If people see poorly in the distance, then perhaps they have minus 1 vision. In such a case, myopia is diagnosed, which must be treated with the help of correction means - glasses or contact lenses. A patient whose visual function has begun to deteriorate is recommended to do eye exercises every day. Myopia of the 1st degree still responds well to treatment, therefore, if it is started early and correctly, it is possible to completely restore vision and the person will see better.
Why is there a problem?
Minus vision means that the patient has progressive mild myopia. The disorder progresses not only in adulthood, but the problem is often detected in children, including infants. Experts identify 2 types of sources that influence vision reduction to -1:
- Anatomical reasons. When the eye grows in the anteroposterior region, it is unable to normally adjust the focus of an object on the retina. In this case, the muscles of accommodation remain unchanged and function normally. If the unit of vision continues to decrease, this means that the disease is progressing and scleroplasty is required.
- Accommodative. Myopia is often the result of weakened muscles that need to be strengthened with eye exercises and other conservative methods. After such procedures, the patient sees better and does not complain of other unpleasant symptoms of myopia.
Pathology can develop if the workplace is poorly lit. Not all patients under the influence of these factors have vision reduced to minus 1. The development of pathology is influenced by several factors, namely:
- unfavorable working conditions that affect visual function;
- insufficient or excessive lighting during work;
- professional activity in which the patient is forced to constantly examine small details;
- problems in the metabolic process.
Vision drops to minus 1 often in patients whose parents or close relatives also experienced varying degrees of myopia. In this case, a genetic predisposition to an ophthalmological disease is established.
Myopia from a medical point of view
Doctors say that up to thirty percent of the world's population have vision problems. However, in developed countries this figure can reach fifty percent. For example, every second resident of Japan, a world leader in technology, is forced to wear glasses or use contact lenses.
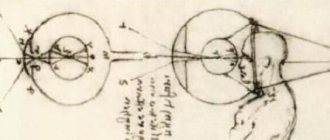
To understand why this kind of difficulty arises, it is worth finding out on what principle the eye works. All that a person sees are rays of light reflected from surrounding objects. They are perceived by the sensitive element of the eye - the pupil . It collects them and focuses them on the retina - the part that transmits images to the nervous system and then to the brain.
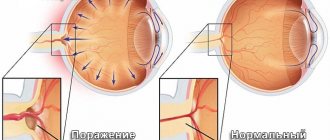
In a healthy person, the point at which light rays are collected lies exactly on the retina. This is why the world around us looks clear. In the case of myopia (from the Greek “myo” - squinting and “pios” - gaze), called minus vision, the rays are focused in front of the retina, after which they begin to scatter again . Due to scattering , the image reaching the brain turns out blurry.
Complications of high myopia
An equally dangerous complication, which can also lead to vision loss, is glaucoma. This disease is characterized by increased intraocular pressure. A person may periodically experience heaviness in one or both eyes at once, blurred vision, increased fatigue, headaches and pain in the eyes. The symptoms are explained by the fact that with glaucoma, degeneration occurs, that is, destruction of retinal tissue.
The danger of this disease is that it may not appear in early stages of myopia. Most often, people over 65 years of age are susceptible to this disease. But sometimes it occurs in 40-45 year olds.
Another complication that occurs with myopia is retinal dystrophy. In its central part, which is responsible for the image, degenerative processes occur.
Refraction of vision
Refraction of vision refers to the process of refraction of light rays in the optical system of the eye. The curvature of the lens and cornea, as well as the distance between them, determines the strength of light refraction.
Types of refraction:
- Emmetropia is normal refraction.
- Myopia – a person has difficulty seeing into the distance.
- Farsightedness – a person has difficulty seeing close up.
How to treat myopia in children, see the material.
With normal refraction, light rays intersect at the focus of the retina, so a person sees all objects well at any distance. To obtain a clear image of an object located nearby, the eyes increase their refractive power, thereby increasing accommodation. With farsightedness, the eyes have weak refractive power . Rays of light intersect behind the retina. Therefore, the eyes are forced to increase the power of refraction, even when a person looks into the distance. To improve vision, you can perform exercises for farsightedness.
And with myopia, the eyes have a greater refractive power, since the rays of light converge in front of the retina.
The higher the degree of myopia or farsightedness, the worse the quality of vision.
Both of these pathologies have three degrees:
- Weak degree - no more than three diopters.
- The average degree is from four to six diopters.
- High degree - more than six diopters.
Determination of refraction
To determine refraction, a special unit of measurement is used - diopters. This unit is needed to indicate the power of refraction. The procedure for determining refraction is called refractometry.
Find out how to choose the right glasses here.
Laboratory refractometer
Refraction is determined using optical glasses or a special refractometer.
Refraction may be different for both eyes. It happens that one eye is nearsighted and the other is farsighted. This is called anisometropia.
One of the methods for determining refraction is retinoscopy. This method consists of observing the movement of the shadow in the lumen of the pupil. To do this, the patient and the ophthalmologist go into a darkened room, where the doctor shines a siascope into the patient's pupil and observes the shadow. Its direction of movement depends on refraction. Retinoscopy is necessary to determine refraction in children.
Retinoscopy measurement process
In order to automatically determine refraction, an ophthalmologist can use instruments such as an autorefractometer or an aberrometer. The first device allows you to evaluate the focus of the rays relative to the retina and identify the direction and magnitude of astigmatism. And the second device makes it possible to determine imperfections in the eyes.
Early symptoms
In less than a year, the patient's vision may decrease to minus 1, while clinical signs are not always immediately noticeable. Pathological changes in the visual organ can be recognized by the enlargement of the eyeball. The patient is unable to normally shift his gaze from distant objects to nearby objects and vice versa. The following symptoms are often alarming when the patient has minus 1 vision:
A sign of such a problem may be the appearance of fear of bright light.
- the appearance of “flies” before the eyes;
- temporary doubling of objects;
- incorrect perception of colors;
- fear of bright light or increased photosensitivity.
If 1 diopter decreases annually, this may signal degradation of eye tissue, as a result of which myopia rapidly progresses. Such a violation threatens complete loss of vision. If the indicators are within “-1”, then you should consult a doctor, since this is the initial stage of myopia. The specialist will select individual therapeutic measures, taking into account the age and causes of the problem.
Deviations
Myopia
Myopia or myopia is a disease in which a person has difficulty seeing into the distance. In this case, the image is focused not on the retina, but in front of it. Vision becomes so blurry because the optical system no longer matches the length of the eye.
With myopia, the eyeball becomes enlarged.
Myopia can be congenital or acquired. Sometimes it can progress. Therefore, the goal of vision correction for myopia is to weaken the refractive power of the eyes so that the image is focused on the retina.
Myopia symptoms:
- Far vision deteriorates;
- The outlines of objects become unclear;
- Objects can merge with each other, double, distort;
- Near vision is preserved.
There is such a thing as false myopia. In this case, due to overstrain of the lens muscle, a spasm of accommodation occurs. False myopia can be treated with medications and special eye exercises.
This article will tell you how to cure astigmatism.
Myopia is very dangerous because it can lead to retinal dystrophy and detachment.
Hypermetropia
Hyperopia or farsightedness is a disease in which a person has difficulty seeing close up. The image of an object is focused behind the retina. Hyperopia develops due to a short eyeball or due to weak refractive power.
With age, vision deteriorates even more significantly, as the eyes lose their accommodative ability - the lens becomes less elastic, its muscles weaken.
Symptoms of hypermetropia:
- Vision becomes blurred;
- Eye fatigue sets in quickly and there is a feeling of discomfort;
- Accommodation and binocular vision are impaired;
- Functionally decreased vision (amblyopia);
- Strabismus may be present in adults.
Farsightedness can be simple, pathological and functional. Simple or physiological hypermetropia occurs when the eye is shorter than necessary to focus light rays on the retina. Pathological hypermetropia develops with various eye pathologies and injuries. And functional farsightedness is observed in the case of paralysis of accommodation.
Astigmatism
Astigmatism is a refractive error that can often be combined with myopia (myopic astigmatism) and hypermetropia (hypermetropic astigmatism).
With this pathology, the sphericity of the cornea and lens is disrupted. Therefore, the optical power is different in different meridians, and part of the image can be focused on the retina, and another part behind it or in front of it.
Astigmatism can be corneal or lens. By its nature it is divided into:
- Congenital. It occurs in childhood and does not affect visual acuity, but only if it does not exceed half a diopter. If astigmatism is more than one diopter, then vision is significantly reduced and treatment is required (correction with glasses or lenses).
- Purchased . Occurs as a result of scarring on the cornea. Scars can be the result of trauma, surgery, or damage.
Astigmatism can contribute to the development of strabismus and rapid deterioration of vision.
Causes, risk factors
It is important to know the most typical causes of myopia development and serious risk factors. Let's focus on the most significant ones.
- Malfunctions of the vascular system. It is known that myopia may well be a complication of some other disease that has a significant impact on the functioning of the circulatory system of the eyes, as well as the entire human body.
- Heredity. Unfortunately, the disease is inherited. It is genetic predisposition that quite often becomes the cause of the development of myopia. There are even relevant statistics: when both parents suffer from visual impairments, the risk of developing such a disease in the child is a record 50 percent. If only one parent is sick, then the likelihood of a decrease in the child’s visual acuity drops to 25 percent.
- Illiterate therapy. Literacy and thoughtfulness of treatment are of great importance. It is known that sometimes doctors make mistakes. For example, lenses and glasses are prescribed incorrectly, and drug therapy is prescribed incorrectly. All this threatens complications and progression of myopia.
- Poor nutrition. The eye membranes constantly renew their tissues. For regeneration and renewal, they need a variety of nutrients. It is extremely important that the diet is well balanced and correct. This is how the eyes will receive the set of vitamins and microelements they need.
- Lifestyle. He also plays a big role. For example, known bad habits have an extremely negative impact on vision. Drinking alcohol and smoking actually cause vision deterioration. You also need to spend more time in the fresh air, take walks more often, since physical inactivity is also dangerous for the visual system. Walking is especially useful when you can relax your eyes and look into the distance.
- Excessive loads. A lot here has to do with academic loads, work responsibilities, but sometimes an unhealthy lifestyle can also be to blame. It is very harmful for eye health to spend too much time looking at the TV screen or computer monitor. All kinds of gadgets are also dangerous. Vision also deteriorates if a person reads too much. That is why it is often observed, for example, that diligent school and university students who strive to study better and strain their eyes significantly more often suffer from visual impairments.
Risk factors should be reduced to a minimum to prevent vision deterioration and myopia progression.
How is diagnosis carried out?
If there is a suspicion of the development of mild myopia, then a comprehensive examination is required. With its help, it is possible to assess visual function and find out the reasons why vision has dropped to minus 1. With a similar problem, they turn to an ophthalmologist. The specialist examines the patient’s visual organs and conducts a vision test using a special table. An important diagnostic measure is ultrasound examination. Using this diagnostic method, it is determined how elongated the eye is, making it possible to confirm or refute a decrease in vision to minus 1. If the diagnosis showed mild myopia, then the patient needs to wear glasses.
Tables to check
Special posters are used to carry out diagnostics. They may contain images of various designs, letters, icons or hooks.
- The most popular among Russian ophthalmologists is a poster depicting letters (Sivtsev’s table).
- Sometimes doctors use the Golovin table, which shows rings with ruptures.
- When checking children, ophthalmologists prefer Orlova's poster with different pictures.
Letters or pictures are located on twelve lines, and their size decreases with each line (starting at the top and going down). On the left side of each line, the symbol “D” indicates the distance from which, with good vision, the subject should see all the symbols. For the top line it is 50 meters, and for the bottom line 2.5. On the right side of the lines, the letter “V” indicates visual acuity indicators, which are correct when the subject reads symbols from 5 meters. This indicator is equal to 2 if the subject distinguishes the bottom line and 0.1 if he sees only the first.
Treatment of myopia in children who have reached adolescence
To achieve a lasting positive effect in the treatment of myopia in adolescents, it is necessary to act comprehensively, without neglecting any possibility of improving or stabilizing the situation. If the cure for the disease occurs successfully thanks to correctly selected measures, noticeable positive changes can be expected after 4-6 months.
The following actions must be taken:
- Step 1. Contact an ophthalmologist with extensive experience and an excellent reputation. First, he talks about the action plan for treating myopia, notes real prospects, and then clarifies the necessary actions, which often have to be done daily.
- Step 2. Taking classes on specially designed devices. They are available in most vision restoration centers, so it is not difficult to apply courses of such treatment at least 2 times a year.
- Step 3. Physiotherapy for the general restoration of a healthy state of the visual apparatus.
- Step 4. Drug therapy.
- Step 5. Scleroplasty. It is carried out to achieve not a direct, but an indirect result. Due to trophic features, such surgical intervention significantly improves the blood supply to the back of the eyeball.
Surgery
This is a radical method, which is prescribed for a high degree of myopia. He:
- allows you to solve the problem in the shortest possible time;
- in some cases it serves as the only chance to preserve vision;
- makes it possible to stop the progressive change in the shape of the eye and reduce the risk of complications.
Surgical treatment of myopia
Various surgical methods are used to combat myopia.
Scleroplasty
The indication for such an operation is myopia, which progresses, annually worsening vision by 1-1.5 diopters. The intervention is performed in an eye clinic and lasts up to 15 minutes. If necessary, it can affect both eyes at once or be combined with other types of correction.
Scleroplasty
The essence of scleroplasty is that a biomaterial is injected behind the eyeball, which increases the thickness of the sclera. A kind of bandage is formed that does not allow the eye to grow in length. Over time, the material grows into vessels, which improves blood circulation and ensures maximum access to nutrients.
Scleroplasty itself does not eliminate myopia, but only helps stop its development. To completely eliminate myopia, you will also need laser vision correction.
Scleroplasty according to Snyder-Thompson
Keratotomy
During the operation, superficial incisions are made on the cornea, which make it flatter and reduce the refractive power. The number and depth of notches are planned in advance, using computer modeling capabilities for this. Special programs allow you to predict the optimal option, taking into account such parameters as:
- degree of myopia;
- patient's age;
- level of daily visual load, depending on profession and habits;
- individual anatomical features of the eyes.
Keratotomy
Keratotomy allows you to correct myopia up to 5 diopters at a time. Among other things, this type of intervention is used to combat congenital and post-traumatic astigmatic defects.
Both operations are performed using a laser surgical instrument, so they are low-traumatic and rarely cause complications during the rehabilitation period. Which one is better to choose in order to get the maximum effect, the doctor decides in each case.
The essence of radial keratotomy
What to do: basic treatment methods
The patient's situation can be corrected by prescribing glasses. Vision minus one lends itself well to therapeutic actions if they are performed promptly and regularly. There are such ways to combat myopia that help stop the pathological process and improve visual function:
- Correction by optical means. The patient is prescribed special glasses or contact lenses aimed at scattering light. There is no need to wear them all the time, but only as needed - when driving a car, working in front of a monitor, etc.
- Therapy with eye exercises. In this way, it is possible to strengthen the eye muscles, which will improve vision. This technique is effective if myopia is of the accommodative type. Additionally, medications are prescribed, including vitamin complexes that include lutein.
- Medicines. It is possible to improve blood flow in the eye muscles using special drops.
- Hardware therapy. If the patient’s vision has decreased to minus 1, then special devices are used. Treatment can be carried out at home, but choosing treatment equipment is required only with an ophthalmologist.
In advanced cases of myopia, radical therapy may be required, including scleroplasty or correction using a laser beam. More often, this technique for negative vision is used in patients with anatomical causes of the disease.
Treatment
You can eliminate the symptoms of myopia, or myopia, with the help of:
- wearing glasses and contacts,
- operations,
- medicines,
- exercises.
Wearing contact lenses or glasses will correct visual inaccuracies. But this method for visual impairment minus 1 is controversial. Its effectiveness depends on the cause of the pathology. If myopia occurs due to muscle weakness, then wearing glasses and contacts will aggravate the situation.
Operations
This type of treatment is only available to patients over 18 years of age.
The following types of surgical intervention are distinguished:
- scleroplasty (strengthening the posterior wall of the lens),
- laser correction (changing the shape of the cornea),
- surgery to replace the lens with an artificial lens.
Laser correction is not possible for myopia of more than 15 diopters. The type of surgical intervention is prescribed by an ophthalmologist.
Medicines
Visual impairment can be restored if special medications are used. Prescribed drugs include:
- 1. Anti-inflammatory: diclofenac, dexamethasone.
- 2. Antibacterial: Albucid, Floxal.
- 3. Vitamins: Quinax, Taufon.
- 4. Moisturizing: Oftagel, Systane.
- 5. Adrenergic blockers: Fotil, Proxofelin.
- 6. Vasoconstrictors: Visine, Okumetil.
- 7. Antiallergic: Allergodil, hydrocortisone.
The dosage and frequency of use are indicated by the ophthalmologist.
Visual processes
People with myopia perceive the world around them differently. They can clearly see objects located close to them. When there are no complications associated with the disease, a person does not have any problems distinguishing nearby objects.
When you turn your gaze to more distant objects, it immediately becomes clear: they are poorly visible. The image is transformed, the “picture” blurs. Unfortunately, in some cases, myopia is also complicated by astigmatism. In this case, patients have difficulty seeing near and far.
Prevention
To ensure that the patient’s vision does not decrease to minus 1, it is necessary to carefully monitor the condition of the eyes. The patient is advised to perform hygiene procedures and eat a balanced diet. The body must have a large amount of vitamins and microelements for the visual system to function normally. If the patient constantly sits in front of the monitor screen or interacts with small objects, then it is necessary to take frequent breaks for eye gymnastics, which prevents vision from decreasing to minus 1 and below. When the first unpleasant signs occur, you should contact an ophthalmologist without self-treatment.
Maximum minus vision
The maximum minus is still unknown to scientists. There are cases when vision reached -35 diopters. With such indicators, the patient does not see anything from a distance of 1 cm. That is, almost complete blindness occurs. Further progression of the disease leads to complete loss of visual perception.
Table. Minus of vision, and how a person sees.
| Values in diopters | Symptoms |
| -0.75 to -2 | A spasm of accommodation appears. This is a disruption of the ciliary muscle, which supports clear vision of objects. The violation is small, but it causes severe discomfort. |
Ordinary text is difficult to see from a distance of 40 cm. The outlines of objects are clearly visible, a person can distinguish them, but they may be blurred.