Why do your eyes hurt when you have a cold?
To understand why the eyes are the first to react to disease, you need a general understanding of their structure and location.
The human eyes are a paired organ that is located in the eye sockets of the skull and consists of the eye itself, connected via the optic nerve to the brain, and auxiliary apparatus (eyelids, muscles, lacrimal organs). The eyes are sensitive to the smallest changes, this applies not only to external stimuli, for example, the constriction of the pupil to light and its dilation to darkness, but also to internal processes. Multiple nerve endings, fibrous fibers of the anterior chamber of the eye, and venous plexuses maintain ocular pressure. All information received from the outside first falls on a nerve impulse, and then along the visual-nervous pathway is transmitted to the occipital lobe of the brain, where visual images are formed.
Attention! The slightest fluctuations in temperature, pressure, infection affect the nutrition of the eye and lead to unpleasant sensations.
A viral infection, entering the body, leads to destruction in several directions:
- Actively reproduces, releasing toxins. In this case, decay products enter the bloodstream, settle on the muscles (including the eye muscles), and the eyes experience discomfort.
- The infection leads to swelling of the mucous membranes, which spreads into the nose. Fluid accumulates in the sinuses, puts pressure on their walls, and since they are located next to the visual organs, it provokes pain in the eyeballs.
You must understand that pain in the eyes is not a disease, but only one of the symptoms of the disease, so drops and tablets will not solve the problem. In case of influenza and acute respiratory viral infections, it is better to take a sick leave to rest at home for a while. Having defeated the fever, the pain in the eyes will go away on its own.
It's not just a cold that hurts your eyes. Imagine that you skate for a long time on only one leg, after some time it will hurt from muscle overstrain. The eye muscles also get tired if you monotonously work at the computer, read, or watch TV. Prolonged tension of the eye muscles in adults leads to dryness, irritation, you don’t want to move your eyes from side to side, you want to cover them and not strain them.
Main clinical manifestations of pathology
Many compatriots are quite normal about the fact that when a person has a cold, a person has a sore throat and a runny nose, a stuffy nose or a loss of voice. Symptoms such as elevated body temperature are not always present.
However, the mucous membranes almost always swell as the body tries to get rid of the virus by secreting fluid. Here lies the answer to the question: why do the eyeballs hurt when you have a cold?
Anatomically, the nose is located close to the organs of vision, and therefore ophthalmological symptoms of the disease develop, but they are not present in everyone and not always.
If manifestations appear, they will be especially noticeable on the second or third day of the disease. Further, the swelling, as well as the pain, will decrease, and already on the fourth or fifth day after the onset of the disease it will disappear completely.
Another cause of inflammation and pain in the eyes during a cold may be the development of pathological processes in the body. This is due to a significant weakening of the immune system after the virus enters the body.
An aggressive disease can cause the development of pathogenic microflora, which is normally contained by the body itself.
Common causes of this condition are:
- Developing sinusitis. Swelling and nasal congestion are the best proof of this and evidence of a pathological process that requires treatment.
- Development of sinusitis. You should be wary of pain that develops not so much in the eye area, but when pressure is applied to the bridge of the nose. Shooting pains may also indicate pathology and therefore require medical intervention.
With sinusitis, a purulent mass begins to accumulate in the sinuses of the nose, which often does not go away on its own. Excessive amounts of it lead to increased pressure on nearby areas. One of these is the eyes.
To prevent dangerous processes, if pain in the eye area increases due to a cold, you should consult a doctor. He will prescribe a diagnostic test, the result of which will give direction for further treatment.
- Inflammation of the conjunctiva. This condition can be treated with lotions and simple washing for a long time and to no avail. If the assumption regarding the inflammatory process is confirmed by a specialist, it will be necessary to carry out correct treatment with antibacterial drugs.
- Intoxication of the body. As a cold develops in the body, bacteria release toxic substances that can cause a lot of harm. The body is poisoned by poisons; they also affect the nerve endings in the muscle tissue of the eyeballs. To prevent intoxication, the doctor recommends taking absorbents. They should be used separately from taking the main medications.
To assess the patient’s condition, as well as the possible presence of complications from the disease, the doctor conducts an examination and may prescribe additional tests.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=
As soon as one of the above conditions is confirmed, the appropriate therapeutic course will be prescribed. It may include both antiviral and antibacterial drugs.
The pain may be localized under both lower eyelids or concentrated under only one. If your cheekbone hurts, the upper part of the gap hurts, the lower eyelid is swollen with a severe runny nose and a pronounced cold, it is quite possible that a pathological process is actively developing under the eye or under the eyes.
If a patient complains of acute pain with a runny nose under one eye, this may be evidence of acute dacryocystitis.
This is a disease that directly affects the tear ducts.
It is located in the very corner of the eye, and the pain itself during such processes is often localized under the eye, but closer to the bridge of the nose.
Often even light pressure on the problem area will be enough to cause severe pain. The condition itself may be accompanied by an increase in temperature, which can easily be confused with a fever from a cold.
A typical manifestation is leaking yellowish, greenish, brownish liquid. If the inflammation is not eliminated, pus can accumulate and then burst either into the nasal cavity or out.
The cause of the spread of pain to the area above the eyes can be various pathological processes.
A cold and a decrease in general immunity, human protection, can lead to the active development of pathogenic microflora, which manifests itself in:
- Rhinosinusitis. This process is characterized by inflammation of the upper sinuses.
- Sinusitis is a dangerous process that leads to the accumulation of purulent mass in the sinuses.
- Ethmoiditis and sinusitis, other diseases that require immediate medical intervention. If such diseases are present, then the pain can be acute or dull, but almost always it radiates to the frontal, temporal region, and can significantly intensify when changing body position, and is especially acute when resting on the side.
The fact that pathology occurs with a cold is evidenced by increased or even acute, sharp pain when sneezing, coughing, blowing the nose, sudden changes in body position, jumping, squatting, etc. This is explained by increased pressure on the exudate.
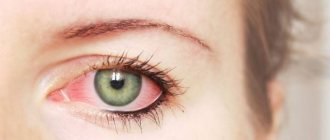
The eye is an important organ that is responsible for vision. Unfortunately, he is quite easy to injure, since he has little protection. The visual apparatus has a unique structure; it contains many nerve endings. With minor external injuries or internal diseases, the eyeball may become inflamed. This violation causes discomfort.
During infectious diseases, pain in the eyes occurs almost immediately and can last even after a cold. However, in addition to these unpleasant symptoms, the disease is always accompanied by additional unpleasant signs:
- feeling of "sand";
- eyes hurt and water;
- eyes hurt when moving;
- eyelids swell;
- discomfort in daylight;
- sensations of heat;
- sometimes the eyes and forehead hurt;
- the eye muscles contract involuntarily.
All these unpleasant sensations do not affect the further functioning of the visual apparatus. However, this pathology causes discomfort and worsens the quality of life. All these clinical manifestations can be eliminated, but it is important to start timely treatment.
Can your eyes hurt when you have a cold? Here we can answer unequivocally that yes, they can! Infectious diseases always manifest themselves with pronounced symptoms that cause unpleasant, painful sensations in the eyes. These include high fever, weakness, headache, drowsiness and eye discomfort.
- Pathogenic microorganisms. When you have a cold, your eyes hurt; this is normal, since many viruses and bacteria penetrate the human body. They begin to actively reproduce and secrete waste products. All these toxins begin to gradually spread throughout the body. Some harmful substances penetrate into the muscles, and the visual apparatus is no exception.
- Inflammatory process in the paranasal sinuses of the skull or sinusitis. This disease develops as a complication of ARVI. With sinusitis, purulent discharge accumulates in the sinuses, the pressure in them increases, which causes unpleasant, pressing pain in the surrounding tissues and organs, including the eyes.
- Conjunctivitis. Often a complication of colds is inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye and eyelids. As a rule, this disease is always accompanied by burning, swelling and photophobia.
- Headache. With a cold without fever and with its increase, pain in the head always develops. It is this that can provoke discomfort in the eyes.
In some cases, to eliminate eye pain, it is enough to simply treat a respiratory disease. However, if this disease has caused complications (sinusitis, conjunctivitis), then it is necessary to consult a specialist and begin quality treatment. After complex therapy, the patient will feel significant improvements in a few days.
Traditional recipes for eye pain
No one doubts the healing power of herbs that have been selected by traditional medicine for centuries. Without medications, our great-grandmothers easily coped with colds, treated barley, tumors and rheumatism. And although you won’t be able to get rid of pain in the eyes during a cold with the wave of a magic wand, you can minimize the discomfort by approaching treatment comprehensively:
- To activate the autonomic centers of the brain, including the vasomotor, adults are advised to take Aralia Manchurian root or Eleutherococcus in the form of alcohol tinctures (30-40 drops in a third of a glass of warm water, 2 times a day before meals). Eleutherococcus has medicinal properties equal to ginseng, contains eleutherosides and anthocyanins (against microbes and bacteria), flavonoids (regulate metabolism), saponins (stimulate the action of the hormonal system), vitamins, essential oils. Tinctures increase blood supply to the brain and have a positive effect on the motor activity of the eye muscles.
- A decoction or extract of hawthorn has a stimulating effect. It is taken 30 minutes before meals - in the morning and at lunch, 20 drops per dose. To make an infusion, take 1 tbsp. spoon of dry fruits, place them in a mortar and press down a little. Then pour the fruits into a glass, pour 200 ml of boiling water, leave for 2 hours in a warm place, strain, take 1-2 tbsp. spoons.
Herbal stimulants should not be taken at night!
- To improve sleep, it is recommended to drink valerian infusion or lemon balm tea in the evening. A decoction of valerian is made in advance: 2 tsp. pour a glass of boiling water over the herbs, leave for at least 10 hours, stir, allow to settle, do not filter. Drink a quarter glass. Can be stored in the refrigerator for several days. To prepare lemon balm tea: 3 tsp. The plants are poured with a glass of boiling water, left for 15 minutes, and drunk immediately.
Cold treatment
For many people, a cold is not a serious illness. But it is important to consider the risk of developing severe complications in the absence of treatment or improper therapy. You should not self-medicate. The doctor will prescribe effective therapy methods for a quick recovery.
At an early stage of development, the basic rules are plenty of fluids and a gentle regime. It is worth noting that antibiotics are prescribed only when complications develop. Viral diseases cannot be treated with such drugs. Many patients make the mistake of choosing to self-medicate with antibiotics.
If you suffer from a cold on your feet, this can lead to the development of complications from the heart, kidneys, and liver. Drinking plenty of fluids will help prevent the development of intoxication that occurs with a viral infection. You can also take antiviral and antipyretic drugs.
For symptomatic treatment, drops for a runny nose, painkillers for headaches, and cough and sore throat medications are used. The drugs come in the form of sprays, tablets, and solutions.
When it is painful for a patient to move his eyes during a cold, this may be a sign of sinusitis or sinusitis. Such diseases are often complications of a cold. Antibiotics are prescribed for treatment. A characteristic symptom is purulent nasal discharge and pain in the forehead. Such pathologies are quite dangerous, so treatment can be lengthy.
Antipyretics
An increase in temperature is the body's protective reaction to viral, bacterial, and infectious pathogens. Doctors do not recommend lowering the temperature to 38 degrees, as this inhibits the body’s protective functions. If the mark rises higher, then this is not a sign of a cold, but of an acute respiratory viral infection. In this case, doctors recommend taking the following antipyretic drugs:
- Ibuprofen;
- Paracetamol;
- Aspirin;
- Mefenamic acid.
Drugs for symptomatic treatment also have an antipyretic effect. These include: Coldrex, Theraflu, Fervex. If your throat hurts badly, you can replace the tablets with rectal suppositories. They are suitable for small children and adults. The cheapest and most accessible medicine in this case is Paracetamol. Medicines can be taken after a doctor's prescription.
Antipyretic drugs for children come in the form of syrups. Nurofen is popular. Suitable for children from birth. Before use, be sure to consult a doctor. This is necessary to determine the treatment regimen and safe dosage. According to the instructions, such drugs are prohibited from being taken for more than 5 days.
Drinking regimen
Drinking plenty of fluids when treating a cold is the key to a successful outcome. A large amount of fluid will help prevent intoxication and fever. Recovery will be faster. In addition, sweating increases. In this way, toxins are removed from the body through the skin.
This process is also necessary, since intoxication tends to develop rapidly. Dehydration is dangerous for children of any age. To quickly restore water balance in the body, doctors recommend using saline solutions.
You need to drink only warm drinks that do not irritate the mucous membranes. For example: tea with honey and lemon, berry and fruit juices, warm water. Light broths will also be useful. They will give you strength and help you recover faster. You need to drink a lot until complete recovery. Doctors do not recommend drinking coffee when you have a cold. For recovery you will need full sleep, as well as rest during the day. Caffeine makes you feel alert and energetic. When you have a cold, this puts additional stress on the body.
Basics of successful treatment
Unpleasant sensations in the eyes arise for various reasons, therefore treatment in each case is individual, however, there are standard rules that will help remove eye pain due to a cold:
Drinking regime
Viruses and bacteria during colds not only feed on the beneficial substances of the human body, but also poison it with toxins, penetrating the blood, muscles, and blood vessels. It is the processes of microbial decay that cause aching in the bones, body temperature, and affect the organs of vision. The more water and herbal infusions you drink, the faster “waste” is washed out of the body.
Bed rest
We have been taught that a cold is not a terrible disease, and it is quite possible to “overcome” it. A completely wrong attitude: for the first three days, the body desperately fights the infection, and any stress (mental, physical) takes away the strength that could have been used to fight the infection.
Treatment
Staying hydrated will help you avoid pain in the eye area due to dryness and dehydration. A large amount of warm liquid will replenish the body's losses. It is important not to overstrain your vision by constantly watching TV or reading books. It is recommended to sleep more so as not to disturb your eyes and give the body time and energy to recover.
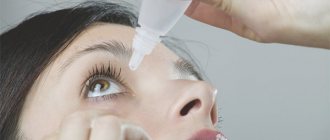
Drops with the effect of artificial tears quickly help solve the problem of dry eyes. In this case, vasoconstrictors for redness, for example, Visine, are not recommended. They increase eye dryness and worsen symptoms.
Antipyretic drugs will help temporarily relieve symptoms, as they also have an analgesic effect. However, it is not recommended to take them more than once every 4 hours or for longer than 3-4 days.
For sinusitis, only relieving swelling will help get rid of eye pain. To do this, use vasoconstrictors or sprays with glucocorticosteroids locally into the nose. The use of systemic antibiotics is also indicated.
To treat conjunctivitis, drops with an antibacterial effect or ointments are used. If pus does not appear, the inflammation goes away without medications.
In the case of pathologies of the visual organs, treatment is selected by an ophthalmologist. This may include anti-inflammatories, systemic antibiotics, and eye patches.
Read also: Dry paroxysmal cough
Dear patients! Remember that only a qualified doctor can make an accurate diagnosis, determine the causes and nature of the disease, and prescribe effective treatment. You can make an appointment with our specialists or call a doctor at home by calling 8-(4822)-33-00-33
Be healthy and happy!
What symptoms may occur with a cold?
The eyes are an organ of vision that suffers from colds, like other body systems. In order to prevent the development of pathological processes and the onset of inflammation, you should adhere to basic hygiene rules and follow the recommendations of your doctor!
As the disease progresses, other symptoms of the disease may appear, including:
- Itching and swelling of the eyes. The areas around the eyes may also swell; the size of the swelling may vary, but this condition requires a visit to the doctor. What is typical is that both the itching and the level of swelling increase at night and immediately after sleep.
- Severe burning of the eyes. The painful sensation can be aggravated by a strong burning sensation, which often goes away after applying lotions and closing the eyes. The best solution in this case would be proper rest and the use of albucid to prevent inflammatory processes.
- Feeling hot and intense redness. This process can also be aggravated when the patient’s whites of the eyeballs and the periocular area turn red. The situation can be corrected by sleep, rest, and a consultation with a doctor, who will recommend, if necessary, a drug suitable for treatment.
- Sensation of sand along with pain in eyeballs during cold. This is a common condition, which is explained by drying out of the eyeballs, their redness and the development of pathogenic microflora. Frequent eye rinsing along with the use of various medications can have a rapid therapeutic effect.
The following symptoms may appear: photophobia, pain when moving the eyeballs, involuntary contraction or twitching of muscles, their spasm, which can also cause unpleasant pain.
Another manifestation is lacrimation, and the fluid that flows out will not always be clean and transparent. It may also be greenish and cloudy
If you have any of these symptoms, it is important to contact your doctor for advice.
What causes pain in the eyes?
Eye pain during the flu is a common symptom. What causes pain in the eyes? Here doctors highlight several factors. The first reason is that the influenza virus can enter the body not only through the respiratory system and mouth, but also through the eyes. In this case, the infection settles on the mucous membrane of the eyes, which is why they begin to hurt with all the subsequent symptoms in the form of lacrimation and photophobia.
An important cause of eye pain that develops with the flu is sinusitis. This is the most common complication that occurs with a viral disease. Sinusitis is a disease that develops in one or more paranasal sinuses at the same time. Depending on the area affected, different symptoms are provoked.
With sinusitis, the nasal mucosa swells, which provokes inflammation of the lacrimal canals, pain in the periocular and frontal area, and increased lacrimation. It is better to eliminate the disease with the help of a doctor who will determine the exact location of the infection and begin effective treatment. If treatment is avoided, the infection will spread, which can lead to a type of sinusitis called sinusitis. And here you can’t do without radical treatment.
However, when treating sinusitis on your own, you can use the following recommendations:
- To relieve inflammation, you can add a little sea salt to the chamomile decoction and rinse your nose with it.
- To ease breathing and relieve swelling in the nose, you should take antihistamines.
- To eliminate mucus and a large number of microbes in the nose, some of which are the microorganisms that provoked the disease, you should rinse your nose daily.
- Homeopathic medicines are suitable for gentle treatment.
Self-medication is allowed for 3-5 days. If during this time the symptoms do not subside or do not disappear at all, then you should seek medical help, as otherwise complications will develop.
go to top
Other causes of pain in the eyes
It is necessary to consider other root causes of why eyes hurt with the flu.
Eye soreness can be caused by: High temperature. At elevated temperatures, discomfort naturally occurs in different parts of the body. Photophobia also appears
When symptoms occur, it is important to lower the temperature. Migraine
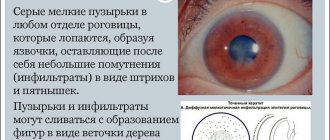
Another symptom of the flu that causes pain in the eyes. The pain will go away only after the migraine passes. Give the patient painkillers and ensure rest. Viral conjunctivitis. Flu weakens a person's immune system, so new infections can easily spread in the body. Viral conjunctivitis is accompanied not only by painful sensations in the eyes, but also by the release of purulent mucus. The main method of therapy is the use of eye drops.
Weakened immune system. This is a common cause in children who have had the flu. The child develops symptoms such as weakness, fever, headaches, sneezing, coughing, dizziness, and aching joints.
Personal reaction to general intoxication. When you get sick, your immune system actively tries to fight the infection. This affects the state of the blood, in which dead virus cells begin to appear. Various symptoms begin to appear, such as loss of appetite, aching joints, sweating, and pain in the eyes.
It is important to follow preventative measures to avoid getting sick
Forecast
If your eyes hurt with the flu, this can be either a symptom of the disease itself or a consequence of the development of complications. Projections will depend on measures taken to treat influenza and its symptoms. If you resort to medical help, then the prognosis will be more favorable. If left untreated, complications may occur such as:
- Pneumonia.
- Disturbances in the functioning of blood vessels and the heart.
- Pathologies in the functioning of internal organs.
- Meningitis.