Varieties
There are 4 types of exophthalmos:
- Permanent , in which neoplasms appear after an injury to the hand, eyes or brain herniation.
- Pulsating , after injury to the eyes and skull.
- Intermittent , manifests itself after tilting the head.
- Progressive malignant , occurs due to dysfunction of the thyroid system.
Also, it can be one- or two-sided , pronounced or inconspicuous .
Classification
The disease is divided into imaginary and true:
- In the first case, the disease manifests itself with congenital asymmetry of the visual apparatus, abnormal development of the skull, or an increase in the palpebral fissure;
- True is diagnosed in case of inflammation and general pathologies, as well as in case of injury to the eye and the appearance of neoplasms.
According to the type of occurrence, exophthalmos is divided into the following categories:
- Constant. Most often it is diagnosed when malignant or benign tumors form in the orbit;
- Intermittent. Develops against the background of pathological processes occurring in the orbital veins. This form of anomaly is characterized by the fact that protrusion occurs only at a moment of strong physical stress, when the vessels are filled with blood. The pathology is most clearly visible if you tilt your head;
- Pulsating. Diagnosed with aneurysm and injuries of the visual apparatus. The main symptom of the disease is pronounced pulsation in the eye. A severe headache is also observed; when the eyelid is closed, a noise is recorded in the upper part of the eye. As the disease progresses, the veins on the forehead and temples become enlarged;
- Hypothalamic-pituitary. It is characterized by rapid development and manifests itself under the influence of increased production of the pituitary hormone. Within a few days, the eyelids swell and conjunctival chemosis begins.
In the absence of deviations, the eyeball extends beyond the orbit by a maximum of twenty millimeters.
| Depending on this parameter, mild, moderate and severe forms of exophthalmos are distinguished. In the first case, the eyes protrude by 21 - 23 mm, in the second the figure reaches twenty-seven millimeters, the severe stage is characterized by a deviation of up to 28 mm. |
Return to contents
Preventive measures
To prevent the development of bulging eyes, it is necessary to follow certain preventive measures. It is imperative to protect the skull and organs of vision from various damages and injuries. In addition, it is imperative to maintain visual hygiene and promptly treat any identified diseases. Do not forget about the treatment of pathologies of the endocrine system and lesions of the nasal cavity.
It is possible to reduce the likelihood of developing bulging eyes by leading a healthy lifestyle. You should minimize the amount of drinks that contain alcohol in your diet. A balanced diet and increased resistance to stress can not only prevent the appearance of bulging eyes, but also other pathologies of the visual organs.
Many pathologies are the result of a person’s inattention to their health. Exophthalmos is considered just such a disease, so it is important to constantly observe prevention and visit a specialist if necessary.
What are the symptoms of exophthalmos
The clinical picture depends on the degree of protrusion of the eye. A slight deviation from the norm does not cause the patient any discomfort. As the disease progresses, the following symptoms appear:
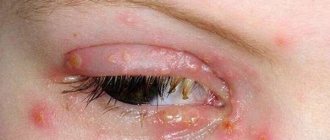
- Swelling and redness of the sclera;
- Diplopia and decreased visual acuity;
- Since it is impossible to completely close the eyelids, the cornea dries out, which can lead to keratitis;
- Limited movement of the eyeball or its complete absence signals the formation of a neoplasm or activation of acute inflammation in the orbit;
- Increased lacrimation;
- Intolerance to bright light;
- When blinking, a person experiences pain.
| If the pathology is not treated, swelling of the optic nerve and its constant compression can lead to blindness. |
Edema exophthalmos
Exophthalmos itself is not a disease, it is only a symptom . Therefore, in order to successfully treat the disease, it is worthwhile to better understand the true reasons that led to the appearance of this deviation from the norm.
Attention! Edema exophthalmos is one of its most dangerous forms, in which the eyeballs literally dislocate from the sockets , which leads to disability of the patient.
Complex forms of protrusion are extremely rare . Most often, everything is limited to quite severe swelling and protrusion of the eyeballs.
Edema exophthalmos develops in patients whose age exceeds forty years. It can occur equally in both men and women. Patients often complain of increased intraocular pressure.
Edema exophthalmos can be either unilateral or bilateral .
Diagnostics
To diagnose this type of disease, the latest equipment available in modern eye clinics is used.
With the help of this kind of equipment, it becomes possible to determine intraocular pressure during exophthalmos, as well as the degree of vascular damage, which necessarily occurs during protrusion phenomena.
Of great importance is an external medical examination , which can and should be performed by a professional doctor.
Symptoms
If we talk about the symptoms of this disease, we can distinguish the following types :
- Pronounced pain, which can only be relieved with heavy analgesics or even drugs. This kind of pain is explained by the fact that as a result of exophthalmos, the nerve fibers are compressed. They are the ones who give the body a signal in the form of pain.
- Edema of the orbital eyelids. Also, the phenomenon of edema can spread to the periorbital area. This kind of edema is quite developed in order to instantly attract the attention of a doctor.
- Complete or partial loss of visual functions. This type of loss is due to the fact that as a result of protrusion, multiple optic nerves are compressed in order to make significant adjustments to the patient's visual pattern.
Treatment
Unfortunately, medicine does not have adequate methods for treating exophthalmos. This disease poses a significant danger to its carrier. Therapy should be carried out by an experienced ophthalmologist, as well as an endocrinologist. Most often, drugs are prescribed that stabilize the patient’s hormonal levels. Here we are talking about prednisolone , which is prescribed in dosages reaching 1200 mg.
The prescription of drugs that contain the active substance “thyroidin” is also of great importance. If we talk about prednisone, then this medication is necessary to relieve the inflammatory process, which always manifests itself with exophthalmos. Thyroidin is able to normalize the functions of the thyroid gland , which is also of great importance for the successful fight against symptoms of diseases.
It is worth noting the importance of local treatment, which consists of prescribing various kinds of eye drops, as well as local drops. Here, most often, we are talking about prescribing a series of hormonal drops, such as Dexamethosone , which help relieve inflammatory processes.
Photo 1. Dexamethasone eye drops 0.1%, 10 ml, .
Also very popular is the use of ointments that contain an antibiotic. Let's say tetracycline ointment.
How does exophthalmos manifest?
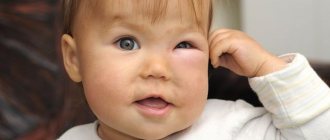
Symptoms of exophthalmos are manifested only by displacement of the eyeballs, but their sizes remain normal. Protruding eyes are observed in humans in a number of diseases - Graves' disease , thrombosis and aneurysms of cerebral vessels , tumors of the orbit and brain , inflammation in the orbit and sinuses, etc.
The so-called edematous endocrine exophthalmos is observed in people suffering from Graves' disease. As this disease develops, a person experiences an enlarged thyroid gland, muscle weakness, lethargy, and symptoms of hyperthyroidism . In the body of a patient with Graves' disease, an abnormal protein is produced, under the influence of which the thyroid gland functions excessively intensively.
In medicine, imaginary and true exophthalmos are defined. Manifestations of imaginary exophthalmos are observed in people who have congenital asymmetry of the eye sockets, some anomalies of the skull, an enlarged palpebral fissure, and increased size of the eyeball. In turn, true exophthalmos is divided into inflammatory, non-inflammatory and tumor.
Protrusion of the eyeball in a person with exophthalmos can be almost imperceptible or very pronounced. With pronounced bulging, hyperthermia and swelling of the eyelids and swelling of the conjunctiva may be observed. Depending on the severity of exophthalmos, the eyeball can either remain mobile or lose mobility to a certain extent. If the eyeball does not move or its mobility is severely limited, the doctor may suspect the presence of severe inflammation in the orbit or intensive development of a tumor. Visual impairment may occur depending on how severe the pathological process is.
In some forms of exophthalmos, the patient's intraocular pressure increases. This is possible with the edematous form, which occurs spontaneously or after removal of a person’s thyroid gland. In this case, the patient may complain of periodic orbital pain and decreased visual acuity.
Pulsating exophthalmos is manifested by protrusion of the eyeball and its pulsation. The development of false pulsating exophthalmos occurs in patients with brain tumors, aneurysms of the orbital vessels and the internal carotid artery. True pulsating exophthalmos is the result of injury and rupture of the wall of the common carotid artery. As a result, arterial blood penetrates into the superior orbital vein, its walls expand and the orbits protrude. With pulsating exophthalmos, the patient may suffer from headaches and periodic tinnitus.
The occurrence of intermittent exophthalmos is associated with a number of eye diseases. It appears when a person tilts his head.
The consequence of the displacement of the eyeballs is damage to the extraocular muscles, which ultimately leads to strabismus . When the eyeballs are displaced and mobility is limited, a person often experiences severe diplopia . Also, with a pronounced displacement of the eyeballs, tight contact between the upper and lower eyelids is impossible. As a result, the cornea of the eye is not sufficiently moistened, and the patient may develop keratopathy , that is, degenerative processes in the cornea, leading to serious inflammatory processes. The most serious complication of exophthalmos is compression of the optic nerve, which occurs due to increased intraocular pressure. As a result, blood flow and signal conduction along nerve fibers are disrupted. The nerve can completely die, and the person develops complete blindness.
Etiology and pathogenesis
EO is an extrathyroidal manifestation of Graves' disease in the form of an autoimmune organ-specific process, usually associated with pretibial dermatopathy. The concept has become widespread according to which antigen-specific mechanisms play a major role in the development of EO with infiltration of orbital tissues by immunocompetent cells, predominantly CD4 T lymphocytes, and to a lesser extent B lymphocytes. Autoreactive T lymphocytes recognize thyrotropin receptor antigen, common to the thyroid gland, orbital fatty tissue and extraocular muscles.
The common antigen can be recognized by T cell receptors on CD4 T cells, resulting in the production of cytokines that further enhance the immune response. In the tissues of the orbit with EO, T-lymphocytes with a Th1 profile predominate (producing interleukin-2, γ-interferon, tumor necrosis factors - TNF).
Adhesion of molecules, the formation of which is mediated by cytokines in the extraocular muscles during EO, plays an important role in the development of the pathological process and antigen recognition. Cellular activation and local expression of adhesion molecules promote the accumulation and migration of leukocytes at the site of inflammation. Fibroblasts of the orbital tissue, which are stimulated by cytokines of T- and B-lymphocytes, are currently considered as key effector cells that produce regulatory mediators that mediate the local inflammatory response in the tissues of the orbit during EO.
Diagnostics
In principle, the disease can be detected with the naked eye. However, in the early stages the disease is not so pronounced, so to make an accurate diagnosis, doctors conduct a number of additional examinations:
- Exophthalmometry. Using a special device, the ophthalmologist determines the degree of protrusion;
- Using a slit lamp, the doctor performs a biomicroscopic examination;
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain;
- X-ray of the skull to exclude orbital fractures;
- Ultrasound examination of the visual apparatus;
- Using an ophthalmoscope, the doctor conducts a general examination of the eye;
- Computed tomography is performed to identify destructive processes in the eyes.
| An ultrasound of the thyroid gland, an x-ray of the organ of vision is also additionally prescribed, and blood is drawn for hormonal tests. |
Return to contents
Thyrotoxic exophthalmos
Thyrotoxic exophthalmos is a consequence of a disease called thyrotoxicosis . It is important to note that this type of disease most often develops in women whose age exceeds fifty years. The phenomena of protrusion are often accompanied by redness of the lower eyelid, as well as inflammatory processes that occur in the eye orbit.
A huge number of visual and computer techniques are used for diagnosis. In particular, the patient is sent to undergo ultrasound, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging . All these methods can provide true information about the condition of the patient's fundus, as well as the condition of the orbital and periorbital areas of the eyes.
Signs
Symptoms that can provoke this disease:
- Increased fatigue and irritability. These symptoms should be classified as general, which are the result of a serious illness.
- tremors .
- Swelling of the lower eyelid.
- Redness of the lower eyelid.
- Serious changes in the fundus of the eye, which lead to increased intraocular pressure.
- Increased sleepiness.
- Serious pain syndrome, which consists of unbearable dull or throbbing pain that may be characteristic of this disease.
How to treat thyrotoxicosis
Treatment of thyrotoxic exophthalmos can be carried out using a wide range of different methods. No method can completely eliminate this type of disease. The first and most common method is that the doctor prescribes conservative treatment , which can and should include a wide range of medications.
Medicines
An endocrinologist may recommend using a common and very inexpensive drug called L-thyroxine. This drug is used to treat endocrine diseases and is successfully used in patients who have certain thyroid diseases. As a result of the influence of this drug, the background of thyroid hormones , and the phenomena of exophthalmos may decrease.
In addition, an ophthalmologist can prescribe medications that can reduce swelling and inflammation. Here we are talking about local therapy. As such therapy, Dexamethasone is prescribed, which successfully fights inflammation.
It is also very important to prescribe eye drops that can reduce high intraocular pressure . Such drugs include Betoptik. These are unique drops that have no analogues. As a result of a unique pharmaceutical mechanism of action, they are able to influence the phenomenon of high blood pressure in order to reduce it or bring it back to normal.
Photo 2. Emoxipine, eye drops, 5 ml, solution 10 mg/ml, .
In cases of thyrotoxic exophthalmos, the retina of the eye is very often affected. Therefore, it is simply necessary to prescribe drops that can support the retina. These drops include "Emoxipin" , which is able to combat the manifestations of hemorrhages in the ocular environment, and can also strengthen the retina.
In addition, quite often the therapist resorts to prescribing prednisolone in tablet form , which can be purchased at any city pharmacy at a low price. Prednisolone is able to reduce inflammation and restore hormonal levels, which is of great importance in the thyrotoxic type of the disease.
Radioiodine therapy
Very often, with thyrotoxic exophthalmos, radioiodine therapy , which can equalize the hormonal levels in the thyroid gland. The meaning of this type of procedure is that the human thyroid gland is capable of attracting huge amounts of iodine.
Therefore, when a given chemical element is introduced into the body, this gland begins its active work in order to absorb the required amount of the element of the periodic table in a matter of hours.
This procedure is most directly related to the treatment of thyrotoxic exophthalmos, because after normalization of hormonal levels , we can observe a decrease in the intensity of symptoms of eye protrusion.
Operation
surgical methods are used to successfully treat exophthalmos . In modern surgical offices, the so-called thyroidectomy , which involves partial removal of the thyroid gland, has become widespread. After this type of operation, we can talk about a significant regression of exophthalmos, but not about its cure.
It is also worth noting that, despite the great popularity of this operation, it has a number of significant contraindications . Such contraindications include the fact that, often, after surgery, thyrotoxic exophthalmos turns into its edematous form, which is the worst prognosis for this disease.
Therefore, before carrying out this kind of surgical intervention, you should always think about the rather sad consequences . It is possible that in some cases it is worth limiting ourselves to only conservative methods of treating an insidious disease.
Changes in the organ of vision in diseases of the thyroid gland
Endocrine ophthalmopathy (EOP)
The first description of the clinical picture of suffering in the soft tissues of the orbit in a patient with diffuse toxic goiter was in 1853. described and published by JR Greves (London), he also proposed the term for the disease - endocrine ophthalmopathy (Greves' disease). In 1840, independent of Graves, Basedow described and published the main symptoms of thyrotoxicosis.
Frequency of occurrence. Every year, thyroid pathology with its primary hyperfunction is diagnosed in 2% of the population
Image intensifier frequency for women is 16:100,000, for men - 2.9:100,000
Endocrine ophthalmopathy (EOP) is an autoimmune disease caused by the formation of specific immunoglobulins and characterized by swelling of the periorbital tissues.
State of thyroid function in EOP: 1. Euthyroidism -18.5% 2. Dysfunction -81.5% -Hyperfunction 73.4% -Hypofunction 26.6%
3. Autoimmune thyroiditis (Hashimoto’s)
4.Hypofunction after
-removal of the thyroid gland -irradiation of the thyroid gland
Most often, this disease occurs between the ages of 35-59 years. Autoimmune thyroidism has been diagnosed since the age of 3. The causes of this disease are multifactorial. The development of endocrine ophthalmopathy occurs due to an imbalance of complex immunological mechanisms that arise against the background of obvious or hidden dysfunction of the thyroid gland. The disease is bilateral in nature (develops in both orbits).
There are changes coming from:
- Extraocular muscles (only the rectus extraocular muscles are affected)
- Periorbital tissue.
As a result of a complex pathological autoimmune process, excessive accumulation of water occurs in the above orbital structures, which leads to excessive swelling of the soft tissues of the orbit.
Clinical picture
- Thyrotoxic exophthalmos
- Edema exophthalmos
- Endocrine myopathy
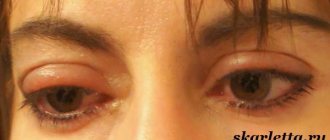
Thyrotoxic exophthalmos - characteristic clinical signs: false wide palpebral fissure, rare blinking, dysfunction of the upper eyelid and extraocular muscles, unusual shine of the eyes, lag of the eyelid when moving the eye down, tremor of the eyelids when closing the eyes, uneven twitching of the eyelids when looking downwards. All of the above symptoms at this stage of the disease are reversible with timely and adequate treatment.
If there is asymmetry in the position of the upper eyelid in the evening, this is a sign of transition to the edematous form of exophthalmos. At the same time, exophthalmos, swelling of the periorbital tissues increases, severe changes appear in the mucous membrane and cornea of the eyes, and non-closure of the palpebral fissure. As a result of swelling of the soft tissues of the orbit, mechanical compression of the optic nerve and orbital vessels occurs, resulting in the development of their functional and structural changes (so-called optic neuropathy). Violation of the outflow of venous blood leads to increased pressure in the aqueous veins, which in turn causes increased intraocular pressure (so-called symptomatic intraocular hypertension).
With the further development of the pathological process in the orbit, the appearance and progression of orbital fibrosis (proliferation of connective tissue) occurs, which leads to irreversible structural and functional changes in the soft tissues of the orbit. With endocrine myopathy, predominant damage to the extraocular muscles occurs, resulting in the development of strabismus, diplopia (double vision), and impaired binocular vision. If, during an ophthalmological examination, disturbances in the position of the eyes in the orbit, disturbances in the joint functioning of the eyes, or eye movement not in full volume are revealed, then together with the endocrinologist and neurologist the cause of these changes is determined.
In case of thyroid disease, a complete ophthalmological examination is carried out (both basic - including determination of visual acuity, measurement of intraocular pressure, examination of intraocular structures and the fundus, and additional - determination of the position of the eyes in the orbit using exophthalmometry, determination of the mobility of the eyeballs, congenial work of the eyes, study of the functions and structure of the optic nerve using computer perimetry and OST of the optic nerve head, respectively, ultrasound scanning of the eyes and orbital structures).
If indicated, a computed tomography scan of the orbits is performed; during this study, the walls of the orbits, changes in the extraocular muscles, the retrobulbar part of the optic nerve and orbital vessels are examined in detail.
Patients, depending on the results of the examination, are examined routinely or urgently in our Clinic by Prof. Brovkina A.F. After which, together with the Department of Ophthalmo-Oncology of the Moscow City Hospital, a set of therapeutic measures is carried out.
Treatment of image intensifier
1. Normalization of thyroid function. 2. Drug treatment (determined jointly by an endocrinologist, ophthalmologist and neurologist, depending on the stage of the disease) 3. Radiation treatment. 4. Surgical (urgent (urgent) - removal of intraorbital pressure, restorative)
You can make an appointment on the clinic website or by phone +7 495 982-10-10
, +7 495
982-10-60
Causes of protruding eyes
In most cases, bulging eyes develop against the background of endocrine diseases.
, which disrupt the functions of all organs and systems in the human body. With this pathology, swelling of the fatty tissue and muscles in the eye sockets leads to scarring.
Most often, both eyes are damaged at once, but there are cases of unilateral exophthalmos. Exophthalmos can appear at any age; in infants, its symptoms indicate congenital diseases.
Less common causes of protruding eyes:
In addition, protruding eyes are detected in people who have congenital, severe inflammation of adipose tissue, and exophthalmos also develops against the background of varicose veins in the organ of vision.
Exophthalmos can be a complication of another pathology - Graves' disease or diffuse toxic goiter. Pathology develops due to a lack of iodine in the body; it provokes the thyroid gland to produce an increased amount of thyroid hormones. They lead to swelling and swelling of the fat pad and eye muscles, causing the development of exophthalmos.
Treatment methods for exophthalmos
Treatment of exophthalmos is selected individually, taking into account the severity of the pathology and the nature of its origin. For bulging eyes, depending on the cause of its development, the following treatment tactics can be used:
- Inflammatory processes: antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, immunostimulants.
- Endocrine ophthalmopathy: correction of hormonal levels using hormones and thyreostatics.
- Autoimmune pathologies: glucocorticosteroids. If there is no effect, the thyroid gland is removed and hormone replacement therapy is performed.
- Exophthalmos in thyrotoxicosis: correction of hormonal levels, elimination of swelling of adipose tissue.
- Diffuse toxic goiter: Mercazolil, microdoses of regular and radioactive iodine.
If there are no provoking factors, then antihistamines and steroids are prescribed. To strengthen the immune system, a course of vitamins and immunomodulators is selected. If the clinical picture is severe, symptomatic treatment is prescribed aimed at eliminating pain, swelling, diplopia and other manifestations of bulging eyes. For imaginary exophthalmos with protrusion of less than 2 mm, treatment is not carried out.
Treatment with folk remedies is impossible.
Endocrine exophthalmos
Endocrine exophthalmos is associated with a kind of imbalance in the functioning of the endocrine glands . As a result of increased production of thyroid-stimulating hormone, you can often experience the phenomenon of protruding eyeballs.
Endocrine glands can increase or decrease the production of various hormones . In case of increased activity, this can lead to serious deviations in human life.
If we talk about the symptoms of this disease, they show great similarity with those symptoms that were described in the case of thyrotoxic exophthalmos . The diagnostic methods for this disease are also similar to those described above.
If we talk about treatment methods, then in cases of endocrine exophthalmos, a course of corticosteroid therapy . There is also radiotherapy , which involves administering high doses of radiation. In addition, surgical treatment methods are used. These include excision of the eye orbit , as well as its decompression .
Causes of exophthalmos
With endocrine ophthalmopathy, disturbances in the functioning of the human immune system are observed. The subcutaneous fatty tissue of the eye orbits swells, and the same happens to the muscles of the eyeball. If the disease begins to be treated at this stage, then significant improvement can be achieved and the eyeball can be returned to its physiological position.
As the pathology progresses, the extraocular muscles become injured and scar tissue forms on them. Such changes are irreversible.
In Graves' disease, against the background of autoimmune thyroiditis, retrobulbar tissue is damaged. The body's own antibodies attack not only the thyroid tissue, but also the tissue of the orbit. Proof of this theory of the development of exophthalmos is the high level of antibodies to thyroid-stimulating hormone receptors.
Antibodies to the muscles of the oculomotor system will be produced in the body more if it is influenced by the following risk factors:
- Emotional shock.
- Past viral infections.
- Poisoning of the body.
- Impact of radiation on the body.
- Genetic predisposition to the development of thyroid diseases.
An inflammatory process occurs inside the orbit against the background of exophthalmos. When fatty tissue is involved, or the patient develops vascular vasculitis, the eye orbits bulge forward due to mechanical pressure on them.
Rare causes that can provoke exophthalmos include:
- Dacryoadenitis.
- Tumors of benign nature.
- Cancerous tumors.
- Skull injuries with bone displacement and hemorrhage into the orbital cavity.
- Phlebeurysm.
- Angiopathy.
Treatment
Ocular symptoms of thyrotoxicosis are treated in conjunction with the provoking disease. This may be conservative therapy, involving a course of taking special medications, surgery, or the use of radioactive iodine, which is also practiced for hyperreactivity of the thyroid gland.
In the early stages of the disease, until the goiter has reached an impressive size, serious changes have not yet occurred in relation to the visual system, for example, only 1 degree of exophthalmos is diagnosed, other symptoms are not yet expressed, then treatment can only be medicinal.
Blockers of intense hormone production, antithyroid drugs and other drugs are prescribed at the discretion of the doctor.
If positive dynamics are not observed, it is not possible to control the functioning of the endocrine system, or the patient initially presented at an advanced stage of the disease, a decision is made on surgical intervention. The operation may be preceded by special preparatory therapy.
Treatment of endocrine ophthalmopathy during pregnancy
Endocrine ophthalmopathy itself does not pose a significant threat to the health of a pregnant woman, and therefore a specific approach for the treatment of endocrine ophthalmopathy in pregnant women has not been developed. However, ophthalmopathy in the majority of cases develops against the background of diseases of the endocrine system, which must be taken under control both in general and during pregnancy in particular. The latter include diffuse toxic goiter and thyrotoxicosis. Their treatment should be carried out under the supervision of specialized specialists.
For the treatment of thyrotoxicosis during pregnancy, small doses of propylthiouracil (up to 200 mg/day) are prescribed. The goal of treatment is to achieve and maintain free T4 concentrations at the upper limit of normal values. Treatment of hyperthyroidism with radioactive iodine during pregnancy is contraindicated, and surgical intervention is prescribed in exceptional cases and complex cases.
For the treatment of diffuse goiter for pregnant women living in an iodine-deficient region, it is advisable to prescribe 250 mcg of iodine. In treatment during pregnancy, preference is given to monotherapy with iodine, less often - combination therapy with iodine and sodium levothyroxine. In both cases, monitoring of thyroid function is necessary, that is, an analysis for the hormone TSH and free T4.
Pulsating exophthalmos
With pulsating exophthalmos, a significant disturbance occurs in the vascular bed. This kind of disorder manifests itself in the fact that vascular tone in the cavernous sinus is upset. Very often, this kind of disease can be observed in children who have a disease called cerebral hernia . If we talk about diagnostics, the following types are used:
- Ultrasound.
- CT scan.
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
The same methods are used as for the types of exophthalmos mentioned above.
If we talk about the main symptoms of this disease, they are similar to the symptoms of thyrotoxic exophthalmos, however, with pulsating protrusion, the patient’s vision does not disappear.
It is disrupted so that the patient has enormous visual discomfort. Often with this disease, we can talk about nystagmus of the eyeballs.
Therapy
The disease is treated with radiotherapy . It is important to use large enough doses of radiation to achieve a significant effect. Small doses of radiation are not able to have a significant effect on this disease.
A radical method in the treatment of pulsating exophthalmos is the method in which the so-called ligation of the carotid artery . As a result of this type of fixation, the pressure on the eyeballs is reduced, which means the symptoms of bulging are reduced.
However, with this surgical method of exposure, serious side effects may occur in the form of increased intraocular pressure. Therefore, the surgeon is obliged to weigh all the pros and cons before performing this type of operation in order to avoid serious complications in the form of complete or partial loss of vision.
How to get rid of exophthalmos?
Before proceeding directly to the treatment of exophthalmos, it is necessary to establish the correct diagnosis and determine why the person developed this condition. The diagnosis is established during an ophthalmological examination, as well as through a detailed interview with the patient, who must tell the specialist in detail about the features of the development of the disease. A special procedure called exophthalmometry is practiced. During such an examination, using special mirrors, the specialist evaluates the location of the eyeballs. If necessary, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging is also used. The information obtained from these studies allows us to more accurately determine the changes that have occurred.
To confirm the diagnosis, sometimes the specialist also prescribes laboratory tests for the patient to determine the level of thyroid hormones.
Treatment of exophthalmos depends on how severe the changes are, as well as on the cause of the development of this symptom. The doctor determines how to treat exophthalmos after establishing an accurate diagnosis. If a patient is diagnosed with endocrine ophthalmopathy , then treatment of bulging eyes is carried out by correcting the functions of the thyroid gland. In this case, a course of treatment with glucocorticosteroid drugs is prescribed. It should be understood that in this case you should not practice treatment with folk remedies, so as not to worsen your health condition.
If a person has an inflammatory process, it is necessary to carry out anti-inflammatory treatment, as well as take medications that reduce the toxic effect of inflammatory processes on the body. Sometimes the doctor may decide to treat with surgery. So, with severe exophthalmos, compression of the optic nerve is eliminated. If the cornea is damaged, partial or complete suturing of the eyelids is possible.
If there is oncological pathology, the patient undergoes surgery and subsequent radiation therapy or chemotherapy.
If a diagnosis of “false exophthalmos” is made and there is a slight physical protrusion of the eyes, no treatment is carried out, but the patient is regularly monitored.
For Graves' disease, treatment is prescribed by an endocrinologist. First of all, the patient must take a course of drugs that help suppress the activity of the thyroid gland. Initially, the doctor prescribes large doses, later they are gradually reduced. Constant monitoring of thyroid hormone levels is important. Complex treatment includes taking glucocorticoids and immunocorrectors.
If there is no effectiveness after treatment with medications, surgery may be performed. During this operation, part of the thyroid gland is removed. Also, treatment of Graves' disease can be carried out using radioactive iodine . However, this method is used to treat older people.
How to relieve swelling with hypothyroidism: recipes
Recipe No. 1. The raw material is lingonberry leaves. Pour 200 ml of boiling water over one teaspoon and boil for ten minutes. Take half a glass half an hour before meals.
Recipe No. 2. A decoction of fresh lily of the valley flowers, dry cocklebur and parsley helps eliminate swelling due to hypothyroidism. The ingredients of the raw material should be poured in equal parts with cold water and brought to a boil. Boil for five minutes, cool. Take a tablespoon before each meal.
Recipe No. 3. Take angelica, rose hips (fruits), celandine, St. John's wort, and licorice root in equal parts. Pour boiling water over the crushed form and cook for ten minutes. Pour the broth into a thermos, where it should sit for four hours. Drink the medicine three times a day, half a glass. It is not recommended to drink this remedy at night. The last dose should be four hours before bedtime.
Prevention methods
The main preventive measure for people with physiological bulging eyes is carefully monitoring their health and visiting an ophthalmologist at least once a year. These patients are automatically at risk and require constant monitoring to identify pathology at an early stage.
Preventive measures also include:
- To eliminate the risk of goiter formation, add more seafood to your diet and use iodized salt;
- Give up bad habits, play sports;
- Avoid stressful situations;
- During hazardous activities, protect your eyes and head from injury;
- Treat infectious and inflammatory pathologies in a timely manner.
Since one of the reasons for the appearance of bulging eyes is helminths, or more precisely, Trichinella, which parasitizes raw meat (especially lard), it is worth reconsidering your diet.
Nutrition during illness
Treatment of the disease includes complex therapy - medication and proper nutrition.
You need to drink a lot of water, at least 3 liters per day. Diet for illness includes the following rules:
- increase daily calorie intake;
- increase micronutrient intake;
- ensure the most complete protein intake, this is the basis for building muscle tissue;
- do not consume stimulants - chocolate, spices, alcohol, coffee;
- do not include foods that stimulate fermentation in the diet - rice, grapes, plums, peaches;
- Avoid fried, salty, sweet foods.
It is recommended to include all types of cabbage in your diet; eat radishes, radishes, spinach, and turnips.
Eating strawberries and peaches helps a lot.
Any meat can be used, as long as it is boiled.
Fish - preferably river, it does not contain iodine.
Only with proper nutrition and medication can you improve your condition and alleviate the symptoms of the disease.
It is very important to understand that proper nutrition plays a significant role in the treatment of thyrotoxicosis.
The following foods should be completely excluded from your diet:
- fat meat;
- fried foods;
- seafood and seaweed;
- hot seasonings and spices;
- chocolate and fatty sweets;
- coffee, cocoa;
- alcohol;
- products containing chemical additives and preservatives.
If these products are not excluded, additional intoxication of the body will occur.
You should also definitely add to your diet:
- whole grain products (porridge, bread);
- low-fat fermented milk products (kefir, cottage cheese);
- vegetables and fruits;
- leafy greens;
- lean meat, boiled or steamed;
- lean fish (boiled or baked);
- herbal teas, juices, compotes.
You should not eat fatty foods at all, especially those saturated with animal fats. You should also avoid rich meat broths and excess amounts of fast carbohydrates (sweets).
Thyrotoxicosis: symptoms
Symptoms of thyrotoxicosis in men and women largely depend on the degree of development of the disease: it is customary to distinguish subclinical thyrotoxicosis, which occurs with vague symptoms or no symptoms at all, obvious thyrotoxicosis - with very characteristic symptoms, but without complications, as well as severe thyrotoxicosis with pronounced manifestations and the development of complications.
The main manifestations of thyrotoxicosis are usually considered to be:
- disorders of the cardiovascular system: rapid rhythm, even with minor physical exertion; tachycardia during sleep, depending on the patient’s body position, rhythm disturbances of a paroxysmal or permanent nature - atrial fibrillation
- feeling of heat, intolerance to stuffy rooms, increased sweating;
- against the background of progressive tachycardia or atrial fibrillation, heart failure may develop - shortness of breath, caused, among other things, by minor physical exertion, swelling of the extremities;
- disruptions in the functioning of the nervous system: can manifest themselves in the form of trembling and spasms, especially in the hands and fingers, as well as in a set of specific behavioral symptoms - fussiness, irritability, absent-mindedness, increased activity, affective lability, sudden mood swings, including a tendency to depression and panic attacks; interruptions in sleep (insomnia, frequent awakenings at night);
- acceleration of metabolism in the body, which is expressed in increased feelings of hunger and weight loss. In this case, not only adipose tissue is most often lost, but also part of the muscle mass, which usually leads to general muscle weakness without the formation of a goiter;
- brittle bones: can also be a manifestation of this disease, since hormones cause the body to lose significant amounts of calcium and phosphorus. Hair fragility, hair loss, dry skin may also occur;
- increased bowel movements (diarrhea), as well as a frequent urge to urinate.
In the early stages, thyrotoxicosis can occur without a pronounced enlargement of the thyroid gland, but with the further development of the disease, a significant increase in the thyroid gland (goiter) is noted, as well as the occurrence of ophthalmopathy, expressed in the occurrence of photophobia, a feeling of “sand” in the eyes, as well as a specific appearance of the eyeballs, that protrude forward - the so-called exophthalmos (considered a characteristic sign of Graves' disease or diffuse toxic goiter).
Also, in the later stages of the disease, women may experience disturbances in the menstrual cycle, up to its complete cessation, and in men, a significant decrease in libido and potency, which in particularly serious cases can lead to infertility in both sexes.
Modern treatment methods make it possible to control the production of hormones and avoid serious consequences of the disease. That is why, when the first manifestations of thyrotoxicosis are detected, it is necessary to contact an endocrinologist.
, since it is much easier to treat this disease in the early stages.
An initial appointment with a specialist for suspected thyrotoxicosis involves collecting an anamnesis (recording the patient’s complaints), examination (primarily palpation of the thyroid gland, assessment of symptoms of ophthalmopathy) and prescribing the necessary blood tests and other diagnostic procedures.
Diagnosis of thyrotoxicosis is carried out mainly with the aim of identifying the main factors in the development of the disease (due to a malfunction of the immune system caused by taking medications, etc.), which involves:
- hormonal study, which allows you to confirm thyrotoxicosis, including testing the level of specific thyroid-stimulating antibodies
- clinical blood test and study of certain biochemical parameters (to identify some complications of thyrotoxicosis on the composition of the blood and the functioning of certain organs, such as the liver)
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland: allows you to accurately assess its size, presence and number of nodes;
- scintigraphy: also an ultrasound, but with the introduction of a special iodine-containing drug, it allows you to determine how quickly the thyroid gland absorbs iodine;
- MRI of the brain: may be performed if there is a suspicion of a pituitary adenoma or other neoplasms that can affect its function
- CT scan of the orbits to confirm tissue damage around the eyeball and extraocular muscles.
Further treatment regimen
If the diagnosis of thyrotoxicosis is initially confirmed, the treatment prescribed by a specialist will be comprehensive and aimed at both eliminating the symptoms and causes of the disease.
Most often, hormone control in thyrotoxicosis involves the use of the following types of effects:
- Taking special medications that inhibit the production of hormones in the thyroid gland and significantly reduce the intensity of the manifestations of the disease. In each specific case, the choice of drugs and dosage is carried out individually, only under the supervision of a doctor. The course of drug treatment for thyrotoxicosis is carried out for at least 1 year, sometimes up to 2 years, under the close supervision of a doctor.
- Treatment with radioactive iodine: one of the radical ways to normalize hormonal metabolism, involving the destruction of an excess number of thyroid cells. Most often, this treatment method involves taking one special capsule containing radioactive iodine.
- Surgical treatment: recommended only if conservative treatment methods do not give the desired result or there are special indications for this type of therapy. In case of thyrotoxicosis, the operation involves partial removal of the gland, leaving a small, about 4 grams, amount of glandular tissue, usually followed by hormonal therapy.
Another additional way to control hormones and normalize the patient’s general condition is a special diet.
Diet for thyrotoxicosis
The diet requires adherence to the following nutritional principles:
- Increasing the amount of foods that slow down the production of hormones: these foods include all types of cabbage, spinach, and radishes.
- Reducing or completely eliminating foods high in iodine, primarily seaweed, as well as seafood, and especially iodized salt.
- Thyrotoxicosis involves an acceleration of metabolism, so the patient's diet should be rich in vitamins, as well as calcium and phosphorus (which involves the consumption of dairy products and cottage cheese) as a preventative measure for fractures.
- If the functioning of the cardiovascular system is disrupted, it is recommended to avoid caffeine-containing drinks, as well as spicy and fatty foods that increase blood pressure. It is recommended to consume meat and fish boiled.
- If stool is disrupted, it is recommended to avoid fermented milk products and other foods that can irritate the intestines.
- Increasing the number of meals to 4-5 times a day.
Most often, if you follow all the recommendations of a nutrition specialist and take medications, it is possible to normalize the level of hormones in the patient’s body and eliminate the unpleasant manifestations of the disease. Monitoring blood tests to monitor hormone levels also play an important role here. It must be remembered that thyrotoxicosis is a disease prone to relapse. You can extend the period of remission and reduce the possibility of relapses in thyrotoxicosis largely by maintaining a correct lifestyle, in particular, being less exposed to stress factors.
Prevention
Prevention of thyrotoxicosis is often complicated by the fact that the disease can be caused by various factors, both external and internal. However, a certain set of preventive actions most often allows you to reduce the risk of failure in the production of thyroid hormones or establish the presence of the disease at an early stage.
Prevention of thyrotoxicosis involves:
- Do not consume little-known dietary supplements or non-medicinal preparations with uncertified iodine content
- If you are taking medications containing large amounts of iodine (for example, the antiarrhythmic drug cordarone), be sure to undergo periodic testing of thyroid hormones
- It is necessary to donate blood for hormones for preventive purposes once a year if there are cases of thyrotoxicosis and other endocrine diseases in the family (there is evidence of a possible genetic predisposition to this type of disease);
- When you detect the first signs of a possible disease, you must contact a specialist and undergo an appropriate examination, which will allow you to establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment that will avoid complications.
Errors and unreasonable assignments
In case of EO, it is unacceptable to begin treatment with the use of corticosteroids in small doses, since this prolongs the period of obtaining a therapeutic effect and increases the risk of relapse. In addition, the use of GCS in small doses can lead to the emergence of steroid-resistant forms of EO.
The use of prednisolone in intermittent courses (as is sometimes recommended in the literature) is not advisable, since with this treatment regimen 20% of the drug is excreted unchanged from the body, and its half-life is quite short (2-3 hours).
Subconjunctival administration of GCS is also ineffective. According to S. Gebert (1961), subconjunctival administration of GCS, in particular methylprednisolone depot, has a minimal therapeutic effect in the form of reducing conjunctival hyperemia.