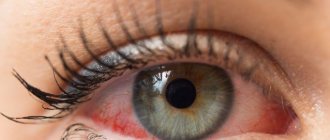
Pain in the eye when blinking is a rather serious symptom that can be a sign of a large number of ophthalmological disorders. The most common diseases that cause discomfort when blinking are conjunctivitis, myositis, blepharitis, and iridocyclitis. An unpleasant sensation also occurs when a foreign body enters.
Pain occurs when the upper eyelid is damaged; it can be of a mechanical or infectious nature. As a result, the skin around the eye becomes red and swollen. Generally speaking, the eyelid protects the eyeball from the penetration of dust and all kinds of particles; if, nevertheless, they linger under the lower eyelid, an inflammatory focus appears there.
Whatever the cause of the pain, it is important to consult an ophthalmologist. It is he who will be able to understand the provoking factors and give practical advice on eliminating pain.
Remember, any pain associated with the organ of vision should alert you, because it is unknown what is hidden behind them. Visual impairment can cost you a lot, including limiting your ability to work and deteriorating your quality of life. To prevent this from happening, pay attention to unpleasant symptoms in a timely manner and consult a doctor.
So, why does the eye hurt when blinking? Next, we will consider common provoking diseases in which it is painful to blink one eye.
Conjunctivitis
The basis of the disease is inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye. Most often occurs in childhood. The infectious process affects both one and two eyes at once. The pathological process occurs in acute or chronic form.
The nature of the inflammatory reaction can be infectious: fungi, viruses, bacteria. Non-infectious factors also occur with conjunctivitis. Thus, experts note the role of an allergic reaction in the mechanism of development of the disease.
The disease manifests itself in the form of the following symptoms: pain when blinking, discomfort in the eyeball, swelling, hyperemia, burning, itching, lacrimation. Patients complain of the presence of a foreign body in the eye, discharge, sticking of eyelashes, and decreased visual acuity. Conjunctivitis can affect your overall health, causing weakness, fatigue, headaches, and hyperthermia.
Conjunctivitis is a common cause of eye pain when blinking.
What to do with conjunctivitis? An experienced specialist can identify conjunctivitis simply by visual examination, but tests will be required to determine the exact type of pathogen. Conjunctivitis is a contagious disease that is transmitted from one person to another. Untreated conjunctivitis leads to the appearance of blepharitis, keratitis, canaliculitis, as well as the process becoming chronic.
Depending on the nature of conjunctivitis, appropriate treatment is selected:
- bacterial – anti-inflammatory and antibacterial agents. Various dosage forms are used: ointments, drops, wiping solutions. Let's highlight the most common drugs: Tobrex, Gentamicin, Oftadek, Albucid;
- viral – Vigamox, Floresan, Dexamethasone.
Why does swelling occur?
There are many reasons why this symptom appears. To accurately determine the nature of the pathology, the doctor focuses on additional manifestations of the disease.
Inflammatory processes
Most often, the upper eyelid swells due to ophthalmological disorders. This occurs much less frequently in other pathologies not related to the organ of vision.
Main ocular causes:
Viral conjunctivitis.
This disease leads to swelling of the mucous membrane of the eye and its eyelids. It appears due to the introduction of viruses into the conjunctiva and the development of an inflammatory process there. The patient complains of a feeling of sand in the eye, lacrimation, photophobia, and decreased visual acuity. It happens that the patient cannot open his eyes due to increasing swelling. Most often, one eye is affected first, and after a few days the infection spreads to the other.
Blepharitis.
The infection affects the edges of the eyelids, causing them to become hyperemic and swollen. Severe itching and discomfort appears. The cause of the disease is an inflammatory process caused by bacteria and mites.
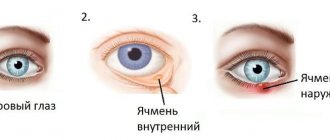
Barley.
The disease develops acutely with inflammatory damage to the hair follicle of the eyelid. Over time, a swelling forms, which gradually turns into a “bump”. It contains purulent contents. After a few days, the formation opens with the release of pus. The patient's eyelid is locally hyperemic and swollen.
Chalazion.
It is a chronic inflammation of the eyelid margin, affecting the meibomian gland and cartilage. It develops when a duct becomes blocked. A secretion begins to accumulate in it, which is an excellent breeding ground for pathogenic microbes.
As a result, a dense round formation is formed in the thickness of the cartilage, painless on palpation. The chalazion becomes noticeable from the skin and creates an aesthetic defect.
Dacryoadenitis.
This is an acute inflammation of the lacrimal gland. The causative agents of infection are viruses or bacteria. Most often this is a secondary process. It develops against the background of other diseases - acute respiratory infections, mumps, tonsillitis, measles, rotavirus and others.
The patient has severe swelling of the upper eyelid. The pathological area is hyperemic and painful. Severe, continuous lacrimation appears.
Other inflammatory causes are acute respiratory infections, frontal sinusitis.
What is Dacryoadenitis:
https://youtube.com/watch?v=kI9hdfk4Usw
Non-inflammatory causes
Most often, swollen eyelids cause the following disorders:
- cardiovascular pathology (heart failure);
- kidney diseases (amyloidosis, glomerulonephritis, heavy metal poisoning, renal failure);
- thyroid function disorder;
- violation of the outflow of blood and lymph;
- oncological neoplasms of the eye;
- excessive salt intake;
- bad habits;
- visual strain;
- lack of sleep.
Attention! Most often, swelling forms in the morning immediately after waking up. It is not accompanied by hyperemia, pain or local fever
The skin of the eyelids is cool and pale.
Allergic reactions
Usually the pathology develops acutely. Its additional symptoms are severe itching, redness, discomfort, lacrimation with photophobia, and nasal congestion.
Swelling of the upper eyelid appears due to the development of an allergic reaction. It can be triggered by:
- food products;
- cosmetical tools;
- household chemicals;
- pollen of flowering plants;
- insect bites: midges, mosquitoes;
- animal fur.
Swelling of the upper eyelid occurs as allergic dermatitis or Quincke's edema. In the first case, the symptom is not so intense, but always occurs with hyperemia and itching.
Quincke's edema is especially dangerous because it can spread to the organs of the respiratory system. Its manifestations are very pronounced. The patient is unable to open his eyes due to severe swelling.
Mechanical reasons
The skin of the eyelid is very thin and delicate. This means that any injury can lead to bleeding and swelling.
Quite often, swelling of the eyelids is observed in women who have undergone tattooing. During the procedure, the paint is driven under the skin. If it is done correctly, the symptom will disappear on its own the next day. Otherwise, tattooing causes an allergic reaction and inflammation.
Myositis
As a result of inflammation of the eye muscles, chaotic pain occurs when blinking, as well as severe swelling. The causes of the inflammatory process can be: hypothermia, prolonged work at the computer, mechanical damage, helminthic infestations, etc.
With myositis, pain occurs not only when blinking, but also when pressing
Treatment includes the use of both conservative techniques and surgical intervention.
Blepharitis
Blepharitis is inflammation of the edge of the eyelids. The disease is difficult to treat and is often chronic. Bacteria, fungi, and mites can lead to blepharitis. In addition, an allergic reaction, anemia, diabetes mellitus, farsightedness, and hypovitaminosis can provoke inflammation.
Blepharitis causes redness of the eye, swelling, burning, and itching. Scales and crusts also sometimes form on the skin of the eyelids. Eyelashes stick together and fall out rapidly.
As for treatment, the selection of therapy is associated with the provoking causes of blepharitis. Some types of disease require special eyelid massage. Whatever the form of blepharitis, the treatment process requires adjusting the diet and strengthening the immune system.
Barley
Meibomian glands provide oily lubrication to the eyelids. Often the cause of stye is clogging of these glands. Active growth of pathogenic microflora leads to the formation of a purulent source. Often the process develops against the background of a weakened immune system or a cold.
Timely use of conservative methods ensures that the disease goes away in just three to four days. Along with the main treatment, it is recommended to drink more fluids and eat foods containing large amounts of vitamin C.
If your eye hurts when blinking, you may suspect a stye.
Diagnostics
Tonometry is one of the mandatory examinations for patients who consult a doctor with such a complaint.
If you experience eye pain, you should consult an ophthalmologist. To establish a diagnosis, the following procedures are recommended:
- ophthalmoscopy;
- biomicroscopy;
- tonometry;
- visometry;
- diaphanoscopy;
- gonioscopy;
- Ultrasound of the eye.
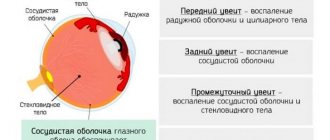
Furuncle, abscess and cellulitis
Allergic swelling of the eyelids and its treatment
Education often affects the corner of the eye. The boil rapidly increases in size. The process often causes an increase in temperature. As a rule, surgery helps eliminate the problem.
Untimely treatment can lead to a dangerous complication - an abscess. The condition leads to drooping of the eyelid, and the person cannot even blink normally. Often such patients experience a migraine attack. With an abscess, a person cannot, not only touch the eye, but even the half of the head on the side of which the abscess is located.
Cellulitis often occurs after a stye or boil. A formation can appear equally under both the left and right eyelids. The disease is dangerous due to the high risk of infection of neighboring tissues of the eye, venous bed and even the brain.
With a boil it hurts to blink. Discomfort increases with touch
Chalazion
A chalazion is an inflammatory process of the eyelid margin around the cartilage. The disease occurs due to blockage of the sebaceous glands. At the beginning of the disease, no external changes in the eye are observed.
But on the inner surface of the eyelid you can find a formation in the form of a small grain. Over time, the chalazion grows, the eyelid begins to hurt, and a feeling of a foreign body appears. A swollen area is visible under the eye.
A large formation inside the eyelid begins to rub and irritate the mucous membrane of the eye. Because of this, inflammation of the conjunctiva and cornea occurs. Vision deteriorates. Fistulas can form, and pus is released through them.
The inflammatory process in the peri-cartilaginous area does not go away on its own. Therefore, if the symptoms of barley do not go away for a long time, then perhaps this is due to a more serious pathology.
Lower eyelid pain
This disease can be cured without surgery only in the early stages. The doctor prescribes antibiotics, physiotherapy and massage sessions. If conservative treatment does not have an effect, then excision of the chalazion is performed.
Despite the fact that the term is rarely heard, the clinical picture of this disease is very depressing and makes you think:
- a dense formation under the eyelid (at the upper or lower edge, round in shape);
- the seal swells either under the skin or in the form of a conjunctival sac;
- the formation adheres to the cartilage tissue (but not to the skin);
- a person loses clarity when perceiving visual images;
- the mucous membrane of the eye is irritated;
- Sharp pain is observed when touching the eyelid and when trying to blink.
Chalazion
List of other causes of pain in the eye when blinking
Let's talk about provoking factors that may not occur so often, but you should also be aware of them:
- incorrectly selected glasses or contact lenses;
- eye fatigue due to prolonged eye strain;
- chalazion - a benign formation on the lower or upper eyelid;
- sinusitis;
- obstruction of the lacrimal ducts;
- Crohn's disease - nonspecific inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract;
- flu and colds;
- neuritis. Inflammation of the peripheral nerves leads to pain when blinking and decreased sensitivity in certain areas.
Best answers
xNerd: rinse with tea... or consult another doctor.
Galoperidol Forte:
Nervous overstrain can make anyone sick!
Alexander Sergeevich:
These are the doctors now! Go to the paid one. After all, the eye is not...
ivanov001:
A bag of tea (drunk) every half hour... It won’t help - you need a serious examination...
Elena Paslavskaya:
Go to a neurologist... You may have had a cold... The doctor should prescribe treatment.
Squirrel:):
What kind of people? They go and answer and don’t understand that I had this too, I advise you to try some eye drops or just don’t pay attention, it will go away on its own, don’t do anything, I was sick for 5 days
ay:
Sometimes the reason lies in poor blood supply to the brain. Go to an appointment with a neurologist, take sedative herbs, medications and something to improve cerebral circulation (mexylol, for example, piracetam...) Good health!
Cleo0851:
Maybe everyone just has stye? This happens sometimes, it begins to ripen, and then slows down. I should talk...
Lena Rusina:
I also had this pain for about 5 days, the ophthalmologists found nothing, and then I looked at the ENT and it turned out that it was inflammation of the trigeminal nerve and sinusitis. So go see your doctor again!
Irinka:
It looks like some kind of spasm, possibly a vasospasm. Maybe a tic, although it would be visible, I have a tic from nerves and then my eyelid also hurts.
Elena Bukina:
Aloe eye drops will calm your eyes
User deleted:
yes it will pass.. drop albucid at night
Baklanova Elena:
It looks like you just have an inflamed nerve. innervating the eyelids and eyes. You need a neurologist, not an ophthalmologist.
Antonina Sviridova:
tetracycline ointment
Cake:
Use gold, only the right kind, better than your parents and grandfathers. with a normal sample - it will help
Pilgrim:
-Once upon a time, when the first long-term wear contact lenses appeared, I acquired this “joy”. This “joy” spoiled my eyes - the feeling - eyes full of fine sand. From fatigue and nervous experiences, the tear in the eye that washes the eyeball disappears . To restore the mucous membrane and relieve pain, I used rosehip oil - it heals. Rosehip oil has many names: -Caratolin, aekol, perhaps now something stronger and more effective has appeared. Search the Internet and treat your eyes yourself. Good luck to you!