stop the further spread of the infection.
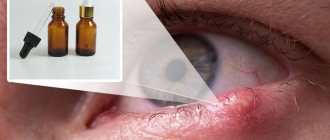
How to treat with an antiseptic
When treating barley with antiseptic agents, you must follow these steps:
- Soak a small piece of cotton wool in vodka or medical alcohol diluted with water in proportions of one to one.
- Squeeze out the cotton.
- Apply it to the place where the stye has formed.
This method is called cauterization. When using it, you should be careful. Be careful not to get the antiseptic in your eye. An alternative to alcohol is iodine or brilliant green. Cauterization of the stye stops inflammation on the day of the procedure.
How to Apply Dry Heat
To treat barley, a boiled egg and salt and flax seeds heated in a frying pan are used as dry heat. They are wrapped in a rag and kept on the barley until completely cooled.
Please note: The formation of pus is a contraindication for heating barley!
Stye on a child's eye
In most cases, purulent inflammation in a child’s eye is accompanied by swelling of the edge of the eyelid, which later leads to the formation of a papule. The source of infection in children most often occurs in the area of the eyelash follicle.
The disease requires mandatory therapeutic measures, otherwise the child’s vision may deteriorate significantly. The inflammatory process in children is accompanied by an increase in body temperature, chills, headaches, and a decrease in the body's protective functions.
The appearance of stye on a child’s eye can be caused by the presence of helminthic infestations, various allergic reactions, gastrointestinal disorders, and others. Since the immune system of children is in the process of development, the body cannot fully counteract the pathogenic effects of pathogenic microorganisms. In addition, immunity can be reduced due to hypothermia, overheating, colds and infectious diseases.
When establishing the first signs of the development of purulent inflammation in the eye, it is necessary to immediately show the child to a specialist - an ophthalmologist. In this case, with early diagnosis of the disease, the necessary therapy can be prescribed. Sulfonamides, in particular Albucid eye drops, are often used to treat styes in children. Ointments for external use have proven themselves well - tetracycline and chloramphenicol.
Eye stye in children at an early stage of its formation can be cured at home. When treating children under 1 year of age, Albucid drops are effectively used. External stye on the eye of a child from 2 years of age can be lubricated with a solution of brilliant green, iodine, and alcohol solutions 4 times a day, using a cotton swab for careful application. Compresses with chamomile are used in the treatment of purulent formation in children of any age.
If a child develops internal styes, hospital treatment is required. In some cases, antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. Most often, treatment of internal abscess in children involves surgical intervention, which involves artificial opening and washing of the cavity of the inflammation site using antiseptic agents.
Barley is a fairly harmless disease if it is diagnosed early and the necessary treatment is applied in a timely manner. The danger to the health, and in some cases, the life of the child, lies in the possible complications that can arise from improper or insufficient treatment of purulent inflammation. Under such circumstances, it is possible to develop a chalazion, a chronic disease characterized by the formation of an eyelid cyst, and treatment measures involve surgical intervention.
The occurrence of barley caused by hypothermia of the child’s body, as well as the frequent accompaniment of colds, may indicate a chronic course of the disease. The causes of relapses are most often immunity disorders or the presence of a focus of pathogenic microflora in the child’s body.
The greatest danger comes from mechanical opening of the abscess, which is likely to further spread the infection, which can cause blood poisoning, the development of sepsis, and death.
Methods for treating barley
Treatment of barley is aimed at conservative elimination of the inflammatory process. If an abscess has formed on the eyelid, which does not open within a week, the doctor resorts to surgical intervention.
Medicines against barley
Conservative treatment involves the use of the following medications:
- Antibiotic eye drops. Designed to stop infection. Penicillin, Levometicin, Tobrom and other drops have this effect. If barley is accompanied by conjunctivitis, then Albucid is prescribed. These medications can be used no more than 6 times a day.
- Antibiotic-based eye ointments. The purpose of use is the same as in the case of eye drops. The difference is that ointments interfere with vision when applied. Therefore, they are applied immediately before bedtime. When choosing an ointment against barley, you should pay attention to its composition. It should not contain corticosteroids. Most often, the doctor prescribes tetracycline or erythromycin ointment.
- Antibiotics for oral administration. Such medications are used for a week if local treatment does not help or there are several foci of inflammation and they cause complications. The purpose of their use is to combat symptoms and pathogens. Ampicillin or Doxycycline are most often prescribed.
- Antiseptics. Prescribed after the abscess has opened. The wound remaining after it is washed with a 30% solution of sodium sulfacyl or furatsilin.
Sometimes a combination of several types of medications is prescribed. If the course of the disease is favorable, one of them is sufficient. Folk remedies give a good effect during the treatment of barley. For example, this recipe:
Before using it, you must make sure that there is no allergy to the components and consult a doctor for advice.
What supports the treatment
Additional treatment is aimed at relieving associated symptoms and strengthening the immune system. Thus, Paracetamol will help reduce the temperature, Motilium will help to cope with nausea. At the moment when the swelling begins to subside and there is no increase in body temperature, the patient may be prescribed physical therapy.
How to speed up the breakthrough of an abscess
To speed up the process of breaking out the abscess, you can apply a warm compress to the eye. It is used until it begins to cool. If it becomes cold, the optic nerve may suffer from hypothermia. If you don't have a fever, you can lie down under a blue lamp. It will become a replacement for UHF therapy prescribed in medical institutions. If all else fails, you need to see a doctor to have the stye surgically opened.
Surgery for barley
Surgical intervention is indicated when the stye does not open for more than 10 days or a chalazion is detected pressing on the eyeball. To release pus from the abscess, the seal is pierced with a needle or an incision is made on it with a scalpel. The resulting wound is washed and treated with antibacterial ointment. To exclude the possibility of infection, protect the eye with a plaster or bandage.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of barley in a child is characterized by an acute onset and rapid increase in symptoms. The formation of external barley begins with the appearance of hyperemia and swelling in a limited area of the eyelid in the eyelash growth area. The child complains of pain when blinking and touching the site of inflammation, tingling and itching. The eyelid swells and thickens, which leads to a narrowing of the palpebral fissure, sometimes to the inability to open the eye. The inflammatory infiltrate quickly increases in size, and on days 2-3, as a result of purulent melting, an abscess with a yellowish head forms at the roots of the eyelashes. After 1-2 days, the barley spontaneously breaks out with the release of purulent contents and necrotic tissue particles. In a child, stye resolution may occur much faster due to the habit of frequently rubbing the eyes. After opening the stye, the child’s pain, swelling and hyperemia of the eyelid decrease, and by the end of the week the signs of inflammation disappear. In severe cases and with multiple styes, the child may be bothered by headache, fever, general weakness, accompanied by enlargement of the parotid and submandibular lymph nodes (lymphadenitis). With internal barley (meibomitis) in a child, inflammation develops less acutely, swelling and hyperemia become more noticeable when the eyelid is everted, redness and irritation of the conjunctiva of the eye may be observed. With internal barley in a child, the abscess is opened from the inner surface of the eyelid into the conjunctival sac. After spontaneous resolution of internal barley, granulation growths of the eyelid mucosa may appear. When a child’s immunity is reduced and there are foci of chronic infection, inflammation of the eyelids can take a protracted course with periodic relapses of stye. Squeezing out the contents of stye in a child is unacceptable, since it is dangerous for the spread of purulent infection with the development of orbital phlegmon, thrombophlebitis of the orbital eyelids, thrombosis of the cavernous sinus of the brain, and in rare cases, purulent meningitis with a risk of death. Malaise.
What actions are prohibited during the formation of barley?
Improper actions during the formation of barley can harm your health. To avoid this, you should not do the following:
- Squeezing out pus or opening an abscess without involving a doctor.
- Use of cosmetics.
- Applying wet compresses to the abscess.
- Warming up barley in which pus has accumulated.
- Visiting baths and saunas.
- Scratching and rubbing the eyes.
It is better to avoid walking if a stye has formed on your eyelid. If there is an urgent need to leave the house, for example, to visit a doctor, then a dry bandage should be applied to the eye.
What is forbidden to do when you are sick?
There are a number of mistakes made by people who try to cure stye on their own. Under no circumstances should you:
- try to get rid of the bubble by squeezing or opening;
- use of cosmetics;
- independently use wet lotions on the site of the disease;
- apply dry or any heat to the place of barley in the presence of pus;
- comb the area of the disease;
- climb with dirty hands;
- is in the cold.
You should definitely go outside with an eye patch on.
Prevention of inflammation
To minimize the risk of stye formation on the eyelid, the following rules must be followed:
- Take your personal hygiene rules more seriously.
- Avoid touching your face and eyes with dirty hands.
- Include foods fortified with vitamins and minerals in your daily diet.
- During cold seasons, take vitamins.
- Don't get too cold.
- Don't expose yourself to stress.
- Allow enough time for rest and sleep.
- Follow your doctor's recommendations when treating illnesses.
- Give up bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol).
- Do not self-medicate by taking medications without medical prescription.
If you have a purulent stye and it does not open within a week, consult a doctor. You cannot squeeze out the pus or open the abscess on your own. This will lead to complications.
Causes of barley
The reasons leading to the occurrence of the disease include:
- Failure to comply with hygiene rules
- Using someone else's or expired cosmetics, dirty brushes and applicators
- Untreated demodex
- Spending a long time in a dusty, dirty room
- Lack of vitamins
- Colds, hypothermia, decreased immunity
- Constant stress
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Worm infestation
- Chronic infection
Often the inflammatory process occurs after rubbing the eyes with dirty hands.
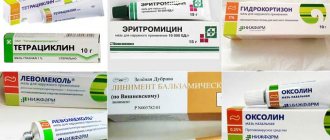
Ointments for stye on the eye
Ointments used in the treatment of purulent eye diseases are no less effective than drops for stye on the eye. The antibacterial agents included in their composition effectively neutralize foci of inflammation, and their consistency allows them to act directly on pathogens. It is important to apply ointments with clean hands, squeezing a small amount onto the little finger, and then applying to the inner surface of the lower eyelid. To treat styes on the eye, use Tetracycline, Erythromycin, and Hydrocortisone ointments.
Erythromycin ointment
known for its pronounced antibacterial effect, neutralizing pathogenic organisms. Erythromycin contained in the ointment is destructive to most pathogenic microorganisms. Erythromycin ointment is used in the treatment of conjunctivitis, keratitis, blepharitis, and stye. Apply the ointment by applying it to the lower eyelid 3 times a day. The treatment period is individual, depends on the stage of the inflammatory process and is prescribed by an ophthalmologist. General restrictions on use are no more than two weeks. Erythromycin ointment is contraindicated for people with severe kidney and liver dysfunction, as well as for allergy sufferers. It is also used in the treatment of conjunctivitis and styes in infants.
Hydrocortisone ointment
known for its anti-edematous effect, reduces the intensity of the inflammatory process during barley, and also has a pronounced antihistamine effect. The ointment is successfully used in the treatment of uveitis, styes, eyelid dermatitis, blepharitis, and conjunctivitis. The ointment helps restore the cornea after chemical and thermal damage.
Tetracycline ointment
has an anti-inflammatory effect during the course of blepharitis, conjunctivitis, keratitis, and the initial stage of development of barley. A mandatory consultation with an ophthalmologist is required before starting to use the ointment, since, despite the absence of significant side effects, in some cases allergic reactions may occur in patients caused by individual intolerance to certain antibiotics. The ointment is not used in the treatment of children under 12 years of age, pregnant and lactating women. Apply the ointment to the lower eyelid 5 times a day. The duration of the course of use is prescribed by a specialist depending on the stage and nature of the disease.