To prevent prolonged work at the computer from becoming a burden, you need to set up your monitor correctly. The most significant parameters that affect the eyes include: brightness, contrast and screen refresh rate. You should also consider the correct placement of the monitor relative to your eyes and the source of natural light in the room.
Nowadays, the activities of many people are directly related to working at the computer. Systematically spending time in front of a PC or laptop screen has a negative impact on visual health. In the evening, people with a sedentary lifestyle often experience tired, red, and irritated eyes. Many people think that the problem lies in choosing the wrong distance from the monitor, but this is not the case.
The comfort of using the equipment is affected by a number of specific screen parameters that must be pre-configured before use.
Selecting and setting up an LCD monitor
Initially, you need to understand what types of monitors there are, since their settings directly depend on this. Truly “harmful” displays have not been produced for a long time, so we can say that all modern models on the market are safe for the eyes if the operating rules are followed.
Previously, CRT monitors were actively used, the functioning of which was based on the use of a cathode ray tube. They were quite damaging to the organs of vision and consumed a lot of energy. They have been replaced by new LCD (liquid crystal) LCD screens, which are gentle on our eyes. Depending on the matrix used, they are divided into three categories: TN, IPS and MVA/VA.
TN matrix
The most affordable option is a screen with a TN matrix, which provides a fairly poor viewing angle. If you look at it from the side, the colors of the picture are greatly distorted, which contributes to rapid fatigue of the visual organs. Correct positioning of the monitor relative to the eyes is extremely important in this case. You should sit directly opposite such a display, otherwise it will be difficult to distinguish a picture or text.
IPS matrix
This type of matrix is the highest quality and safest for the eyes today. It provides a good viewing angle and color saturation. The disadvantage of such a screen is its high cost. As a rule, IPS matrix is found in laptop monitors in the middle and high price segments.
MVA/VA matrix
The best option in terms of price-quality ratio is the MVA/VA matrix. It is somewhat inferior to IPS in terms of color saturation, but it is almost impossible to notice this with the naked eye. Such monitors provide a good viewing angle, but at the same time cost an order of magnitude cheaper than IPS. This is a good choice for those who spend a long time at the computer.
Since CRT monitors are no longer used, let's look at how to set up a LCD monitor with any of the matrices described above.
Please note that screen parameters for comfortable work may vary in each specific case. It all depends on the individual characteristics of the human visual system. However, there are a number of simple recommendations that should still be followed.
Rules for “safe” work with a computer (monitor).
The computer has provided us with new wonderful and useful technical capabilities; it has freed us from many tedious manual operations and saves our time, but we must not forget that improper or excessive use of computer technology can harm our health. Very “active” users face completely unexpected troubles. Which ones and how to avoid them? It's time to learn a few simple but very important computer security rules.
Life on Earth developed under conditions of constant fluctuations in the electromagnetic environment. The human brain takes a very long time to adapt to this. In the end, in the process of evolution, he “selected” a frequency close to natural (10 hertz) for his own bioelectric waves and began to work on it. Like a person on the deck of a ship during a storm, our brain tries to adapt to the “rolling” caused by fluctuations in the electromagnetic environment. When the frequency of external electromagnetic radiation (EMR) changes, it mobilizes more and more reserves. At the same time, those parts of it that are responsible for receiving and analyzing information are switched to repelling the wave attack. With intense EMR, our brain is no longer able to maintain balance; it seems to go into “deaf defense” and the person loses all ability for analytical thinking, falls into deep depression, and ceases to navigate in space. In all cases of abnormal external influences, the brain, first of all, mobilizes its adaptive capabilities to the detriment of its other functions, in particular the regulation of physiological processes. This results in poor health, headaches, increased blood pressure, irritability, memory difficulties and much more. In other words, things are bad for the organism that has low individual adaptability of the nervous tissue of the brain to changes in the electromagnetic environment and fewer internal reserves.
Until relatively recently, it was believed that weak EMR (unlike radiation and ionizing radiation) does not have any serious effect on biological objects and therefore does not pose a threat to health. It was only in the early 90s that scientists began to understand that low-intensity, high-frequency EMR could negatively affect a living organism.
The impetus for research in this area was the rapid spread of radiotelephones. Even a layman knows what happens to a steak placed in a microwave oven. And how does the same radiation, only of lower intensity, affect the brain of a radiotelephone user, who is located at a distance of only one or two centimeters or less from him? The Americans were the first to sound the alarm when a number of lawsuits were filed against manufacturers of radio telephones and owners of cellular networks by relatives of people who actively used such devices during their lifetime and died of brain cancer.
Sanitary standards in Russia have introduced a maximum EMR power limit of 10 microwatts, but for the vast majority of cell phones in our country (mostly imported), EMR is 10-100 times greater than the maximum permissible value. As recent studies have shown, such radiation negatively affects the hypothalamus, endocrine system, vestibular analyzers located in the middle ear, and the retina of the eye. In addition, it must be borne in mind that the tissues of the human body are heterogeneous; for example, in the brain there are tissue areas that, due to high conductivity, are capable of absorbing significantly more EMR energy than neighboring ones. The possibility of such local overheating was reliably established even before the invention of the radiotelephone. When certain doses (by the way, very insignificant) of high-frequency radiation were exceeded, microscopic areas were observed in the brains of experimental animals that turned out to be literally welded. Therefore, it is possible that such a phenomenon can lead to brain cancer.
A very important, if not the main role is played by the frequency parameters of EMR, no matter how low their intensity. In frogs, rats, rabbits, cats, and monkeys, a variety of disorders were observed as a result of non-thermal irradiation: from the formation of plaques clogging blood vessels and cardiac arrhythmias to suppression of conditioned reflexes and catalepsy. All this applies not only to EMR of radiotelephones, but also of many devices, including household ones. In terms of the degree of harmful impact, personal computers successfully compete with cellular communications.
Why do millions of people experience a lot of discomfort and pain when doing work that involves only their hands and eyes? In all likelihood, the answer is to be found in the particularity of this activity, which is characterized by sitting for many hours in a fixed position in one place with your eyes glued to the screen. However, experts say that there is nothing in computer-related work itself that makes back pain, physical discomfort or visual impairment inevitable. Of course, long-term work at a computer places additional demands on the human visual system. Eyes dart from paper to screen and back. Hundreds, thousands of times a day you have to change from one way of reading to another. This is why vision problems cause the most complaints among workers.
The main cause for concern and the main threat to health is immobility, static posture, especially the main muscles that need a dynamic mode of operation (especially the intraocular and ciliary muscles). Therefore, when working with a computer, first of all, you need to think about creating a special motor mode for the muscles of the eyes and the whole body. The second important task is to reduce the influence of electromagnetic radiation (EMR) generated by the computer.
According to electrophysiological, biochemical and psychological analyzes of the functional state of users, after only 45 minutes of work on a personal computer that is not equipped with a protection system, a tendency to overload the main regulatory systems of the body was revealed. There are groups of people who, due to individual physiological and, possibly, psychological characteristics, are not recommended to work with a computer at all, regardless of the degree of protection of the user from its radiation.
But personal computers (PCs) aren't just dangerous for those sitting in front of a display. Their EMR spreads evenly in all directions from the monitor within a radius of 1 to 2.5 meters.
Effect on the eyes. When working on a computer, the main load falls on the eyes. Therefore, it is especially difficult for the nearsighted and farsighted. They automatically try to compensate for poor vision by changing their body position. They lean toward the screen, squinting, trying to get a better look at the text. Posture becomes poor, and sooner or later your neck starts to hurt. This leads to severe headaches and decreased performance. Regular glasses are rarely suitable for working on a computer screen. You need special glasses with double and even triple lenses, designed for a strictly defined distance to the screen. Exactly describe to the ophthalmologist your workplace, how you sit at it, monitor settings and lighting features. It makes sense to purchase glasses only according to individual prescriptions and you will learn to maintain correct posture while working. Your performance directly depends on this. In all cases, glasses with mirrored lenses are needed (mirror glasses will help avoid glare, they are transparent and increase contrast).
The ideal workplace. The concept of an ideal workplace includes seven main requirements that ensure comfortable working conditions at the computer, maintaining efficiency and well-being during the day:
— computer desk with an adjustable keyboard platform;
— extra-long cable that allows you to place the keypad in a place convenient for you;
— a special chair with adjustable height and backrest angle;
— large screen with adjustable brightness and contrast;
— anti-glare screen that protects the video terminal from reflected glare;
— tilt-articulate monitor stand for installing the screen at the desired angle;
- if you have to retype a lot of text materials, then buy a special tablet (it is attached to the monitor and allows you to avoid unnecessary eye movements and neck turns - a trifle, but comfortable).
When choosing a location for your computer, consider:
— maximum focal length;
— no glare;
- proper lighting of the room.
Additionally for efficient work:
— it should be possible to shift your gaze to a far distance (this is one of the most effective ways to relax when working with a computer);
- you cannot sit facing a wall or window, but if this happens, place a large mirror at the top of the monitor on the table to see the farthest objects behind your back;
— please note that the source of glare can be lamps, uncurtained windows or any bright objects (for example, your shirt or white blouse). In order to make sure there are glares, you need to turn off all the lights in the room and look at the non-working screen (do not use the maximum screen brightness, adjust it);
- if you have gotten rid of all sources of glare, but now, quite possibly, your workplace has begun to seem dark to you (this can become a problem - few people like to work in a dimly lit room). Make sure that the light sources are distributed evenly, making sure that none of them falls into your field of vision when you look at the screen;
— for illuminating working documentation, a table lamp with an adjustable shade is most suitable; be sure to ensure that the light is not irritating and does not fall on the computer screen.
Correct position at the computer:
- distance from the screen - sit so that your eyes are at a distance of 45 - 60 cm from the screen;
- eyes above the screen - sit so that your eyes are 15 - 20 cm above the center of the screen;
- hands - fingers have the greatest freedom of movement when they are at the level of the wrists or slightly below;
- wrists - they should also be kept either at the level of the elbows, or slightly lower, and the hands themselves should be low enough so that the shoulders are lowered and relaxed (thanks to this, the hands will also relax);
- sit upright and straight - use a high swivel chair with a comfortable back, the back of the chair should correspond to the natural arch of the spine in the lower back, and the back of the thighs should be in contact with the seat (Fig. 1);
- position yourself in front of the computer in a way that is comfortable for you - your legs should be bent at a right angle, your knees should be at hip level (or lower), and your feet should be crossed and placed on the floor or stand.
Rice. 1.
While sitting at the computer, control your posture, the position of your hands, and be sure to alternate work with rest.
Use small “reminder programs” that will prompt you to rest after certain periods of time. Rest is necessary not only to “unload” the eyes. Anyone who actively works on a computer makes about 50,000 keystrokes per day. The load on the arms is impressive. Aches and swelling of the joints, impaired skin sensitivity, a feeling of numbness in the hands - this is not a complete list of unpleasant sensations that occur in approximately 20% of active users. In America, such problems have long been classified as occupational diseases of office workers. Meanwhile, preventing their occurrence is not easy, but very simple.
The abundance of papers and working with a computer makes your eyes very tired. Try to train yourself to relieve stress during the working day by following the recommendations below:
- Place green and blue postcards on your desk. “Color therapy” will help you in moments when you feel overstressed. Take a look at the postcards and relax a bit. Blue and green colors lower blood pressure (but red, orange and yellow increase).
- Even if you are very busy, take a moment to step away from your work and take a break. Concentrate your gaze on the far wall and, without looking directly at the objects, try to mentally describe them (color, shape, etc.). Do the same, turning in the other direction.
- Grimaces help relieve tension and relax the facial muscles. Pull out your lips and chant “ty-yu-yubik.” And then smile and say the word “vi-i-iski” with pleasure. This pleasant exercise improves blood circulation, strengthens facial muscles and makes the skin firmer and more elastic (just try to speak quietly or completely silently, otherwise you may distract or scare your colleagues).
- Sit correctly at your desk. The keyboard and screen should be located strictly in front of you, any displacement from the central axis is fraught with problems with the spine (in particular, thoracic radiculitis, with which, as people say, you can’t breathe or gasp), as well as pain and loss of sensation in the hands, which are especially annoying at night.
- Instead of spending hours typing on keys, sort out your email and make a phone call. The more often you change the position of your hands, the better for them.
- Sitting in front of the screen, listen to yourself: the slightest discomfort, even a slight headache should serve as a signal to stop working. The principle of coping has unpleasant consequences for your health.
An adult needs to take a short break every hour (or better yet, every 45 minutes) of work. In just a minute, stretch your neck a little, bend forward and to the sides a few times, rotate your shoulders and hands, especially your right hand, which is usually occupied by the “mouse.” The general principle of such mini-gymnastics is to ensure blood flow to all organs.
After working for a long time at a computer with a color monitor, sometimes even black and white objects seem to be painted in different colors. Is it dangerous? Ophthalmologists say: this is not a disease, but a property of normal vision. The brain remembers intense colors better and does not want to part with “pleasant memories” for some time. Massage your eyelids and the “rainbow” will disappear. In the future, when working at the computer, take breaks from work more often (every 45 minutes). You can also use special relaxation computer glasses, which have recently become very popular, especially among active users. These glasses not only protect your eyes, but also relieve fatigue. You can work in them for 5-7 hours without getting tired.
There are also a number of simple requirements for organizing efficient and safe work:
- Computer work is contraindicated for people with weakened immune systems, those suffering from heart disease and allergies, as well as pregnant women. Those who intend to become operators, especially people with impaired vision or nervous disorders, should first consult with medical specialists. This is necessary in order to better know your capabilities and dose the load correctly.
- The room where the computer is located should be spacious enough. Chairs, armchairs, sofas, beds should not be placed within a radius of 2.5-3 meters around it.
- The computer must be connected to a three-prong outlet.
- The monitor, keyboard and computer case should be directly in front of you. With a diagonal monitor position, you will have to continuously spin in your chair. This will inevitably affect your posture.
- The computer must be installed so that light does not fall directly on the screen. Otherwise the screen will flicker. By the way, direct light is harmful not only to you, but also to your monitor. The optimal position when working is sideways to the window, preferably to the left.
- On the sides and back of the computer, it is advisable to place “green protection” from indoor plants (preferably cacti; the protective properties of aloe, agave, primroses, and cyclamens are somewhat weaker).
- When purchasing a monitor, make sure that it is subject to the “Low Radiation” standard. This inscription is placed not only on the packaging, but also on the monitor body itself. For over 6 years now, all monitors produced in the world have been subject to mandatory certification for their harmless impact on the environment. Each new generation of displays has increasingly stronger protection, for example, radiation from thin monitors with a screen based on liquid crystals is no more than from a radio.
- Electromagnetic radiation from modern CRT monitors (which have become very rare) is concentrated in the area behind the screen. Please take this into account when installing your computer. The monitor should be located along the wall or in a corner, so that the back is not directed into the interior of the room.
- Some people use a regular television screen as a monitor. This should not be done. Radiation from a TV screen is ninety times higher than from a CRT monitor screen.
- When a CRT monitor is turned on, it generates an electromagnetic field. It’s easy to check its intensity: run the back of your hand at a distance of a few millimeters from the switched on monitor. If you clearly hear characteristic crackling sounds, it means that the electromagnetic field is really present. This shouldn't happen with a well-protected monitor. The hinged safety screens used in older models are often ineffective. Newer models were produced with built-in protective screens.
- Operators are advised to wear shielding fabric vests at work.
- The duration of work on the computer should be reduced on the eve and on days of unfavorable geomagnetic conditions.
- To maintain normal skin moisture, women who work on a computer are advised to take a cool shower on their face in the morning and evening, and not to wipe the skin after it, but to let it dry.
Monitor setup: basic parameters
Discomfort when working at a computer for a long time is often associated with incorrect screen settings. This can be easily corrected by making certain adjustments to them. We advise you to familiarize yourself with what screen settings to set so that your eyes are less tired during the day.
The most common parameters that affect a person’s visual system when working on a laptop or PC are: screen resolution, as well as its contrast, brightness and image refresh rate. Those who care about eye health are advised to pay attention to these characteristics.
What screen resolution should I choose?
Experts say that the optimal screen resolution is the “native” one, which is often automatically set by factory settings. In this case, the picture will be clearest, which will reduce the load on the visual organs. Some users increase or, conversely, decrease the standard screen resolution to improve the usability of certain applications. However, this often results in the picture looking blurry.
How to configure:
- You need to right-click on the “Desktop”.
- Select the “Screen Resolution” item in the window that appears (may also be called “Properties” or “Options”, depending on the operating system);
- Select the “Screen Resolution” tab and set the “native” resolution, opposite which there is a “Recommended” comment.
What screen brightness should I set?
As a rule, the brightness of an LCD monitor is selected individually in each specific case. However, it should be remembered that it is tiring for the visual organs to work with too high or, conversely, too low monitor brightness. The choice of this option depends not only on the type of display, but also on the level of natural light in the room.
Adjust the brightness to suit your eyes, taking into account the individual characteristics of the visual system.
To do this, change the setting until you begin to comfortably perceive images and text on the screen.
How to configure:
- You need to go to the “Control Panel” and select the “Power Options” tab.
- Select the optimal brightness settings (experimentally).
You can also change this parameter by simultaneously holding down the Fn button on the keyboard and one of the special keys to increase or decrease brightness. As a rule, they depict a sun with a plus and a minus. However, this feature is present on all devices.
What contrast should I choose?
The contrast of the monitor also directly affects the comfort of working at the computer. Overly saturated images put increased strain on the visual organs. To avoid this, a person needs to select a contrast parameter that matches the individual characteristics of his visual system.
How to configure:
- Go to the Start menu and then Control Panel.
- Find the Monitor Color Calibration section and select the appropriate tab.
- Adjust the contrast by choosing the setting that is optimal for your eyes (experimentally).
What screen refresh rate should I set?
Setting this indicator largely depends on the type of device itself. For example, old-style monitors (CRT) require a frequency of at least 85 Hz, otherwise the eyes will become very tired due to image flickering.
Working with a liquid crystal display is quite comfortable at a frequency of 60 Hz. Changing this setting is quite easy.
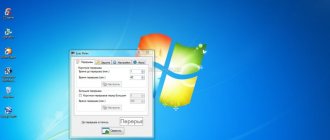
How to configure (for Windows XP):
- Right-click on the “Desktop” and select the “Properties” section.
- Go to “Settings” - “Advanced” - “Monitor”.
- Set the desired value in the “Screen refresh rate” line.
Adjust the light
First of all, adjust the brightness of your monitor. If the screen is too bright or too dim, your eyes will quickly become tired. Determining the comfortable level is simple: if in bright room light the monitor looks like a matte white sheet of paper, then the brightness is normal. Also try to avoid glare to avoid eye strain and focusing problems. There should be no reflections from windows or other light sources on the screen, and reflections from the monitor should not fall on the keyboard or table.
The best lighting option in the workspace is diffused light, in which the light flux is evenly distributed over all surfaces, without contrasting shadows and reflections. Light intensity should ideally vary depending on the time of day. As you move from morning to evening, the light in the room should become warmer - change from bright blue (stimulating) to yellow (calming). The easiest way to reproduce the rhythm of natural light is to insert lamps of different color temperatures into a regular chandelier and switch them throughout the day.
What is the optimal distance from the eyes to the monitor?
To work comfortably at the computer, you need not only to adjust the display, but also to maintain the correct distance from the screen to your eyes. It should be at least 50-60 centimeters. If a person’s vision does not allow comfortable working with text at such a distance, it is necessary to enlarge the font or use vision correction devices. This is the optimal distance from the eyes to the monitor, which is not recommended to be exceeded.
Quite often the display is placed too low or too high in relation to the organs of vision, which also leads to excessive fatigue. The monitor needs to be at the same level as your eyes. It should also be remembered that a properly organized workplace can significantly increase a person’s efficiency. The computer or laptop should not be located opposite the window. This creates an uncomfortable feeling, especially if the brightness of natural light exceeds the brightness of the display.
By following these simple rules, you can reduce the risk of eye fatigue at the end of the working day.
If you use contact lenses, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with the wide range of products on the Ochkov.Net website. From us you can profitably order contact correction products from popular brands.
A little about children
For children, recommendations regarding the correct posture are no different. It is important to remember that a primary school student is not recommended to use any device that has a display for more than half an hour a day - not only a computer, but also a TV, tablet or laptop.
For middle school, one hour per day is allowed, for high school students - two hours. Naturally, no one follows these recommendations: teenagers actively use smartphones, which does not improve their vision.
It is also important to remember that it is difficult for children to adhere to recommendations for maintaining a proper sitting position at the computer. It is difficult for a child not only to sit in one position on a chair, but also to often and simply sit in one place for a long time.
What's the best way to proceed? That's right, don't let him use the computer at all, even if it hurts a lot. If the parent’s heart trembles, be there and control how the child sits in the chair and correct him if necessary.