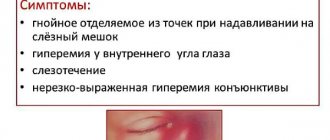
Symptoms of dacryocystitis
With dacryocystitis, most often 1 eye becomes ill. This pathology is accompanied by unpleasant sensations, among which are the following signs of the disease:
- Swelling
- Sharp, cutting pain in the area of the affected eye
- Dizziness
- Involuntary release of tears
- Inflammation of the eyelids
- The appearance of mucus and pus when pressed
- Redness
- General weakness
- Blueness of the skin in the area of the optic duct
- The appearance of a veil before the eyes
- Filling of soft tissues with blood
- Softening of the skin near the lacrimal sac
- Incorrect movement coordination
- Narrowing or complete covering of the palpebral fissure
Diagnostics
It can be quite difficult for parents to independently examine the child, since the baby may desperately resist attempts to put pressure on the inflamed lacrimal sac. However, not every mother will risk doing this on her own. Therefore, the ophthalmologist always begins the examination with palpation of the lacrimal sac and determining the nature of the discharge.
To confirm the diagnosis, a special technique is used, which is called the “Vest tubular test”. The nasal passage on the side of the affected eye is tightly closed with a cotton swab, and a contrast agent (collargol solution) is instilled into the eye.
If the tubule is patent, within a minute or two traces of a dye will appear on the cotton swab. In case of obstruction, the cotton wool remains clean. In case of obstructed circulation, which occurs when the lacrimal duct narrows, traces of collargol on the tampon appear with a great delay. That is why the West test is evaluated not only after 2-3 minutes, but also after 15 minutes, if there were no traces of dye on the tampon the first time.
To determine the extent of the blockage or narrowing, doctors may perform diagnostic probing. During the procedure, the tear duct will be irrigated. If the liquid flows only from the eye and does not enter the nose, doctors will be able to determine at what level the obstruction has arisen.
To do this, smears of the contents that are released during palpation are sent to a bacteriological laboratory for analysis. This allows you to establish the exact name of the pathogen and prescribe adequate and effective treatment.
In difficult cases, other specialists are also invited for treatment - an ENT specialist, a surgeon, a facial surgeon, a neurosurgeon and a neurologist.
In newborns and infants, diagnostic procedures are usually carried out according to a simplified procedure - an examination by an ophthalmologist and an analysis of bacterial culture of the contents of the lacrimal sac are sufficient.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnostic tests to determine tear duct obstruction include:
Fluorescent dye test. The test is done to check how well the eye's drainage system is working. A drop of a special solution with a dye is dropped into the patient’s eyes. If after a few minutes of normal blinking a large amount of dye remains on the eye, then there is a problem in the outflow system.
Probing the lacrimal canal. The doctor may use a special thin instrument to probe the canal to check its patency. During the procedure, the canal expands, and if the problem existed before the procedure, it may simply be resolved.
Dacryocystography or dacryoscintigraphy. This test is designed to obtain images of the ocular outflow system. Before the examination, a contrast agent is instilled into the eye, after which an X-ray, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging is performed. The dye highlights the tear ducts in the pictures.
Diagnostic features
To confirm or refute the diagnosis, an ophthalmologist must conduct an examination. First of all, the patient must undergo a special diagnostic procedure in which the condition of the nasolacrimal ducts, or more precisely, their patency, is checked.
At an appointment with an ophthalmologist
A common and effective diagnostic measure is the West test. It is as follows. The doctor drops a special orange liquid into the patient's eyes and inserts a cotton swab into the nose. If this tampon changes color quickly enough, then the functioning of the nasolacrimal ducts is not impaired. But if after 2-3 minutes the cotton swab still remains white, this indicates poor patency of the lacrimal ducts. After the doctor makes a diagnosis, he prescribes an appropriate course of treatment. The sooner it starts, the greater the chances of a quick and successful recovery.
Test Vesta
Treatment
Which doctor should I contact?
It is necessary to visit an ophthalmologist for consultation. He will prescribe the appropriate treatment option.
You will also have to visit a pediatrician and an ENT doctor. The specialist will offer one of the treatment options:
- Conservative (drug, antibacterial therapy, massage of the lacrimal sac to break through the membrane that does not allow tears to escape, probing).
- Surgical intervention.
- Laser dacryocystorhinostomy (used in newborns if medications are useless).
Massage
Massage in the fight against dacryocystitis is very effective, this method is especially suitable for those mothers who are very afraid of words like “medicines” and “antibiotics” and are ready to do anything to ensure that they never have anything to do with their babies.
The procedure should be carried out immediately after washing the eyes. For the first time, the massage is performed by a doctor, arranging a kind of “master class” for the mother.
Next, it is done by the mother - through gentle, pressing movements on the lacrimal sacs. Massaging movements should be made from top to bottom. You should not press too hard, but weak pressure will not give the desired result.
The appearance of purulent discharge indicates that the mother is doing everything correctly. Massage should be done six to eight times a day.
The hands with which the mother will carry out the procedure should be cleanly washed and with short-cut nails.
In general, for the period while the child is still small, it is better for the mother to completely abandon long nails. It may be fashionable, but for the baby it is a constant threat of injury.
Massage of the lacrimal canal - Internet project “Your massage”
Eye rinsing is necessary, but it cannot be the main method of treating the disease.
This should be done carefully and carefully, passing the swab from the outer corner of the eye to the inner
The tampon removes purulent discharge and for a moment it may seem that everything has gone away, but after a while the eye begins to fester again.
Medications
In addition to massage, medications are prescribed: instillation of a warm solution of Furacilin, as well as disinfectant drops Vitabact and Levomycetin.
As for Albucid, which is popular among the people, many doctors are wary of it. Firstly, it thickens the embryonic film rather than eliminating it, and secondly, it severely burns the mucous membrane of the baby’s eyes.
Probing is a very serious measure and is prescribed when massage and eye drops have no effect. This procedure is very painful, and therefore is performed under local anesthesia.
The tear duct is cleared and expanded with a special probe, then rinsed with an antibiotic.
Surgery is used after 6 months of age if the plug in the tear duct has become so hard that it can only be removed through surgery.
There are two types of intervention: endonasal and external. The first method is preferable, since intervention through the nose is the least traumatic and does not leave a scar on the face.
The operation is performed under local anesthesia with the child in a sitting position.
Folk remedies
Despite the fact that dacryocystitis itself is not life-threatening, it is still a bacterial disease and therefore can only be cured by means prescribed by a specialist.
“Folk” remedies for its treatment can be used, but only with the agreement of a doctor.
Compresses with herbal infusions - mint, dill, chamomile - give a good effect; lotions with tea leaves; instillation of Kalanchoe into the eyes.
In no case should you rely on the advice of “grandmothers” who recommend putting breast milk in the baby’s eyes or, even more extreme, his own urine!
This can achieve only one thing - additional pathogenic bacteria will enter the eye, which is already sick, exacerbating the process.
Many mothers, having discovered dacryocystitis in their baby, decide that “it will go away on its own.”
In principle, this is possible - very often the disease really goes away quickly, even before the age of 1 year, since the lacrimal sac and ducts increase as the child grows, and the membrane that interferes with tears breaks.
The fact that the treatment gave results or the disease actually went away on its own is indicated by the cessation of manifestations of dacryocystitis.
But even in this case, the last word will be with the ophthalmologist - only he can make a conclusion about the absence of the disease.
General information
Dacryocystitis is a disease of the organ of vision, accompanied by an inflammatory process of infectious etiology, localized in the lacrimal canal (bag) of the eye.
The pathology is often based on a congenital defect in the anatomical structure of the structure of the eyes and nose, which prevents the outflow of tear fluid. However, cases of this disease are also common in adults. Women are more susceptible to developing dacryocystitis, which is due to the narrowness of the nasolacrimal ducts.
Against the background of stagnation of fluid in the lacrimal sac, caused by difficulties with its removal from the nasolacrimal canals, stagnant processes develop, which are a prerequisite for the spread of pathogenic microorganisms. This leads to the development of an inflammatory process, accompanied by the formation of thick mucus and pus in the canals.
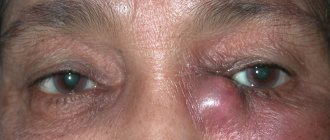
Swelling in the inner corner of the eye, swelling under the eyes, constant and uncontrollable lacrimation, pain and the appearance of purulent discharge when pressing on the area of the lacrimal sac are the main signs of the disease, which should prompt the need to visit a therapist or ophthalmologist.
In adult patients, inflammation of the lacrimal sac develops against the background of the lack of timely and adequate treatment of infectious diseases affecting the organs of vision, and in fact is a complication of past pathologies, as a result of which in most cases it occurs in a chronic form.
Symptoms of the disease
Blockage of the tear duct in children is often confused with the usual problem, and the wrong problem is treated for weeks. To distinguish conjunctivitis from dacryocystitis, you need to take a closer look at the newborn baby.
- You may notice that your newborn's eyes will occasionally tear from one or both eyes for no apparent reason when the baby smiles. This suggests that the tears simply have nowhere to go, and the excess flows down the cheeks.
- Then stagnation occurs. Dirty tears that washed the eyeball accumulate in the sac, forming a “swamp”. At this stage, the inflammatory process occurs, we see redness, swelling, swelling, all signs of conjunctivitis.
- At the next stage of dacryocystitis, the newborn’s eyes begin to sour, at first only after sleep, then constantly.
- Then they appear, and when you press on the swelling in the projection of the lacrimal sac, pus flows out of it.
- Over time, the process worsens, and antibacterial treatment gives only temporary results.
Treatment
Very often, doctors offer inpatient treatment for dacryocystitis to adults and children. Treatment methods before and after softening of the infiltrate are different.
Before the infiltrate matures, therapeutic methods are often used in the form of:
- Physiotherapy to accelerate the maturation of the abscess (UHF therapy, dry heat in the lacrimal sac area).
- Vitamin therapy.
- Opening a mature abscess.
After opening the infiltrate, therapeutic measures include:
- Draining the wound with rinsing with antiseptic solutions (furatsilin solution, hydrogen peroxide or dioxidine).
- Using broad-spectrum antibiotics orally or by injection for 7-10 days (usually penicillins or aminoglycosides), often in combination with sulfonamide drugs.
- Local use of antibiotics in the form of ointments (tetracycline, erythromycin, etc.) and instillation of antibacterial drops (miramistin, gentamicin, sodium sulfacyl, cypromed, etc.)
- In pediatric practice, eye drops with antibiotics (Tobrex, Vigamox, Vitabact, Albucid) are used for treatment.
- In case of severe intoxication (more often in children), detoxification solutions are used intravenously (in the form of calcium chloride, glucose, gemodez with ascorbic acid, hexamethylenetetramine).
- Surgical treatment of dacryocystitis is possible after relief of acute inflammation (dacryocystorhinostomy). In this case, the cavity of the lacrimal sac is drained surgically. This method is used mainly in adult patients who suffer from repeated inflammation of the lacrimal sac with constant relapses. Occasionally, the method is also used in pediatric practice (for chronic forms of dacryocystitis), requiring “jewelry” technology from surgeons to preserve full vision for the child. The operation is not performed in acute forms of the disease or in cases of exacerbation with purulent discharge from the lacrimal sac. Rehabilitation after surgery lasts about a month and includes local use of rinsing and instillation with antiseptic solutions.
- Use of modern methods of laser and endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy as surgical treatment. This low-traumatic surgical technique allows you to do without a visible postoperative scar. According to indications, a similar method of surgical treatment is used for children or newborns. In this case, instead of a scalpel, a laser mounted in an endoscope is used.
Compared with traditional surgery, the laser endoscopic method allows you to do without hospital treatment, general anesthesia and postoperative bleeding. However, this type of intervention is more expensive and is not indicated for all patients.
With dacryocystitis, patients are prohibited from using many activities related to contact with the cornea (using contact lenses, applying bandages, ultrasound methods, tonometry, etc.). Such methods can lead to the formation of purulent ulcers of the cornea.
Treatment of tear duct obstruction
Treatment depends on the specific cause of the blockage or narrowing of the canals.
Sometimes multiple treatments are needed to correct the problem. If an infection is suspected, your doctor will likely prescribe antibiotics.
If the tumor has caused the obstruction, treatment will focus on controlling the tumor. To do this, the tumor is usually removed surgically.
Conservative treatment
In a large percentage of infants, congenital tear duct obstruction resolves on its own in the first months of the child's life. If this does not happen, the doctor will first recommend giving the child a special massage, and will prescribe drops containing antibiotics to fight the infection.
Minimally invasive treatment
Minimally invasive methods are used to treat congenital tear duct blockages in young children when other methods have failed. The most common method is bougienage, in which a special tube is inserted into the lacrimal canal, restoring its patency. The procedure does not require anesthesia and takes only a few minutes. After bougienage, your doctor will prescribe antibiotic eye drops to prevent infection.
Surgery
Surgery is usually prescribed for adults and older children with acquired tear duct obstruction.
They are also prescribed for congenital obstruction if all other methods have been ineffective. Surgeries are necessary to reconstruct damaged or underdeveloped tear ducts. One of the operations, dacryocystorhinostomy, involves creating a new passage between the nasal cavity and the lacrimal sac. Such operations are quite complex and are performed under general anesthesia.
After surgery, patients will need to take medications for some time. The doctor may prescribe a nasal spray to relieve swelling of the mucous membrane, as well as eye drops to prevent infection and reduce post-operative inflammation.
Why is tear duct probing necessary?
A child in the womb does not have free communication between the nasal cavity and the nasolacrimal duct. The exit hole is closed by a thin membrane, which in most children disappears by the time of birth. In this case, the nasolacrimal duct is usually blocked with a gelatin plug, which prevents amniotic fluid from entering the baby’s body. When a child is born, begins to breathe and cry, this mucous lump comes out of the duct, enters the nose and is removed by obstetricians.
If at birth the nasolacrimal duct is not freed from the natural plug, the baby develops dacryocystitis
However, it also happens that due to anatomical features or anomalies, the plug does not come out of the nasolacrimal canal. Because of this, stagnation occurs in it. After some time, the newborn develops dacryocystitis - complete or partial obstruction of the lacrimal ducts. The baby's eyes first water, and then begin to fester and become inflamed.
Dacryocystitis can be either congenital or acquired as a result of injuries, inflammatory processes in the eyes or nose, as well as various diseases. This disease can affect both children and adults of all ages. However, while acquired dacryocystitis often requires complex surgical interventions, the congenital form usually resolves spontaneously or as a result of rinsing and massage.
If, after conservative treatment, the baby’s eyes continue to fester, doctors refer the child for probing - mechanical restoration of the patency of the nasolacrimal duct using a special instrument - a probe. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia and does not last long. However, probing does not guarantee a cure: after a certain period of time, the discharge may reappear. With repeated intervention, the probability of complete recovery is 95–98%.
Constant tearing is the first sign of dacryocystitis
As a rule, doctors are in no hurry to send babies with “sour” eyes for probing. They often recommend that parents wait up to 3-4 months to get rid of the problem with massages and eye drops. If by this time there is no improvement, probing is performed, which usually completely eliminates all symptoms.
Causes
In adults, dacryocystitis occurs due to narrowing and closure of the nasolacrimal duct. Due to the narrowing of the channels, fluid circulation is disrupted. As a result of this, stagnation of the tear secretion occurs, in which microorganisms begin to actively develop.
Swelling of the tissues surrounding the nasolacrimal duct occurs as a result of inflammatory diseases of viral or bacterial origin (respiratory infections, chronic rhinitis, sinusitis).
The disease can also be caused by:
- fractures of the bones of the nose and orbit;
- damage and disruption of the integrity of the lacrimal canaliculi;
- nasal polyps;
- penetration of debris, dust and other foreign bodies into the eye.
Also, the following factors may contribute to the occurrence of the disease:
- metabolic disease;
- diabetes;
- weakening of the immune system;
- allergic reactions;
- interaction with chemicals hazardous to the organs of vision;
- sudden temperature fluctuations.
Treatment of dacryocystitis in children
For congenital dacryocystitis, newborns are treated with massage, probing and eye rinsing. In case of a secondary disease, complex surgical interventions are required to partially or completely restore impaired tear production.
Drug treatment is used to prevent infections and fight pathogenic bacteria. For this, a number of anti-inflammatory drugs, drops, ointments, antibiotics are used, and in rare cases, hormonal drugs are used.
What children's drops should be chosen for the treatment of dacryocystitis?
All medications must be prescribed by your healthcare provider. The most common and effective drugs are the following:
- "Collargol" - anti-inflammatory and bactericidal drops;
- “Signecef” is an antibacterial drug in which the active substance is the antibiotic levofloxacin, which is active against staphylococci, streptococci and enterobacteria, which can rapidly and actively multiply in the favorable environment of the lacrimal canals;
- "Tsipromed" - similar in its action to "Signetsef", is considered its analogue;
- “Albucid” is not advisable for use in newborns; it causes a burning sensation and thickening of the embryonic film. It is used only as prescribed by a doctor; in cases of eating, other drops are powerless;
- "Tobrex" is a quickly effective bactericidal agent, a strong antibiotic;
- "Levomycetin" - can be prescribed both in the form of drops and in the form of ointments. The ointment should be placed at night, behind the child’s lower eyelid;
- "Ophthalmoferon" is an antimicrobial and antiviral drug from the interferon family. It has a local anesthetic effect, which can reduce the feeling of discomfort and burning in the eyes;
- "Floxal" - used for the treatment of inflammatory diseases of the eye parts that are caused by bacteria sensitive to this drug (streptococci, staphylococci, salmonella, shigella, etc.);
- "Vitabact" is an antimicrobial drug that, in addition to bacteria, also has an effect on some types of viruses and fungi that can cause concomitant diseases with dacryocystitis;
- "Vigamox" - used to treat inflammation caused by microorganisms resistant to other antibacterial drugs;
- “Gentamicin” is prescribed in the form of both drops and ointments, with concomitant inflammatory processes of the lacrimal sac and canal.
If the doctor has prescribed several medications, they should be taken at least 15 minutes apart. A prerequisite for drug treatment of dacryocystitis is the combination of the latter with massage.
How to properly massage a child with dacryocystitis?
Before starting the massage, you need to thoroughly wash your hands and treat them with a special antiseptic or use sterile gloves.
Next, you should carefully squeeze out the contents of the lacrimal sac and clean the eyes of pus and mucus by rinsing with a solution of furatsilin
After carrying out the preparatory manipulations, you can begin the massage. It is best to carry it out before feeding and at least five times a day, in the first 2 weeks of the disease, up to 10 times a day is recommended.
Step #1.
We place the index finger on the inner corner of the baby's eye, with the pad of the finger towards the bridge of the nose
It is important to know that the massage is correctly performed with the index finger.
Step #2
Lightly press on this point. The pressure should be moderately strong in order to break through the film that closes the tear duct.
Step #3
Use your fingers to move downwards along the bridge of your nose, without ceasing to press on the skin. This movement should be sharp and confident. This is necessary in order to tear, and not stretch (as with normal stroking) the film, which prevents the movement of fluid from the lacrimal canal into the nasal cavity. With the help of such sharp movements, you push the fluid and pus that has accumulated above the septum into the nasal cavity.
Step #4
Once your finger reaches the bottom of the bridge of the nose, it is best to slightly release the pressure, but do not lift your finger from the skin, and return it to its original position at the corners of the eyes.
Step #5
Then repeat steps 2 and 3. During one massage session you need to make 10-13 of these movements, but no more, so as not to stretch the septum in the canal.
If you do everything correctly, you will be able to see how tears with pus begin to emerge from the tubules into the eyes. If massage does not produce any results within 23 weeks, probing of the lacrimal canal is performed.
Symptoms
Dacryocystitis of the eye has a variety of symptoms. In children, the disease can be suspected if the corner of the eye turns red or tears periodically roll out, or the eye begins to sour. Do not self-medicate; immediately show your baby to an ophthalmologist.
As for adults, we list the symptoms as they increase:
- the appearance of wet eye syndrome, constant tears in the eye;
- lacrimation in the cold;
- deterioration, blurred vision;
- excessive lacrimation, inflammation, redness of the lacrimal caruncle (corner of the eye near the nose);
- inflammation spreads to the lacrimal canal and lacrimal sac, symptoms include the appearance of swelling and purulent discharge;
- significant swelling, soreness of the eyelids or places of projection of the lacrimal canal;
- Possible enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes, increased body temperature.
One of the indirect signs of beginning obstruction of the lacrimal canal is lacrimation in the cold. Cold additionally narrows the outflow channels and increases tear production, and in the presence of disturbances, profuse lacrimation is observed, which may not have existed before.
Symptoms of tear duct obstruction
Obstruction of the tear duct can be observed either on one eye or on both sides.
Signs of this disease may be due to direct blockage of the canals or an infection that develops as a result of the blockage:
Excess tear fluid (wet eyes). Frequent inflammation of the eye (conjunctivitis). Inflammation of the lacrimal sac (dacryocystitis). Painful swelling in the inner corner of the eye. Mucous or purulent discharge from the eye. Blood in tear fluid. Blurred vision.
Diagnostics
To make and confirm the diagnosis of dacryocystitis, an examination of the child by a pediatric ophthalmologist will be sufficient, but in severe forms of the disease, the patency of the nasolacrimal duct is checked. This test is based on instilling a contrast (dye) substance directly into the conjunctival sac. For this purpose, the Bugaev and West test is used.
Test Vesta
A clean cotton swab is placed in the nasal passage while the Collargol solution is placed in the eyes. If the tampon does not stain within 5-10 minutes, the child is diagnosed with obstruction of the lacrimal ducts.
Bugaev's test to determine the disease dacryocystitis
Bugaev's test or fluorescein instillation test - a fluorescein solution is instilled into the child's eyes and examined with a special lamp with a blue filter. Then the number of areas that are not painted over and the number of point defects (flaws) of the conjunctiva and cornea of the eye are counted. More than 10 defects or breaks in the tear film indicate pathological changes in the eye.
Also used as diagnostics:
- diagnostic probing (washing the tear ducts),
- passive nasolacrimal test to confirm canal obstruction,
- Ultrasound of the eyeball or biomicroscopy,
- contrast radiography of the lacrimal ducts (iodolipol solution) – used to clarify the level of blockage or narrowing of the lacrimal ducts,
- bacteriological culture of discharge - to determine the causative agent of inflammation.
All these methods make it possible to thoroughly study all the structures of the eyeball and make a correct diagnosis in order to prescribe correct and effective treatment for dacryocystitis.
Prevention
The congenital form of dacryostenosis cannot be prevented. The embryonal film is formed in each fetus during intrauterine development. And if it does not burst at the first cry of the child, you will need to eliminate it yourself or with the help of doctors. Acquired lacrimal canal stenosis can be prevented using basic hygiene rules. You should not touch your eyes with dirty hands, you should use contact lenses correctly and visit an ophthalmologist regularly.
These methods will prevent the development of dacryostenosis and will significantly increase the effectiveness of therapy when pathology is detected.
Stenosis of the nasolacrimal duct is a pathology of the structure of the nasolacrimal duct, which occurs as a result of its chronic inflammation.
If left untreated, the risk of tear duct obstruction increases. There is a congenital form of stenosis pathology.
Diagnosis of dacryocystitis in newborns
With dacryocystitis, a newborn's tears flow all the time
As a rule, the doctor is able to confirm this diagnosis during the first examination of the baby. If this cannot be done immediately, additional diagnostic methods are used:
- Using collargol solution. The substance is instilled into the eyes of a small patient, after placing a tampon in the nose. Within 5-10 minutes, the solution should color the tampon, but if this does not happen, a conclusion is drawn about poor patency of the nasolacrimal duct. This factor is evidence that dacryocystitis of the newborn is developing, the treatment of which is better not to delay;
- X-ray, for which a special contrast agent is used. Thanks to the latter, it is possible to determine which lumen the tear duct has.
It is advisable to consult a doctor (pediatrician or ophthalmologist) at the moment when the parents notice the problem. Considering that the phenomenon may subside on its own by 2 weeks of age, some parents wait until this moment without contacting a specialist. If the problem has not disappeared by this time, you should definitely visit a doctor.
Treatment methods
Dacryocystitis in the early stages of development can be successfully treated in the shortest possible time. To achieve a faster and more positive effect, therapy must be comprehensive. To eliminate the cause and manifestations of the disease, methods such as drug treatment and special massage are used.
What are the causes of cleft palate in infants? Read about it here.
Medication
To eliminate the inflammatory process and speed up tissue regeneration, special drops are used that have antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. They use medications such as:
- Vigamox;
- Gentamicin;
- Levomycetin.
The drops must be instilled 2-4 times a day, having previously cleared the eye of pus using a Furacilin solution.
Small children, as a rule, do not like having drops placed in their eyes; this procedure is extremely unpleasant for them.
Therefore, parents need to know how to properly drip into their baby’s eyes, while causing a minimum of discomfort:
It is important to maintain good hygiene. If a special pipette is used to instill drops, it must be boiled
Before instillation, you must wash your hands thoroughly. It is best to swaddle your baby tightly to limit his movements. This will protect the child from unexpected injuries during the process of instilling drops. Use the fingers of your left hand to open the child’s eyelids, lightly holding them in this state, after which 1-2 drops are instilled. The remaining product must be blotted with a sterile cotton swab.
How to do a special massage?
Massage must be performed regularly, 5-6 times a day. It is best to carry out the procedure shortly before feeding.
Before performing a massage, you need to swaddle the baby, wash your hands with soap, and wash the baby’s eyes (if pus has accumulated in them).
The massage technique is as follows:
- The fingertips are applied to the area of the lacrimal sac (the fingertips look at the bridge of the nose).
- Light pressure movements are applied to this area of the eyes in the direction from the eye to the bridge of the nose.
- The number of massage manipulations (movements) is 10-20 times.
During the massage, fluid is released from the lacrimal sac, which will need to be removed at the end of the procedure. To do this, use a cotton pad moistened with Furacilin solution.
Why is massage necessary? Properly selected massage movements create pressure differences in the area of the lacrimal sac and canaliculi. This promotes the removal of the plug clogging the tubules and rupture of the membrane.
Dr. Komarovsky will tell you in this video how to do a special massage when the tear duct is blocked:
Probing
In some cases, conservative treatment methods, unfortunately, are not enough. In this case, probing is necessary. The operation is prescribed in such cases as:
- profuse lacrimation;
- an extensive inflammatory process, covering not only the area of the lacrimal sac and tubules, but also nearby tissues;
- lack of positive results after conservative treatment;
- abnormalities in the development of tear ducts.
The operation is performed under local anesthesia: special drops with an anesthetic effect are instilled into the baby’s eyes.
After this, a special probe is gradually introduced into the lacrimal canal of the eye (it must be inserted at a right angle using gentle rotational movements).
The probe helps to expand the lacrimal canal and remove the formed plug from it. After some time, the probe is removed, and the lacrimal canals are washed with an antiseptic solution.
After this, a diagnostic test is performed again using a contrast dye, this test allows you to verify that the operation was successful and the problem has been eliminated.
After completion of the operation, it is necessary to apply conservative therapy techniques for a week, in particular, instill antibacterial drops in the child and perform a massage procedure.
This will avoid complications and relapses of pathology.
Treatment of dacryocystitis in newborns
Treatment of dacryocystitis in newborns should be comprehensive and carried out under the supervision of an ophthalmologist. Acidity of the eye should be eliminated, for which disinfectant solutions are used. Antibacterial drops are also prescribed if the child has significant purulent discharge.
READ ALSO: how to do a massage for dacryocystitis in newborns: video
The key to treatment is massage, which is used to break through the plug by increasing pressure in the tear duct. As a rule, massage is recommended to be done for 10-14 days. If the procedures do not help, probing of the nasolacrimal duct is prescribed.
INTERESTING: what to do if a newborn’s eyes fester?
Special massage
The purpose of the massage is to remove accumulated mucus and pus in the lacrimal sac and help eliminate obstruction (blockage) of the canal. The procedure is performed at least 3 times a day (preferably during each feeding) for 3 minutes. Step-by-step massage technique:
Place your thumb or index finger on the lacrimal sac, which is located between the nose and the inner corner of the eye. Apply light pressure and make several movements from bottom to top, trying to rid the bag of contents
Using a sterile tissue, carefully remove the exudate that comes out of the lacrimal openings. Next, make movements from top to bottom - from the eye to the wing of the nose. Some ophthalmologists recommend alternating straight movements with circular ones.
INTERESTING: what color are the eyes of newborns and at what age does the shade change?
Drug therapy
In parallel with the massage, local medicinal treatment is indicated. Before the procedure, it is necessary to apply antiseptic drops to the eye to get rid of discharge. Prescribed:
READ ALSO: how to put drops in a child’s eyes if he doesn’t give and is capricious?
- Miramistin,
- Chlorhexidine,
- Furacilin (see also: how to use furatsilin to treat eye diseases in newborns?).
In some cases, regular saline solution is sufficient. After the massage, the use of ophthalmic antibacterial agents is indicated, which can be used for children:
- Eye drops "Levomycetin" for newborns,
- Phloxal,
- Vigamox,
- Tobradex,
- Tobrex.
You should not instill Albucid, as this remedy causes a strong burning sensation.
Probing
If improvement does not occur within 10-14 days, bougienage is indicated, i.e. expansion of the narrow lumen of the duct. This event is also called “washing”. First, anesthesia is used in the form of drops, then a special cylindrical probe is inserted into the upper nasolacrimal canal and moved down to the bone.
After the procedure, the canal is washed with antiseptic solutions, and subsequently, in order to prevent the development of inflammation, with antibacterial drops. In rare cases, rinsing may have to be performed several times if the canal becomes blocked again.
When is radical surgery required?
Sometimes the flushing and bougienage procedure do not produce results and do not allow the plug in the duct to be broken, or the child experiences significant swelling and inflammation of the lacrimal sac tissue. In such cases, surgical cleaning is recommended - endonasal dacryocystorhinostomy, which is also indicated for chronic dacryocystitis after reaching the age of 2-3 years.
The purpose of surgical manipulations is to clean the canal and provide conditions for high-quality drainage (removal) of tears, which requires the formation of an anastomosis between the lacrimal sac and the nasal cavity.
There are other ways to restore the functions of the nasolacrimal duct - intubation (insertion of a silicone tube that forms a natural duct), laser dacryocystorhinostomy, fracture of the nasal bones. Many of them have contraindications, so such measures are prescribed on an individual basis, depending on the age and condition of the patient.
After treatment, the effect of lacrimation may persist for some time, while other symptoms (tissue inflammation, hyperemia, mucopurulent discharge) disappear without a trace. This is explained by the presence of edema in the area of the duct. In this case, repeated rinsing of the canal with antiseptic drugs or saline is prescribed.
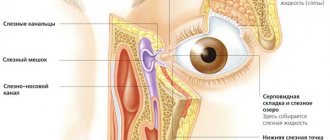
General information about the disease
Dacryocystitis is an inflammation of the lacrimal sac. This cavity is located at the inner canthus. Normally, the tear secretion flows from it through the duct into the nostrils. If the movement of fluid is disrupted due to narrowing or blockage of the sac, pathogenic microbes accumulate in it. They cause inflammation.
Symptoms of dacryocystitis:
- narrowed eye slit;
- tearfulness;
- swollen lacrimal sac;
- local pain syndrome;
- accumulation of mucus and pus in the corners of the eyes;
- swelling, redness of the conjunctiva, lacrimal caruncle and semilunar fold.
If the movement of fluid through the lacrimal canal is impaired due to narrowing or blockage of the sac, pathogenic microbes accumulate in it, which cause inflammation.
Dacryocystitis in children
The pathology is often diagnosed in infants due to birth injuries. 5 percent of babies are born with obstruction of the lacrimal ducts. Ophthalmologists distinguish congenital dacryocystitis as a separate form of the disease. It also occurs in children in the first years of life, when the body is just forming. Developmental anomalies lead to dacryocystitis in infants when the tear ducts are partially or completely absent.
During intrauterine growth, a gelatin plug forms at the bottom of the nasolacrimal duct in the embryo. It prevents amniotic fluid from entering the lungs. When a baby is born, the plug is pushed out with its first cries. Paths open for tears. Sometimes the canal clears out in the first two weeks of life. When this does not happen, the baby develops inflammation of the lacrimal sac.
Pathology in adults
In adult patients, dacryocystitis is usually diagnosed at 30-60 years of age. Women suffer from it 6 times more often than men, since their tear ducts are narrower.
Women are more likely to suffer from dacryocystitis than women.
Normally, the fluid produced by the lacrimal glands moisturizes the eyes and flows to their inner corners. There are points leading into the channels. Through them, the secretion moves into the lacrimal sac. From it, moisture flows through the channel into a new cavity.
Due to obstructed lacrimal ducts, fluid drainage is impaired. This leads to its accumulation in the lacrimal sac. When the secretion stagnates and the cavity becomes infected, inflammation begins.
Blocked tear duct - causes and treatment
One of the most common ophthalmological diseases in children and adults is obstruction of the lacrimal ducts.
The resulting blockage of the tear ducts is medically called dacryocystitis.
This pathology manifests itself with the same symptoms as many other eye diseases, which makes it necessary to undergo examination by a specialist at the first problems with the eyes. An accurate diagnosis is necessary to prescribe the correct treatment.
Statistical data from medical practice indicate that most often the pathology of the lacrimal ducts is diagnosed in women whose age is from 30 to 60 years. At the same time, men encounter this disease much less often.