Causes of blurred vision
There are the following reasons for the appearance of this symptom:
Refractive errors
- Myopia. Blurry vision in one eye or both eyes may be a sign of nearsightedness. A person tries to squint his eyes and experiences eye strain and a headache.
- Astigmatism. Blurred vision at all distances is a symptom of astigmatism. The appearance of astigmatism is caused by the irregular shape of the cornea. Astigmatism can occur only in one eye or in both eyes.
- Farsightedness. Blurred vision from farsightedness causes objects at close range to become blurry. In cases of high farsightedness, even distant objects may be blurry.
- Presbyopia. If you are over 40 years old and have begun to experience blurred vision when looking at small print and objects at close range, then this is presbyopia. The condition is associated with loss of elasticity of the lens.
Cataract
The appearance of blurred vision, as well as glare and “halos” around light sources, can be signs of cataracts.
Glaucoma
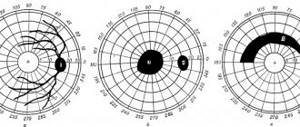
Foggy vision or “tunnel vision” may indicate glaucoma. Symptoms may include a gradual or sudden narrowing of your visual fields, accompanied by the development of severe blurred vision.
Age-related macular degeneration
Gradual loss and blurring of vision combined with distortion of straight lines are signs of macular degeneration. Leading cause of vision loss in old age
Vitreous opacities
The appearance of destruction of the vitreous body is also accompanied by this symptom.
Chronic dry eye syndrome
Dry eye syndrome can affect your vision, causing occasional blurred vision.
Migraine
Often, with a migraine, flashes of light, flickering and blurred vision appear before an attack.
Pregnancy
Deterioration of vision and blurred vision during pregnancy is associated with changes in hormonal levels. Hormones during pregnancy can change the shape and thickness of the cornea, causing this symptom.
Wearing contact lenses
Violation of the terms of wearing lenses causes the appearance of protein deposits in them. which can cause blurred vision.
What does fog in the eyes mean, reasons and how does the phenomenon manifest itself?
blurred background defocusing city people crowd
Sometimes, when looking at surrounding objects, you get the feeling that there is a haze or a veil in front of your vision, and the “picture” becomes unclear, and in addition you may feel dizzy. This phenomenon is known in ophthalmology, but it does not have a medical name, and despite this, such a symptom can tell an experienced specialist a lot.
Foggy eyes and its symptoms
The appearance of fog before the eyes is almost always a sign of some kind of ophthalmological disorder, but this is not necessarily a pathological deviation. Sometimes this is a temporary phenomenon associated with a disorder of the functions of the visual organs.
Attention! Blurred vision can affect one eye (unilateral) or both eyes (bilateral). In this case, the veil may not be continuous, but may be located in certain areas of the visual field, the acuity of which is lost.
Causes of foggy eyes
In most cases, the causes of blurred vision are exclusively ophthalmological in nature, including:
1. Clouding of the lens, characteristic of cataracts.
In patients aged sixty years and older, this is the most common cause of foggy vision, and it can occur in one or both eyes.
2. Opacities on the cornea.
This can occur both due to inflammatory pathologies and as a result of burns (thermal and chemical), injuries of various origins and degenerative processes.
3. Pathologies affecting the optic nerve.
In this case, fogging is the very first and relatively “harmless” symptom, and after some time, in addition to the uncomfortable fog, the patient may also experience pain.
4. Retinal lesions.
This includes all types of uveitis, diabetic retinopathy, chorioretinitis and macular degeneration.
Very often, fog occurs due to refractive errors such as astigmatism, farsightedness or nearsightedness.
Remember! As a rule, the problem is solved with the start of using optics, but if even when putting on contact lenses, a person’s fogging does not go away, this is a reason to look for the cause in other ophthalmological pathologies.
What if the fog is in only one eye?
Blurring often occurs in only one of the organs of vision. Almost always this indicates diseases such as iridocyclitis, conjunctivitis and keratitis of various origins. But it is possible to say precisely about such reasons only in the presence of other characteristic additional symptoms (redness of the conjunctiva, pain in the eyes, loss of the visual field). Sometimes fogging remains for some period after a person has cured one of the above diseases.
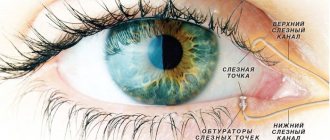
This phenomenon is normal if it lasts only a few days: this is the period of restoration of the tear film, disturbed during the instillation of eye drops. If the fog does not go away, you need to contact an ophthalmologist, who will prescribe drops of the “artificial tear” group: they help restore this protective layer and the fog will quickly disappear.
Fog in the head and eyes
This phenomenon may be due to several reasons:
– development of glaucoma;
– state of alcohol intoxication;
– vasospasms;
- hypertonic disease.
Keep in mind! In glaucoma, fog occurs due to deformation of the eyeball, which in turn occurs when intraocular pressure increases.
As for vasospasms, these are spasms of the ocular vessels, as a result of which slight oxygen starvation of the tissues of the eyeball occurs and this kind of refractive error is observed. But in this case, the fogging passes quickly.
In case of alcohol poisoning, the causes of fog in the head and eyes do not lie in the field of ophthalmology: we are talking about a toxic effect on the brain.
As a result, he cannot control the organs of vision, synchronize their actions and “adjust clarity.”
Diagnostics
Symptoms such as fog in the eyes are a subjective sensation of a person, and at the same time, everyone describes such a sensation differently, and the degree of fogginess may be different for everyone.
Important! For this reason, ophthalmologists cannot draw conclusions about the presence of a disease based only on anamnesis. It is necessary to carry out a number of diagnostic measures:
1. After taking a history, the patient may have blood taken for general and biochemical analysis, as well as a urine test. Such methods make it possible to detect inflammatory processes in the body, assess the general condition and identify diabetes (if this disease is present, fog may also appear before the eyes).
2. A more detailed diagnostic method is biomicroscopy, which allows you to identify inflammation and swelling specifically in the organs of vision. This method also makes it possible to detect leukocytes, lymphocytes, cellular fluid and adhesions in the middle membranes of the eyes - the presence of such objects indicates uveitis, which is also characterized by clouding.
3. Additionally, in case of such complaints, intraocular pressure is measured, an increase in which indicates the possible development of glaucoma.
Treatment for foggy eyes
There is no treatment for eye fog as such. When contacting an ophthalmologist and after performing all the necessary tests, the doctor must establish the root cause why the patient has such visual impairment. It is possible that the treatment will be transferred to another specialist: for example, if diabetes is the cause of the fog, the endocrinologist is competent to give the patient recommendations on proper nutrition and prescribe insulin and other appropriate medications.
Sometimes the cause of fog can be pathological processes in the brain. In this case, a neurologist or oncologist comes into play. In this case, the patient is additionally prescribed an MRI and CT scan of the brain, since tumors that arise near the visual centers of the brain can also influence the development of such vision defects.
Need to know! The simplest case is refractive error: just choose the right glasses or contact lenses and the problem will be resolved.
Interestingly, the correct selection of optics for the initial stage of cataracts in many cases also eliminates this disorder.
How to treat cloudy eyes
Glasses, contact lenses, or refractive surgery (LASIK) are the most common ways to correct refractive errors.
Age-related presbyopia affects almost everyone over the age of 45. Most people use reading glasses or special lenses (multifocal, bifocal or progressive lenses for presbyopia).
For chronic dry eye syndrome, artificial tears or moisturizing gels will help.
Cloudy eyes due to cataracts can be treated with surgery. For glaucoma, it is necessary to prescribe eye drops that reduce eye pressure. In some cases, surgical treatment is necessary.
Causes
Blurred vision is most often caused by abnormalities in the structure of the visual organ. Among such deviations are:
- Development of the inflammatory process in the structures of the visual organ. The process is caused by infection, mechanical damage or dystrophy. If treatment is neglected, temporary pathologies caused by burns or injuries can become chronic;
- Cataract, which is characterized by clouding of the lens of the organ of vision. This disease most often develops in older people;
- Pathologies of the retina of the visual organ in a chronic form (uveitis, etc.);
- The initial stage of development of pathology in the optic nerve. A concomitant symptom is a nagging pain in the eyeballs when performing any motor activity of the visual organ;
- The effect of the active elements of eye drops on the retina (drugs can cause temporary blurred vision);
- Swelling of the cellular structures of the cornea or the development of formations of a benign or malignant nature;
- Insufficient visual acuity due to the development of astigmatism, myopia or farsightedness;
- Spending a long time in front of a computer monitor.
Preventing blurred vision
Here are some tips to help you avoid cloudy eyes:
- Visit your eye doctor regularly to ensure early diagnosis of conditions that may be causing cloudy vision.
- If you wear contact lenses, strictly observe wearing times and personal hygiene
- If you have a history of hypertension and diabetes, be sure to visit an eye doctor once every 6 months
- If you have chronic dry eye syndrome, use moisturizing drops to reduce symptoms.
Treatment
Blurred vision can only be cured by identifying the cause of this condition. Often, a patient with such a symptom requires emergency hospitalization and immediate surgical intervention (for example, during an acute attack of glaucoma). Due to the high probability of serious complications, at the first appearance of fog in the eyes, you should consult an ophthalmologist.
When choosing a center where you want to receive medical care, you need to pay attention to the ophthalmology clinic that has fairly modern equipment, experienced specialists, and does not require long waiting in line. It is important not to put off taking care of your vision too long!
Diagnostics
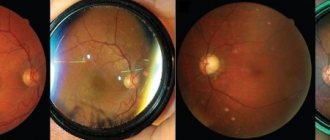
To conduct a diagnostic examination in patients with similar symptoms, it is necessary to perform biomicroscopy with a slit lamp. In this case, inflammatory hyperemia can be detected in the endothelium.
With intermediate uveitis, inflammatory cells are found already in the vitreous substance, as well as aggregates in its lower and anterior regions. Also, with uveitis, there are signs of an exudative process, which leads to the appearance of membranes lining the lower part of the ciliary body. It is quite easy for a doctor to visualize cells and inflammatory aggregates in the vitreous substance, but only an experienced specialist can see the membranes of the ciliary body.
In the case of posterior uveitis, the main signs of pathology are strands or individual cells in the vitreous substance. Sometimes areas of damage to the fundus and inflammatory reactions in the choroid are detected.
The consequences of uveitis can be the most threatening, therefore, if such signs are detected in a patient, treatment should be prescribed as soon as possible.
Video from a specialist about the symptom
Glaucoma
According to experts, the most common cause of blurred vision is glaucoma, accompanied by increased intraocular pressure. This condition certainly leads to a decrease in visual acuity, at the same time there is a feeling of a slight veil before the eyes. Meanwhile, glaucoma may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Significant pain in the temples and eyes;
- Rare but intense headaches;
- The appearance of halos and rainbow circles around the light source;
- Feeling of fog before the eyes.
For glaucoma, as well as for retinal vasospasms, an ophthalmological examination is prescribed, which can reveal both corneal edema and shallowing of the anterior chamber of the eye. And in case of neglect of the condition, excavation of the optic disc may also be observed, along with its pallor.
Cataract and uveitis
Often, blurred vision is a consequence of cataracts and uveitis. And if cataracts can be identified by clouding of the lens or vitreous, then uveitis may not have clearly defined signs. The only thing is that there is a gradual decrease in vision, accompanied by clouding with dark-colored floating spots. But the usual signs of the disease, such as photophobia, severe pain and redness, can appear only in acute iritis or iridocyclitis. However, if there is a rush of blood to the perilimbus or constriction of the pupils, then this may clearly indicate acute anterior uveitis.
Treatment: which methods are effective?
Drug therapy
Treatment tactics are determined by the doctor; self-medication is prohibited. Depending on the cause of fog in the eyes, drops and liniments are recommended, shown in the table:
| Pharmgroup | Name |
| Antibacterial | "Levofloxacin" |
| "Tobrex" | |
| "Tobradex" | |
| "Albucid" | |
| "Gentamicin" | |
| "Neomycin" | |
| "Levomycetin" | |
| Against dry eyes | "Lecrolin" |
| The drug "Artificial tear" | |
| "Systane Ultra" | |
| "Cromohexal" | |
| "Oxial" | |
| "Taufon" | |
| "Quinax" | |
| "Emoxipin" | |
| Vitamins | "Strix forte" |
| "Okuwait Lutein Forte" | |
| "Vitrum Vision forte" | |
| "Complivit Oftalmo" |
Other methods
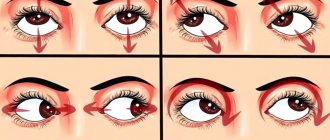
To see better, it is recommended to wear corrective glasses and contact lenses to eliminate fog. If you are tired, it is recommended to make ice compresses or lotions with a decoction of chamomile, sage, string, and St. John's wort. To do this, pour 5 g of the plant into 200 ml of hot water, let it brew, cool, filter and apply a cotton pad soaked in the product on the right and left eyes. The haze will pass and vision will improve if you do daily exercises: moving your eyeballs up/down, sideways and diagonally. If the fog in the eyes does not go away, surgical intervention is recommended - laser coagulation, vitrectomy, extracapsular extraction.
Causes of fog in one eye.
Some inflammatory eye diseases (keratitis, conjunctivitis, iridocyclitis) may be accompanied by symptoms other than blurred vision in one eye. And it is these symptoms that prompt people to see a doctor. These include:
- pain in the eyes
- redness of the eyes
- loss of a specific area of vision in the visual field (visual field loss)