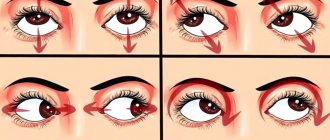
In the modern world, there are various diseases of the organs of vision, which are sometimes very difficult to combat. A disruption of the normal structure of the vitreous body of the eye, in which it loses its transparency, is called destruction of the fibers of the reticular structure of this part of the visual organ. This condition is characterized by such manifestations as blurred vision, dots and spots flickering in front of the eye.
At first, these manifestations may not even affect the quality of life. However, without proper treatment, destruction can only intensify. This will lead to serious visual impairment. Often such processes occur against the background of age-related changes, as well as under the influence of a number of negative factors. To identify the exact causes of destruction, it is worth undergoing a comprehensive examination.
How is cloudiness of the eye body treated? Destruction can be reduced using folk remedies. This therapy is considered safer than traditional medicine. Folk remedies help restore vitreous tissue and normalize blood circulation in the eyeball. Using these procedures helps slow down the process of vision deterioration. In this review, we will look at the main treatment methods and their effectiveness.
Retinal detachment
Retinal detachment occurs when the retina, a thin layer at the back of the eye, pulls away from the blood vessels that provide it with essential oxygen and nutrients.
According to the National Eye Institute, symptoms can appear quickly. Without prompt treatment, permanent damage and vision loss can occur.
Symptoms of a retinal detachment may include:
- gray or black spots floating in the field of vision;
- shadows on the sides or in the middle of the field of view;
- flashes of light that may occur in one or both eyes.
Treatment of retinal detachment
Without prompt treatment, retinal detachment can cause permanent vision damage.
Treatment will involve reattaching the retina. The doctor may recommend freezing, laser surgery, or surgery.
Causes of blurred vision in one eye
The root causes that provoked the appearance of blurred image quality in one eye are:
Infectious lesion
Infection by infectious microflora is possible after surgery, failure to comply with hygiene rules, or by air. The pathology develops with additional symptoms and inflammation, and also leads to blurred vision.
Mechanical injury
Due to foreign particles entering the visual organ, damage to the visual organ develops. Trauma leads to a decrease in picture quality. Particles can get into either 1 eye or 2 at the same time. To eliminate foreign particles, it is necessary to rinse the visual organ under running water. For more active tissue regeneration, it is recommended to avoid prolonged work at the monitor and not to overload the visual apparatus.
Inflammatory reactions of the conjunctiva
Temporary one-sided clouding of the picture develops as a result of the inflammatory process in the conjunctival area. Additional symptoms of the pathological condition are swelling of the eyelids and intense lacrimation. In rare cases, the formation of purulent masses is observed.
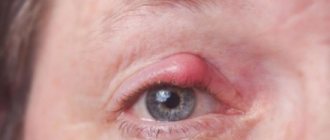
Barley
An abscess forms in the eyelid and can block the view of one of the eyes. If pathology appears, it is advisable to consult an ophthalmologist to prevent the development of an abscess.
Retinal detachment
The disease develops due to thinning of the retina. A complication of the pathology is complete loss of vision. The root causes of detachment are age-related degenerative processes and diseases of the eyeball.
Overwork
Due to prolonged work at the monitor and overstrain of the eye organs, fatigue of the visual apparatus appears. There may be a temporary blurring of the picture of a one-sided or two-sided nature.
Age-related changes in the lens
After 50 years, changes in the functioning of the visual apparatus begin, which are associated with the age factor. Farsightedness develops and chronic pathologies become more complicated. To reduce destructive processes, it is advisable not to overwork the visual apparatus and balance the diet.
Oncological formation of the nervous system
Neoplasms lead to circulatory disorders and mechanical damage to the visual apparatus. Due to the development of the tumor, loss of vision in the eye that is closer to the disease is possible.
Diabetes
Increased blood glucose levels cause retinal damage. Sugar pathology negatively affects the vascular system of the body. The visual organs may lack nutrients, which leads to one-sided blurred vision.
Cardiovascular diseases
Vessels transport useful components to all organs and systems. Disturbances in the functioning of the vascular system lead to hypoxic conditions or a lack of useful components.
Drying of the conjunctiva
Due to interaction with the environment, the mucous membrane bears the greatest impact of negative factors. As a result of their action, drying out or increased evaporation of moisture from the surface of the visual organs is observed. To eliminate the pathological condition, it is recommended to use appropriate medications as needed.
Glaucoma
Due to the development of glaucoma, the image in one of the organs of vision may become clouded. Jumps in blood pressure inside the eye cavity provoke a deterioration in the functionality of the vascular system of the visual apparatus. To restore picture clarity, a consultation with an ophthalmologist and properly selected therapy is necessary.
Loss of vitreous transparency
Cloudiness of the vitreous body causes hemorrhages in the eye cavity. A characteristic symptom of the pathological condition is the formation of floating spots in front of the visual apparatus. Surgery is necessary to eliminate the clouding.
Refractive errors
Pathological conditions provoke the development of anomalies:
- myopia;
- astigmatism;
- farsightedness.
Incorrect or prolonged wearing of contact lenses
As a result of prolonged wearing of lenses, inflammation of the eyeball occurs, and the quality of the image when looking at it deteriorates. Improper hygiene procedures provoke the addition of pathological microflora.
Concussion
A concussion occurs after a head injury. Along with vision changes, concussion symptoms may include:
- mood changes
- confusion
- amnesia
- headache
- dizziness
- drowsiness
Treatment for concussion
Once the doctor is satisfied that the injury is not severe, treatment will focus on relieving symptoms. The victim may need to rest for approximately 24-48 hours.
You can also take over-the-counter pain medications to reduce headache symptoms.
You should not take medications that may alter cognitive function or sleep patterns, as this may mask the symptoms of a concussion.
Stroke
Strokes can cause blurred vision in one or both eyes. Symptoms of a stroke include:
- numbness of the face, leg, or arm, usually on one side of the body;
- confusion and difficulty speaking or understanding;
- vision problems in one or both eyes;
- difficulty walking, as well as dizziness and lack of coordination;
- sudden and severe headache.
If you suspect a stroke, you should immediately call an ambulance. The following rules will help you quickly identify a stroke:
- Face : Ask the person to smile, with a stroke one side of the face will be lower than the other.
- Arms : Ask the person to raise both arms; in a stroke, one arm will fall.
- Speech : Ask the person to repeat a simple phrase. During a stroke, a person will pronounce it unintelligibly.
- Time : If any of the listed symptoms are detected, call an ambulance immediately, minutes are counting!
Endophthalmitis
Endophthalmitis is a severe infection and inflammation of the fluid or tissue inside the eye. In addition to sudden blurred vision, symptoms of endophthalmitis may include:
- Pain in the eyes;
- redness of the eyes;
- sensitivity to light.
If not treated quickly, endophthalmitis can lead to blindness.
Treatment of endophthalmitis
Treatment may include injections of antibiotics or antifungal medications. Emergency surgery may be required.
Flashing of flies before the eyes as a symptom of other diseases
Sometimes floaters can be evidence of more serious problems in the body. Therefore, if there is a sudden increase in the number of such opacities, you should definitely consult an ophthalmologist.
It is especially important to receive timely medical care in cases where, in addition to floaters, the patient also observes sparks, lights, and a sudden loss of peripheral vision.
In some cases, eye floaters are symptoms of:
- retinal detachment
- bleeding in the eye
- retinal tear
The above violations require immediate medical intervention from experienced doctors. If all the necessary assistance is not provided on time, the patient may completely lose his vision.
Almost every person faces this problem - redness of the eyes, causes, treatment methods
You can learn how to treat strabismus in children by reading this publication.
What causes diplopia, as well as ways to combat this disease, can be found in this article:
Signs of floaters in the eyes
Floaters move with eye movement. As a rule, they disappear if the patient tries to focus on one of them. In this case, floaters in the eyes can take on different shapes, for example, black or gray dots, curved lines, thread-like stripes, rings and cobwebs.
Once floaters appear in the eyes, they are unlikely to completely disappear over time, but after some time their number may decrease.
Giant cell arteritis
Giant cell arteritis, also called Horton-Magath-Brown syndrome or temporal arteritis, is an inflammation of the blood vessels in the temples.
In addition to blurred vision, temporal arteritis may also cause headaches. Typically, this disease only affects adults over 50 years of age.
Treatment of giant cell arteritis
To prevent permanent vision damage, your doctor will prescribe immediate treatment with corticosteroids.
Age-related macular degeneration
Age-related macular degeneration is a disease that can affect the retina, causing blurred vision.
According to the National Eye Institute, age-related macular degeneration is more common in older adults, and it can develop in one or both eyes.
Treatment for age-related macular degeneration
According to the National Eye Institute, there is no treatment for early stages of age-related macular degeneration.
Lifestyle changes, such as stopping smoking, can help slow its progression in the early stages.
If the disease progresses, your doctor may recommend medication injections into the eye to relieve symptoms, or laser treatment to slow vision loss.
Complications
Sometimes destruction causes such visual impairments that do not allow a person to live a normal life. However, the disease may not cause discomfort in the initial stages. But, if treatment is not started in a timely manner, the destruction will rapidly progress and ultimately cause irreversible changes in the structure of the vitreous body. Cloudiness of the vitreous humor of the eye is only the first sign.
Possible serious consequences of this condition include the following:
- visual acuity disappears and complete blindness ultimately occurs;
- the retina detaches;
- wrinkling of the vitreous body.
Macular hole
Macular holes are small tears or holes in the retina and usually affect people over the age of 60.
With a macular hole, a person may notice distortion or blurriness when looking straight ahead, and straight lines may appear wavy.
Treatment of macular hole
Some macular holes may heal over time. However, in most cases, your doctor will recommend a surgical procedure called a vitrectomy.
Eye infections
Some eye infections may require prompt medical treatment, depending on the severity of the symptoms.
Keratitis
Keratitis is an inflammation or infection of the cornea. Symptoms of keratitis include watery eyes, redness, irritation and pain in the eyes.
Treatment will depend on the underlying cause of the inflammation, but may include antibiotics, antiviral or antifungal medications in the form of eye drops or tablets.
Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis is a bacterial or viral infection that affects the blood vessels in the membrane around the eyeball. Allergies can also cause conjunctivitis.
Symptoms of conjunctivitis may include blurred vision, discharge from the eyes, and a pink or red color to the white of the eye.
Your doctor may prescribe topical or oral antibiotics for a bacterial infection or recommend over-the-counter antihistamines for conjunctivitis caused by allergies.
There is no treatment for a viral infection.
Orbital cellulitis (orbital cellulitis)
Cellulitis is a bacterial or fungal infection that can affect the eyelids and eyeball.
Symptoms of orbital cellulitis may also include bulging eyes, problems with eye movement, and fever.
Treatment may include antibiotics and surgery to drain the fluid.
Uveitis
Uveitis is an inflammation of the uvea, the choroid of the eyeball that also contains the iris.
Doctors separate inflammation of the iris itself, calling it iritis.
Uveitis is usually caused by bacterial or fungal infections.
Symptoms may include blurred vision, pain and sensitivity to light, and the disease may affect one or both eyes.
To treat uveitis, your doctor may prescribe steroid medications.
How to treat eye diseases in children under one year old
After returning from the maternity hospital, parents should closely monitor the development of the baby, not missing the moments of development of visual functions. The first visit to an ophthalmologist lasts up to three months. It is during this time that most congenital diseases are diagnosed. If pathologies have not been established, the next visit to the doctor is planned when the child reaches six months and the main structures of the eye begin to mature, affecting the focusing of the image.
The first symptoms of most diseases before one year of age are:
- the appearance of strabismus;
- slow tracking of a moving object or its complete absence;
- discharge that can accumulate on the eyelids and in the corners of the eyes;
- redness of the tunica albuginea.
As a rule, impaired function is restored with adequate treatment. Therefore, you should not put off visiting a doctor and self-medicate. At the ZIP 100% clinic, after consultation, the doctor will offer the most painless and informative examination. The necessary treatment and surgical intervention are carried out by high-class specialists.
When to ask for help
If you experience severe blurred vision and one or more of the following stroke symptoms, you should call 112 or go to your nearest emergency department:
- numbness or weakness in the face, leg, or arm on one side of the body
- confusion and difficulty communicating or understanding others
- difficulty walking, dizziness, or lack of coordination
- Strong headache
Loss of vision or blurry vision accompanied by severe eye pain requires immediate treatment. This will help prevent further damage to the eye and help identify any serious underlying condition that is causing the cloudy vision.
Risk factors
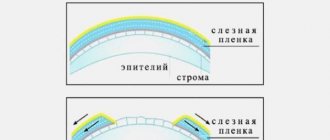
Proteins are a dense and fairly large outer shell of the visual system. Cloudy eyes may indicate the presence of disorders not only in the sclera, but also in the tear film, cornea, and conjunctiva.
The visual apparatus has a rather complex structure, the functioning and regulation of which is carried out by certain centers of the brain. The causes of failures of this system can be pathologies of the structure of the eye itself, damage to nerve fibers, as well as various kinds of disorders of the brain and central nervous system.
I would like to immediately note that the protein does not always become cloudy due to some kind of disease. Sometimes this occurs due to severe eye strain, for example, after spending a long time in front of the TV or computer. Changes in eye color are observed during emotional shock and lack of sleep.
Cloudiness in the eyes can also be associated with a change in the chemical composition of the blood, which occurs when overworked or spent a long time indoors. Age-related changes can lead to thinning of the membranes of the visual organ. During pregnancy, hormonal changes occur. It is difficult for the body to cope with such a restructuring, which is why cloudiness is sometimes observed. To identify the provoking factor, it is best to consult an ophthalmologist.
However, the causes of cloudy eyes can be much more dangerous.
Let's highlight the main risk factors:
Signs of cataracts and glaucoma
- increased intracranial pressure;
- glaucoma – increased intraocular pressure;
- blepharitis - inflammation of the eyelid;
- acidosis - acidic reaction of the blood;
- migraine;
- dry eye syndrome;
- myopia – myopia;
- hyperopia – farsightedness;
- corneal injuries;
- cataract – clouding of the lens;
- violation of the integrity of the tear film;
- vitreous opacification;
- fibrous dystrophy;
- tumor process;
- burn;
- violation of water-salt balance;
- presbyopia – senile farsightedness;
- thorn, scotoma;
- anemia – low hemoglobin;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- hypoglycemia – decreased blood glucose;
- astigmatism – absence of a focal point;
- bad habits: smoking, overeating;
- conjunctivitis - inflammation of the conjunctiva;
- exposure to ultraviolet radiation;
- Raynaud's disease;
- exposure to toxins - nicotine, lead, ethyl and methyl alcohol;
- improper use of contact lenses;
- consequence of surgery;
- penetration of a foreign body.
As the membrane becomes thinner, the sclera may acquire a bluish tint. Redness is usually caused by pathologies of an inflammatory nature.
A newborn baby's eyes are cloudy, and his gaze seems to wander and is shrouded in a veil. This is a variant of the norm. The baby tries to look around, but is still unable to focus his gaze on something.
Blurred vision often occurs after a bad sleep