We often hear questions from uninformed people about whether farsightedness is a plus or a minus. In order to correctly answer these kinds of questions, it is necessary to understand the principle of operation of the human visual organs and study possible problems that may arise.
The eye is one of the most complex organs in the human body. The interaction of the visual system with the cerebral cortex allows the transformation of light rays coming from the outside world into visual images. To understand how this happens, it is necessary to consider what the human eye is made of.
Structure of the eye
The eye is a very complex optical system that consists of many parts.
- Cornea. Through it, light waves enter the eye. It is an organic lens, with the help of which light signals diverging on the sides are focused.
- The sclera is the outer opaque layer of the eye, which does not actively participate in transmitting light.
- The iris is something like a camera diaphragm. This part regulates the flow of light particles and performs an aesthetic function by determining the color of a person’s eyes.
- The pupil is a hole in the iris that regulates the amount of light rays entering the eye, as well as filtering out curved, distorting rays.
- The lens is the second strongest lens in this human organ, located immediately behind the iris. Depending on the distance to the object, it changes its optical power. At a small distance it strengthens, at a large distance it weakens.
- The retina is a spherical surface onto which the surrounding world is projected. Moreover, the light, passing through two collecting lenses, hits the retina upside down. The information is then converted into electronic impulses.
- The macula is the central part of the retina that recognizes clear color images.
- The optic nerve is a transporter of information processed by the retina into nerve impulses to the brain.
Treatment
The goal of treatment for farsightedness is to change the eye's ability to focus images on the retina rather than behind it. The most common and effective ways are wearing glasses, doing some exercises, and surgery.
Conservative treatment
People with farsightedness wear glasses when reading, working on a computer, watching TV, or other activities that require focusing their gaze at close distances. In addition to glasses, you can wear contact lenses. They are comfortable during sports and other activities that require physical activity.
Conservative treatment methods also include wearing special training glasses, ultrasound therapy, vacuum massage, electrical stimulation, and taking vitamins, which can significantly improve vision without resorting to surgery.
Surgical intervention
Laser methods will give the cornea the desired curvature, so that the image can fall on the retina. In some cases, it is necessary to use lensectomy (removal of the lens), replacing it with a special intraocular lens, photorefractive keratectomy, thermokeratoplasty, thermokeratocoagulation.
The laser will relieve hypermetropia and astigmatism. After the operation, the shape of the cornea and refraction change. As a result, you can correct your vision at +6 diopters. Before the laser, the ophthalmologist examines the eyes, assesses the degree of farsightedness and decides whether this procedure is necessary.
It is important to identify contraindications for surgery. The entire laser treatment process takes 30 minutes and is painless and gives very accurate results.
There are several laser methods: LASIK, Femto LASIK, SUPER LASIK. These are the fastest ways to correct farsightedness. Everything is done under local anesthesia. After the operation, you can go home the same day. Surgery enhances refraction abilities.
Thermokeratoplasty is the application of coagulates with a metal needle to the cornea, which ultimately tightens it, increasing the refraction of the central optical zone. Laser coagulation differs from keratoplasty in the use of laser radiation.
The laser technique costs from 17 thousand rubles . Other options cost 25 thousand (LASIK) or 50-60 thousand rubles (Femto, SUPER). Prices for all operations are indicated for one eye.
Read on - Solcoseryl eye gel. Description of the drug.
The article (more details) describes the character of people with chameleon eyes.
Prevention of Blepharitis!
If all of the above methods are ineffective, a multifocal lens can be implanted inside the eye. With this method, diseases of the highest degree are treated.
Medicines
If we talk about drops and other drugs, then a special medicine for the treatment of farsightedness has not yet been invented.
Drops are used only to eliminate some associated symptoms:
- if, with farsightedness, unpleasant sensations appear in the eyes, perhaps the cause is an infection, for the treatment of which certain drops are used, or the now typical dry eye syndrome, for the elimination of which Visin Pure Tear, Artificial Tear or Taufon are used,
- if age-related farsightedness is accompanied by cataracts, for its treatment doctors can also prescribe drops that slow down its development and stimulate metabolic processes,
- if farsightedness is additionally accompanied by allergic reactions to certain objects, Claritin, Prenacid or other drugs may be prescribed.
Medicines with vitamins are also often prescribed, but they should not be used constantly, but only in courses. In any case, you should follow the doctor's instructions and not self-medicate.
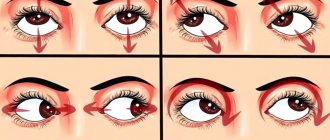
Exercises
Scientists have created special exercises that help restore visual acuity and completely get rid of hypermetropia. They also help prevent its occurrence if a person is genetically predisposed to it.
Please note - the price of tetracycline ointment. Review of prices in the CIS.
In the news (here) instructions for Riboflavin.
Analogs of Indocollir eye drops! https://moezrenie.com/lechenie/kapli-dlya-glaz/indokollir-bystraya-pomoshch-pri-bolyakh-glaz.html
The course of exercises must be performed every day. Each exercise is performed 5-10 times.
- Sitting in a comfortable, relaxed position, you need to look ahead. First, without sudden movements, you need to turn your head to the right, turning your eyes along with it, slowly return to the starting position, and then turn to the left.
- Sitting in a relaxed position, you need to move your gaze from a distant to a near object: first look into the distance for 2-3 seconds, and then look at your index finger or pencil located 25-20 cm from your face for 3-5 seconds.
- Sitting on a chair with a straight back, you need to bend your elbows and put them behind your head. In this case, you need to bend back and put your feet on your toes in front of the chair. Then the arms and legs relax.
- Sitting in the starting position on a chair with your arms down, you need to slowly raise your right hand to your right shoulder, then do the same with your left hand. Then you need to stretch both arms in front of you and slowly relax your arms, returning to the starting position.
- Sitting in a comfortable position, you need to massage the occipital region and neck area with the fingertips of both hands, making movements from top to bottom.
- Sitting in a comfortable position, you need to raise your right hand to eye level and make clockwise circular movements with your fingers at a distance of about 40 cm from the eyes, following them with your gaze, without turning your head. Then the left hand rises and the direction of rotation changes.
Another set of exercises was developed by W. Bates, and it was based on the fact that the main problem of hypermetropia is eye strain when trying to look at an object, and therefore the exercises are mainly aimed at relaxation:
- Every day for 10-15 minutes you need to read a book with small print, holding it at a distance of 30 cm from your eyes, without using glasses, in good and dim lighting. The dull color helps to relax the eyes. If you can’t read without glasses right away, you can do the exercise with them on first.
- While reading a book, you need to look at the white clean space between the letters and lines.
- Even with senile farsightedness, the following exercise can help. It is necessary to hang Sivtsev’s table in a dark place so that the letters can be seen from a distance of about 5 m. This exercise will require some effort on the eyes. You need to pick up a small format of Sivtsev’s table, providing good lighting. First you need to read the large table (as many lines as possible), and then turn your gaze to the small table and move it between the lines on a blank paper, not forgetting to blink.
- Near a window or on the street, you need to shift your gaze from distant objects (sky, wall, grass) to a manual format table.
- It is useful to watch movies, watch flying birds, and follow any moving objects.
- Another useful exercise is large turns while concentrating your gaze in front of you. You need to stand facing the window, preferably one with bars or other vertical alternating objects. You need to stand straight, arms relaxed. The body must be slowly turned to the left, stand parallel to the left wall, then also smoothly turn it to the right. The gaze should always be directed in front of you, with the head and shoulders moving together. You can very easily check whether your eyes are relaxed at the same time: if close objects (bars on the window) elude your gaze in the opposite direction, and distant objects (outside the window) move in the same direction as the turn is being made, then you have succeeded in achieving relaxation.
Types of vision problems
Vision problems can appear at absolutely any age (they can even be congenital). The cause of some of them is a malfunction of the retina or optic nerve. However, most diseases of the visual system are caused by a violation of the refractive characteristics of the eye. The consequence of this is defocus, and the person loses the ability to see objects clearly. That is, human vision is impaired. “Plus” and “minus” indicate the degree of refraction of light (either the rays are not refracted enough, or they are refracted too much). There are several main types of visual impairment in humans.
Methods of treatment and vision correction for plus 3 and 2
The best choice for correcting myopia -1 would be daily contact lenses that do not need to be stored in solution, cleaned, disinfected, etc. Every time correction is required, for example while driving, you just need to put on a new pair of lenses and enjoy high contrast and visual acuity.
Which lenses to choose to correct myopia minus 1:
- Dailies Total 1 - light and comfortable lenses, well moisturized and at the same time perfectly transmit oxygen to the cornea, as they are made using innovative technologies; water-granient material is used in production.
- 1-Day ACUVUE TruEye - ideal for sensitive eyes, adaptation to such lenses is not required, since these ophthalmic products are practically not felt on the eyes, this model has high oxygen permeability characteristics, the eyes are comfortable in the lenses for 10-12 hours.
- Dailies AquaComfort Plus - lenses with a triple humidification system and a protective filter against ultraviolet radiation, are often recommended by ophthalmologists as the first choice model.
Contact lens manufacturers produce products in a wide diopter range. People with a slight degree of myopia can choose lenses that best meet their requirements for comfort, wearing mode, and service conditions. Since vision minus 1 allows you to see surrounding objects quite clearly, the need for correction will arise periodically.
Is farsightedness a plus or a minus?
Let's return to the main question. So, is farsightedness a plus or a minus? Farsightedness (also known as hypermetropia) is a visual impairment in which a person has difficulty distinguishing objects located nearby, but can clearly distinguish small details of distant objects.
Thus, the strength of glasses prescribed to a patient is measured in diopters. For farsightedness, glasses with a collecting effect are installed, which perform part of the functions of the lens. Such glasses are called positive, and therefore farsightedness is a “plus”. Or “minus”, for example, is used for myopia. Consequently, glasses with a scattering effect, which are called negative, are used in treatment.
Degrees of farsightedness (hyperopia) in children.
- Weak, up to 3.0 diopters. This decrease in vision is considered physiological and can be compensated as the child’s body grows and develops. Weak farsightedness in a child under 6-7 years of age may be normal. No glasses required.
- Average, up to 5.0 diopters. The child sees worse in the distance and poorly near. Wearing glasses is required.
- Strong, over 5.0 diopters. Vision is reduced, objects both far and near are difficult to see. Without wearing glasses, amblyopia (low vision) can develop.
If already during the first examination a high degree of farsightedness is revealed, correction is necessary - constant wearing of glasses.
Main causes of farsightedness
So, as already stated, farsightedness is an eye disease in which the image is focused behind the retina. The degree of development of hypermetropia depends on the eye’s ability to refract light rays and on accommodation (the ability of the lens to change its shape depending on the distance to the object):
- Weak (up to +2 diopters).
- Medium (from +2 to +5 diopters).
- Strong (more than +5 diopters).
There are two causes of farsightedness:
- The eyeball is too short, and therefore the longitudinal ocular axis is short. Most often, this visual disorder is hereditary.
- Insufficient refractive properties of the visual system. With age, the human lens loses elasticity and corresponding abilities.
There is also the possibility of a combination of these two reasons.
What does farsightedness mean in children?
Children should be born with hypermetropic refraction (farsightedness). As the head and eyeballs grow, farsightedness decreases and returns to normal by about 7 years. With proper development of the eye, farsightedness up to 3.0 diopters is normal and as the child grows it decreases by 0.5 diopters per year. However, congenital farsightedness of more than 3.0 diopters is a pathology of eye refraction and causes poor vision.
Refractive error (focusing) depends on the structural features of the eye. This is an innate property that cannot be changed or “cure.” Consequences caused by farsightedness require treatment: amblyopia, strabismus. For the first time, the state of refraction in children is determined during an examination by an ophthalmologist at 6-12 months. During annual examinations, it is necessary to monitor the state of refraction in order to prevent the development of possible complications.
Symptoms of farsightedness
The main symptom is poor near vision. At the same time, the patient sees objects located in the distance well. However, over time, the pathology may intensify due to the loss of the accommodative properties of the lens.
The main symptoms, the presence of which prompts you to consult an ophthalmologist with suspected hypermetropia, include:
- Impaired near vision.
- Disturbance of “distant” vision.
- Increased eye fatigue when working.
- Visual fatigue when reading books.
- Frequent conjunctivitis and other inflammatory processes of the eyes.
- Strabismus in childhood.
Symptoms and diagnosis
The main symptoms or manifestations of farsightedness are:
- poor near vision,
- rapid eye fatigue when reading and working on a computer,
- burning eyes, headaches.
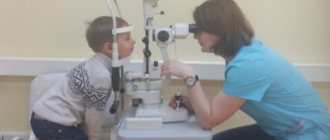
Diagnosis of hypermetropia occurs by checking visual acuity using the Sivtsev table. Also, the diagnosis of farsightedness involves the use of a phoropter and the use of autorefractometry.
Keratometry and echobiometry methods are used to measure the optical power of the cornea and the length of the longitudinal axis of the eye. In young children, diagnosis is carried out only after forced dilation of the pupils, which weakens the accommodation of the eye.
Risk factors
When progressing is observed, without correction it can cause amblyopia, cause complete loss of vision or strabismus.
If a child has weak hypermetropia from +3.0 and the “plus” increases, then there is a chance of developing strabismus due to muscle strain.
The following categories of people are most often affected by farsightedness:
- often occurs in children and young people; in mild forms, the disease rarely manifests itself;
- senility develops in people who work a lot on a PC, read, sew, and strain their eye muscles throughout their lives;
- The development of senile farsightedness is a natural process for all people after 40 years of age. But the progression of the disease is slowed by exercise.
Prevalence
- Hypermetropia is common among children and adults. It occurs in 9 out of 10 babies, but does not require treatment and goes away with age. 4 out of 10 adults have this disease.
- About 25% of all people have this anomaly.
- Almost all babies have developed farsightedness. With age, this defect disappears as the eyeball grows.
- Senile lens occurs due to the fact that the lens stops changing its curvature. The process begins after 25, and by the age of 40-45, vision deteriorates and it is no longer possible to read at a distance of 25-30 cm. By the age of 60-70, accommodation weakens.
- In children, the disease may be congenital. Vision does not return to normal even after some time.
Diagnosis of vision problems
As soon as you feel a decrease in visual acuity, you need to seek help from a specialist. The standard diagnostic procedure includes the following steps:
- Visual acuity study. For this purpose, a special vision table is used. Nowadays, Sivtsev, Golovin or Orlova tables are used (mainly in children).
- Examination of the fundus using a mirror and ultrasound.
3. Selection of lenses of the required power, carried out using a phoropter.
Methods of treatment and vision correction for plus 3 and 2
With relatively small deviations from the norm, external manifestations are weakly expressed. Vision plus 1 in children is not accompanied by significant difficulties (painful reactions). The following behavioral characteristics of a child may indicate a higher level of farsightedness:
- often closes his eyes, relieving tension and fatigue;
- performs manipulations with small objects at a great distance;
- complains of pain, dizziness, pain.
In some cases, hypermetropia provokes conjunctivitis, excessive lacrimation, and allergies.
It is not recommended to make independent decisions without consulting an ophthalmologist. It is necessary to remember that it is relatively simpler to eliminate physiological problems identified at an early stage. The critical age is 12-13 years. After this, the effectiveness of therapeutic and preventive techniques is significantly reduced.
If a child has plus 2 vision, a positive result can be obtained using special eye exercises. Also used:
- change in diet;
- hardening;
- reducing the load on the visual organs (limiting reading and computer games);
- hardware physiotherapeutic procedures.
The causes of visual impairment can be anatomical and accommodative. Accommodative disorders, when diagnosed in a timely manner, can be successfully treated with the use of special eye drops. If refractive errors arise as a result of changes in the structure and proportions of the eyeball, a long period of therapy and, possibly, constant wearing of glasses will be necessary.
Diagnosis of myopia:
- checking the visual acuity of each eye according to the Sivtsev table;
- measurement of intraocular pressure;
- visual field check;
- measuring eye refraction using a refractometer;
- examination of the retina and optic nerve;
- keratotopography - examination of the cornea;
- biomicroscopy (examination of the eyeball is performed).
Treatment of farsightedness
In order to never be bothered by vision problems, you must be guided by the following principles:
- Observe lighting conditions.
- Alternate visual stress with physical relaxation.
- Train visual muscles both with the help of special gymnastics for the eyes and with the use of modern technologies (including computer and laser).
- Conduct early diagnosis and correct vision correction (includes mandatory periodic examination by an ophthalmologist).
- Perform general strengthening exercises, supported by proper nutritious nutrition.
Taking these preventive measures will help preserve your vision. Plus, of course, don’t forget to undergo periodic examinations with an ophthalmologist.
Vision correction is performed using glasses or eye contact lenses, which are prescribed to the patient in a special prescription after a full examination.
In addition, eye surgery is moving forward with huge strides and now allows a person to stop wondering whether farsightedness is a “plus” or a “minus”.
Myopia minus 1: symptoms
The symptoms of farsightedness in a child will depend on its severity. So, for example, with its weak manifestation, the eyes will quickly get tired, dizziness will appear, and headaches are possible. With a moderate degree, the condition of a small child is hysterical, he sleeps poorly, and various inflammations of the visual organs, such as blepharitis and conjunctivitis, may bother him. Visual acuity at close range is low, but distant objects are clearly visible to him.
Severe farsightedness is characterized by poor vision of objects not only near, but also at long distances.
Since children from 1 to 6 years of age with hypermetropia cannot concentrate their vision on one object for a long time, and, accordingly, perform the same work for a long time, they become irritable and sometimes withdrawn. They are often tormented by a burning sensation and the sensation of a foreign object in the visual system.
In this article
It is not always possible to detect mild myopia on your own, because people often attribute this condition to ordinary fatigue or eye strain. If vision is normal, then many people do not even know that myopia is a minus, and hypermetropia is a plus. The question of whether it is necessary to wear glasses for mild myopia arises among those who have never had vision problems and who have been found to have slight refractive errors.
Myopia minus 1 - symptoms:
- slight distortion of objects located at a far distance;
- the shape, color and size of distant objects are distinguishable, only small details are not visible;
- when you squint, visual acuity improves slightly;
- nearby objects are clearly visible;
- with increased visual stress, severe eye fatigue is observed;
- periodically a person is bothered by pain and stinging in the eyes;
- blurred vision in poor lighting, impaired twilight vision.
Myopia minus 1 - what does it mean? With such myopia, light rays do not reach the retina, but are focused in front of it, which leads to difficulty viewing distant objects. They become fuzzy and lose their outline.
Diagnostics
An accurate diagnosis and determination of visual acuity with an indicator of -2 can be made through a detailed examination of the patient, which is carried out by an ophthalmologist.
Examination of the fundus using ophthalmoscopy
If myopia is suspected, patients are prescribed:
- 1. Testing vigilance using a table containing 12 lines with letters whose size decreases.
- 2. Measuring the length of the eye using ultrasound biometry. This method allows you to measure the depth of the organ of vision, its anterior chamber, and determine the thickness of the lens and cornea at different points.
- 3. Assessment of the refraction of the eye, which consists of tracking the movement of shadows in the pupil when the organ is illuminated by a light beam reflected from the mirror, when rotated, a shadow appears against the background of the pupil. Its position depends on the refraction of the eye. Used to determine the degree of myopia.
- 4. Examination of the fundus of the eye by ophthalmoscopy using an ophthalmoscope to assess the condition of the retina, its choroid and optic nerve head.
Such diagnostics are sufficient to confirm the pathology, determine its stage and causes of development.
Differences between myopia and farsightedness
There are only a few significant differences between myopia and farsightedness. The differences lie in their nature of manifestation. For example, with farsightedness, a person sees distant images well, while myopia is explained by a clear perception of nearby images.
The second important difference lies in the reasons for the formation of pathology. Myopia is not associated with age-related changes, but may be a hereditary pathology. But farsightedness most often develops as a result of age-related changes, and is passed on from parents; farsightedness cannot. Nevertheless, both diseases cause a person a lot of discomfort and interfere with a normal life. Find out about the features of treatment and diagnosis of congenital farsightedness here.
Causes of childhood farsightedness and methods of its treatment
What is hyperopia or farsightedness?
Farsightedness or hypermetropia is a state of refraction in which the center of focus is behind the retina (as if behind it). This will result in good distance vision. The child clearly sees all objects located remotely. But those that are at close range are blurry, their contours are unclear.
Causes of farsightedness in children
Among the causes of farsightedness in children there will actually be three main factors:
- violation of the structure of the eye,
- heredity,
- glaucoma.
Parents who also suffered from hypermetropia in childhood should be especially attentive. After all, farsightedness treated in time will allow the child to get rid of the need to wear glasses or contact lenses in adulthood.
If farsightedness in a baby develops as a result of glaucoma (high intraocular pressure), then this can lead not only to a decrease in visual acuity, but also to blindness (as a result of the harmful effects of negative factors on the retina).
Hypermetropia of newborns
First of all, it should be said that all babies are farsighted from birth. In newborns, the structures of the eyeball are not yet fully formed. As a result, it seems to be shortened. This fact leads to the fact that the center of refraction is located behind the retina. It is normal for a newborn to be farsighted (about 3 diopters). With age, the structures of the eye develop and farsightedness decreases, in a year it is + 2.5, in two years - respectively + 2, and by about 3 years, children's farsightedness (hyperopia) should be 1.5 diopters.
However, for one reason or another, this may not happen, and then hypermetropia will turn into a disease. To prevent this from happening, farsightedness must be corrected with glasses and treated. It must be identified before the age of 6 years.
Types of hypermetropia
Treatment largely depends on the degree of refractive error. Ophthalmologists distinguish between a low degree - in which the impairment is up to 3 diopters, moderate up to 5 and severe over 5. Thus, all newborns have moderate farsightedness.
Why is hypermetropia dangerous?
At the same time, it is bad if there is a deviation in any direction. If the reading is higher, the child may develop strabismus, and if the reading is lower, myopia may develop.
Hypermetropia leads to frequent conjunctivitis and can also provoke lazy eye syndrome. It is characterized by poor visual acuity with a completely healthy eye. There are no deviations, but the child’s eyes see poorly (correction with glasses does not give any results).
Another consequence of farsightedness can be amblyopia.
What is amblyopia? The fact is that hyperopia, if not treated in time, leads to amblyopia. This ophthalmological disease develops like this: the baby sees a blurry picture, his brain receives unclear signals. As a result, neurons lag behind in development, and amblyopia occurs.
Treatment of farsightedness in children with amblyopia
Treatment of farsightedness in children with amblyopia will be lengthy, but in most cases it gives an excellent result - the child’s vision is completely restored.
However, with this ophthalmological disease, it is no longer possible to correct vision with glasses alone; additional types of therapy will be required. Doctors usually prescribe about 6 types of procedures. Electrical procedures, magnetic therapy, special gymnastics, correctional courses, proper nutrition and drug treatment.
Almost all types of treatment are painless and have a number of game elements. Courses of therapy 5-6 times a year. Between them, it is also necessary to continue treatment at home. These are special exercises, gymnastics, adherence to sleep and exercise patterns, proper nutrition.
With timely detection and adequate treatment, the baby can be completely cured and will not need glasses or contacts in adulthood.
How to determine the quality of vision in children?
Although it is necessary to identify developmental disorders of the eye as early as possible, it is almost impossible to do this before 1 year without an ophthalmologist.
Only he can say that the baby’s farsightedness does not correspond to the age norm. The developmental disorder of the eye should be noticed before age 6 years, but is usually detected by age 3 years.
If abnormal farsightedness is detected in older children (4, 5 or 6 years old), this means that it was simply not noticed in time, and it existed from birth.
In order to prevent the development of the disease, you should show your child to an ophthalmologist at least once a year. He will be able to accurately determine whether your baby’s level of farsightedness corresponds to age standards and whether correction is necessary.
Symptoms of childhood farsightedness
Refractive error in children most often goes away without symptoms. Children don’t know how things can be different and therefore don’t complain.
Sometimes the child may have a headache, he will be irritable and restless, in some cases children experience a burning sensation in the eyes. Often, children with farsightedness become withdrawn.
After 6 years, children go to school, and here hypermetropia will lead to poor performance, inattention, irritability, and poor children's sleep.
Therefore, by the age of 6, this disease must be detected, and treatment must begin.
Types of myopia
If there are disorders that lead to distortion of visual perceptions, the rays do not hit the retina in a focused manner. The type of myopia depends on the nature of the impairment.
Anatomical myopia
Anatomical myopia is characterized by an altered shape of the eyeball, which has an elongated shape. For this reason, focusing of the rays occurs before they hit the retina at the slightest tension of the lens. This disease in most cases is a genetically determined pathology, and its development begins at an early age.
Properly selected glasses reduce tension in the eye muscles. Refusal of them leads to increased compression of the eyeball and progression of the disease.
Sometimes organ degradation occurs too quickly, and even glasses do not help patients. To prevent further vision loss, surgical correction is prescribed.
Accommodative myopia
This is another type of pathology that can develop as a result of exposure to negative factors on the body. However, congenital predisposition also plays a decisive role in this process.
The pathology develops as a result of atrophy of the eye muscles, which are responsible for the functioning of the lens and changes in its shape.
Normal accommodation is the ability of the visual organ to clearly visualize objects with relaxed muscles, regardless of distance. It is ensured by the coordinated functionality of three elements of the eye: the ciliary muscle, the lens and the ciliary ligament.
As a result, its optical power increases by 12-13 diopters, the light rays are focused, and the image is seen clearly. In the case when there is no stimulus for accommodation, the ciliary muscle relaxes and the refractive power of the visual organ decreases. Therefore, it focuses into the distance.
This disease is somewhat milder compared to anatomical myopia. The farther the gaze is directed, the more the lens must contract in order to refract the light rays coming to it and focus them.
When the muscles of the lens are relaxed, its compression cannot be sufficient to ensure the correct focus of rays coming from a long distance. The result of this is myopia with atrophy of the muscles of the organs of vision.
Most often, the disease is diagnosed in children whose eye muscles develop slowly or often experience spasms when overexerted.
With such myopia, glasses are not prescribed, as they will increase atrophy of the eye muscles.