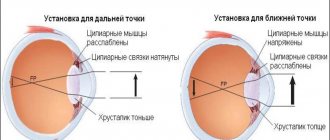
Causes
Predisposing factors to the development of pathology are:
- scleritis;
- genetic abnormalities;
- destructive processes in the eyeball area;
- parasitic diseases;
- uncontrolled use of medications;
- prolonged rubbing due to incorrectly selected corrective optics;
- pathological lesions of the eyelids;
- allergic reactions;
- entry of foreign particles into the organs of vision;
- due to surgery, namely complications after it;
- parasites entering the eye chamber.
Feedback on treatment results
Reviews from patients indicate that the choice of treatment method for conjunctival cysts is purely individual. Surgical intervention or drug treatment is based on determining the size of the formation and the degree of spread.
- Marina, 34 years old, Olenegorsk: “I treated a conjunctival cyst twice. The first time - with the help of drops. It resolved quite quickly. It’s just not clear: spontaneously or due to the effects of the drug. Now I had to have surgery because the pathology had returned. It went by very quickly. There’s nothing left anymore.”
- Vladimir, 40 years old, Nizhny Novgorod: “The cyst appeared not so long ago. It grew very quickly. It became difficult and painful to watch. The doctor decided to perform surgery. After it, the eye began to look terrible. I had to resort to plastic surgery. Everything is fine now, I hope there will be no relapse.”
- Svetlana, 58 years old, Saransk: “My grandson has a small lesion on the white of his eye. They showed him to the ophthalmologist. It turned out that it was a cyst. The doctor recommended not to use anything for now. And he turned out to be right. The cyst resolved on its own in just a couple of weeks.”
See the world with healthy eyes
Classification
Depending on the root causes that provoked the development of the disease, several forms of cysts are distinguished:
- Implantation. Develops as a result of trauma to the organs of vision and penetration of the integumentary epithelium into the eye cavity. Occurs as a result of surgical intervention.
- Congenital. Pathology develops against the background of abnormalities during intrauterine development. It is possible to diagnose the pathology after the birth of the child.
- Stromal. The cyst is characterized by spontaneous appearance and resorption. The disease is reborn in a new zone. Education is characterized by rapid growth.
- Exudative. It is a consequence of glaucoma. Develops as a result of prolonged use of anticholinesterase medications.
- Spontaneous. Develops without taking into account predisposing factors. It is divided into 2 subspecies: pearl and serous forms.
- A dermoid cyst is a benign formation in the area of the visual apparatus. Pathology develops against the background of disturbances in the intrauterine development of the fetus. Externally it is characterized by round or oval shapes. The growth of dermoid formation is slow.
- Post-inflammatory. The cyst progresses during the rehabilitation period or due to stagnation of the lymph process. An additional provoking factor is the inflammatory process in the area of the eye apparatus.
- Retention. Progresses at the sites of damage. The provoking factor is trauma. Externally, the formation resembles a ball filled with mucus. In this pathological condition, there is no pain syndrome.
Depending on the number of neoplasms they are divided into:
- single;
- multiple.
Neoplasms develop in various areas of the visual apparatus:
- subepithelial;
- intraepithelial.
Depending on the type of formation, the following types of cysts are distinguished:
- pearl;
- conjunctival cyst;
- serous;
- iris pigment cyst;
- exudative;
- degenerative corneal cyst.
Causes
All conjunctival cysts can be divided into congenital and acquired. The former are quite rare, arising as a result of genetic pathologies of the visual organs or individual structural features of the eyeball. The most common type is retention tumors of the acquired type. The most common factor that provokes the formation of a dermoid cyst of the conjunctiva is damage to the transparent membrane by infectious agents. The pathological process can develop against the background of the following diseases:
- conjunctivitis;
- scleritis;
- microphtholmia and other congenital eye diseases;
- blepharitis;
- canaliculitis.
The following reasons for the formation of dermoid formation on the conjunctiva can also be identified:
- eye injuries;
- impaired lymphatic drainage;
- parasitic diseases;
- turning of the eyelids;
- degenerative processes in the eyeball;
- surgical intervention;
- inflammatory processes;
- long-term use of certain eye drops.
A conjunctival cyst does not always arise as a result of any pathological process. Sometimes the formation is formed due to severe rubbing of the eyes or even for no apparent reason.
Symptoms
The main symptomatic manifestations of the formation of a corneal cyst are:
- narrowing and blurred vision;
- the appearance of translucent dots before the eyes;
- dull bursting pain;
- eyelid deformation;
- reduction in picture quality;
- narrowing of the field of view;
- blurry outlines of objects when looking at them;
- formation of floating flies;
- conjunctival hyperemia;
- increased intraocular pressure;
- the appearance of a yellowish area.
Possible consequences
Complications of dermoids in children can be the most serious - they can negatively affect the developing visual system and cause serious visual impairment (astigmatism, strabismus).
The lack of therapy creates the preconditions for complications such as:
- cavity growth;
- restrictions on the mobility of the eyeball;
- decreased visual acuity;
- cyst germination into the cornea of the eye;
- degeneration of a cyst into a neoplasm of other types, including malignant;
- increased intraocular pressure, which can provoke a whole range of pathologies (optic atrophy, retinal detachment, glaucoma).
Reference! A cystic cavity can cause changes in the shape of the eyelids and/or create a cosmetic defect.
Treatment
Removal of the cyst takes place according to several methods of therapy:
Surgical intervention
If there is a small-scale formation, it is eliminated using laser equipment. This technique allows not only to eliminate the cyst, but also to destroy the pathological cells next to it. Due to the manipulation, there is no need for a long rehabilitation period. Large formations are eliminated by surgery. Anesthesia is used for the procedure to reduce pain.
Drug therapy
To eliminate the pathology, drops with a corticosteroid composition are prescribed. Additionally, antibiotics and desensitizing drugs are used. Therapy can stop the progression of the pathology, but does not completely cure. To treat cysts, medications are prescribed:
- Oftalmoferon;
- Albucid;
- Aktipol;
- Oftan.
To eliminate swelling and lacrimation, antiallergic drugs are prescribed.
Traditional herbal medicine
It is treated using traditional medicine recipes, permissible only after consultation with an ophthalmologist, which is necessary to prevent the development of complications. Several ways to treat education:
- wash the area of formation with morning dew;
- treatment of the affected area with algae infusion;
- bury the organs of vision with a solution of cornflowers.
Treatment methods for dermoid on the eye
The choice of dermoid treatment method depends on:
- localization of education;
- quantities;
- extent of distribution;
- reasons for occurrence.
Medication
Conservative treatment includes:
- eye drops;
- antibiotics;
- glucocorticosteroids;
- trichloroacetylic acid injections.
The following are prescribed as eye drops:
- moisturizing (Defislez, Alkon Systane, Slezin);
- anti-inflammatory (Dexamethasone, Inndocollir, Tobradex).
During treatment of a conjunctival cyst, it is forbidden to use contact lenses to avoid additional infection.
To prevent dry eye syndrome from interfering with your life and work, use Cationorm eye drops.
Differential diagnosis
Operations
If there is no effect from conservative methods, the patient may be indicated for surgery:
- surgical;
- laser
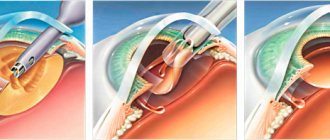
Surgical intervention:
- carried out in the presence of a voluminous education;
- Before surgery, local anesthesia and contrast agent are administered;
- the painted area is removed and a self-absorbing suture is applied;
- In some cases, plastic surgery is performed.
Laser Application:
- necessary for small-sized formations;
- the affected area is cauterized with a special beam.
Artificial tears will help relieve discomfort
Advantages of laser surgery:
- short rehabilitation period;
- absence of cosmetic defect;
- bactericidal, anti-inflammatory effect;
- there is no chance of infection;
- passes almost always without complications.
This method is not used for large lesions due to the risk of burning the conjunctiva. The contents heat up and the cyst may rupture.
After any intervention, the patient is prescribed a gentle regime and anti-inflammatory therapy. Forbidden:
- lift weights;
- visit the pool and sauna;
- use cosmetics;
- wear contact lenses.
In some cases, treatment of the cyst is not indicated for the patient. Regular outpatient monitoring and specialist supervision are carried out. Even after removal, the risk of pathology returning remains.
The tumor may fester. Inspections should be performed as often as possible.
Read what the diagnostic method of keratometry is here.
Non-steroidal pain reliever
Complications
If you have a genetic predisposition to congenital formations, you must visit an ophthalmologist at least 2 times a year. After removal of the tumor, it is advisable to avoid visual stress. Complications of the disease develop due to a large formation. There may be an increase in the level of pressure inside the eye cavity and a decrease in image quality. After the manipulation, to prevent complications, it is advisable to:
- limit physical stress;
- It is forbidden to self-prescribe medications;
- reduce the load on the visual apparatus.
Symptoms and diagnosis
You can suspect the presence of a cyst based on the following signs:
- visual presence of yellow or brown spots on the white of the eye;
- tearfulness;
- pain in the eyes;
- discomfort;
- redness of the white;
- movement of the eyeball may occur;
- sometimes there is a cloudy spot in visual perception.
Sometimes the cyst does not manifest itself in any way other than being visible on the sclera. Even if other symptoms are not felt, you should consult a specialist.
When an invisible enemy creates noticeable problems - eye demodicosis symptoms and treatment.
Tearfulness is one of the first signs of cyst development
Diagnosing education is not difficult. This is done by using:
- visual inspection;
- ophthalmoscopy;
- visometry;
- tonometry;
- biomicroscopy;
- histology and biopsy of the material (after removal).
Tissue examination after separation of the cyst is necessary to determine the atypicality of the formation.
How to treat retinal dystrophy is described in detail in the article.
Retention view
Before starting treatment, carefully read the instructions - instructions for using Katachrom eye drops.
Prevention
The main preventive recommendation against the development of pathology in the area of the visual apparatus is compliance with hygiene rules. Prevention can reduce the likelihood of a neoplasm:
- Before going to bed, be sure to wash off cosmetics from the organs of vision;
- follow the rules for wearing devices to correct picture quality;
- carry out preventive exercises at least 2 or 3 times a week;
- carry out daily hygiene of the sebaceous glands;
- balance your diet by filling it with fresh vegetables and fruits.
Diagnostics
An experienced ophthalmologist can suggest a diagnosis even during an external examination of the patient.
And to clarify you need to do:
- examination using a slit lamp. If the cyst is located in the eye and not on the eyelids;
- visual acuity test;
- visual field check;
- eye pressure measurement;
- X-ray, tomography;
- histological examination (if there is a suspicion of malignancy).
Useful video
The appearance of a cyst is provoked by many factors, not only external influences, but also internal causes. The most common form of formation is a dermoid cyst. Due to removal of the formation, short-term rehabilitation is observed. If small cysts are eliminated, recovery is possible the next day.
Author's rating
Author of the article
Alexandrova O.M.
Articles written
2031
about the author
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale!
( 1 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
If you have any questions or want to share your opinion or experience, write a comment below.
Classification by type
According to histological characteristics, they are divided into:
- Stromal. - Appear anywhere in the eyeball. - They can grow intensively, then they resolve on their own and disappear. - High probability of relapse.
- Epithelial. - Formed during the intrauterine growth of the baby. - Consist of epithelial tissue. — They are translucent and have a brown tint. “They can also be diagnosed in adults when the growth begins to increase in size.
- Pearl. — Dense neoplasm of bluish-white color.
- Conjunctival. — The surface consists of epithelium, inside there are secretory secretions. Divided into: • Implantation. After eye surgery. • Retention. Stagnation of lymph and other fluids.
- Serous. — Transparent capsules with liquid inside.
By localization they are divided:
- cyst on the cornea of the eye. You can't always notice them on your own. Diagnosed during a routine examination by an ophthalmologist;
- formation in the eyeball area;
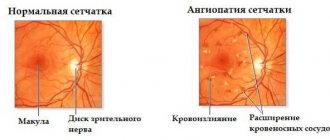
- neoplasm of the retina. At the same time, vision decreases;
- cyst on the eyelid.
Several pathologies may occur. Then doctors diagnose polycystic disease. This is how a lower eyelid cyst can form and then appear on the upper eyelid.
Causes of the disease
Heredity is one of the main factors of the disease.
A cyst can appear in the womb, early or teenage years. Chronic illnesses, abuse of tobacco products, and various alcoholic beverages carry the greatest risk to the fetus. And they lead to the appearance of dermoids in the eyes. Another cause of the neoplasm can be trauma, wounds, mechanical damage, surgery, or removal of the pterygium. According to ophthalmologists, a parasitic and inflammatory process can lead to the disease. There are cases when the disease occurs without any prerequisites.
Impaired fluid outflow from the glands and inflammatory processes can be caused by low-quality decorative cosmetics. It contains a lot of oils that cause clogged pores.
Hypothermia also causes cyst formation. It is often found on the lower eyelid, but can also appear on the upper eyelid. The pathology is not related to the skin. If you press on it, it will be able to move freely. The eyelid turns red. And the sizes can vary from a few millimeters to 1 cm.
Diagnosis of the disease
To make an accurate diagnosis of a cyst that has formed, it is worth going through a number of procedures:
- External examination of the skin of the eyelids and face.
- Visiometry - this study reveals a person’s visual acuity, which may be reduced due to certain diseases.
- Perimetry.
- Analgizemetry - allows you to determine the sensitivity of the cornea.
- Biomicroscopy of the eye.
- Examination of the eyes for the presence of transparency of their environment.
- Ophthalmoscopy.
Chalazion treatment
If we talk about Moll cysts, then you will have to take scrapings from the affected skin to determine antibodies to the virus. A general blood test is also taken to determine whether inflammation is present in this disease. When diagnosing a dermoid cyst, computed tomography or MRI is considered an effective method; they visualize in detail the required area with the cyst.
Varieties
There are several types of the disease in question. Each person has a specific treatment program.
- Exudative. It is a consequence of glaucoma.
- Congenital. Appears due to the separation of part of the iris, which protrudes beyond the mucous membrane.
- Traumatic. Damage leads to it. For example, during impacts or as a result of surgical work.
- Post-inflammatory. It originates from illiterate treatment of concomitant diseases.
- Spontaneous. The reasons for the appearance cannot be determined. Such a cyst is usually transparent, and its relative inconspicuousness makes it difficult to detect.
- Dermoid. Solid in consistency. Characterized by disturbances in the development and order of movement of epithelial cells. As a result, vision deteriorates and the eyeball becomes displaced. Often occurs against the background of Goldenhar syndrome (for example, certain abnormalities of the ears).
- Pigmentary. It is provoked by potent anticholinesterase drugs designed to reduce intraocular pressure. As a rule, for recovery it is enough for the drug to stop entering the body.
- Retentional. The most harmless form. This is a thin-walled bubble filled with colorless contents. In most cases it disappears on its own. It only causes discomfort when it is located in the center of the organ.
| Single and multiple cysts are also distinguished. The former affect the upper or lower part of the eyeball, the latter - the proximal fornix of the conjunctiva. |
Single and multiple cysts are also distinguished. The former affect the upper or lower part of the eyeball, the latter - the proximal fornix of the conjunctiva.
Specifics of treatment in children
Preschoolers and newborns are more susceptible to developing dermoid cysts than adults. The reason is a violation of the development of the embryo. Drops and ointments will not help here. The patient’s readiness to “go under the scalpel” is determined by the ophthalmologist to whom the parents register the baby.
During a fifteen-minute operation performed on a child under seven years of age, general anesthesia is used. Local anesthesia is used for older children. In a boy or girl, conjunctival cystosis requires regular monitoring in the hospital. There is a risk of developing astigmatism, strabismus, and amblyopia.
What is a cyst
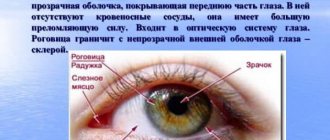
The human eyeball is covered with a thin mucous film - the conjunctiva, which performs a moisturizing and protective function. Cystic formations that appear on the membrane are small yellowish or pinkish bubbles filled with liquid.
The pathology is benign, but it is noted that lack of treatment can lead to the transformation of the defect into a severe tumor.
It is quite easy to notice the cavity - the cyst is based on the anterior chamber of the eyeball. The neoplasm can be seen more clearly in the photo.
Complications and prognosis
The operation and postoperative period proceed favorably in most cases. The visual organ is being restored. Relapses are rare and are possible when the capsule is not completely removed.
Possible complications after surgery:
- Hemorrhages due to mechanical trauma to tissue.
- Infectious complications due to the penetration of microbes during or after surgery.
- Dehiscence of the seam if the doctor’s recommendations are not followed.
- Corneal erosion due to trauma.
If complications occur, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. Seeking help in the early stages allows you to quickly cope with complications.
Symptoms of the disease
The pathology of the conjunctiva is not difficult to detect with the naked eye - the formation looks like a small bubble filled with liquid.
Often the disease is asymptomatic and does not cause discomfort. There are cases when a cystic cavity forms overnight, and during the day not a trace remains of it. Accordingly, such a neoplasm can be visualized only in the morning.
The most common signs of the presence of a hollow vesicle on the conjunctiva are the following symptoms:
- redness of the outer mucous membrane of the eye, in particular the area around the cyst itself;
- sensation of sand or foreign body in the eye;
- involuntary lacrimation;
- pressure inside the eye;
- limiting the field of view;
- points before the eyes;
- discomfort and pain, characterized by dryness in the eye;
- cloudiness and blurriness of images observed by a person.
In complex forms of the disease, displacement of the eyeball and blurred vision may occur.
Prognosis and prevention
When the presence of a conjunctival cyst is established, there is no need to panic. If you promptly contact an ophthalmologist, the likelihood that the problem will go away is high. He will tell you the details of prevention that speeds up recovery and reduces the risk of relapse.
Commonly recommended measures:
- wash off makeup at night
- exclude mascara and eyeliner if symptoms persist
- refuse lenses
- daily washing with warm water
- apply damp cotton wool
- prefer foods containing a lot of omega-3 fatty acids (fruits, flaxseed oil, vegetables)
- gentle massage of the eyelids against swelling, five-minute sessions twice a week (squeezing liquid is prohibited)
- undergo examinations (if relatives have a similar disease, consultations with a doctor are needed at least twice a year)
- fight redness with compresses (a decoction of guava leaves is prepared, gauze is soaked in the solution, the “application” is placed on the eyelid three times a day).