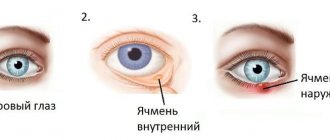
Migraine
According to the Migraine Research Foundation, migraine is the third most common disease in the world. It affects 18 percent of women and 6 percent of men. Migraines are characterized by throbbing, one-sided pain that is sometimes felt around the eyes.
This condition is associated with sensitivity to light and sound and is aggravated by movement. Sometimes people with migraines experience nausea and vomiting. Migraine attacks can last from several hours to several days. There are a number of medications available to treat migraines.
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a very common disease and is the second leading cause of blindness.
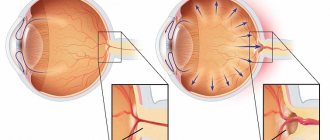
Glaucoma is characterized as a set of disorders in which there is progressive damage to the optic nerve, which carries signals between the eye and the brain. This damage is associated with increased eye pressure.
People with glaucoma may experience headaches, eye pain, light sensitivity, nausea, and vomiting. If this occurs, you should immediately consult an ophthalmologist due to the risk of vision loss.
Why does my left eye hurt?
Unpleasant sensations can arise as a result of penetration of a foreign object into the organ of vision. Specks are removed from the surface of the mucous membrane without medical assistance as a result of blinking or with tears. If a foreign body has penetrated the eye, then medical intervention cannot be avoided.
The causes of pain in the left eye can be:
- Damage to the muscular system of the organ of vision.
- Injury.
- Infectious pathologies.
- Failure in the circulation and outflow of intraocular fluid.
Muscle damage most often occurs due to overstrain of the visual apparatus. Such pain is localized in one or both eyes, accompanied by redness of the whites and a sensation of the presence of a foreign object.
There are so-called non-dangerous causes of unpleasant symptoms:
- Sedentary work. If a person is in an uncomfortable position all day long, working at a computer or driving a vehicle, then by the evening his nerve endings become numb. This causes pain on the left side of the head. To avoid such discomfort, change your position more often, take a break and warm up.
- Hot weather. At elevated temperatures, a large amount of moisture is removed from the body, blood vessels dilate, and blood circulation slows down. The brain does not receive enough oxygen and sends an SOS signal in the form of pain. In hot weather, try to stay in the open sun as little as possible and drink more non-carbonated water.
- Frequent stress and emotional overload. If a person is constantly worried or worried, the neck muscles automatically tense. This causes pinched nerve endings and poor circulation in the brain. Avoid negative emotions and quarrels. If dizziness and noise additionally occur, visit a doctor and undergo a course of medication.
Giant cell arteritis
Giant cell arteritis (or Horton's disease), which mainly affects people over 50, is a disorder in which arteries throughout the body become inflamed. The temporal arteries are most often affected.
Symptoms may include headache, eye pain, blurred vision, double vision or loss of vision, and pain when chewing. Fever, stiffness, and muscle pain may also occur. Giant cell arteritis should be treated promptly as it can lead to blindness.
Causes of pain
The causes of secondary pain in the occipital part of the head on the left back can be associated with various diseases and disorders:
- Injuries in the head and neck area.
- Vascular pathologies of the circulatory system supplying the brain.
- Intracranial pathologies of non-vascular etiology.
- Intake, withdrawal, use of substances of different groups (medicines, narcotic drugs, alcoholic beverages).
- Infectious lesions of the brain, other organs and systems.
- Malfunctions of the autonomic system, disruption of homeostasis (self-regulation).
- Changes in the structural structure of intracranial and external cranial elements (medullary substance, nasal sinuses, eyes, ears, oral cavity).
- Mental illnesses.
- Tumors in brain tissue.
Pain in the left side of the back of the head often develops as a result of cranial neuralgia. To determine the causes of cephalalgia, it is worth paying attention to the accompanying symptoms. For example, if, simultaneously with cephalgia, ear pain and hearing impairment are observed, most likely the symptoms are associated with an infectious-inflammatory process in this area - otitis media, labyrinthitis.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
With osteochondrosis with localization of the pathological focus in the cervical region, periodic compression of the nerve roots occurs, which provokes cephalgic syndrome. If the cause of pain in the left occipital part of the head is osteochondrosis, the painful sensations are periodic and acute. Attacks occur when turning the neck, sudden movements of the head.
Migraine
The cause of the condition when the back of the head on the left in women hurts may be migraine, which is one of the primary forms of cephalalgia. It is characterized by unilateral localization. In this case, the back of the head on the left side of the head hurts regularly (the frequency of paroxysms can exceed 8 episodes per month). The duration of the attack varies significantly (several hours or days).
The pain is pulsating. More often detected in women (65-70% of cases). Often the pathology debuts at the age of 10-40 years. Often accompanied by vomiting and increased sensitivity to light and noise stimuli. A harbinger of paroxysm is often observed - an aura.
Myositis
If you have a headache in the back of the head on the left, there is a high probability of cervical myositis. The disease is an inflammatory process occurring in skeletal muscle tissue. The cause of inflammation can be infections, microtraumas, overexertion, and hypothermia. Pathology is often detected in professional athletes.
Spondylosis
If the left occipital part of the head constantly, moderately hurts, in patients of the older age group the doctor will suspect spondylosis, which causes chronic pain in the occipital parts of the head in 85% of cases. The pathology is characterized by destructive changes in the structure of the bone tissue of the spine, which occur as a result of the natural processes of aging and wear. The disease is accompanied by degeneration of the fibers that make up the fibrous rings of the spinal column.
Myogelosis
Myogelosis is a consequence of chronic increased muscle tone. The disease is characterized by hardening of muscle tissue. When performing muscle work, interconnected processes of protein destruction and restoration occur. If the rest period after muscle tension is shortened, the process of protein recovery is disrupted, which leads to hyaline degeneration (formation of cartilage tissue) of muscle fibers.
Changes in tissue structure are associated with prolonged stay in a position that is uncomfortable for the spine, a sedentary lifestyle, poor posture, and stress. Localization of the pathological process in the cervical region provokes conditions when the head hurts in the back, lower left. According to experts, pain with myogelosis of the shoulder and cervical region develops in the neck area, then radiates (spreads) to the lower parts of the head.
Neuralgia
Sharp pain in the back of the head on the left may reflect the process of irritation of the cranial nerves with sensory fibers. These include the vagus, occipital, trigeminal, glossopharyngeal. Painful sensations appear as a result of stretching or compression of nerve endings and roots. In cases where the occipital nerve is affected, the headache is localized on the left side in the occipital region.
Typically, cephalgia manifests itself acutely, intensely, and occurs or intensifies when changing the position of the head or chewing. It is paroxysmal (repeated attacks) in nature, radiating to nearby and distant areas of the head. For this type of cephalalgia, the formation of trigger zones is typical. Even a slight impact on the trigger zone provokes a severe attack.
Other sources of pain
A central (hypochondriacal) primary form of cephalgia is distinguished when it is not possible to accurately determine the mechanisms of its occurrence. Typically, the cause of pain in the left side of the head in this case is a decrease in the threshold of pain sensitivity. Pathological changes occur as a result of an imbalance between the processes of excitation and inhibition of the structural elements of the central nervous system.
Failures are more often associated with deterioration of neurohumoral regulation. Cephalgic syndrome can be triggered by life-threatening conditions. These include acute disturbances of blood flow in the brain, heart attacks, strokes, tumor processes, meningitis, abscess, and intracranial hemorrhages. To identify the causes of pain in the left side of the back of the head, you need to make an appointment with a neurologist and undergo a diagnostic examination.
Histamine headaches
Histamine headaches can cause severe pain in one eye, usually lasting 15 to 45 minutes, but sometimes lasting up to three hours. Several headache attacks may occur each day. Other symptoms include nasal congestion, runny nose, and sweaty face.
Horner's syndrome may also occur; at the same time, one eyelid droops, the pupil becomes small, and the size of the pupils of the eyes is different. Histamine headaches are more common in young men and in those who use tobacco and alcohol. Treatment is usually symptomatic.
What pathologies lead to pain in the left eye?
Infectious anomalies are the most common cause of discomfort in the visual system. Pathogenic microorganisms enter both from the external environment and from internal systems. These could be viruses that cause ARVI, shingles, etc.
As a rule, pain initially appears in one eye. However, if the infection continues to spread throughout the body, it will spread to the second eye. Sometimes the pain causes inflammation of the eye membranes (uveitis) or other vital organs. Such pathologies require urgent treatment, as they can lead to relapse.
Migraine
One of the most common causes of eye pain. Unpleasant sensations spread to the entire left side of the head. When symptoms worsen, vomiting, nausea, chills, increased sweating occur, and light and noise are difficult to tolerate. During a severe attack, there is a disturbance in the sense of smell.
Possible odor hallucinations, for example, the patient perceives the “aroma” of a rotten egg. Everything that he imagines and feels during the period of exacerbation persists for several hours, or even days. When the pain subsides, fatigue and drowsiness come.
Osteochondrosis
In addition to migraine, the reason why the left eye hurts can be osteochondrosis. Salts accumulate between the joints in the back, resulting in pinching of the vessels in the neck that lead blood flow to the brain.
Lack of nutrients causes swelling of the artery, and the transport of oxygen to the main organ of the central nervous system is disrupted. Because of this, patients often complain of dizziness and pain. Sometimes pulsation occurs on the left side and in the temple area. This deviation occurs due to increased intracranial pressure. The pain can be nagging or sharp. Return to contents
Weather changes
Increased sensitivity to weather changes can also cause spasm. As a result, pain appears in the left eye and ear, in the area of the back of the head and forehead. When the weather becomes capricious, the atmospheric pressure changes. As a result, arterial and intracranial pressure increases or decreases.
There is aching in the bones, pain on the left side of the head, aching in the neck and teeth. The unpleasant sensations are not so pronounced, but last up to two days. It seems that the left side of the head has become very heavy. Weakness and loss of strength occur.
Infections
Due to the “attack” of the body by harmful bacteria and microbes, a sharp pressing pain appears in the left side of the head. A cold ear “sends” an unpleasant sensation to the back of the head. There is spasm of the facial and neck muscles. It causes a boring pain in the head when walking or exercising.
Sometimes the left eye and ear hurt due to poor posture and damage to the vertebrae. Their incorrect position increases the load on the muscles and ligaments, which also leads to unpleasant symptoms.
Tumor
A huge danger lurks if the pain on the left side of the head is due to tumors in the brain. In such situations, unbearable pressing or sharp pain occurs in the temple area. Vomiting and nausea are possible.
Sometimes there is loss of hearing and vision or partial impairment of these functions. The appetite disappears, the person cannot sleep. Usually pain occurs after a night's rest or in the first half of the day.
Stroke
One of the most terrible causes of unpleasant symptoms. Such a diagnosis causes excruciating and increasing pain. Facial expressions, speech, and coordination of movements are impaired. The main manifestation of a stroke is fainting and pain in the left side of the head.
Due to a violation of orientation in space, “seasickness” occurs. A stroke requires immediate medical attention and hospitalization.
Neurological type problem
Sometimes unpleasant sensations arise due to mental disorders. For example, frequent stress, tense family situations, problems at work. Painful sensations arise in difficult life circumstances. Most often, people do not understand what caused the stress. In such situations, it is better to seek help from a psychologist.
Trigeminal neuralgia
Trigeminal neuralgia is a rare condition that affects the trigeminal nerve, which is responsible for communicating sensations from the face and forehead. Trigeminal neuralgia attacks consist of extremely severe shock or burning pain in the areas controlled by the trigeminal nerve.
The pain can last from a few seconds to several minutes, sometimes recurring for two hours. Currently available treatment is not always effective and the disease may progress.
Less common causes
Other, less common causes of headaches that radiate to the left eye can be problems with the blood vessels. After a stroke involving certain arteries in the brain, up to 25 percent of people experience pain in the eye on the side where the stroke occurred. Blood clots or tears in the carotid artery in the neck can lead to eye pain but are usually associated with other associated symptoms (eg, Horner's syndrome).
A brain hemorrhage due to injury or a ruptured aneurysm can cause eye pain, although there will usually be other symptoms as well. Finally, sinus infections rarely lead to the formation of a clot in a vein in the brain called the cavernous sinus. Cavernous sinus thrombosis causes headaches and eye pain, as well as problems with eye movement, sensitivity to light, bulging of the eye, and swelling around the eye.
Malignant brain tumors and tumors that have metastasized to the eye can also cause left eye pain and headaches. However, conditions such as brain tumors that increase intracranial pressure often cause headaches on both sides.
Main reasons
Below are the most common causes of head and eye pain.
- Overwork. This reason is the most common. In this state, a person experiences unpleasant sensations after working at the computer, stress, or a hard day at work. There is a feeling as if there is a squeezing hat on the head, which prevents you from feeling comfortable. This condition is due to the fact that the vessels of the shoulder girdle have received a spasm, which has consequences in the form of impaired blood supply. This condition radiates not only to the head, but also to the eyes. This pain has an extremely unpleasant feature: it continues even after the main cause has been eliminated. To prevent this phenomenon, you need to try to rest as much as possible and not be stressed.
- Migraine. This reason is also common, and most often the headache occurs on only one side. This may be the temporal or frontal region. The cause of this pain occurs in people between the ages of 25 and 40, and women suffer from migraines much more often than men. If the cause is migraine, then before the pain itself there may be a slight tingling sensation, and even numbness of the limbs. Despite the wide popularity of this disease, doctors have not yet invented a universal cure for treatment. Therefore, people suffering from this disease have to follow the basic principles - rest as much as possible, remain calm, and lead a healthy lifestyle.
- Increased intracranial pressure. An acute attack can occur when coughing and improper movements, and most likely the cause is increased pressure inside the skull. Only a specialist can determine this cause of headache by performing a brain tomogram or puncture.
If specialists detect an increase in blood pressure, the doctor will prescribe effective treatment, but with such a diagnosis it is worth following general recommendations - avoid coffee, energy drinks, and alcohol.
- Intracranial hematoma. If you have suffered a severe blow to the head or been injured and experience headaches some time after the incident, this may indicate a concussion. To exclude this cause, a brain tomogram is performed; if the diagnosis is confirmed, surgical intervention is possible. If the diagnosis is a concussion, then the doctor must determine the severity, and the general recommendations are as follows: you need to sleep as much as possible, not engage in physical labor, and get proper rest.
- Pre-stroke condition. If this particular condition is the cause of pain in the head and eye on one side, then you can verify this yourself. Just measure your blood pressure. If it is too high, you must call an ambulance. This cause of headache and eye pain appears in people over 50 years of age.
- Vascular aneurysm. With this disease, the head often hurts on the left or right, and the pain radiates to the eye. The pain throbs and causes a lot of discomfort, and if you move your head, the pain may intensify. If the first symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor.
- Meningitis. The main symptom of this disease is a constant headache, which grows and becomes stronger. Subsequently, it can spread not only to the eyes, but also to the ears and neck.
- Brain tumor. With this disease, the pain is of an increasing nature, it becomes stronger day by day. In addition, not only does pain appear in the head and eyes, but nausea and dizziness also occur.
Only a doctor can determine an accurate diagnosis!