An appointment with an ophthalmologist is a service that includes a comprehensive examination of the visual organs in accordance with medical standards. The initial appointment with an ophthalmologist includes the following list of diagnostics:
- Visometry – checking visual acuity;
- Autorefractometry – study of eye refraction;
- Pneumotonometry – determination of intraocular pressure;
- Biomicroscopy – examination of the anterior segment of the eye;
- Ophthalmoscopy – examination of the fundus of the eye.
Children
The visual system is formed in the prenatal period, and its development continues after birth until approximately 16 years of age. Therefore, medical examinations by an ophthalmologist are mandatory for all minors. Up to a year, the child needs to be shown to an ophthalmologist at least three to four times - immediately after birth, at one month, at six months and at one year. In a one-month-old baby, the doctor checks first of all the anatomical condition of the eyes and the absence of defects. At the age of six months, you can preliminarily evaluate the baby’s vision; in a one-year-old child, a specialist can determine the refraction.
Subsequently, until graduation, the child must be shown to an ophthalmologist once a year. If pathologies and refractive errors are detected, then visits to the doctor may be more frequent.
How is an appointment with an ophthalmologist in “Constellation”
When a person comes to our clinic for the first time, the doctor conducts a survey to identify existing complaints and collect anamnesis. Based on the information received, the inspection begins.
Visual acuity testing is mandatory, even if the person is not bothered by anything and does not experience any discomfort. If the test shows changes in the refraction of the eyes, the client undergoes a refraction test procedure. At the end of these manipulations, the doctor determines whether it is necessary to select glasses for the patient. If such a need arises, we select the appropriate optical correction.
For people over 35 years of age, when diagnosing the condition of the visual organs, intraocular pressure must be measured. This allows you to determine your predisposition to glaucoma or identify the disease in its early stages and take measures to prevent the disease. Next, the patient moves to another room, where special equipment is used to examine the anterior segment of the eye and assess the condition of the fundus.
Note that the entire diagnostic complex is performed on a narrow pupil. Mydriatic drops that dilate the pupil are used according to indications. The initial appointment takes about 20-30 minutes, and when the pupil is dilated, it takes a little longer - about 45 minutes.
Adults over 40 years old
40 years is the age limit after which physiological changes begin in the eyes. The structure of the lens may change, clouding occurs, and intraocular pressure increases. Those who have crossed the 40-year mark increase the risk of developing glaucoma, cataracts, presbyopia and a number of other pathologies. Some diseases are dangerous because they are irreversible and because they lead to blindness. Timely regular medical examinations (at least twice a year) will help detect the disease at an early stage, which in some cases will help slow down the progression of the disease or even stop the deterioration of vision.
Who should visit an ophthalmologist regularly:
- those who have vision problems wear glasses or contact lenses;
- with a hereditary predisposition (if one of your relatives has vision problems: cataracts, glaucoma, myopia, farsightedness, astigmatism);
- women planning pregnancy, especially those with a high degree of myopia;
- pregnant women;
- people who work at a computer every day;
- people who have undergone a long course of treatment with hormonal drugs;
- people with high or low blood pressure relative to age norms;
- people who have suffered eye injuries, inflammatory diseases (uveitis, iridocyclitis, etc.) of the eyes, eye surgery;
- people with diabetes;
- people over 45-50 years old, even if there are no vision complaints;
- children, especially in the first years of school;
Who cares about dry and red eyes?
Such symptoms are familiar to many modern people, especially those who actively use gadgets and spend a lot of time at the computer. Constant work of the eyes at close range creates excess tension and disrupts the normal functioning of the accommodative apparatus. Rarely blinking leads to dry mucous membranes, redness and discomfort. However, many people are accustomed to relieving such symptoms with the help of moisturizing drops. Often they are used even without consulting a specialist, without seeing a problem with dry eyes. But ophthalmologists warn: such clinical signs are always a reason to consult a doctor. The cause of dryness and redness should be determined by a doctor after a thorough diagnosis. Sometimes symptoms may not indicate eye fatigue, but an inflammatory process that can lead to complications.
The listed categories of patients are not the only ones who should undergo regular medical examinations by an ophthalmologist. You need to make an appointment with a doctor if you have any alarming symptoms of vision, be it decreased image clarity, “spots” before the eyes, a feeling of a veil, discharge from the eyes or other signs. It’s better to find out during the examination that there’s nothing wrong with you than to miss the onset of a serious illness that will lead to serious consequences.
MagazinLinz.ru team
Additional examinations
If a pathology or disease is detected, you may be offered additional examinations. Depending on the type of deviation detected, the patient has the opportunity to undergo:
- Gonioscopy – examination of the angle of the anterior chamber of the eye in case of glaucoma;
- Computer perimetry – peripheral field measurement;
- Ophthalmoscopy in conditions of cycloplegia - a more detailed examination of the fundus of the eye for a dilated pupil.
- Pachymetry – measurement of corneal thickness;
- IOL calculation – selection of artificial lens diopters;
- Ultrasound of the eye.
These studies are carried out as prescribed by the doctor and the personal wishes of the patient. They are intended for a more in-depth study of pathology, searching for the source of the disease and prescribing competent treatment. These types of diagnostics are independent services and are not included in the cost of the initial appointment.
Colorblindness test
Deviations in color perception are a congenital disease. A person who has such deviations may not be aware of their presence. Usually colorblind people do not distinguish between green and red colors.
The danger of the disease is that the driver does not understand which traffic light is on and may start driving through a red light, perceiving it in the green spectrum.
To determine color sensitivity, ophthalmologists use the Rabkin table. All people are divided into three types based on the ability to perceive colors and shades:
- Trichromantics are a large group that includes people who do not have pathology. The number of perceived shades of faces with normal color perception differs from innate abilities. Artistically gifted people see several dozen times more different gradations of tones than ordinary people.
- Protanopes are patients who do not perceive the colors and tones of the red spectrum.
- Deuteranopes do not recognize the color green.
What diseases does an ophthalmologist diagnose and treat?
The specialist diagnoses and treats diseases of the eyeball itself and auxiliary organs: the eyelid and the conjunctiva covering it, lacrimal glands, orbit, supplying vessels and nerves. During the consultation, he checks visual acuity and identifies the anatomical features of the visual apparatus.
For early diagnosis of specialized diseases, an ophthalmologist in Moscow uses absolutely safe examination methods that do not require special preparation of the patient. They make it possible to identify not only an existing disease, but also to develop a correction or treatment plan. In the future, the doctor monitors its effectiveness and, if necessary, makes adjustments.
In specialized clinics, the ophthalmologist works in collaboration with other specialists:
- an ophthalmologist who corrects vision using optical means and prescribes pharmaceuticals;
- an optometrist who performs a number of highly specialized studies and selects a system of exercises to train the eye muscles and restore vision.
Do not allow eye disease to become chronic. Seek help from a specialist who can prevent irreversible consequences.
Ophthalmology studies the functioning of the organ of vision, through which a person receives up to 90% of information about his environment, and pathologies that cause deterioration of visual functions.
The ophthalmology department of the Trit clinic provides qualified medical care to patients with various eye diseases.
- Correction of refractive errors (myopia, farsightedness, astigmatism) is carried out by selecting glasses and lenses and monitoring the dynamics of the process in adolescents.
- Observe and treat patients with cataracts, prepare them for surgical treatment.
- Monitor eye pressure in glaucoma, develop a medication regimen and prepare for surgery.
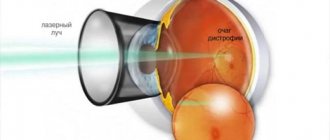
- Develop a plan and monitor the progress of treatment for retinal dystrophy and partial atrophy of the optic nerve.
- Diagnose and treat acute inflammatory diseases caused by infection of the eyeball and conjunctiva.
- The formations of the eyelids and conjunctiva are removed on an outpatient basis - if necessary, with a biopsy.
- Help patients with eye injuries.
The clinic has built a well-functioning patient care system, allowing for diagnostics and ophthalmic surgical interventions.
Advanced surgical technologies for the treatment of glaucoma and cataracts are used, including the development of a long-term maintenance therapy program for each operated patient.
In addition, the clinic’s specialists are proficient in modern methods of treating the following diseases:
- retinal disinsertion
- extraocular filling (uncomplicated cases of retinal detachments).
- diabetic retinopathy
- acute vascular pathology of the eye (retinal vein thrombosis, hemophthalmos, circulatory disorders in the vessels of the retina and optic nerve)
- chronic allergic conjunctivitis
- keratitis
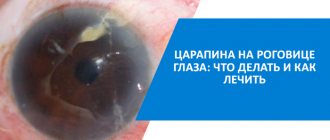
- corneal clouding
- vitreous opacities
- retinitis
- uveitis
- eye diabetes.
How is vision checked in preschoolers?
The next important stage of vision testing in children is carried out before the child goes to school. At this age, ophthalmologists already use a different method. The child’s visual abilities are tested using the Sivtsev table, which is well known to each of us. It was compiled by Soviet ophthalmologist Dmitry Aleksandrovich Sivtsev. As a rule, it implies knowledge of the alphabet, although in fact, the child will only need to know seven letters, which is exactly what the table includes.
In most cases, if not 100%, this table is used in conjunction with another, developed by another Soviet ophthalmologist Sergei Selivanovich Golovin. It is a set of rings by the Swiss scientist Landolt, the sizes of which decrease from top to bottom. According to ophthalmologists, it is much easier to determine the quality of vision using two tables at the same time, as this provides a more accurate result. The verification principle is similar to the previous one, which we described earlier. The ophthalmologist takes the future student to a distance of five meters from the tables of Sivtsev and Golovin hanging on the wall and asks him to close one eye. From this distance, the child must name the tenth line, that is, the bottom one. The next condition is to close the other eye and look at the tables in the same way, determining which line is best visible. If the child does not make a single mistake, this indicates that he has 100% vision.
Vision check at three years
The vision of a three-year-old child is checked according to the table of ophthalmologist Orlova. This method is considered ideal for testing visual functions due to the fact that preschool children, in most cases, do not know the alphabet, and in the Eagle table the letters are replaced by drawings. The table itself consists of 12 lines located below and below, consisting of various pictures, the size of which decreases towards the bottom. To test vision using the Orlova table, the doctor sits the child at a distance of at least 5 meters from the table itself, usually hanging on the wall. He must definitely check with the little patient which line he sees best. Ideally, it should distinguish the tenth line. If this is so, it means that visual acuity is 100%. If, from a distance of five meters, a preschool child is able to recognize only the drawings shown on the first line, then the result is only 10%. During the examination, it is very important for parents accompanying the child to ensure that the child does not squint or spin around in the chair.
How is a newborn's vision checked?
If we talk about the very first vision test, it is carried out in the maternity hospital, after the baby is born. If, during an examination by an ophthalmologist, any deviations from the norm were detected, then an ultrasound scan is prescribed for a more accurate diagnosis. As a rule, all newborns are farsighted. This refractive error occurs due to the fact that the newborn’s eye is somewhat flattened, and therefore visible objects are projected further than the retina. The acuity of visual functions is quite low and, according to various estimates, can be from 0.005 to 0.015 diopters according to standard tables, reaching 0.01 by the end of the first month of life. As for light sensitivity, it is minimally developed in newborns. If an ophthalmologist shines a laser pointer into a baby’s eyes, the baby will at most close his eyes or try to look away. A normal reaction usually develops no earlier than 3-5 weeks.