Astigmatism is not considered a dangerous disease, however, under the influence of some reasons it tends to develop into myopia, or other complex eye diseases that can have a bad effect on vision, and as a result a person can lose it completely.
Since everyone knows that pregnancy and childbirth greatly affect vision, worsening it, expectant mothers should know how astigmatism and pregnancy are related - is it possible for girls to give birth with this disease?
Despite all the warnings, it is possible to give birth with astigmatism, but for such a case there are a number of indications and contraindications that need to be clarified by an ophthalmologist. This will help prevent vision damage during childbirth, even if this pathology is present.
What it is?
Astigmatism and childbirth - is it possible to give birth?
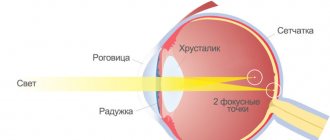
Source: birth-info.ru It is quite difficult to explain what astigmatism is (as well as to correct it). Astigmatism is one of the most common causes of low vision. Often astigmatism is combined with myopia (myopic astigmatism) or farsightedness (hypermetropic astigmatism).
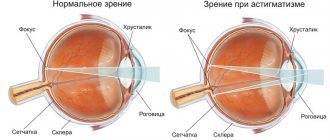
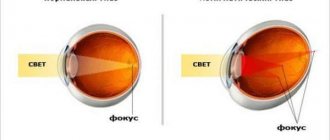
Astigmatism in Latin means absence of a (focal) point. Astigmatism occurs due to the irregular (non-spherical) shape of the cornea (less commonly, the lens). In normal condition, the cornea and lens of a healthy eye have a smooth, spherical surface.
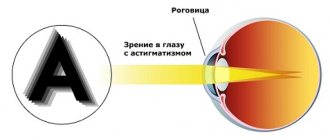
With astigmatism, their sphericity is impaired. It has different curvature in different directions. Accordingly, with astigmatism, different meridians of the surface of the cornea have different refractive powers and the image of an object when light rays pass through such a cornea is distorted.
Some areas of the image may be focused on the retina, others - “behind” or “in front” of it (there are also more complex cases). As a result, instead of a normal image, a person sees a distorted one, in which some lines are clear, others are blurred.
You can get an idea of this by looking at your distorted reflection in an oval teaspoon. A similar distorted image is formed with astigmatism on the retina. Experts distinguish between corneal and lens astigmatism.
But the influence of corneal astigmatism on vision is greater than that of the lens, since the cornea has a greater refractive power. The difference in the refraction of the strongest and weakest meridians characterizes the amount of astigmatism in diopters. The direction of the meridians will characterize the astigmatism axis, expressed in degrees.
Astigmatism is a defect in the optical system of the eye. In this case, the refraction (or reflection) of rays in different sections of a passing light beam is not the same. As a result, the image of objects becomes blurry, each point of the object is displayed as a blurry ellipse.
And the whole picture, as if in a “distorting mirror,” turns into the so-called “Sturm conoid” figure. In practice, the main complaint is deterioration of distance vision, often blurry near vision, blurred and bifurcated objects.
Causes of astigmatism
In childhood, astigmatism, which does not lead to visual impairment, is a normal variant. It develops because the cornea and lens develop unevenly. In this case, you need to ensure that visual acuity does not decrease by less than 1 diopter.
No more than 10% of children need treatment. In this case, the disease most often has a congenital nature and one of the parents suffers from astigmatism.
The likelihood of developing pathology increases in the following cases:
- The person is an albino.
- A person has retinitis pigmentosa.
- The child was born with alcohol syndrome.
- The human cornea is cone-shaped rather than hemispherical.
- In humans, the optic nerve is underdeveloped.
- The patient has a congenital deformation of the jaws and teeth, which affects the wall of the orbit and the eyeball.
All of these pathologies are congenital. In this case, both eyes of the child will suffer with varying degrees of intensity.
Acquired astigmatism can develop in the following cases:
- The resulting injuries to the cornea caused scars to form on its surface.
- Previous surgical interventions on the organs of vision.
- Lens subluxation due to rupture of the ligament of cinnamon.
- Vitamin A deficiency.
- Keratitis and conjunctivitis,
- Diseases of an infectious nature that can lead to inflammation of the eyes.
Classification
- combination with myopia;
- combination with farsightedness;
- mixed.
Astigmatism, which is complicated by myopia or a mixed type, poses a danger to the mother at the time of childbirth. Increased stress during the pushing period can cause partial or complete retinal detachment. This in turn often causes vision loss.
Most modern doctors believe that astigmatism and natural childbirth can easily be combined. The woman undergoes many examinations and receives medical recommendations. Only a doctor can accurately decide whether a woman can safely give birth on her own or whether a caesarean section will be required.
If there is a risk of retinal detachment, of course, surgery is prescribed and the mother’s organs of vision are not subject to stress. Retinal detachment is the process when it loses contact with the vascular network that feeds it. Because of this, destructive processes begin that affect visual acuity. In the worst case, the person goes completely blind.
Firstly, the amount of astigmatism matters - up to 1 diopter, astigmatism is considered physiological, weak. That is, as a rule, it does not require correction. But if it reduces vision even of such a small magnitude, alas, it needs to be corrected.
Medium degree - up to 2 diopters, high - 2-3 diopters and more than 3 diopters - this is very high astigmatism. There are other classifications, but this one best reflects the effect on defocus. Secondly, there are two types of corneal astigmatism: regular and irregular.
With regular astigmatism, there are two main refractive cross-sectional planes, within which the optical power does not change - weak and strong. There is at least some kind of regularity in such optics, even if the axes are oblique or there is a large difference in their optical power.
Regular astigmatism - in this case, two parts can be distinguished where the cornea has different degrees of refraction. This type of astigmatism can be corrected with glasses or soft contact lenses.
Irregular astigmatism - in this case, the two parts cannot be separated because there are many optical axes. This type usually develops as a result of damage to the cornea, such as during an accident (scar tissue forms), or due to uneven bulges of the cornea (keratoconus).
Irregular astigmatism is usually difficult to correct; sometimes hard contact lenses or laser treatments on the cornea can be useful. Third, the type of astigmatism depends on the location of the strong axis. If the strong axis is vertical or deviates no more than 30 degrees from the vertical, straight astigmatism.
If the strong axis is horizontal ±30 degrees, the astigmatism is reverse. If in between there is astigmatism with oblique axes. Direct astigmatism slightly increases the depth of focus, reverse astigmatism worsens visibility more, but both of these options are well corrected.
But correction of astigmatism with oblique axis glasses and lenses is worse. In astigmatic eyes, there are two perpendicular cutting planes with the greatest and least refractive power.
Fourthly, depending on how the focus is related to the retina, astigmatism is divided into myopic (myopic), farsighted (hypermetropic) and mixed - this is when in one eye part of the image falls in front of the retina, and part behind the retina.
For example, minus two and minus four - then this is complex myopic astigmatism, plus two and plus four - complex farsighted astigmatism, plus two and minus four - mixed. Myopic astigmatism is indicated by a “-” sign, farsighted astigmatism by a “+” sign, and with mixed astigmatism there are “+” and “-” in the eye.
Types of astigmatism. Classification
Astigmatism can be either a congenital or acquired eye disease. According to the degree of complexity, the disease is distinguished: - weak - less than 3 diopters; - average - from 3 to 6 diopters; — high — more than 6 diopters.
The degree of complexity of the defect is related to visual acuity. The initial degree (up to 3 diopters) does not have a significant effect on the functioning of the eyeball. The disease in many cases is combined with other pathologies of the visual system: - hypermetropic astigmatism - curvature of the cornea + farsightedness; — myopic astigmatism — corneal defect + myopia; - mixed astigmatism - the presence of signs of both myopia and hypermetropia.
Reasons for appearance
The cornea and lens of a healthy eye have a smooth, spherical surface. With the development of astigmatism, this sphericity is disrupted and light rays passing through the deformed lens or cornea are focused on the retina not at one point, but at several.
Objects are not clearly perceived by the eye. The most common cause of the disease is heredity. Astigmatism can also be acquired. Its appearance is facilitated by cicatricial changes in the cornea, which occur as a result of eye injury.
Astigmatism can be caused by ophthalmological operations, inflammatory and degenerative processes, and corneal clouding. Astigmatism is quite often combined with farsightedness (hypermetropic astigmatism) or myopia (myopic astigmatism).
There is so-called mixed astigmatism, which combines elements of farsightedness and myopia. With mixed astigmatism, one part of the light beam is concentrated behind the retina, and the other in front of it.
"Astigmatism" in translation means lack of focus
– congenital features of the structure of the eye, which are formed in the womb. As a rule, if parents have this disease, then their children are more likely to have it too.
Astigmatism can be acquired. For example, a child’s visual impairment was not detected in time or he refuses to wear glasses. The child is growing, but at the same time he is constantly squinting and straining his eyesight. Chronic diseases can complicate the situation. All this leads to malnutrition of the cornea and the development of astigmatism.
Maya Lonskaya: “Astigmatism is also provoked by constant inflammation of the cornea, chronic conjunctivitis, trauma or surgical interventions on the eye.”
A disease such as keratoconus can also lead to the progression of astigmatism. Most often it affects young men, tall and thin. Why this disease appears is not known exactly, but among the provoking factors, experts identify hormonal disorders and pathologies of the thyroid gland.
Maya Lonskaya: “With keratoconus, a disturbance occurs in the layers of the cornea. It becomes thinner and stretches out, taking on the shape of a cone. Deformation of the corneal layer interferes with the anatomical function of light refraction.”
Is it possible to give birth with astigmatism?
Every day, many happy, but extremely worried expectant mothers come to the appointment to be examined by an ophthalmologist for antenatal consultation. Needless to say, the number of people suffering from myopia today worries the minds of many ophthalmologists.
In our country, many myths were born, the authors of which were partly the doctors themselves, partly not the most savvy patients. Let's look at some of them: If a girl has moderate and high myopia, she will not be able to give birth naturally, she will be “caesareaned.”
If we consider this problem from the perspective of not the most knowledgeable ophthalmologists, then it seems to them that if a patient has a high degree of myopia, his retina must necessarily detach during the pushing period. Why they think so cannot be answered by any doctor.
Apart from the vague “well, the retina is stretched,” there is nothing more to say. In fact, the retina in myopia is indeed different from the retina of people with emmetropia. But judging the condition of the retina only by numbers is extremely stupid.
Mandatory measures
It is necessary to examine the patient’s periphery for dystrophic diseases of the retina, silent tears, etc. The retina can be in extremely poor condition even in people with good visual acuity. In turn, in the presence of high myopia, the condition of the retina may be completely normal, and the girl will be able to give birth naturally.
And nothing bad awaits her from the visual organs. Myopia is not the rarest pathology. If we look at this problem from the perspective of the pregnant women themselves, then it is also quite obvious that the upcoming birth frightens the majority of patients.
The temptation to plunge into anesthesia, and then wake up and see your baby, without screams, tension, etc., is very great. Of course, they understand that the operation of delivery is not safe, but since the doctor said so, then it must be done, as if nothing depends on it.
If you look at this problem from the perspective of an obstetrician-gynecologist, then everything is quite obvious. Childbirth can naturally last 20 hours, and all this time you have to wait, “catch” it, “watch the dilation.” And all this can start at night, on top of everything else.
What about surgical delivery? We draw up an operating plan, record the time and that’s it. We will start with high precision and finish when we planned. So what should patients who have a high degree of myopia and are expecting the birth of their baby do? Some go for an in-person examination to look at the condition of the retina.
Even the presence of very large problems with the retina does not mean the need for surgical delivery; there are many ways to correct this situation and give birth naturally. They don’t want to give birth themselves because “their vision will deteriorate.” This happened to my mother/aunt/friend.
This myth is so absurd that it is about the same as proving that you are not a camel. Carrying out childbirth naturally does not affect the level of myopia, farsightedness, or astigmatism. The mechanism of development of these ametropias does not imply its development so rapidly due to physical activity.
Indications for caesarean section
Myopic astigmatism occurs:
- low degree (myopia up to 3 diopters);
- medium degree (3-6 diopters);
- high (myopic astigmatism above 6 diopters).
There are no absolute contraindications for conceiving, bearing and giving birth to a child for women with poor vision. With the first two options, natural childbirth is possible. With degree 3 myopia, eye strain should be avoided. That is, delivery is only possible by caesarean section, because during the period of pushing it is impossible to avoid it.
And this is dangerous for a woman with the following complications:
- retinal disinsertion;
- complete loss of vision;
- ocular hemorrhage with loss of visual acuity.
Indications for surgical delivery include other vision problems:
- dystrophic changes in the retina of the eyes with myopic astigmatism;
- a sharp decrease in visual acuity during pregnancy;
- signs of retinal detachment;
- eye surgery less than 1 year after.
Complex myopic astigmatism during pregnancy
In the first trimester of pregnancy, all women should visit an ophthalmologist. This is especially important for those who have reduced visual acuity, severe myopia with astigmatism, increased intraocular pressure and have previously had eye surgery.
Generally, pregnancy does not have a negative impact on vision. A woman with myopia and astigmatism most often does not experience problems with her eyes, even if she is severely nearsighted or has had laser vision correction in the past.
Sometimes during pregnancy, visual acuity may decrease. The reason for this may be an increase in blood pressure due to gestosis. The second time during pregnancy a woman should visit an ophthalmologist at 30 weeks. If the doctor notices negative dynamics, he must prepare a conclusion for the obstetrician about possible options for delivery.
If necessary, the ophthalmologist will evaluate the condition of the eyes before delivery at 36 weeks. There are no absolute contraindications for conception, pregnancy and childbirth in women with myopic astigmatism. However, you should listen to the opinion of your ophthalmologist and postpone childbearing for a while if you have the following problems:
- if a year has not yet passed after any surgical correction of severe myopia;
- high myopia, in which there has already been retinal detachment once;
- severe myopia of the only seeing eye;
- serious eye injuries with partial loss of vision.
If a woman has problems with her eyes, during pregnancy she must be observed by an ophthalmologist and strictly follow all his recommendations. And, of course, agree with the recommended delivery option. Only in this case can you preserve your vision and find the happiness of motherhood.
Preventive measures for astigmatism during pregnancy
Pregnancy is a test for a woman’s body as a whole. Atypical workload and overwork can lead to serious and sometimes irreversible damage to various organs. To avoid deterioration of vision while carrying a child, you must:
— systematically attend scheduled preventive examinations with an ophthalmologist; - take care of proper lighting; This is especially true for doing small work, handicrafts or reading; - perform gymnastic exercises for the eyes; - minimize the time spent at the computer and watching TV, alternate this activity with periods of 10-15 minute rest; - pay attention to the diet and balance of nutrition; - give up bad habits: smoking, drinking alcohol.
Treatment of myopic type astigmatism during pregnancy
Conservative therapeutic measures during pregnancy do not differ from treatment in other situations:
— vision correction with glasses; — correction of the defect using lenses; — hardware therapy.
You should consult an ophthalmologist and choose a vision correction method, select lenses individually and wear them as recommended by your doctor.
Prognosis for childbirth
Will I be able to give birth on my own or will a caesarean section be required? Any woman who has certain vision problems worries about this. It is very difficult to answer this question unambiguously. After all, in many ways the decision about how childbirth will take place is based on a number of factors.
Such as: the condition of the fundus and retina, general condition, age, etc. Caesarean section is a surgical operation in which the fetus is removed through an incision in the anterior abdominal wall and uterus. The risk to a woman's life and health during a caesarean section is 12 times higher than during spontaneous childbirth.
Therefore, like any other surgical operation, a caesarean section is performed strictly according to indications. A caesarean section is performed in cases where spontaneous birth is impossible or is dangerous to the life of the mother or fetus.
Unfortunately, one of the most common reasons for recommendations for cesarean section is dystrophic changes in the retina. The risk of retinal detachment in women with myopia and changes in the fundus increases during natural childbirth due to pressure changes in the mother.
In modern medicine, preventive laser coagulation is used to prevent the spread of degenerative changes in the retina and, accordingly, reduce the risk of retinal detachment. This procedure involves what is called “welding” of the retina in weak spots and around breaks.
Scarring occurs at retinal coagulation points. As a result, a strong connection between the retina and the choroid occurs. The coagulation technique involves applying several rows of coagulates along the periphery of the retina.
What is the danger?
Astigmatism during pregnancy most often does not affect the woman’s condition in any way. But if astigmatism is accompanied by high myopia (myopia), then this can be dangerous. Stress during childbirth can create a risk of retinal detachment, which in turn often results in blindness.
Astigmatism is a violation of the correct sphericity of the cornea or the shape of the lens. With such disorders, several meridians of refraction of light rays and several foci on the retina are formed on the retina, as a result of which the image of an object will be blurry.
Often women suffering from astigmatism worry about how their pregnancy and childbirth will go. In order to answer this question, the woman needs to be examined. The fact is that astigmatism can be of different types. Pregnancy and astigmatism are not always a danger.
In the vast majority of cases, astigmatism does not affect pregnancy in any way, and pregnancy also does not have a negative effect on vision function. But with nearsightedness (myopic) astigmatism, a woman’s vision may be in danger.
Astigmatism is always combined with myopia or farsightedness. Simple or complex farsighted (hypermetropic) astigmatism will not pose any risk of complications during pregnancy.
Simple and complex myopic (myopic), as well as mixed (myopic and hyperopic) astigmatism can be complicated by complete or partial retinal detachment. Pregnancy is a condition that can be complicated by late toxicosis (preeclampsia), one of the symptoms of which is high blood pressure.
With myopia, the eyeball becomes enlarged, which leads to stretching of its membranes and blood vessels. This leads to a disruption in the nutrition of the retina, which causes defects to appear on its surface, and even retinal detachment can occur.
Retinal detachment leads to a sharp deterioration in vision and even blindness. With an increase in blood pressure, the threat of retinal detachment with high degrees of myopic astigmatism increases significantly. This is why women who suffer from high myopic astigmatism are not always allowed to become pregnant.
During childbirth, muscle tension also poses a risk of retinal detachment. Therefore, with high degrees of myopic astigmatism, delivery is often performed by cesarean section. Retinal detachment is a condition in which the retina of the eye loses contact with the choroid and moves away from it.
In the normal state, the retina is held to the choroid by connecting itself with the cells of the choroid. Intraocular pressure from the vitreous humor (the gelatinous substance that fills the space between the retina and the lens) is also important.
Retinal detachment causes decreased or distorted vision, and in some cases, complete loss of vision. If retinal detachment is suspected, the pregnant woman should be hospitalized immediately.
Delay can lead to complete and irreversible blindness, since during retinal detachment the fluid that is formed gradually (and sometimes very quickly) separates the retina from the choroid, and the retinal nerve cells die, which makes the process irreversible.
First aid for retinal detachment
First aid for retinal detachment consists of performing an operation to solder the retina and choroid using a specially caused aseptic (without infection) inflammatory process. The operation is performed with a laser.
Thus, pregnancy and astigmatism are not always dangerous. A real threat to the health of a pregnant woman arises from myopic or mixed astigmatism. Therefore, if astigmatism is suspected, a woman should undergo a full examination in order to know for sure that nothing will threaten her life and health during pregnancy.
Signs of retinal detachment
Due to excessive load, detachment from the vascular network can begin both during pregnancy and during childbirth. A sign of this complication is photopsia (sparks, lightning before the eyes), distortion of the image, fluctuations, floaters.
The Right Action
If there is a suspicion of retinal detachment during pregnancy, the woman should be immediately hospitalized in a hospital. The likelihood of vision preservation depends on the speed of assistance provided. Due to the detachment of the retina, fluid is released, which speeds up the process.
In addition, nerve cells die at this time, and this is irreversible. Laser surgery is performed to repair the gap as soon as possible. Astigmatism and natural childbirth are quite compatible in most cases, but with the myopic type, it is worth taking care of your future and preparing for the birth of a child by cesarean section - this method will save the vision of the mother of the newborn.
The main thing is correction
Tell me, can astigmatism be cured?
Mikhail, Kostroma
– If we are talking about congenital astigmatism, it is more correct to talk not about its treatment, but about correction. Most often, using special glasses with a so-called cylindrical component, which allows you to correct the refraction of each meridian separately and thus achieve high visual acuity. However, the disadvantage of this method is that with a high degree of astigmatism (above 3 diopters), patients tolerate this method of correction less well. Sometimes doctors have to go to the extent of reducing the cylinder force in glasses, improving their tolerability, but at the same time worsening vision.
Article on the topic
Second eyes. What glasses suit you? The second way is to use contact lenses. Until recently, we used hard contact lenses for severe astigmatism. Now there are soft, so-called toric lenses. They are quite difficult to select, but very effective.
There are also surgical approaches to correcting astigmatism, which allow you to straighten the shape of the cornea and make it spherical. But the question of the possibility of their use can be resolved in each specific case after a detailed examination.
Symptoms
Manifestations of astigmatism are accompanied by decreased visual acuity and image distortions. Objects are subject to splitting, stretching, blurring and indistinctness. Symptoms of myopic astigmatism are related to its degree:
- Low degree is characterized by the presence of myopia up to 3 diopters.
- With an average degree, myopia is detected from 3 to 6 diopters.
- A high degree is indicated by the presence of astigmatism of more than 6 diopters.
Any degree of astigmatism is combined with the following symptoms:
- Regular headache.
- Tearing.
- Difficulty concentrating vision.
- Curvature of the image shape.
- Blurred image and its splitting.
If there is a low degree of astigmatism, the expectant mother may not be aware of the disease. This is due to slight distortion of the image, which is perceived as normal. With low and moderate degrees of astigmatism, natural birth is allowed.
If there is high degree of astigmatism, then surgical delivery is indicated. Strain on the eyes during labor can cause serious consequences:
- Retinal detachment.
- Complete or partial loss of vision.
- Loss of visual acuity due to ocular hemorrhage.
Indications for a cesarean section are also:
- Dystrophic changes in the retina.
- Significant deterioration of vision during pregnancy.
- Symptoms of retinal detachment.
- Eye surgery that was performed less than a year ago.
Does astigmatism affect childbirth? Is it possible to give birth with astigmatism?
This disease can be either acquired or congenital. In most cases, it is combined with other ailments of the visual organs.
- Myopic astigmatism - in this variant, a corneal defect is combined with myopia.
- Hyperopic - with this astigmatism there is not only curvature of the cornea, but also farsightedness.
- Mixed - the presence of both previous points.
There are three degrees of distribution, which depend on the presence of visual acuity:
- weak - less than 3 diopters;
- average - from 3 to 6;
- high - more than 6.
Hereditary eye diseases
Many young mothers are afraid that their chronic illnesses can be inherited by their baby.
Is it so? Most modern ophthalmologists adhere to this opinion, and believe that the disease can still be transmitted from mother to child.
In some cases, astigmatism is acquired, but if the mother or father suffers from it, the child is very likely to develop a deviation.
The disease is mainly corrected with glasses and contact lenses. However, it is possible to get rid of the disease permanently only with the help of laser intervention.
Diagnostics
Source: geektimes.ru
Since astigmatism is an optical defect, firstly, the optics of the eye are carefully examined. And only an ophthalmologist will give the correct conclusion. There are a number of tests for this: research on an autorefractokeratometer, an aberrometer, a phoropter with the selection of trial lenses to determine visual acuity with maximum correction.
A very interesting radiant figure gives an idea of how much astigmatism is present - if you look at the center of the figure from below, some of the lines will be sharper, and some will “blur” for those who have astigmatism.
In phoropter tests, the ophthalmologist also has a number of techniques in his arsenal to clarify the presence of astigmatism, its axis and magnitude. And this process is always quite time-consuming - this can be confirmed by those patients who have done, for example, SMILE.
Checking tests with “fogging, cross-cylinders with force and axial tests” takes 20-30 minutes. So, when it has been determined that there is still astigmatism, you need to determine “who is to blame” - the cornea or the lens.
Examination of the cornea should include keratotopography - study of the relief and optical power of the cornea over its entire area, optical coherence tomography, which determines the thickness, morphology and geometry of the cornea also over its entire area, examination of the posterior surface of the cornea using a Scheimflug camera to determine irregularities of the anterior and posterior surfaces of the cornea , confocal microscopy - examination of the posterior layer of the cornea (endothelium).
Based on the results of this examination, we can already conclude how healthy the cornea is. Sometimes astigmatism is associated with the lens - its shape, the presence of various opacities in it, or a change in its position in space; such astigmatism is called lenticular astigmatism.
And it happens that the cornea is incorrect and the lens is distorted, then the result will affect the final optics as a whole. We can also study the anterior segment of the eye by performing ultrasound biomicroscopy in order to examine parts of the eye that are inaccessible to other methods and measure them.
Yes, by the way, for children there is a pediatric autorefractometer that can be used to measure the optics of a child’s eye, non-contact, when you don’t need to press anything to his forehead and everything happens at a distance of 1.5-2 m. This is important, since children are generally capricious and they look poorly (or even refuse to look) where the ophthalmologist asks, and late diagnosed astigmatism leads to serious consequences. It is not available in all clinics, as it is expensive. It's called PlusOptix.
Treatment
If astigmatism is not treated (or treated incorrectly), the disease can lead to a sharp deterioration in vision, amblyopia, strabismus and other types of visual impairment.
If astigmatism is treated correctly, then, as a rule, vision is completely restored, visual acuity improves (a person sees clearly), and all the pain symptoms that accompany this disease are eliminated.
Currently in medicine there are several methods for treating astigmatism, both conservative and surgical. Here are the main ones:
Optical vision correction
Optical vision correction for astigmatism involves the use of medical glasses and contact lenses.
Glasses are the most common method of vision correction, especially for astigmatism in children. To treat astigmatism, special glasses with cylindrical lenses are used. Depending on the type of astigmatism, cylindrical lenses can be positive or negative.
Glasses for astigmatism are considered the simplest, most accessible and cheapest way to correct vision. At the same time, this correction method is not without its drawbacks. In particular, glasses cause a lot of inconvenience to the patient: dirt accumulates in them, they fog up, and do not allow them to play sports.
Glasses limit peripheral vision and also disrupt the stereoscopic effect, which is especially important for drivers. And in case of accidents or falls, glasses can break and cause injury to a person. Special contact lenses are often used to correct mild astigmatism.
For a long time, doctors only had hard contact lenses, which were very inconvenient to use. However, over time, it became possible to use special toric and spherical lenses, which are more convenient to use, although not without drawbacks.
Only an ophthalmologist can select contact lenses to correct astigmatism. Recently, new orthokeratolytic lenses have been used for vision correction. These are lenses for night wear, which are made of special gas-permeable plastic.
During sleep (within 8 hours), while a person wears these lenses, the curvature of the cornea changes, which persists for about a day, after which such lenses must be reinstalled before bedtime. The patient should know that after prescription of medicinal glasses or contact lenses, he must be regularly observed by his attending ophthalmologist.
Both glasses and contact lenses need to be promptly changed to stronger or weaker ones, depending on the type of astigmatism and the course of the disease. It should also be understood that neither glasses nor contact lenses can completely eliminate the problem of astigmatism.
They are only capable of correcting vision, and other treatment methods are used to treat astigmatism.
Laser vision correction
Recently, excimer laser correction has been actively used to correct vision with astigmatism.
Although laser correction using the LASIK method is a surgical procedure, it is difficult to call it an operation. The entire procedure lasts only 10-15 minutes using local anesthesia. During the procedure, the doctor uses a microkeratotome to separate the top layer of the cornea.
This is necessary to provide the laser with access to deeper layers. Then the laser evaporates part of the cornea, and the flap removed by the microkeratotome is returned to its original place and fixed with collagen. There is no need to apply any stitches, since the epithelium along the edge of the flap is restored on its own.
The rehabilitation period after laser vision correction is minimal. Already 1-2 hours after the operation, the patient sees much better, and within a week, vision is completely restored.
Astigmatomy
This is a surgical method for treating astigmatism, the essence of which boils down to the fact that special arc micro-notches are applied to the periphery of the cornea, which makes it possible to weaken refraction along the enhanced axis of the cornea.
Astigmatomy is usually performed for myopia or mixed astigmatism. Refractive lens replacement. If the cornea is too thin and has a high degree of deformation, the patient may be indicated for refractive lens replacement.
The patient undergoes surgery to implant an artificial lens, which corrects the visual impairment observed with astigmatism.
Recently, in modern ophthalmology, excimer laser correction has been used to correct low-grade astigmatism (up to 3 D). The essence of the procedure is this: a “cold” beam evaporates a thin layer of the cornea, changing its curvature.
This technique is one of the latest developments in refractive surgery, so it has many advantages:
- painlessness;
- highest precision of manipulation;
- gentle effect on the cornea;
- multi-level equipment protection system, thanks to which correction is carried out without failures;
- good performance.
Among other things, the procedure itself, as a rule, takes no longer than 15 minutes, and the laser operates for 30-50 minutes during the entire correction period. A few hours after the operation, the patient can already look at the world normally, but his vision is fully restored in 5-6 days.
Non-surgical method
Vision correction with soft contact lenses or glasses does not meet the requirements of a dynamic life, because such means create a lot of inconvenience. For example, children cannot fully engage in their favorite sports, and there are many restrictions for adults.
For this reason, orthokeratology is becoming increasingly popular in the world. We are talking about the use of Paragon CRT night wear lenses made of gas-permeable polymer. The mechanism of action of such therapeutic lenses has some similarities with laser vision correction.
But the main difference is that the curvature of the corneal surface changes temporarily, and during sleep. Clinical trials show that after eight hours of wearing night lenses, the altered shape of the cornea remains for a long period (up to a day).
The benefits of refractive therapy are obvious because astigmatism is treated without surgery.
Complications
Whether it is possible to give birth with astigmatism naturally without using a cesarean section will only be determined by a thorough examination by an ophthalmologist. Farsighted astigmatism and childbirth are a very real combination, because the hypermetropic form does not threaten complications, the effect on the retina during pushing and contractions is insignificant, and there is no threat of detachment.
Existing danger
Childbirth with astigmatism and myopia requires special attention from specialists: simple and complex forms of myopic deformation of the cornea can lead to complete or partial retinal detachment. Complications can be caused by muscle tension and increased pressure during pushing and contractions.
To avoid detachment, they often resort to childbirth by cesarean section: during the operation, the mother’s body is not subject to physical stress and the retina does not detach. Detachment is a process during which the retina loses contact with the vascular network that feeds it.
Depending on the degree of alienation from the vessels, negative changes occur that affect visual acuity: distortion or decreased function is possible, and in particularly difficult cases, absolute blindness. Retinal detachment is also affected by intraocular pressure.
Myopic astigmatism is dangerous during childbirth; in some cases, during pregnancy planning, ophthalmologists do not recommend giving birth to a child due to the high probability of becoming completely blind and becoming disabled.
Mixed astigmatism is also an indication for delivery by cesarean section due to the risks listed above. Whether a cesarean section is necessary for astigmatism in a particular case can be determined only after examining the fundus and measuring intraocular pressure.
Interesting Facts
If there are or are discovered any vision problems, then you will have to prepare for childbirth especially carefully. Do not ignore visiting not only an obstetrician-gynecologist, but also an ophthalmologist. It happens that during pregnancy something happens to the eyes: toxicosis and other complications of pregnancy can affect the state of vision.
After all, hormonal changes occur in the body, which affects everyone differently. And the eyes are one of the organs that experience its effects.
- Women who wear contact lenses sometimes complain that they feel uncomfortable during pregnancy. Try wearing glasses and then return to contact lenses after giving birth.
- Sometimes it may seem that your vision has deteriorated since the beginning of pregnancy. Pregnant women are sometimes too suspicious (which is understandable), so their confidence in a possible deterioration of vision often turns out to be unfounded. However, such fears may still have a basis in reality.
- During diagnosis, ophthalmologists examine not only the degree of refraction, but also the condition of the retina. Are there any degenerative changes or tears on it? The task is to maintain the retina in good condition, to ensure that there are no hemorrhages or ruptures. It is also mandatory for doctors to examine the fundus of the eye and measure eye pressure.
- Vascular changes very often cause the effect of “floaters before the eyes.” These things are not always dangerous, but it is certainly worth bringing them to the attention of a doctor. Sometimes this may also indicate retinal pathology. So it’s best to get examined once again and make sure that nothing bad is happening to you.