The diagnosis of “myopia” is known to many. Myopia or myopia is a vision pathology characterized by clear vision of objects at close range and blurred vision of distant objects.
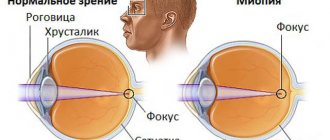
This disorder occurs as a result of improper refraction of light rays when passing through the optical media of the eye, and the formation of the image does not occur on the retina, as it should be, but in front of it (true refractive myopia).
Share
Tweet
Share
Cool
Send
What is myopia?
The optical system of the human eye is almost perfect. We have the ability to distinguish colors and their many shades, adapt to different lighting conditions, and see objects both near and far. If there are any changes in the organs of vision, the functioning of the entire system is disrupted. Thus, the abnormal shape of the eyeball or the surface of the cornea, problems with the lens, ciliary muscle, can become an obstacle to creating the suitable conditions necessary for focusing images on the retina. Myopia is inherited if a child inherits the shape of the myopic parent's eye, features of the cornea, etc.
Myopia is a refractive error in which the light flux is focused in front of the retina, so a person sees only close objects well, and distant ones seem blurry, indistinct, without contours. How can myopia be corrected? Usually glasses and contact lenses with appropriate diopters. Vision correction products are selected in such a way as to cause a minimum number of side optical effects.
Methods for correcting myopia.
Today there are many methods for correcting myopia. The most common of them are glasses and lenses . However, both glasses and lenses have their drawbacks. Glasses interfere with leading an active lifestyle, playing sports, dancing, and swimming. The lenses are difficult to use and are not suitable for everyone.
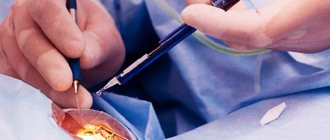
Myopia can be eliminated by laser vision correction , as well as by implanting phakic lenses or replacing lenses with artificial ones.
If the patient wants to get rid of glasses and contact lenses, his parameters are suitable for this type of surgery, and there is no concomitant severe eye pathology, laser correction is performed, which can be performed using the LASIK, Femto-LASIK, ReLEx SMILE, PRK . On average, it lasts 7-10 minutes per eye and is performed under local drip anesthesia. As a rule, the patient is not given general anesthesia during surgery. If the patient is severely allergic, a leukopenic drop test is performed before surgery.
For example, in the Almaty SMILE Vision clinic, such operations are performed on the EX500 WaveLight Alcon laser unit and the Carl Zeiss VisuMax femtosecond laser. Laser vision correction is one of the shortest operations in terms of rehabilitation period. The eyes begin to see better the next day and even on the day of surgery. Drops in the postoperative period are most often dripped for three days. And within a day or two after the operation, patients can begin their work.
The optimal age for vision restoration using laser correction is from 18 to 45 years. After 45-50 years, lens replacement surgery is more appropriate. However, everything is individual, and you need to consult a doctor.
Vision with myopia: symptoms
Myopia with insufficient correction and exceeding visual load standards can progress. This becomes a serious obstacle to laser vision correction, and also significantly reduces the quality of life of patients with myopia. Therefore, early diagnosis is extremely important.
How myopia manifests itself:
- low head tilt - this symptom should be monitored by parents of children prone to myopia, as the main sign of a developing pathology;
- constant feeling of eye fatigue, inability to clearly see distant objects;
- increased lacrimation or, conversely, dryness, burning in the eyes - this is how the body reacts to increased stress and overexertion;
- frequent ailments and headaches against the background of decreased performance and increased fatigue.
For a long time, myopia can go unnoticed, since blurred vision is often attributed to fatigue. In order not to miss the onset of the disease, you need to know the symptoms of the disease and promptly contact specialists for qualified help. Why does vision deteriorate?
Causes of poor vision
There are many reasons why vision can deviate significantly from the norm. These include congenital pathologies and past infectious and viral diseases that have a detrimental effect on the general condition of the body, as well as injuries to the eyes and head. Is myopia inherited? Yes, but it is not the disease that is transmitted, but a hereditary predisposition to it. The exact cause cannot be determined during a routine examination by an ophthalmologist, so patients who suspect myopia are prescribed a full ophthalmological examination.
The examination is carried out with a normal pupil and with a dilated one. This allows you to obtain extensive information about the state of all ocular structures. It happens that a person does not see several lines on a letter table, but this does not mean that he is myopic. The cause of the disorder may not be anatomical, but accommodative. Visual acuity in this case is impaired due to spasm of the ciliary muscle, which is responsible for accommodation. This disorder is called false myopia, and if it is diagnosed in a timely manner, it can be treated quite successfully within a couple of weeks or months.
The essence of genetics
All information about a person is encrypted in genes. Each trait, including the risk of various diseases, is encoded by two genes: one passed on by the mother, the second by the father. The combination of two genes determines the characteristics of the trait.
Genes are located on chromosomes: 22 pairs of somatic chromosomes, and the 23rd pair determines the sex of a person (XX and XY). Genes can be dominant (major, designated A, B, C) or recessive (a, b, c).
Genetic information is transmitted autosomally (through somatic chromosomes) or linked to sex chromosomes (the trait will appear in a certain sex).
In an autosomal mode of inheritance, a dominant trait will appear in any combination of genes (AA, Aa), and a recessive trait will appear only in the form of a homozygote (aa).
- dominant A – codes myopia of weak and moderate degree (up to -4);
- recessive b—encodes severe myopia (from -4 or more).
Thus, a child who has inherited the combination of genes AA, Aa, bb from his parents will be born with myopia. A child with the genetic code aa, Bb, BB will be healthy in this regard and have good vision. At the same time, a person with Bb genes is a carrier of the disease, and there is a risk of transmitting the disease to their children.
Due to various options for the transmission of genetic information, it may happen that, for example, parents with good eyesight may have both a healthy child and a baby with myopia. And parents who both suffer from this disease can get a child without vision problems.
Is myopia inherited or not?
The likelihood that myopia of one or both parents will be passed on to the child is very high. The child inherits the shape of the eyeball, cornea and features of other important structures of the human optical apparatus, so vision problems can arise both immediately after birth and during life, when appropriate conditions are created.
When talking about whether myopia is inherited, experts focus on the fact that it is the predisposition to myopia that is inherited. To prevent the conditions for the development of myopia from being activated, myopia should be prevented from the earliest years of a child’s life: do not strain the eyes, take vitamins that are good for vision, and spend active time in the fresh air. All this will have a beneficial effect on the condition of the child’s visual organs, and the optical system will be formed without pathologies. Myopia is transmitted to children and progresses if the first symptoms were not noticed in a timely manner and treatment for the disease was not started.
Myopia gene
Is myopia passed on to children? Most children of myopic parents inherit only a predisposition - that is, certain factors that contribute to the development of myopia. If the parents—the child’s mother and father—suffer from myopia, there will be more such factors, and accordingly, the likelihood of myopia in the child will increase.
How is myopia transmitted? The myopia gene RASGRF1, located on chromosome 15, is responsible for the inheritance of myopia. Every person has it, but its variants vary, so scientists recommend calling it "the gene whose variants are associated with myopia." The myopia gene can be passed on from both mother and father. Astigmatism is also inherited in 50% of cases. Some retinal diseases are also hereditary. In people prone to myopia, there is a lengthening of the anterior-posterior axis of the eye, which can affect focusing. As a rule, the gradual development of myopia begins with a combination of several negative factors.
Degrees and types
The degrees of congenital myopia are the same as those of the acquired form. According to the nature of the course, myopia can be non-progressive and progressive. Often a child is born with a high degree of myopia. This is another significant difference compared to the acquired form, which develops gradually.
Depending on the severity of the pathology, 3 degrees are distinguished:
- Weak myopia – up to 3 diopters.
- Average myopia – up to 6 diopters.
- High myopia – more than 6 diopters.
Myopia is divided into the following types:
- Refractive myopia – the axis of the eye is normal, but the lens and cornea are larger than normal.
- Mixed myopia - two indicators are outside the normal range.
- Combined myopia is an atypical combination of the size of the eyeball and the refractive medium.
- Axial myopia - the eyeball has an elongated shape, but refractive indices are within normal limits.
Diagnosis of predisposition to myopia
Medical examinations of young children are carried out regularly in local clinics. If there is a hereditary factor, diagnosis should be complete and include examination using modern instruments. How is myopia transmitted? Usually in the form of certain factors such as the elongated shape of the eye, atypical shape of the cornea, etc. Detailed diagnostics allows you to see all the features of the optical system of the eye. If there are changes, the patient will receive a treatment regimen for mild or moderate myopia or a plan of preventive measures aimed at preventing myopia.
Testing for myopia:
- checking distance visual acuity using a table, determining eye refraction and the degree of myopia;
- ophthalmoscopy, examination with a slit lamp - an informative method of examining the fundus of the eye, allows you to assess the condition of the retina, optic nerve head, choroid;
- determination of visual fields, study of color perception;
- measuring the length of the eye - allows you to determine the tendency to myopia and the causes of myopia progression.
Typically, hereditary myopia appears between the ages of 6 and 12, and then continues to progress until the age of 21. After the growth of the visual apparatus is completed, vision stabilizes. Parents of myopic children should prevent rapid deterioration of vision and direct all efforts to prevent the progression of myopia.
How to avoid inherited myopia
Those children who clearly have a predisposition to myopia, for example, during the examination a small or zero reserve of farsightedness was recorded, must follow all the instructions of the ophthalmologist. Since myopia is inherited, parents who are aware of the threat of such a pathology must create favorable conditions for the normal development of the child’s visual organs.
What is recommended if you are prone to myopia:
- routine examinations - you cannot ignore regular examinations by an ophthalmologist, because myopia can appear at any time and it is very important to correct your vision immediately;
- exercises on vision simulators, daily visual gymnastics - eye exercises help strengthen the extraocular muscles and improve blood flow to the organs of vision;
- special diet for myopia - it is necessary to include in the menu fish, meat broths, dietary rabbit meat, eggs, leafy greens, vegetables, fruits rich in vitamins A, B, C, E;
- blueberry extract;
- therapy with mydriatic drops - such treatment is prescribed if, with developing myopia, a spasm of accommodation is also observed; taking medications can improve vision by several diopters.
Physiotherapeutic procedures using magnetic therapy, electrical stimulation, and laser therapy devices are quite effective in childhood and adolescence. The action of the devices is aimed at improving blood circulation in the organs of vision, training the accommodative muscle, which has a positive effect on eye health.
Recommendations for the prevention of myopia in children and adolescents with a genetic predisposition
Prevention of myopia in children should be carried out from a very early age.
Since no method of treating myopia provides a 100% guarantee of getting rid of the disease, I would like to analyze in detail the methods of prevention aimed at preventing the development and progression of myopia.
Children with a family history of myopia should be seen by an ophthalmologist, examined by a doctor twice a year and strictly follow all recommendations.
- Compliance with the rules when reading (it is not recommended to read while lying down, in transport, lighting should be sufficient).
- Compliance with the rules when watching TV (time limit, viewing before bedtime is not recommended, it is forbidden to be at a close distance from the screen).
- Compliance with the rules when working on a computer (time limits, breaks in work, the monitor should be located at a distance of about 40 cm).
- Limiting children's use of modern gadgets: phones and tablets.
- Active leisure time, frequent walks.
- Daily exercises for the eyes.
- Compliance with dietary recommendations including the inclusion of meat and fish dishes, broths, eggs, herbs, vegetables and fruits in the diet.
Myopia or myopia: unique information!