| Phenylephrine | |
| Are common | |
| Systematic name | 1-(meta-Oxyphenyl)-2-methylaminoethanol/( R )-3-[-1-hydroxy-2-(methylamino)ethylphenol |
| Chem. formula | C₉H₁₃NO₂ |
| Rat. formula | C9H13NO2 |
| Physical properties | |
| State | white or yellowish powder |
| Molar mass | 167.205 g/mol |
| Thermal properties | |
| T. float. | 143-145 °C |
| Classification | |
| Reg. CAS number | 59-42-7 |
| PubChem | 6041 |
| Reg. EINECS number | 200-424-8 |
| SMILES | O[ [email protected] ](c1cc(O)ccc1)CNC |
| InChI | 1S/C9H13NO2/c1-10-6-9(12)7-3-2-4-8(11)5-7/h2-5,9-12H,6H2,1H3/t9-/m0/s1 SONNWYBIRXJNDC-VIFPVBQESA-N |
| ChEBI | 8093 |
| UN number | <— UN number —> |
| ChemSpider | 5818 |
| Data given is based on standard conditions (25 °C, 100 kPa) unless otherwise stated. | |
Phenylephrine
(Mesaton, Mesatonum). 1-(meta-Oxyphenyl)-2-methylaminoethanol. The gross formula is C9H13NO2.
Sometimes available as an acid salt ( Phenylephrine hydrochloride
): C9H13NO2⋅HCl.
Synonyms: Adrianol, Almefrin, Derizene, Idrianol, Isophrin, Neophryn, NeoSynephrine, Phenylephrini hydrochloridum, Phenylephrine hydrochloride, mSympatol, Visadron, etc.
Pharmacological authorities
Pharmacodynamics.
Mezaton is an α1-adrenergic agonist that slightly affects β-adrenergic receptors of the heart. It does not contain catecholamine, as it contains only one hydroxyl group in the aromatic core. Reduce arterial tension and arterial pressure (with possible reflex bradycardia). Compounded with norepinephrine and epinephrine, the arterial pressure moves less sharply, and is even more trivial, as it is less similar to the effect of catechol .
-methyltransferase. Do not increase the blood volume. The action begins immediately after administration and continues for 5-20 minutes after internal administration. If administered slowly, the action will last up to 50 minutes. With internal lingual administration – up to 1-2 years.
Pharmacokinetics.
After internal lingual administration, the systemic bloodstream is absorbed quickly. The binding to blood plasma proteins is low. Almost completely metabolized in the liver. It is produced in the form of metabolites.
Indications and contraindications
Ophthalmologists use this drug in the following cases:
- diagnostic examination of the patient, in particular, a detailed examination of the fundus;
- provocative testing for narrowing of the internal angle of the anterior chamber of the eye;
- treatment of iridocyclitis, anterior uveitis;
- asthenopia, adhesions on the posterior wall of the eyeball;
- angle-closure glaucoma;
- irritation with severe dry eye syndrome;
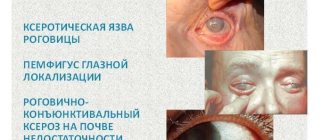
- sharply increased intraocular pressure caused by various reasons.
Since the drug has a rather aggressive effect on blood vessels, it cannot be used by everyone and not always even topically. The instructions for use of these eye drops indicate the following contraindications:
- chronic increase in intraocular pressure;
- heart failure;
- open injuries to the organs of vision;
- hyperfunction of the endocrine system organs;
- increased lacrimation of the eye;
- some hereditary diseases;
- increased levels of porphyrins;
- elderly patient – over 50 years old;
- individual intolerance to the active components of the drug.
For the examination and treatment of elderly patients, this drug is used with great caution, only in the complete absence of contraindications.
Contraindicated
Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug. All types of arterial hypertension, cardiosclerosis, halothane or cyclopropane anesthesia, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, pheochromocytoma, fibrillation of the scutum, occlusive disease of the vessels: arterial thromboembolism Ia, atherosclerosis, obliterative thrombangitis (Buerger's disease), Raynaud's disease, blood vessels to spasms during frostbite, diabetic endarteritis, thyrotoxicosis , tachyarrhythmia, metabolic acidosis, hypercapnia, hypoxia, closed-cuta glaucoma, severe aortic stenosis, acute myocardial infarction, porphyria, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, cervical diabetes bet. Patients with illnesses of the anterior molecules, who have severe movements, are at risk of clogging. One-hour administration with MAO inhibitors for 14 days after their stagnation. Summer age patients.
Analogs
As analogues of the drug, medications containing phenylephrine as an active component can be considered.
Irifrin is not a complete analogue of the drug. The product is produced in the form of eye drops.
Adrianol is considered as an analogue of the drug based on the active substance. The active ingredient in the drug is phenylephrine. The product is produced by pharmacological companies in the form of drops for nasal use. The drug is used to eliminate the symptoms of vasomotor and allergic rhinitis.
Interactions with other medicinal drugs and other types of interactions
Reduces the hypotensive effect of diuretics and antihypertensive drugs. Neuroleptics similar to phenothiazine reduce the hypertensive effect of the drug. MAO inhibitors, oxytocin, alkaloids, tricyclic antidepressants, methylphenidate, adrenergic agonists cause a presorry effect and arrhythmogenicity of Mezaton. b-adrenergic blockers change the cardiostimulating activity of the drug. Administration of the drug to aphids before receiving reserpine may cause the development of a hypertensive crisis due to depletion of catecholamine reserves in adrenergic terminals and increased sensitivity to adrenergic drugs. Inhalation anesthetics (including chloroform, enflurane, halothane, isoflurane, methoxyflurane) increase the risk of severe anterior atrial and ventricular arrhythmias, which sharply increases the sensitivity of the myocardium to sympathetic omimetics. Ergometrine, ergotamine, methylergometrine, oxytocin, doxapram increase the severity of the vasoconstrictor effect. Reduces the antianginal effect of nitrates, which, in turn, can reduce the presoric effect of Mezaton and the risk of guilty arterial hypotension (simultaneous stagnation is allowed in advance until the necessary therapeutic effect is achieved ). Thyroid hormones increase (mutually) the effectiveness of the drug and are associated with the risk of coronary insufficiency (especially with coronary atherosclerosis).
Suspension of Mezaton under an hour of gentle treatment for the correction of arterial hypotension on aphids, congestion of substances that stimulate sexual activity (vasopressin, ergotamine, ergometrine, methylergometrine), can cause persistent pain Pregnancy of arterial pressure in the post-natal period.
Features of stagnation. Before starting or during shock therapy, obligatory correction of hypovolemia, hypoxia, acidosis and hypercapnia.
The drug should be used with caution in case of evidence of atrial fibrillation, arterial hypertension in a small amount of blood flow, hypovolemia, and ventricular arrhythmia.
During the treatment period, monitor the ECG, arterial pressure, pulmonary blood volume, blood flow at the ends and at the site of injection. In patients with arterial hypertension in cases of drug-induced collapse, it is necessary to maintain the arterial pressure of the systole at the level of the inferior systolic by 30-40 mm Hg. Art.
Useful properties of the drug
These eye drops are based on chemicals that activate alpha-adrenergic receptors.
They, in turn, have a constricting effect on blood vessels and increase blood pressure, which leads to dilation of the pupils.
At the same time, contraction of the smooth muscles of the conjunctiva occurs, which leads to the duration of the effect, which occurs within half an hour and disappears only after 5-6 hours, but in children the effect of a dilated pupil can be observed longer.
As a rule, the need for a patient to instill mesaton himself is extremely rare. This is mainly done by a specialist, who in this case uses specific instructions.
To achieve the effect of a dilated pupil, one drop in each eye is enough, but in cases where the pupil begins to narrow earlier than an hour later (which is quite rare), additional instillation may be required.
If the drug is used to treat ophthalmological diseases, the patient himself can do the instillation.
Important! The dosage in this case is one drop three times a day, and the course of treatment is determined individually and depends on how the inflammatory process proceeds and at what stage it is.
Method of congestion and dosage
The drug should be given to adults internally, internally and subcutaneously. A single dose of the drug when administered intravenously for colapse is 0.1-0.3-0.5 ml of 1% dilution. When a single dose of the drug is administered intravenously, dilute it with 20 ml of 5% glucose or 0.9% sodium chloride, and administer it at random. If necessary, repeat the administration.
The drug can be administered intravenously, for which 1 ml of 1% dose of Mezaton is mixed with 250-500 ml of 5% dose of glucose.
When administered internally or subcutaneously, a single dose for adults is 0.3-1 ml of 1% dose.
For local anesthesia, add 0.3-0.5 ml of 1% dose per 10 ml dose of anesthetic.
To prevent “wheezing syndrome”, after trival infusion of the drug (repeated reduction of arterial pressure per administration of the drug), the dose should be changed incrementally.
The infusion is renewed when the systolic arterial pressure decreases to 70-80 mm Hg. Art.
General doses for adults with internal and subcutaneous administration: single – 10 mg, additional – 50 mg. The typical dose for intravenous administration to adults: single dose – 5 mg, additional dose – 25 mg.
Indications for use
As an ophthalmological treatment (in addition to its use in diagnosis), the drug mezaton is prescribed for the following indications:
- complex treatment of accommodation spasm in childhood;
- iridocyclitis;
- irritation due to dry eye syndrome;
- anterior uveitis;
- reducing the activity of exudative processes of the iris.
The drug is also recommended as an auxiliary diagnostic tool for suspected angle-closure glaucoma, asthenopia, and adhesions in the back of the eyeball.
In order to exclude the development of systemic adrenergic effects, the drug should be used with caution in combination with monoamine oxidase inhibitors. If maximum pupil dilation is required, additional topical atropine is required.
If maximum pupil dilation is required, additional local application of atropine is required.
Important! Mezaton can be used with any other ophthalmic drops only at intervals of 15-20 minutes and after consultation with your doctor
Side effects
On the side of the cardiovascular system:
attacks of angina pectoris, bradycardia, increased or decreased arterial pressure, tachycardia, cardiac arrhythmias (especially when administered at high doses), increased heart rate.
On the side of the nervous system:
headache, restlessness, restlessness, confusion, fatigue, restlessness, weakness, pale skin, tremor, swelling, bleeding in the cerebrum.
On the side of the grass tract:
tediousness, vomiting.
On the side of the dichotomy system:
dyspnea
Allergic reactions:
skins withering, itching.
From the side of the organs:
pain in the eyes, conjunctival hyperemia, allergic reaction on the side of the eye, mydriasis.
On the side of the thyroid system:
destruction of the slash, shading of the slash.
Inshi:
increased sweating, hypersalivation, tingling and cold ends, hot flashes, hyperglycemia.
The drug can be administered under the nose, possible changes at the injection site, necrosis.
Side effects, overdose
Possible negative manifestations from the organ of vision after instillation:
- burning;
- redness, irritation of the conjunctiva;
- discomfort in the eyes;
- blurred vision;
- lacrimation;
- increased intraocular pressure in closed-angle, narrow-angle glaucoma.
Side effects from the heart and blood vessels: rhythm disturbances, increased blood pressure, reflex bradycardia. From the central nervous system: dizziness, sleep disturbance, headache, agitation, tremor of the extremities. Negative reactions may include weakness, shortness of breath, pale facial skin, and nausea.
Read more Signicef eye drops - instructions and analogues
Symptoms of overdose more often occur when using drops independently, when a person adds a larger amount of solution or uses it more often than the ophthalmologist prescribed. An overdose can manifest itself in the form of side effects of varying severity, most often a rise in blood pressure, reflex bradycardia. Alpha-blockers are used for treatment. The choice of drug depends on the symptoms that appear.
Analogs of Mezaton eye drops
Like any drug, Mezaton has several analogues. This includes the following drugs.
Atropine. Eye drops that are aimed at dilating the pupil. The action begins within thirty minutes after instillation. Prescribed for inflammatory processes, eye injury and a tendency to form blood clots in the vascular system of the visual organ. Contraindicated in children under seven years of age with glaucoma and synechea of the iris.
Use with caution during breastfeeding and in pregnant women. Adverse reactions are possible in the form of rapid heartbeat, redness of the eyelids and conjunctiva, swelling and pain in the head. Cyclomed
Eye drops that are an analogue of mezaton. They are used to dilate the pupil in order to accurately diagnose eye disease, treat myopia or inflammation of the anterior chamber, and before surgery. Adverse reactions include the appearance of dry skin and mucous membranes, disturbance of orientation in space and overexcitation of the psyche. The drug is suitable for use in children of different ages. Irifrin. Eye drops that are prescribed for the treatment of iridocyclitis, uveitis and glaucomocyclic crises, before surgical procedures, as a treatment for dry and red eye syndrome and for dilating the pupil for fundus examination. The product is produced in ampoules of two and a half and five milliliters. In the first case, drops are prescribed to premature and infants. Contraindicated in old age, with increased susceptibility to components, with liver failure and hyperthyroidism. Adverse reactions may occur in the form of swelling of the conjunctiva, contact dermatitis, tachycardia and general weakness.
Useful properties of the drug
These eye drops are based on chemicals that activate alpha-adrenergic receptors.
They, in turn, have a constricting effect on blood vessels and increase blood pressure, which leads to dilation of the pupils.
At the same time, contraction of the smooth muscles of the conjunctiva occurs, which leads to the duration of the effect, which occurs within half an hour and disappears only after 5-6 hours, but in children the effect of a dilated pupil can be observed longer.
As a rule, the need for a patient to instill mesaton himself is extremely rare. This is mainly done by a specialist, who in this case uses specific instructions.
To achieve the effect of a dilated pupil, one drop in each eye is enough, but in cases where the pupil begins to narrow earlier than an hour later (which is quite rare), additional instillation may be required.
If the drug is used to treat ophthalmological diseases, the patient himself can do the instillation.
Important! The dosage in this case is one drop three times a day, and the course of treatment is determined individually and depends on how the inflammatory process proceeds and at what stage it is.