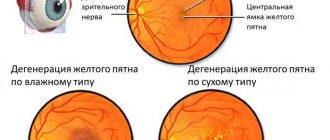
Progressive myopia: causes
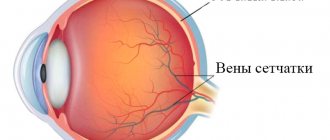
This eye pathology usually develops in childhood. It can be congenital, hereditary and acquired. Often, signs of myopia begin to appear at the beginning of school, when visual load increases sharply. In this case, vision deteriorates almost always with an existing hereditary predisposition. The main factor influencing the development of myopia is the eyeball being excessively elongated along the anteroposterior axis. Light rays entering the eye and refracting through optical media are then focused not on the retina, but in the area in front of it, causing distant objects to appear blurry and indistinct.
What is progressive myopia?
With the standard course of myopia, if the patient uses the correct means of correction, the optical power of the eyes can remain at the same level or decrease by no more than 0.5-1 D per year. However, as myopia progresses, vision deteriorates by more than 1 diopter per year. This situation is very dangerous, as it will inevitably lead to loss of vision. In addition, in the case of rapidly developing myopia, disturbances occur in the eye structures. Retinal detachment may begin, and the vitreous body may become cloudy.
The decline in vision can be quite rapid: its quality can deteriorate by several diopters per year. In these cases, correction means no longer help, since they are not able to stop the pathological growth of the eyeball. With a significant minus optical power, the eyes get tired of contact lenses and even more so of glasses. In such situations, there is only one way out - surgery.
Reviews from parents
Marina, 37 years old. My daughter is now 12 years old. Her vision began to decline even when she just started school. Now it is -6 diopters. We contacted an ophthalmologist to perform an operation that could stop the progression of the disease. After scleroplasty, my daughter’s vision remained at the same level, and 1 year has passed since then. Therefore, I am glad that we turned to a doctor for help in a timely manner.
Oleg, 31 years old. Our child is already 14 years old. He has been wearing glasses since he was 8 years old. My vision began to deteriorate in kindergarten, at about 5-6 years old. At first, we used conservative treatment, used physical procedures, medications, and hardware therapy. But none of these methods helped. Then the ophthalmologist advised us to undergo scleroplasty. The rehabilitation period after the procedure passed quickly. Now my vision has stopped deteriorating, which we are very happy about.
Causes of development of progressive myopia in childhood
Parents with severe myopia should be attentive to the state of vision of their children, as they belong to a risk group due to a hereditary factor. The progression of myopia may be influenced by the following reasons:
- Long and intense work with small objects at close distances, as well as uncontrolled spending time with gadgets and at the computer.
- Violation of the organization of the workplace: incorrect chair height, insufficient lighting, incorrectly installed monitor.
- Lack of vitamins and microelements beneficial for the eyes and general condition.
- Hormonal changes during adolescence.
- Injuries to the organs of vision.
- Past severe infectious diseases.
If myopia has already been diagnosed previously, then it is not immediately possible to detect its progression, and in the meantime, the eye structures can be significantly damaged. That is why it is necessary to check your visual acuity at least once every six months. The doctor will be able to notice the changes that have occurred and take appropriate therapeutic measures. Even if the child has not previously been diagnosed with myopia, parents should pay attention to the child’s behavior. Children themselves are not yet able to explain what they are experiencing, and older children may deliberately hide the fact of deteriorating vision because they do not want to wear glasses or are afraid that they will not be allowed to sit at the computer.
What methods are used to stop the progression of myopia?
In childhood, many types of surgical interventions are prohibited, including those on the organs of vision. Thus, laser correction and some other operations are contraindicated before the age of 18. The only way that is acceptable to prevent vision deterioration is scleroplasty surgery. This is a reliable and effective way to stop the progression of myopia.
Today, there are several types of this surgical intervention, differing in the type of materials used and the method of their implementation. Scleroplasty is performed under general or local anesthesia; the operation takes from 30 to 50 minutes. Its essence is to strengthen the scleral area of the eye by applying plates or introducing a special gel into the eyeball, which, adhering to the tissues of the sclera, does not allow it to change its shape and stretch.
The operation takes place in one day. By evening you can leave the medical facility on your own.
Possible risks in children
Surgery to stop the progression of myopia rarely causes complications, as it is a low-traumatic operation. However, this is a fairly large-scale surgical intervention, so there are still certain risks. These include: Graft displacement - may occur due to insufficient fixation of the reinforcing plates. It is characterized by redness of the eyes and the sensation of a foreign body in it. Repeated correction of myopia will help eliminate this problem. Allergy - occurs in a small number of cases. To stop the process, anti-inflammatory and antihistamines are used. If the effect is insufficient, then a repeat operation is performed, during which the material is replaced. Transplant rejection occurs in approximately 3% of cases. The problem is corrected with a repeat operation, during which the graft is replaced.
Who is scheduled for surgery?
The procedure is recommended for children and adolescents from 8 years of age if they have a deterioration in vision of more than 1 diopter per year, starting from a degree of minus 4 diopters and above. During this period, active growth of the eyeball along the anteroposterior axis occurs, and scleroplasty makes it possible to slow down this process. After the procedure, the number of vessels increases and the blood supply to the eyeball improves. However, scleroplasty does not restore visual acuity - this requires laser surgery, which can be done only after reaching 18 years of age in the absence of contraindications.
Scleroplasty is performed under general or local anesthesia, the procedure takes from 30 to 50 minutes. You don't need to go to the hospital for this. Some time after scleroplasty, you can leave the clinic on your own.
The operation can also be prescribed for women with high myopia if they want to give birth naturally. After it is carried out, the risk of retinal detachment during the birth process is reduced.
Indications and contraindications
Eye scleroplasty, like any other type of surgical intervention, is prescribed only when other (gentle) therapeutic methods are powerless to help.
Scleroplasty surgery is indicated:
- with active pathogenesis of myopia, i.e. when vision drops by one or more diopters per year;
- if visual acuity is between -4 and -6 diopters;
- in case of intensive growth of the eyeball in the longitudinal direction;
- myopic women (visual acuity -5/-6 diopters) planning pregnancy.
However, there are reasons why scleroplasty is contraindicated, namely:
- children under 7 years of age, since the natural growth of the visual organs can provoke a relapse of ophthalmic disorders;
- thinned scleral membrane (dystrophy phenomenon);
- the presence of acute inflammatory or infectious processes;
- existing eye diseases;
- allergies to drugs used in treatment;
- psychoemotional disorders.
Preparation for scleroplasty
Before the operation, the child is examined by a pediatrician and an ophthalmologist, and the necessary clinical tests are collected. Next, a full diagnostic eye examination is carried out, which includes:
- checking visual acuity using special tables;
- biomicroscopy is a procedure using a slit lamp that allows you to assess in detail the condition of the anterior segment of the eye (lens and cornea), as well as exclude inflammatory processes;
- refractometry makes it possible to determine the objective refraction of the organs of vision;
- echobiometry allows you to measure the axis of the eyeball, the depth of the anterior chamber, and the thickness of the lens.
After studying blood tests, the pediatrician gives permission or refusal to perform scleroplasty. On the day of surgery, you should completely avoid eating and drinking.
How to prepare for surgery?
The operation is performed on an outpatient basis, anesthesia is performed with drops, or general anesthesia can be used. Usually after just a couple of hours the patient goes home. The duration of the operation is only 30-50 minutes.
Attention! The length of the recovery period can be affected by factors such as the age of the child, the type of surgery performed, the severity of the disease, etc.
Carrying out the operation
Preparation for sclerotherapy consists of a general ophthalmological examination, an assessment of the child’s condition by a pediatrician, and a series of studies. After this, eye biomicroscopy, refractometry and echobiometry are performed. The final decision on the possibility of surgical intervention is made by the pediatrician, based on a number of laboratory tests (tests for HIV, hepatitis C, urine and blood parameters, etc.). You will also need to take an electrocardiogram and do fluorography.
ECG
On the day when scleroplasty will be performed, the child should not be fed or given water. In some cases, sedatives or antihistamines may be prescribed.
What types of scleroplasty are there?
This operation has been well studied in medical practice and has a low percentage of complications. There are three types of scleroplasty, which differ in the type of materials used, as well as in the method of their introduction and attachment to the back wall of the eye:
- simplified;
- simple;
- complex.
Simplified scleroplasty. During this procedure, a small incision is made in the eyeball, then a special sterile gel (biopolymer, synthetic or natural) is injected through it using a syringe. After some time, the biological mass hardens, sticking to the sclera, and prevents its further stretching.
Simple scleroplasty (according to Pivovarov). The doctor makes 4 incisions in the sclera, then 0.5-1 cm flaps are inserted under it. The flaps can be made of metal-plastic, silicone or donor sclera. Sutures are then placed on the conjunctiva. Some time later, the flaps are fused to the outer shell, helping to strengthen the posterior wall and preventing further stretching of the sclera. After several months, blood vessels grow into the flaps, and this contributes to better blood supply to the posterior pole of the eye.
Complex scleroplasty (according to Snyder-Thompson). To carry it out, the doctor makes 5-7 mini-incisions on the sclera. The extraocular muscles are also temporarily dissected, and pre-prepared biological material is introduced into the incisions. Sutures are then placed on the conjunctiva. Doctors classify complex scleroplasty as a separate category. This is a major surgical procedure during which a reinforcement plate must be placed in close proximity to the macula and optic nerve. To do this, a long flap is inserted behind the eyeball and sutured to the sclera, preventing it from further stretching.
The specialist decides which type of scleroplasty to prescribe depending on the degree of myopia, the rate of its progression, the individual characteristics of the eyes, and the patient’s age.
Execution technique
During the operation, a graft is used - a special scleroplastic material obtained from biological tissues or synthetically, which is previously subjected to multi-stage processing and cleaning. The graft is gradually either replaced or overgrown with newly formed connective tissue. As a result, a single “sclera-graft” complex is formed, increasing the biomechanical stability of the eye membranes, which ensures the stabilizing effect of this surgical intervention. More information about types of scleroplasty
Postoperative period
After scleroplasty, you need to be at rest for two to three hours, then the eyes are examined by a surgeon. If there is no inflammation, the patient is discharged home. The rehabilitation period ranges from 15 to 30 days (depending on the type of scleroplasty). For the first few days, it is recommended to use a protective blindfold, which must be changed every day. After it is removed, you need to carry out a two-week course using antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drops. After completing the recovery period, you must see a doctor. He will examine your eyes to make sure they have healed well and there are no additional problems.
Possible complications
As with any surgical intervention, negative consequences may occur after scleroplasty. In general, this operation is one of the safest in surgery, with almost no complications. However, risk is never eliminated. For example, a child or an adult may have an allergic reaction to a reinforcing material, even if it is of biological origin, not to mention polymer components - they are foreign to the visual organs in any case.
Sometimes it happens that the flaps are not fused tightly enough to the back wall of the eyeball, so they can move later. Externally, it may look like a tumor under the conjunctiva. In such a situation, a repeat procedure is performed to suture the flap or remove the incorrectly attached part. In general, scleroplasty is a safe and proven way to stop progressive myopia in children from 8 to 16 years old, when other methods of eye surgery are prohibited at this age.
Rehabilitation
After the operation is completed, the rehabilitation period begins. During this you must adhere to the following rules:
- use of all medications prescribed by the doctor (painkillers, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial drops, which are applied under a sterile bandage);
- periodic change of a sterile bandage, which must be kept on the eye for several days;
- reducing the load on the eyeballs by not looking at the computer, phone, TV and other electronic means, as well as reading books;
- wearing sunglasses outdoors to reduce eye strain from ultraviolet radiation;
- It is forbidden to sunbathe in open sunlight, visit a solarium, sauna, bathhouse for 1 month after surgery to eliminate the risk of bleeding and hemorrhage;
- a ban on engaging in vigorous physical activity to prevent tissue rupture or complete elimination of the effect of the procedure;
- ban on the use of facial cosmetics for the entire period of rehabilitation.
You must see a doctor a few days after surgery, as well as after 1 and 3 months. During this period, he will examine the eyeball, identifying the presence or absence of an effect from the operation. If it was successful, the eye tissues will gradually heal, and vision will stop deteriorating.
To check your vision function, you need to see a doctor every 6 months.
What not to do after scleroplasty
It is necessary to take care of your eyes after scleroplasty, being careful in your actions and not exposing them to excessive stress for at least two weeks.
So, you need to cancel visits to the pool, sauna, sports training, and any physical activity in general. It would be advisable to limit watching TV, spending time with gadgets and in front of the computer to prevent severe eye strain.
After scleroplasty surgery, you need to refrain from too heavy physical activity, for example, strength sports, for two years. It is also better to beware of team games with projectiles (ball, puck) to eliminate the risk of them getting into your eyes.
What happens after surgery
Two hours after the operation, the surgeon examines the patient. If no complications were noticed, he is sent home. Rehabilitation lasts 4 weeks. For several days the patient is forced to wear an aseptic dressing, which must be changed regularly. After its removal, treatment continues with drops with anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects. It is also necessary to follow a gentle regime, which involves avoiding physical activity, visiting swimming pools, watching TV for long periods of time and reading. In addition, heavy physical activity and sports should be avoided for two years after the operation. It is worth noting that the operation is designed to stop the progression of myopia, but does not improve vision. Therefore, you should not stop treating myopia and give up glasses and contacts.
Contraindications for scleroplasty
Despite the fact that this procedure is allowed to be performed even in childhood, it also has a number of contraindications. Let's take a closer look at them.
- Scleroplasty is prohibited for children under 8 years of age. Since the eyeball grows quite actively during this period, there is a risk of relapse of the myopic process.
- If the sclera is too thin, there is a risk of significant damage.
- Existing scars on the surface of the visual structures can become an obstacle to the uniform attachment of the reinforcing strips.
- Exacerbation of current chronic diseases, such as diabetes, heart failure and others, can also cause a deterioration in the patient’s condition during surgery.
- If there are bacterial or viral diseases, it is also better to postpone scleroplasty until recovery. At this time, general immunity is reduced, which may interfere with the effectiveness of the rehabilitation period.
- The presence of ophthalmological diseases is also a serious contraindication to scleroplasty surgery. With existing keratitis, conjunctivitis, uveitis and other pathologies, severe inflammation of the intraocular tissues - endophthalmitis - can develop.
If the obstacle is temporary (exacerbation of a chronic disease, eye inflammation), then surgery can be scheduled two weeks after recovery. If allergic reactions are detected in a patient, the question of the advisability of surgery should be decided individually. In most cases, scleroplasty is performed after allergy testing for materials used in surgery.
Doctors constantly remind us of the importance of early diagnosis of any disease; the successful outcome of treatment largely depends on this. The task of parents is to be attentive to the state of their child’s vision, especially in the presence of genetic pathologies or a hereditary factor. Regular examinations by an ophthalmologist should become the norm in this situation. If you use glasses or contacts, you should also have your visual acuity checked every six months to make sure they match the optical power of your eyes. Remember, our health largely depends on our attentive attitude towards it.
MagazinLinz.ru team
Patient reviews of the results of the procedure
The average cost of intervention for one eye varies from eighteen to twenty thousand rubles. The majority of patients who have undergone scleroplasty claim that the operation helped them return to their normal lives. Many of them could not calmly move around the room, as myopia was rapidly progressing. They always needed glasses everywhere.
Most patients note the fact that the procedure did not restore their vision, but stopped its decline. And for many people, this was the first step towards completely restoring eye sharpness.