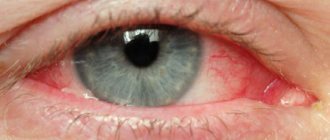
Glaucoma is a chronic disease. To slow down pathological changes in the fundus of the eye, it is recommended to adjust your lifestyle in accordance with contraindications for this disease.
Medicines. When visiting a doctor about any disease, you must inform the specialist that you are being seen by an ophthalmologist in connection with glaucoma. There are a number of medications that are contraindicated for this pathology:
|
|
Diet. Excessive indulgence in salty, pickled, sweet and fatty foods is contraindicated in any form of glaucoma. Regular consumption of alcohol is strictly prohibited.
Physical exercise. All types of activities associated with tilting the head down, for example, working in the country, are contraindicated. Some types of fitness and sports are also not recommended. Exercises involving heavy lifting and jumping are generally contraindicated.
Lighting. A long stay in the dark negatively affects the hydrodynamics of the eye, so reading, watching TV, working and performing daily household chores is necessary in sufficiently bright lighting. Prolonged stay in darkness or twilight is contraindicated. In summer, when going outside, it is recommended to use sunglasses with high-quality UV filters. Any activity in the sun without wearing a hat is contraindicated.
Cold and warm. Both low and high temperatures (as well as sudden changes in them) can worsen the condition of patients with glaucoma. Therefore, prolonged exposure to the cold is contraindicated, especially in the wind, as well as in direct sunlight.
What drugs are contraindicated for glaucoma?
List of medications to avoid:
- Corticosteroid eye drops can worsen open-angle by damaging the already abnormal trabecular meshwork in the eye. This occurs in most people with open-angle disease who use steroid medications.
- Drugs with anticholinergic properties may have a negative effect on patients with the narrow-angle form of the disease. Medicines block the action of acetylcholine, which transmits signals from one nerve cell to another. Such drugs are used to treat asthma, urinary incontinence and gastrointestinal problems. Many medications used to treat depression can have side effects in patients with the narrow-angle form of the disease. These include selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) such as Prozac (fluoxetine) and Paxil (paroxetine). Tricyclic antidepressants such as Elavil (amitriptyline) and Tofranil (imipramine).
- Antiallergy medications containing diphenhydramine put patients at risk.
- Sulfonamide-containing medications. There are certain medications that can cause angle closure in some people. Examples of medications that contain a sulfonamide include Topamax (topiramate), Diamox (acetazolamide), Sumycin (tetracycline), and Bactrim (trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole).
- Oral steroids help reduce inflammation and immune system activity. This type of medication may affect eye pressure in individuals who have open-angle glaucoma.
We recommend reading: Laser treatment of glaucoma
There are contraindications among sleeping pills. It is not recommended to use Yunisom and Donormil. Antibiotics are also not allowed to be used. If there is an infection, you should remind the doctor about the existing eye pathology to select the optimal drug.
Reminder for a patient with glaucoma
Glaucoma is insidious - it creeps up unnoticed, it can carry out hidden destructive work for a long time, only to then erupt into a sudden, seemingly catastrophe.
Untreated, advanced glaucoma inevitably leads to decreased vision and complete blindness.
An eye that no longer sees light can cause severe pain, and then there is nothing left but to remove it.
(Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, prof., d.m.s. Nesterov A.P., prof., d.m.s. Egorov E.A.)
Keeping this in mind, you will probably not be too lazy to visit an ophthalmologist’s office on a preventive basis and check the condition of your eyes.
Young people rarely get glaucoma; it usually develops after age 40. If you are at this age, a preventive examination is mandatory.
Diabetes mellitus and atherosclerosis predispose to the development of glaucoma. People suffering from these diseases should pay special attention to protecting their vision. A hereditary predisposition to glaucoma has been established. If any of your blood relatives have had or have glaucoma, you are at increased risk. The essence of this disease is a periodic or constant increase in intraocular pressure. Why is it rising?
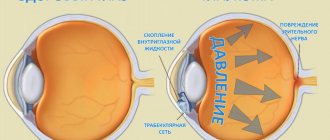
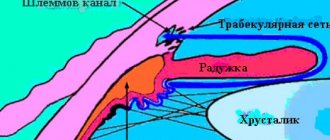
Imagine the events taking place in your eye day and night: every minute about two cubic millimeters of moisture enters it and the same amount must flow out. The amount of intraocular pressure is determined by the balance of inflow and outflow, and with glaucoma, the outflow is impaired, excess moisture remains in the eye, and the pressure increases. The fact is that moisture flows through a special drainage system, consisting of a porous diaphragm, which is located in the corner of the anterior chamber of the eye, and microscopic tubules that remove moisture after filtering through the diaphragm into small blood vessels on the surface of the eye. Increased pressure compresses and deforms the fluid outflow pathways, which contributes to a further increase in IOP.
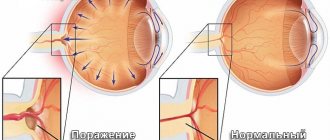
You may not feel the increased blood pressure, but that doesn't make it any less dangerous. The higher the pressure, the longer it remains at high levels, the more the optic nerve suffers. Gradually, its atrophy sets in, it fades and dies. And along with it, vision dies.
Normal intraocular pressure is considered to be between 9 and 22 mmHg. Art. But if your blood pressure was measured with a Maklakov tonometer and it turned out to be a little higher, don’t be alarmed! At the moment of measurement, the tonometer (weight) presses on the eye, which increases the readings. The so-called tonometric pressure is considered normal within the range of 17-25 mmHg. Art.
Having diagnosed glaucoma, the doctor will usually tell you its form - open-angle or closed-angle. The difference between them is the mechanism that increases pressure.
In angle-closure glaucoma, the disease occurs when the peripheral portion of the iris covers the angle of the anterior chamber of the eye, making it difficult for fluid to reach the drainage system. Having no outlet, it accumulates in the eye, and intraocular pressure increases.
With an open-angle form, access to the drainage system is open, but its own filtration capacity is impaired, and therefore moisture again flows out of the eye with difficulty. The end result is the same - increased intraocular pressure.
The open-angle form is “worse,” perhaps, only because it is asymptomatic for a particularly long time and is detected in the later stages.
Angle closure is more frank - with a strong increase in pressure, it can manifest itself with an acute attack: pain occurs in the eye, brow ridge, temple, the affected eye seems to be covered with fog, rainbow circles appear when looking at a lamp or other light source.
The attack can be stronger or weaker, more often it occurs in the evening. This means you need to rush to the doctor immediately!
A mixed form of glaucoma is also possible, when there is both a partial blockade of the angle of the anterior chamber of the eye and a deterioration in the filtration capacity of the drainage system.
The conclusion that the doctor will write to you may contain the Latin letters A, B, C. This indicates the level of intraocular pressure: A - within normal limits, B - moderately increased (up to 33 mm Hg), C - high (above 33 mmHg.).
The following diagnosis is also possible: “Normal pressure glaucoma.” Most often in these cases, the pressure remains in the upper limit of normal, but blood circulation in the optic nerve is sharply deteriorated and, therefore, its functions are impaired.
The doctor selects treatment taking into account not only the characteristics of glaucoma, but also your general condition. It is almost impossible to completely cure this disease - it is chronic. But with timely, correct and systematic treatment, the development of glaucoma can be stopped and good vision can be maintained.
Tune in to resist the disease, which means to accurately, accurately, and patiently follow the doctor’s orders.
The basis of treatment is drugs that reduce intraocular pressure. Typically these are eye drops and it is likely that you will be using them for the rest of your life. However, you have a chance: with age, glaucoma can become “burnt out” - this means that vision is maintained within certain limits, the pressure stabilizes, so there is no longer a need to constantly lower it.
The instillation technique is simple, you can easily master it yourself, and very soon this procedure will become as familiar as, say, brushing your teeth in the mornings and evenings.
Important material on this topic: treatment of glaucoma in Moscow
So, look up, pull down the lower eyelid with the index finger of one hand, and instill the medicine with the other. The conjunctiva holds only one drop, no more is required. Bury the second one if you are not sure of an accurate hit.
Try not to touch the eyelashes and eyeball with the tip of the pipette, so as not to disrupt the sterility of the medicine and not to injure the eye. True, most bottles with eye drops are now equipped with plastic droppers with a safety tip.
The drugs of first choice today are prostaglandin analogues ( xalatan, travatan, lumigan) . They are very convenient to use, because... They are instilled only once a day, and the hypotensive effect lasts more than a day. Depending on the level of initial intraocular pressure, the effect is 3 – 12 mmHg or more. In some cases, with long-term use of drugs in this group, side effects are observed in the form of increased eyelash growth and changes in the color of the iris.
is now widely used to treat all types of glaucoma . In pharmacies, this drug comes under different names: ofthimolol, arutimol, okumed, timoptic... Timolol is not only effective, but also convenient - it is usually instilled only 1-2 times a day.
The shelf life of factory-produced eye drops is at least 2 years, but after opening the bottle they can be used for no more than a month. Those prepared in a pharmacy have a short shelf life - 7 days from the date of preparation. Before opening the bottle, both drops can be stored at room temperature in a dark place, and after opening - in the refrigerator.
Like any medicine, eye drops can have side effects. For example, alphagan, clonidine , while reducing intraocular pressure, can simultaneously reduce total arterial pressure, which, for example, is undesirable for a hypotensive person.
Increased sensitivity to a particular drug is possible, and then immediately after instillation there is a burning sensation, discomfort, the eye may turn red, and sometimes a headache begins, the heartbeat quickens, and arrhythmia appears. You must inform your doctor about such sensations, and he will select another remedy or advise how to mitigate the complications that arise.
The ophthalmologist also needs information about what chronic diseases you suffer from. After all, some eye drops are contraindicated for diabetes, bronchial asthma, chronic lung diseases, and heart failure. Such patients are usually prescribed betaxolol (Betoptik).
If you are prescribed pilocarpine, pay attention to which version. The aqueous solution should be instilled 3 times a day, and extended-release solutions (methylcellulose, polyvinyl alcohol) - no more than 2 times a day. In recent years, pilocarpine has been used relatively rarely due to its constricting effect on the pupil and the possibility of developing cataracts.
In cases where one drug cannot reduce intraocular pressure to normal values, combination drugs are used. Since they contain two components, the effect of such drugs is higher than from one of the components ( Xalacom, Ganfort, Cosopt, Azarga, Combigan, Fotil ).
In the treatment of glaucoma, not only eye drops are used, but also medications taken orally, for example, acetazolamide (diacarb). This drug, which reduces the production of intraocular fluid, also has a moderate diuretic effect, and potassium, necessary for cardiac activity, is washed out with urine. Therefore, potassium orotate and panangin are usually prescribed along with diacarb. Try to enrich your diet with foods containing a lot of potassium. These are baked potatoes, dried apricots, zucchini, bananas.
is also taken orally in the form of a 50% solution . To improve the taste, you can dilute it with fruit juice and add citric acid. This drug is usually prescribed for an acute attack of glaucoma.
If you have such an attack, and it is impossible to quickly get to a doctor and you don’t have glycerol at hand, use a saline laxative, for example, magnesium sulfate (“bitter salt”), dissolving about 30 g (a full tablespoon) in ½ glass of water.
The complex of drug treatment for glaucoma also includes drugs that improve cerebral circulation and stimulate metabolic processes - trental, cavinton (vinpocetine), picamilon, tanakan, mildronate, multivitamins (mainly group B). Recently, antioxidants (emokipin, lipoic acid, mexidol) . You may be taking such medications as prescribed by a therapist or neurologist - tell your eye doctor about this so that he can adjust the treatment.
If you are offered physical therapy, in particular stimulation of the optic nerve and retina using weak electric currents or magnetic fields, go ahead with these procedures! They are quite effective and completely safe.
Trust in laser and surgical methods - such an operation can be life-saving for you in a situation where other means have already been exhausted. Surgical interventions for glaucoma are now well developed, performed quickly and painlessly.
Don’t delay surgery – time is precious when treating glaucoma! The course of this disease largely depends on your lifestyle.
♦ Work as much as your age and general health allow, do not strain yourself. Avoid physical and nervous overload. The maximum weight that can be lifted is 10 kg.
♦ Even weeding the beds can become an overload for you if you work at an angle. Adapt some kind of bench or chair - and don’t bend over. Whatever you do - read, draw, knit, do not sit with your head bowed or in poor lighting.
♦ You can watch TV, but also in good lighting (not in the dark!) and in the correct position, so that your head is neither tilted nor thrown back.
♦ When reading and other intense visual work, take short breaks of 10-15 minutes every hour.
♦ Eat rationally according to your age, prefer vegetable dishes, fish, raw vegetables and fruits, limit animal fats and sugar.
♦ Liquids, if there are no other indications for this, may not be particularly limited, but you should not immediately drink more than a glass. Tea is even beneficial, since the caffeine it contains improves blood circulation in the eye tissues and increases intraocular pressure in rare cases. A cup of coffee is not forbidden, but to be sure, it is better to do a caffeine test (ask your doctor with this request): you need to measure intraocular pressure before you drink coffee, and 1-1.5 hours after that.
♦ If you are a smoker, stop smoking immediately! Nicotine is harmful to your eyes.
♦ Do not wear tight collars, ties, or anything that impedes blood circulation in the head and neck area.
♦ Good sleep is very important to you. Introduce evening walks into your daily routine; If you can’t sleep, take 2-3 teaspoons of honey at night with warm water, and take warm foot baths.
♦ Follow the prescribed instillation regimen exactly. If you have to leave home for a long time, don't forget to take them with you.
♦ With angle-closure glaucoma, sudden changes in lighting are difficult for the eyes. Before visiting a movie theater or other darkened premises, take pilocarpine drops to prevent pupil dilation.
♦ Visit your doctor regularly. Even if intraocular pressure has stabilized, follow-up examinations are recommended every 3 months.
*For writing, materials from the supplement to the magazine “Health” were used (Glaucoma, MD, Prof. E. A. Egorov)
Exercise stress
Regular physical activity is important for the patient, as is proper nutrition and sleep.
Light exercise, fitness, and cycling tend to cause a decrease rather than an increase in IOP. There are a few exceptions to this rule.
People who already suffer from visual field loss need to be aware of their condition. For example, these defects may result in a ball not being seen in time while playing tennis or an approaching danger remaining undetected while riding a bicycle.
Preventative measures such as laser iridotomy or pre-exercise pilocarpine may prevent IOP elevation.
Sports that require intense physical activity, head tilts with sharp turns, and blows to the head are contraindicated. In such cases, blood rushes intensely to the head, arterial and intraocular pressure increases.
Sauna
IOP in patients reacts in the same way as in healthy people when visiting a steam room or sauna. It decreases and then returns to its original level after about an hour. However, there is no evidence that saunas are beneficial.
Doctors recommend avoiding the sauna and being careful with your favorite pastime. The sauna is definitely beneficial for the body, but if you have glaucoma, it is better to limit its use.
High temperature puts a strong strain on blood vessels and the heart. When you stay in a sauna for a long time, your IOP increases. This is not a strict contraindication, but only a limitation.
Lifestyle
Glaucoma itself can seriously disrupt your normal lifestyle, especially if it is diagnosed late enough. If you regularly take the prescribed treatment and follow the doctor's instructions, the course of the disease will slow down. But there are also unforeseen situations, since glaucoma has become much “younger”.
Dream
If you have glaucoma, you should not sleep on a low pillow - it should be high enough and hard enough so that intraocular fluid does not accumulate and there is its outflow. After waking up, you need to get up immediately.
If it is impossible to sleep on a high pillow, you can purchase a special bed with a raised backrest, or place something under the legs of the bed so that the edge on which you place the pillow is higher.
Pregnancy and lactation
Today, alas, no one is surprised by glaucoma in young women. It occurs in both pregnant and lactating women. In itself, it does not interfere with pregnancy and lactation, but the stress associated with this period can aggravate the condition of the eyes. And the drugs themselves for the treatment of glaucoma enter the baby’s blood through the placenta, since it is not a barrier for them. Treatment during this period must be carried out under the special supervision of both an ophthalmologist and a doctor managing the pregnancy. Natural childbirth is prohibited, as it creates increased stress on all muscles and blood vessels, and therefore on the blood vessels of the eyes. It is not uncommon for small vessels in the eye to burst even in healthy women, let alone a patient! Therefore, only a caesarean section is necessary.
During lactation, you should also be under the supervision of an ophthalmologist and regularly check your eye pressure and visual field. Eye drops for glaucoma are most often recommended to be replaced with others, since they can pass through the bloodstream into breast milk and cause visual impairment in the child. During lactation, it is necessary to regularly examine the baby's vision to prevent the development of glaucoma in him.
Glaucoma in children
Unfortunately, this phenomenon occurs quite often, there is even congenital glaucoma. To prevent the disease from getting worse, you should strictly adhere to the recommendations of doctors.
For children, there are the same restrictions as for adults, the main thing is not to overstrain your eyes.
Some sports are prohibited for children - strength sports and those where you need to strain your eyesight, as well as gymnastics.
Air travel
Until the recent past, air travel was strictly contraindicated for a person diagnosed with glaucoma. But modern airliners are equipped with all climate control systems, they maintain constant pressure, so you can fly on such planes.
TV and computer
Today it is impossible to imagine your life without a computer. For many people, their work involves it, and they have to sit in front of a screen for many hours. The question of whether it is possible to work on a computer with glaucoma is especially acute for these people, because this inevitably strains a person’s eyes. The pressure in them always increases, even in a healthy person, but with glaucoma this happens much stronger and faster. So a person with this disease should be especially careful and follow the correct work schedule.
What to avoid:
- Too long continuous work - in addition to radiation from the screen, the eye receives too much stress, it is necessary to give it rest
- The room should not be dark when working - it is important to ensure good lighting. You need to work with special glasses.
- When working with small text, you should not strain your eyes; you should use a screen magnifier.
When watching TV, there must be additional lighting in the room. You can’t watch it for a long time; while watching it, give your eyes a rest from time to time.
It is best to wear special glasses with green lenses at this time for people with glaucoma.
The lighting should be bright enough and located behind you. This way the light will not hit your eyes.
Working with small objects
With such work, the eyes quickly tire, even in healthy people. People with glaucoma should avoid such work if possible. If this is not possible, you need to make sure that there is good lighting - in no case cold colors, and use a magnifying glass.
Driving a car
In principle, glaucoma does not interfere with driving, especially at the onset of the disease. However, to prevent it from progressing, you should not drive in the dark or when there is very bright sunlight - all this contributes to severe eye strain and increased pressure in them. The best time to drive is on a cloudy day, only when there is no fog. When driving, you should wear special glasses for glaucoma. And when driving, take a break of 15-20 minutes every hour so that your eyes can rest.
Sources used:
- Glaucoma and cataracts. Treatment and prevention / Leonid Rudnitsky. - M.: Peter, 2012.
- Therapeutic gymnastics according to Fokhtin against myopia, farsightedness, glaucoma, cataracts / V.G. Fokhtin. - M.: Eksmo, 2013.
- Eye health. Diagnostics, treatment, prevention / E.V. Shcherbakova. - M.: Eksmo, 2009.
- First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
Emotional condition
Individuals are advised to lead as relaxed a lifestyle as possible. You should avoid stressful situations and maintain a calm and measured manner.
In primary open-angle glaucoma, emotional disturbances and symptoms of maladjustment are often observed. Negative emotions contribute to an increase in intraocular pressure in patients with the open-angle form of the disease.
A stressful situation, depression and a suppressed anger reaction contribute to vascular spasms and poor circulation in the brain, retina and optic nerve.
If you monitor your emotional state and correct your psychological status, you will have a positive effect on your hemodynamics.
Glaucoma Treatment Methods
Conservative and surgical techniques are used in the treatment of glaucoma.
Conservative therapy includes the use of antihypertensive drops and medications that improve blood supply and metabolic processes in the nervus opticus. Surgical methods for treating ocular glaucoma restore the outflow of aqueous humor.
| The goal of antihypertensive treatment of glaucoma is to achieve a “tolerant” level of ophthalmotonus, at which no pathological changes occur in the optic nerve fibers. |
Ophthalmologists strive to reduce the level of ophthalmotonus by 30% of the original level.
General algorithm for the treatment of eye glaucoma, newly diagnosed:
- Prescription of an antihypertensive monodrug. Additionally, neuroprotectors and agents that improve blood supply to the optic nerve may be recommended.
- IOP control after 10-14 days. If the target pressure is achieved, the next control is in a month.
- In case of insufficient compensation of ophthalmotonus, additional prescription of a 2nd pharmaceutical agent with a different mechanism of action with IOP control after 10-14 days.
- If the effect is insufficient, therapy is supplemented with a 3rd drug and the issue of surgical treatment of glaucoma is discussed.
The decision to operate is made only according to indications after monitoring the course of the disease. But if there are indications, it is impossible to delay surgical intervention - lost visual functions are not restored.
Pregnancy
Every medicine used during pregnancy is considered potentially dangerous to the fetus. However, do not be discouraged and despair. Treatment during pregnancy is carried out and has a beneficial effect on both the condition of the mother and the future baby.
Women planning a pregnancy are advised to consult an ophthalmologist. The doctor will select the most gentle treatment that maximally protects the mother and fetus.
You can only take medications that are prescribed by your ophthalmologist. Strictly follow the dosage and treatment regimen.
sunlight
When working for a long time in an overly lit room or being outside, intraocular pressure increases. Therefore, it is recommended to take breaks from working with the PC and wear sunglasses (sold with or without diopters) when going outside.
Patients are contraindicated to work night shifts. Poor lighting forces the pupil to dilate to capture more light to transmit images to the brain. This prevents the outflow of fluid from the chambers of the eye, and there is a high risk of a jump in IOP.
Surgical treatment of glaucoma
Glaucoma surgeries are aimed at draining aqueous humor through openings artificially created with a laser or scalpel. Shunt and valve drainages have been developed and used in Russia since 2009 to evacuate intraocular fluid from intraocular cavities into the subconjunctival space along new outflow pathways. Artificial drainages are successfully used in the treatment of congenital and secondary glaucoma.
Surgical treatment of eye glaucoma is performed according to the following indications:
- decompensation in stages I-III of the disease against the background of maximum drug therapy;
- unstable course with periodic increases in ophthalmotonus;
- individual intolerance to all groups of medications to reduce IOP or contraindications to their use;
- decrease in the patient’s quality of life due to the need to use 2 or more medications;
- the patient’s inability to comply with the treatment regimen, regular violations of the medication regimen.
The main problem of surgical intervention leading to recurrent hypertension is excessive scarring of the newly created outflow tracts.
Glaucoma surgeries are divided into:
- interventions to “open” the PC angle - goniotomy, iridocycloretraction, iridectomy, etc.);
- fistulizing - creating new holes for drainage - non-penetrating deep sclerectomy (including installation of drains), trabeculectomy, sinusotomy;
- aimed at suppressing the secretion of the ciliary body - cyclocoagulation, cyclocryoapplication, cyclodiathermy.
For open-angle glaucoma, LTP is most often performed - laser trabeculoplasty (or its version - selective LTP) or non-penetrating deep sclerectomy (if laser intervention is not possible).
Contraindications to laser surgery:
- high persistent ophthalmotonus;
- lack of pigmentation of the trabecular meshwork in the UPC;
- inflammatory processes in the eye;
- insufficient transparency of optical media (corneal scar or dystrophy, swelling, etc.).
When IOP is compensated or inflammation is relieved, the laser surgeon will perform LTP as planned.
For closed- or narrow-angle glaucoma, peripheral laser iridectomy (PLIE) is performed. It presents several through holes at the root of the iris, which allows you to “slightly open” the trabecular meshwork. In some cases, a combined operation is performed (LPT and PLIE simultaneously).
Microsurgical techniques for antiglaucomatous operations are more traumatic, but with proper experience and good technique they can significantly reduce the level of ophthalmotonus.
Alcohol
Ethyl alcohol (ethanol) is a hyperosmotic molecule. Alcohol consumption tends to increase IOP when used regularly. The implication is that alcohol may reduce IOP in the short term (just for a couple of hours or so), but will have a negative effect in the long term.
The positive effect occurs due to the diuretic properties of alcohol and its effect on reducing the secretion of aqueous humor in the ciliary body. Neither the benefits nor harms of alcohol in glaucoma have been proven in patients with this diagnosis.
Nutrition
Patients with glaucoma are recommended to eat mainly dairy-vegetable foods with nutritional supplements, microelements, vitamins, vegetables and fruits. You should limit the consumption of strong coffee and tea, and avoid smoking, since nicotine has a toxic effect on the central nervous system, optic nerve and retina.
Moderate consumption of wine is possible, but not strong alcoholic drinks. You should limit your fluid intake (tea, water, milk, soups). Their total quantity should not exceed 5 glasses per day. You need to eat 4-5 times a day, preferably at the same hours. Dinner should be 2-3 hours before bedtime. It is necessary to exclude smoked meats, fried meats, salty foods, and hot seasonings from the diet. It is better to cook food in vegetable oil. It is advisable to consume boiled lean meats and fish. Dairy products (kefir, yogurt, yoghurt, cottage cheese), as well as vegetables, berries, and fruits, are healthy.
Air travel
Air travel rarely affects intraocular pressure (IOP). Because cabin air pressure is carefully regulated as the plane ascends and descends, eye pressure changes little.
However, the movement of air affects the volume of gases in the air. This is relevant for those who have recently had retinal surgery. During surgery, a gas bubble is placed in the eye to help keep the retina in place. The blister is usually present for 6–8 weeks.
Changes in altitude can cause the gas bubble to expand and increase IOP. Therefore, people who have had a gas bladder inserted during retinal surgery are advised to avoid air travel for the next few months.
In contrast, gas bubbles are not used for glaucoma surgery, so people with glaucoma usually have no restrictions on air travel after surgery. However, it is best to consult a doctor before traveling, especially after any type of surgery.