Treatment of pathology
Self-resorption of the abscess is mainly observed when it is localized on the outside of the eyelid.
This is also typical for internal formations, but much less frequently, and there is always a danger of purulent exudate spreading from the damaged eyelid throughout the entire mucous membrane of the eye. The consequence of this pathological condition can be the development of various infectious diseases in a person. Therapy for styes inside the lower eyelid is carried out using various medications and physical procedures, and when the pathological process becomes complicated, surgical intervention is indicated.
Ointments
When eliminating internal formation on the lower eyelid, the following ointments are considered the most effective:
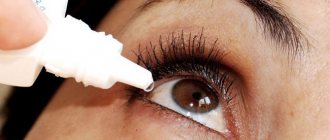
- Tetracycline ointment. This product is considered absolutely safe, and its use eliminates the possibility of burns on the mucous membrane or cornea of the eye. It is recommended to use the drug immediately after the first signs of conjunctivitis appear until they are completely eliminated. Tetracycline ointment must be applied to the inside of the eyelid several times a day.
- Hydrocortisone ointment. The drug has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect and is most often prescribed for complicated forms of the disease. The ointment should be applied to the eyelid not from the inside, but to the eyeball itself. The product can be used no more than three times per session and avoid excessive eye strain throughout the entire treatment period.
- Erythromycin ointment. This product has a broad spectrum antibacterial effect, but if used incorrectly, it can cause the development of allergic reactions.
Drops
The use of ointments in the treatment of internal conjunctivitis in the lower eyelid is recommended to be supplemented with:
- vasoconstrictor;
- anti-inflammatory;
- antimicrobial;
- hormonal agents.
The patient may be prescribed the following drops:
- Albucid. Today, drops are one of the inexpensive and safe means for the treatment of many infectious diseases of the organs of vision. At the same time, Albucid has some contraindications for its use and adverse reactions such as discomfort in the eyes, burning and itching are possible.
- Tobrex. Such drops are an alternative to Albucid and act on the source of inflammation, destroying pathogenic microorganisms and accelerating the process of resorption of ulcers.
- Gentamicin. Drops are an antibiotic, therefore they are mainly prescribed for the treatment of complicated forms of the disease. In addition, this drug is used if it is not possible to cope with conjunctivitis with the help of Tobrex.
In addition, to eliminate the disease, vitamin complexes and drugs that improve the functioning of the immune system can be prescribed.
Physiotherapy
An effective method of combating formation on the eyelids is UHF eye therapy using a low-thermal dose. The duration of the procedure is 8 minutes and it must be carried out over several days. In addition, it is possible to speed up recovery through microwave treatment.
When barley appears, in order to speed up the formation of an abscess, you can perform infrared irradiation of the eyelids or a dry air shower for 5-15 minutes several times a day. It is not allowed to apply warm compresses to the inflamed organ of vision, as this can cause maceration of the skin and penetration of microbes into other sebaceous glands.
ethnoscience
It is possible to speed up the patient’s recovery with the help of alternative medicine, but before using them it is recommended to consult a specialist.
A calendula compress is considered an effective remedy, which is recommended to be used as often as possible. Its help is usually resorted to in situations where it is necessary to carry out careful treatment and not damage the mucous membrane of the organ of vision. To prepare it, you need to brew 10 grams of a medicinal plant with 200 ml of boiling water and leave the mixture for at least 3 hours. After a while, the product needs to be filtered and compresses used on the lower eyelid as often as possible throughout the day.
It is recommended to wash your eyes with a decoction prepared from:
- wild rosemary;
- birch buds;
- chamomile;
- bird cherry color.
It is necessary to take the herbs in equal proportions and brew 10 grams of the resulting herbal mixture with a glass of boiling water. The decoction should be kept for at least half an hour, then filtered and washed with it on the inflamed organ of vision.
Types and symptoms
Depending on the characteristic signs and conditions of occurrence, there are different types of blepharitis.
Simple - the edges of the eyelids are moderately swollen, red, there is itching, burning, the patient blinks frequently, and a caustic foamy liquid forms in the inner corners of the eyes.- Scaly - the edges of the eyelids are thickened, reddened, and dry pityriasis-like scales form on them from the epithelial tissue of the sebaceous glands and the outer layer of the skin. The scales grow tightly together with the skin between the cilia. If you remove the scale, the skin underneath is plump, congested with blood, and thin.
- Ulcerative - purulent inflammation of the hair cavities of the eyelashes is observed, this is manifested by yellow purulent crusts between the hairs (at the base). If you tear off such a crust (usually along with an eyelash), small ulcers are visible from which blood flows.
- Meibomian - the meibomian (sebaceous) glands are inflamed, secretion production is impaired. If you tear off the purulent crust (along with the stuck together cilia), purulent fluid comes out of the cavity.
- Rosacea – small, reddish-gray nodules and ulcers are observed on the edges of the eyelids. This type of disease often develops due to simple acne.
- Demodectic mange is caused by the eyelash mite demodex. The patient feels unbearable itching, the edges of the eyelids turn red, peel, thin out and eyelashes fall out. The tick metabolite is toxic and can cause general poisoning of the body.
Symptoms of blepharitis worsen if the patient treats the eyelids with cosmetics (cream, tonic), stays in the sun or in a solarium.
If ulcerative and meibomian blepharitis is not treated, the skin becomes overgrown with connective tissue, as a result of which the growth of eyelashes is disrupted, they stop growing, and fall out partially or completely. The edges of the eyelashes become deformed, thicken, and the eyelashes curl under the eyelid. As a result of gross changes, pathological processes in the cornea may develop.
How to quickly cure stye on the eye?
You can find a lot of material on how to treat stye, but no one will give you better advice than an experienced doctor. The external effect and painful syndrome can be relieved with lotions, but with the underlying disease that provoked the appearance of barley, you must definitely go to the hospital.
Medications
When diagnosed with stye on the eye, treatment with medications involves constant monitoring by a doctor. If you have no idea how to cure stye on the eye, and are encountering this disease for the first time, the doctor will prescribe you medication, which includes:
- external treatment of barley with ethyl alcohol, brilliant green, iodine or calendula tincture;
- anti-inflammatory eye ointments: hydrocortisone or tetracycline;
- antibacterial eye drops: tsipromed or chloramphenicol.
Folk remedies
To treat barley, herbal remedies that have antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effects can be used. Thus, aloe has long been used to treat the disease.
You need to take an aloe leaf, chop it and pour a glass of boiled water at room temperature. The product should sit for several hours. Dip gauze into the resulting infusion, squeeze it out, and then apply it to the affected area of the eyelid.
The prepared product should sit for an hour. To treat stye, you need to soak a cotton pad in the infusion and then apply it to the affected eyelid. Repeat the manipulation two to three times a day.
Chamomile is widely known for its anti-inflammatory effects. To prepare a remedy for barley, you need to take two tablespoons of chamomile and eyebright, pour a glass of boiling water and cover with a lid. When the broth has cooled, you need to moisten a cotton pad in it, squeeze it a little and apply it to your eyelid.
Antibacterial therapy
To destroy the infection at the site of the inflammatory process, also after opening the abscess, many doctors use drops and ointments based on antibiotics to treat barley. This is due to the fact that staphylococcus is a bacterial infection.
Antibacterial drops for barley: “Levomycetin” (1-2 drops of a 5% solution 3-4 times a day, for 5-15 days), “Floxal” (1 drop 2-4 times a day, for 7- 14 days), “Tsipromed” (5 drops 3 times a day).
Ointments are applied to the lower eyelid 2 times a day, but not more than the period specified in the instructions for the drugs. The effectiveness of ointments is higher, which is due to their thick consistency, which is why they stay in the treated area much longer than drops.
Drops and ointments must be at room temperature so as not to cold the optic nerve. If you have a stye on your eye, do not cover it with cosmetics or apply makeup.
Some doctors consider it inappropriate to use antibacterial drugs for external barley, reserving the right to use them for internal localization of the disease.
Maintenance therapy
The development of infectious diseases, including eye stye, in most cases is associated with a weakening of the body’s protective functions, the role of which is played by the immune system. The effectiveness of treatment for eye stye increases when the immune system is strengthened.
A wonderful stimulator of the immune system is vitamin C (ascorbic acid), large amounts of which are found in rose hips, cranberries, sorrel, lemon, raspberries, currants and other gifts of nature.
An important part in this matter is the additional intake of vitamin complexes, because vitamins actually strengthen and support the normal functioning of all organs and systems
At elevated temperatures, the following are prescribed: Paracetamol, Ibuprofen. For nausea, the following are prescribed: Motilium, Cerucal. For symptoms of intoxication, detoxification therapy is also appropriate.
Surgery
Surgical treatment of barley is used in cases of long-term disease, when the abscess does not open spontaneously, as well as in the case of the development of chalazion - meibomian gland barley, when the enlarged compaction begins to put pressure on the eyeball.
Surgical treatment of stye is based on puncturing the abscess with a needle or making a small incision with further drainage of the inflamed area, placing an antibacterial ointment in this area. The consequences of surgical intervention are not visible, and the treatment itself with this method is usually carried out without complications.
In case of chalazion, the “bone” is cut out, the purulent contents are removed from this place, and instead of it, an antibacterial ointment is applied, after which the eyes are sealed with a plaster for several hours, or the eye is fixed with a monocular bandage.
Development of the disease
The development of barley, as we have already said, is possible due to a combination of two main factors - penetration of an infection under the skin, in our case staphylococcus and weakened immunity.
Staphylococcal infection is almost always present on the surface of the skin, but the body’s protective functions do not allow it to spread inside the body, however, some factors that weaken the immune system still play an important role in the development of staphylococcal diseases.
Among the main reasons for a weakened immune system are stress, hypothermia, the presence of various diseases, especially infectious ones, and vitamin deficiency (hypovitaminosis). Of course, if a person adheres to the rules of personal hygiene - does not touch his eyes or face with dirty hands, then the spread of infection is also minimized.
If the infection penetrates under the eyelid, it can settle in the meibomian gland duct. Next, the infection begins to actively multiply in these places. At the same time, an inflammatory process develops. First, at the site of the inflamed bulb, healthy cells die and begin to fester.
The site of inflammation begins to swell, turn red, increase in size, forming some kind of hard compaction. In addition to external signs, as the disease develops, a person feels severe itching, and when touching the inflamed area, pain.
Due to the peculiarity of the localization of potentially vulnerable areas of stye formation, swelling and pustules appear only on the edges of the upper or lower eyelid. The formation of an abscess usually occurs 2-4 days after infection of the eyelid.
At this stage, the conjunctiva also turns red. A small ball with yellowish purulent contents forms on the seal. More than one abscess can also form on one eyelid.
Full ripening of barley occurs in 3-7 days. Severe infection against a background of weakened immunity can additionally cause an increase in body temperature to 38 ° C, nausea and other signs of intoxication of the body.
After full ripening, usually on the 3-4th day, under the pressure of purulent masses, the abscess breaks through, the pus along with dead tissue comes out, after which the pain goes away and the stye on the eyelid resolves, however, if the stye does not go away for more than one week, consult an ophthalmologist.
After spontaneous opening of the abscess, the swelling quickly subsides, and literally the next day, only slight swelling remains, but the redness of the eyelid remains for another couple of days.
Sometimes the abscess does not open without permission, and the barley spontaneously resolves, but there are cases when the usual form of the disease turns into the so-called cold barley (chalazion).
A characteristic feature of chalazion is the long development and course of the inflammatory process, which lasts about 1-2 months. In some cases, if a chalazion does not go away on its own, it requires surgical removal.
Risk factors
The opinion that barley occurs due to hypothermia of the body is not entirely correct: hypothermia is one of the risk factors that contributes to the development of the inflammatory process, while the inflammation itself is caused by a bacterial infection, and in some patients - by a skin mite (Demodex).
Symptoms
Barley
Hordeolum develops due to a combination of two factors - infection and a decrease in the body's defenses. The pathology begins with the penetration of bacteria into the hair follicle of the eyelash. It settles in the bulb or sebaceous gland of Zeiss.
Active reproduction of the infection causes an inflammatory process, healthy cells die and begin to fester. First signs:
- hyperemia;
- itching;
- swelling;
- soreness to touch;
- there is a twitching feeling inside.
Papule formation occurs on days 2–4.
Swelling becomes more intense, this is due to impaired lymph movement. The mucous membrane turns red, an apex forms, which causes a feeling of tightness. The resulting tubercle resembles a grain, which is why the disease is called barley. On the 4th day, a cloudy white liquid appears on the surface - this is pus located under a thin film.
On days 5–6, the exudate breaks out. The swelling begins to go away after a few days. The redness is still there.
Chalazion
Hailstones look like barley. Looks the same and feels the same. Only the first symptoms disappear within 1–2 days, but the swelling remains and continues to grow slowly. First signs:
- soreness;
- redness;
- swollen eyelid;
- moderate irritation.
The formation can reach a size of up to 5–6 mm in diameter. A chalazion forms a noticeable swelling and cosmetic defect. When examining the eyes from the conjunctiva, an area of local redness with a central grayish zone is detected.
Furuncle
It is impossible to notice a boil; symptoms appear in stages. But at first, the flow can be confused with barley or chalazion. A boil on the eyelid is manifested by an itching sensation. Later, the area becomes swollen, red and painful.
Such signs bother the patient for 2 or more days. The transition of inflammation to a purulent form is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- uncontrollable lacrimation;
- formation of thick discharge in the corners of the eyes;
- the appearance of a boil head that differs from healthy skin in color (usually yellow or yellowish-white).
Dacryocystitis
The symptoms of the disease are quite specific.
In the chronic course, lacrimation and swelling in the area of the lacrimal sac are observed; if you press on the swelling, a purulent secretion will appear. The acute form of dacryocystitis manifests itself with more severe symptoms. Patients complain of the following symptoms:
- narrowing or complete closure of the palpebral fissure;
- overflow of the lacrimal caruncle with blood;
- inflammation of the eyelids and semilunar fold;
- thinning of the skin;
- increased body temperature;
- an abscess that opens with purulent contents leaking out.
Abscess
A significant increase in eyelid size is manifested by severe swelling and hyperemia. The patient loses appetite, develops general malaise, and increases body temperature. Patients become drowsy and lethargic.
Symptoms of eyelid abscess:
- outer skin is tense;
- the tissues of the eyelid may show signs of damage or ulceration;
- when there is more secretion inside, the skin becomes more tense, and its vibration when pressed is noticeable—fluctuation;
- the eyelid droops;
- a burning sensation appears in the eye, the quality of vision decreases;
- the skin becomes yellowish in color;
- soreness of nearby lymph nodes.
With a spontaneous breakthrough, pus is observed, sometimes with blood clots.
Why do blackheads appear?
Blackheads (open comedones) are miniature cysts that form in hair follicles when fat oxidizes and mixes with dead skin cells. A distinctive feature is the dark head, which protrudes slightly above the surface of the pore. Blackheads most often bother those with oily or combination skin. Unlike open comedones, closed ones form under the top layer of skin. Fat accumulates in the follicle without oxidizing under the influence of oxygen. This cosmetic problem is also called whiteheads. In this case, bacterial flora is often present, which provokes the inflammatory process.
An open comedone has a black head, and a closed one has a white head.
The common cause of both types of comedones is excess sebum production, which is provoked by increased levels of testosterone, the male sex hormone. That is why these cosmetic problems most often appear during adolescence. After all, during this period there is an active production of male hormones.
For the same reason, open comedones may appear during pregnancy, since the placenta produces additional testosterone. Blackheads may be more pronounced during ovulation, when a significant dose of male hormone is released. Before menstruation, open and closed comedones become larger due to increased sebum production under the influence of progesterone, which is active in the second phase of the cycle. This is how the glands react to changes in hormonal levels.
During pregnancy, there is an increase in the production of testosterone, which is one of the reasons for the appearance of black spots.
Pathological processes such as:
- inflammatory diseases of the liver and biliary tract;
- gastritis;
- inflammation of the duodenum, which interferes with the absorption of nutrients;
- diseases of the thyroid gland associated with a decrease in its function;
- inflammatory bowel pathologies: proctitis, colitis, sigmoiditis;
- hormonal disorders associated with taking appropriate medications;
- pancreatitis;
- diabetes;
- pathologies of the adrenal glands.
Inflammation of the stomach and duodenum can cause the appearance of open comedones
The following factors can contribute to the occurrence of open comedones:
- frequent stress that provokes hormonal fluctuations;
- an abundance of fatty foods in the diet;
- being overweight;
- improper facial care: infrequent washing, dry skin, etc.;
- use of low-quality cosmetics;
- smoking.
The causes and factors contributing to the appearance of both types of comedones are largely similar. This problem rarely bothers people with dry skin, since their sebaceous glands produce less secretion.
Stye on the eye - treatment
How to treat barley, how to get rid of it? Treatment of barley includes the following points:
1. Drug treatment: 1.1. Stimulating faster maturation; 1.2. Antibacterial therapy. 2. Maintenance therapy. 3. Surgical treatment.
Important! Under no circumstances should barley be squeezed out! It is necessary to wait for its maturation and unauthorized opening, as well as the extraction of the contents of the abscess
1. Drug treatment of eye stye
At the stage of barley ripening, the inflamed area must be treated with antiseptics - ethyl alcohol, an alcohol solution of brilliant green, calendula tincture, etc.
At this stage of the inflammatory process, you can go in two ways - wait for the barley to ripen spontaneously, or accelerate its ripening. For faster healing, medications are used after opening the abscess.
1.1. To accelerate the ripening of barley, you can perform the following procedures:
- apply a warm compress to the inflamed area, just make sure that when it cools down, it does not remain on the eye, otherwise there is a risk of catching a cold of the optic nerve, which is fraught with serious complications;
- For these purposes, a doctor can use UHF therapy, which is based on the use of a high-frequency electromagnetic field.
- at home, you can use a blue or Biocon lamp, but their use is allowed only in the absence of high body temperature.
1.2. Antibacterial therapy
To destroy the infection at the site of the inflammatory process, also after opening the abscess, many doctors use drops and ointments based on antibiotics to treat barley. This is due to the fact that staphylococcus is a bacterial infection.
Antibacterial drops for barley: “Levomycetin” (1-2 drops of a 5% solution 3-4 times a day, for 5-15 days), “Floxal” (1 drop 2-4 times a day, for 7- 14 days), “Tsipromed” (5 drops 3 times a day).
Antibacterial ointments for barley: “Tetracycline ointment”, “Hydrocortisone ointment”, “Floxal”.
Ointments are applied to the lower eyelid 2 times a day, but not more than the period specified in the instructions for the drugs. The effectiveness of ointments is higher, which is due to their thick consistency, which is why they stay in the treated area much longer than drops.
Important! Drops and ointments must be at room temperature so as not to cold the optic nerve. Some doctors consider it inappropriate to use antibacterial drugs for external barley, reserving the right to use them for internal localization of the disease
Some doctors consider it inappropriate to use antibacterial drugs for external barley, reserving the right to use them for internal localization of the disease.
If you have a stye on your eye, do not cover it with cosmetics or apply makeup.
Maintenance therapy
The development of infectious diseases, including eye stye, in most cases is associated with a weakening of the body’s protective functions, the role of which is played by the immune system.
The effectiveness of treatment for eye stye increases when the immune system is strengthened.
A wonderful stimulator of the immune system is vitamin C (ascorbic acid), large amounts of which are found in rose hips, cranberries, sorrel, lemon, raspberries, currants and other gifts of nature.
An important part in this matter is the additional intake of vitamin complexes, because vitamins actually strengthen and support the normal functioning of all organs and systems
At elevated temperatures, the following are prescribed: Paracetamol, Ibuprofen.
For nausea, the following are prescribed: Motilium, Cerucal.
For symptoms of intoxication, detoxification therapy is also appropriate.
Surgery
Surgical treatment of barley is used in cases of long-term disease, when the abscess does not open spontaneously, as well as in the case of the development of chalazion - meibomian gland barley, when the enlarged compaction begins to put pressure on the eyeball.
Surgical treatment of stye is based on puncturing the abscess with a needle or making a small incision with further drainage of the inflamed area, placing an antibacterial ointment in this place.
In case of chalazion, the “bone” is cut out, the purulent contents are removed from this place, and instead of it, an antibacterial ointment is applied, after which the eyes are sealed with a plaster for several hours, or the eye is fixed with a monocular bandage.
The consequences of surgical intervention are not visible, and the treatment itself with this method is usually carried out without complications.
How to prevent open comedos
To prevent the problem from occurring, it is necessary to properly care for your skin, namely:
- Wash your face daily using special products suitable for your skin type. It is important to observe the temperature regime. At the same time, you can wash your face with cool water in the morning and warm water in the evening to wash away all the sebum and dead cells that have accumulated during the day.
- Use a scrub or peeling several times a week. Regular exfoliation will prevent clogged pores. For these purposes, it is recommended to use both store-bought and homemade products: coffee, salt, oatmeal, etc.
- Once a week, deep clean the pores of impurities. To do this, you can use film masks, adhesive strips and a special extractor that allows you to squeeze out the comedone.
- Use toners that contain salicylic acid, which can soften the contents of pores and remove excess sebum.
- Use creams containing adapalene and its derivatives. Such products reduce the activity of the sebaceous glands, preventing the release of large amounts of fat. For prevention, it is enough to apply the cream 2-3 times a week.
- During the hot season, it is important to protect the skin from ultraviolet rays using special creams with filters.
- Do not wash your face with soap every day; instead, it is better to use special foams and gels.
Regular use of the scrub helps prevent the appearance of blackheads
To avoid the occurrence of open comedones, it is recommended to use only high-quality cosmetics and be sure to remove makeup before going to bed.
To prevent the appearance of blackheads, I use exfoliating products 3 times a week. In my case it’s a coffee scrub, sometimes I also use apricot kernels. Such products perfectly exfoliate the skin and cleanse pores, preventing the accumulation of oil. At least the number of blackheads after the procedure is reduced and new ones do not appear. Additionally, 3 times a week I apply Clenzit gel to the skin, which helps prevent the appearance of open and closed comedones. I do not recommend using this product more often, as the skin begins to itch and peel.
Measures to prevent blackheads - video
Recommendations from dermatologists
Preventive recommendations from specialists:
- To improve skin condition, it is recommended to reduce the consumption of fatty and carbohydrate foods, giving preference to proteins. The diet should contain more plant fiber. It is necessary to exclude fast food, instant products, and also not to overuse chocolate. All junk food affects the density of sebum (sebum).
- Do not overdry the skin with alcohol-containing lotions, which further activate the sebaceous glands.
- Try not to touch your face with your hands.
- If your skin is oily, you shouldn't wash your face every few hours. To eliminate excess fat, it is recommended to use mattifying wet wipes or tonics based on herbal decoction.
- Stop smoking and do not abuse alcohol.
- Use peelings with fruit acids once a month to deeply cleanse pores.
- Eliminate gastrointestinal diseases, since the composition of sebum (sebum) largely depends on the quality of food digestion.
- Drink more clean water, up to 2 liters per day.
- Relieve constipation in a timely manner.
- Do not perform mechanical cleaning of pores too often, especially at home.
Fatty foods affect the density of sebum, so it is recommended to exclude them from the diet.
“Black dots” (comedones) are nothing more than an accumulation of sebum. The production of sebum by the sebaceous glands is the norm; another thing is that if the skin is not taken care of, it will accumulate in the hair follicle and lead to the formation of enlarged pores. Oxidizing in air, sebum acquires a dark color. I recommend using exfoliating preparations weekly to normalize the outflow of sebum (scrubs, light homemade chemical peels); enzymatic peels can be applied to lighten blackheads. Periodically, mechanical cleaning is possible (according to indications). Under no circumstances should you remove these elements yourself if there is inflammation.
Samodelkina Ksenia Aleksandrovna (dermatologist)
https://health.mail.ru/consultation/153106/
It is necessary to avoid highly abrasive scrubs with large and coarse particles, as they injure the skin, as well as alcohol-containing lotions and tonics, because they violate the protective barrier of the skin. I also do not recommend abusing special strips for blackheads. They can irritate the skin and cause inflammation. You should not squeeze out blackheads yourself. This can lead to scarring and infection. Seek help from professionals! The most effective ways to get rid of blackheads are facial cleansing and peeling. If you don't cleanse your skin at all, excessive accumulation of sebaceous secretions can lead to even larger pores. I recommend atraumatic ultrasonic facial cleansing using the Skin Master device, chemical peelings based on mandelic and azelaic acids Purless M-peel, pyruvic acid and retinol Red Peel, laser peeling using the Fraxel Dual device (evens out skin microrelief).
Anna Pleshkova (cosmetologist, dermatovenerologist)
https://gmt-clinic.ru/news/mnenie-eksperta-kak-izbavitsya-ot-chernyh-tochek
Prevention and elimination of open comedones: the opinion of a dermatologist - video
In order to prevent the appearance of blackheads, you need to follow the rules of hygiene and eliminate everything harmful from your diet. It is also necessary to monitor hormonal levels and the functioning of the digestive system. If the problem occurs and is aggravated by the appearance of acne, it is recommended to consult a dermatologist who will help find out the cause and eliminate it.
- Author: Ksenia Kalugina
Rate this article:
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
(1 vote, average: 4 out of 5)
Share with your friends!
Origin and symptoms of ulcers on the eyelid
Purulent formations can provoke the following diseases and conditions:
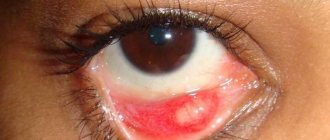
- An abscess is an acute inflammatory process in which an abscess with purulent contents forms on the mucous membrane of the eyelid. This process is a complication that provokes other eye diseases (hordeolum, blepharitis, meibomitis and others). The abscess has a yellowish, sometimes gray color, and it is very painful to touch. After the wound bursts, purulent fluid flows out of it, the pain immediately disappears. An abscess has the same symptoms as cellulitis.
- Molluscum contagiosum is a viral disease caused by poxvirus (smallpox virus). Previously, doctors associated the occurrence of pathology with the vital activity of the mollusk. You can become infected with the virus through contact with a carrier, using someone else's towel or other personal items. A feature of this infection is the formation of dense formations on the mucous membrane of the lower eyelid, which are painless when touched. The disease can lead to chronic keratitis, conjunctivitis, and blepharitis.
- Stye is an abscess on the edge of the lower eyelid. This disease is caused by staphylococcus of the sebaceous gland. The main sign of the disease is the appearance of a bulge on the mucous membrane of the eyelid, which causes pain. There is redness of the skin around the seal, and the conjunctiva also becomes inflamed. Usually the abscess breaks out in 2-4 days. Sometimes several seals form on the eyelid at once.
- Blepharitis is an inflammatory process in the area of the ciliary end of the lower eyelid. This disease is mainly chronic.
Types of blepharitis:
- angular,
- ulcerative,
- scaly,
- meibomian.
Symptoms common to all types of blepharitis are a feeling of eye fatigue, heaviness of the eyelids, and sensitivity to bright light. The eyelids become slightly swollen, dense, and reddened. The patient feels itching and burning in the eye. In some cases, eyelashes begin to fall out. Blepharitis is a complication of certain skin diseases, such as seborrheic or simple contact dermatitis, allergies, acne, lice.
- A furuncle or boil is a bulge in the eyelid area that has purulent contents and is accompanied by swelling. A black dot forms inside the boil, which is called a necrotic center. After the boil breaks out, the pus comes out along with the necrotic core. Almost always, after the wound heals, a scar remains on the affected area.
- Impetigo is a skin disease that spreads to the eyelid from other parts of the body. It is transmitted through contact and household contact. The abscesses are small in size and heal on their own within 2 weeks. This disease does not cause any complications. Its causative agents are streptococci and staphylococci. Children most often suffer from impetigo.
- Meibomitis is an inflammatory process in the meibomian glands (glands of the cartilage of the eyelid). This disease is caused by coccal forms of bacteria. The symptoms of meibomitis are similar to those of stye. They differ in that with barley, the abscess forms on the edge of the eyelid, and with meibomitis - in its depths. Sometimes the abscess needs to be opened surgically. Yellow or gray crusts form in the corners of the eyes. Discharges constantly come out of the glands, which can provoke the development of chronic conjunctivitis.
Varieties
There are several different types of the disease, which differ both in their causes and in their manifestations. Here are its main subspecies:
- Simple blepharitis. The most basic version of the disease manifests itself due to itching of the eyelids and pronounced redness of their edges.
- Meibomian blepharitis. Traditionally, it manifests itself in the form of hypersecretion simultaneously with inflammation of the sebaceous glands of the cartilage of the eyelid, which are called meibomian. The secretion, at the same time, may be removed in insufficient volumes; as a result, when the purulent crusts are removed, pus begins to appear underneath them.
- Scaly blepharitis. When a person develops scaly blepharitis, which is also known as seborrhea of the eyelids, the edges of the eyelids become red and thickened, special scales are formed from the epithelium of the sebaceous glands and epidermis, which tightly adhere to the skin near the base of the eyelashes, hence the name of the problem.
- Rosacea. This is blepharitis, which is characterized by the appearance of barely noticeable reddish-gray nodules on the skin of the eyelids, which are covered with small ulcers. Sometimes this type of disease is also accompanied by common acne.
- Demodectic blepharitis. This is a type of disease that is caused by a special type of eyelash mite, which normally lives in the body of almost every person. But gradually their number increases, and the immune system weakens, which is why a similar disease occurs.
- Ulcerative blepharitis. It occurs when inflammation of the eyelash hair follicles occurs, and this inflammation is purely purulent in nature. Purulent crusts appear, under which bleeding miniature ulcers remain.
- Allergic blepharitis. A manifestation of a disease that occurs due to a person’s allergies.
- Chronic blepharitis. When the problem is started, it gradually moves into its chronic stage - and then its elimination becomes a more difficult task, chronic blepharitis is more complex in nature. In addition, such chronic blepharitis can be combined with chronic conjunctivitis.
There is also a classification of the disease according to its anatomical characteristics. Highlight:
- Angular, when predominantly the corners of the eyes become inflamed.
- Posterior marginal, when the edges of the eyelids are affected.
- Anterior marginal, when only the ciliary edge of the eyelid is affected.
What is stye on the eye?
Barley on the eye is a disease of the eyelid, characterized by inflammation of the hair follicle of the eyelash, the Zeiss sebaceous gland or the lobule of the meibomian gland.
Other names for the disease are hordeolum.
The hair follicle and sebaceous gland of Zeiss are located on the outside of the eyelid, and the meibomian gland is located inside, and therefore, they separate the external or internal barley. Another input from this information is that it is more correct to call this disease stye of the eyelid, and not the eye, however, to expand the circle of readers, in the article we will call it stye of the eye.
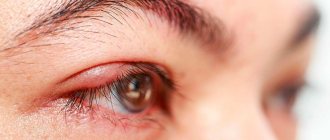
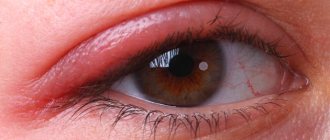
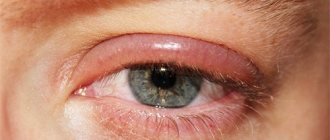
The main symptom of stye is inflammation and swelling of the eyelid, which, as the inflammatory process develops, turns red, increases in size, begins to hurt, and then a sac with purulent contents forms.
The main culprit of barley on the eyelid is Staphylococcus aureus (about 95% of all cases of the disease), however, inflammation is unlikely with strong immunity, so the development of the disease is due to a combination of the two above factors.
Development of the disease
The development of barley, as we have already said, is possible due to a combination of two main factors - penetration of an infection under the skin, in our case staphylococcus and weakened immunity.
Staphylococcal infection is almost always present on the surface of the skin, but the body’s protective functions do not allow it to spread inside the body, however, some factors that weaken the immune system still play an important role in the development of staphylococcal diseases.
Among the main reasons for a weakened immune system are stress, hypothermia, the presence of various diseases, especially infectious ones, and vitamin deficiency (hypovitaminosis).
Of course, if a person adheres to the rules of personal hygiene - does not touch his eyes or face with dirty hands, then the spread of infection is also minimized.
Development of barley. The development of barley begins with the penetration of infection into the eyelash follicle, which is actually a “micropocket” for the eyelash, and moving further, staphylococcus settles in the eyelash bulb, which is its root or a small branch - the Zeiss sebaceous gland. If the infection penetrates under the eyelid, it can settle in the meibomian gland duct. For a better understanding of the localization of the disease, below is the structure of the eyelid with these places (highlighted in red):
Next, the infection begins to actively multiply in these places. At the same time, an inflammatory process develops. First, at the site of the inflamed bulb, healthy cells die and begin to fester. The site of inflammation begins to swell, turn red, increase in size, forming some kind of hard compaction. In addition to external signs, as the disease develops, a person feels severe itching, and when touching the inflamed area, pain.
Due to the peculiarity of the localization of potentially vulnerable areas of stye formation, swelling and pustules appear only on the edges of the upper or lower eyelid.
The formation of an abscess usually occurs 2-4 days after infection of the eyelid. At this stage, the conjunctiva also turns red. A small ball with yellowish purulent contents forms on the seal. More than one abscess can also form on one eyelid.
Full ripening of barley occurs in 3-7 days.
Severe infection against a background of weakened immunity can additionally cause an increase in body temperature to 38 ° C, nausea and other signs of intoxication of the body.
After full ripening, usually on the 3-4th day, under the pressure of purulent masses, the abscess usually breaks through, the pus along with dead tissue comes out, after which the pain goes away and the stye on the eyelid resolves on its own, however, if the stye does not go away for more than one week, contact ophthalmologist. After spontaneous opening of the abscess, the swelling quickly subsides, and literally the next day, only slight swelling remains, but the redness of the eyelid remains for another couple of days.
Sometimes the abscess does not open without permission, and the barley spontaneously resolves, but there are cases when the usual form of the disease turns into the so-called cold barley (chalazion). A characteristic feature of chalazion is the long development and course of the inflammatory process, which lasts about 1-2 months. In some cases, if a chalazion does not go away on its own, it requires surgical removal.
Symptoms of the disease
At the beginning of the development of the disease, the patient feels itching of the ciliary edge of the lower eyelid. Scratching the eyes makes the itching worse. Redness of the skin appears in the area where the eyelash exits at the edge of the lower eyelid. Over a short period of time, the affected area of the eyelid swells, becomes tense, and is very painful when pressed. In advanced cases, in the absence of treatment, the patient's entire eyelid area swells, and it becomes impossible to open the eye.
In people with chronic diseases (especially in patients with diabetes mellitus, HIV infection), barley can be multiple. In such cases, local symptoms are accompanied by a general reaction of the body, characterized by high temperature, enlargement of the occipital and postauricular lymph nodes.
After a few days, uncomplicated barley begins to regress. A purulent point appears in the central part of the formation, and a purulent core gradually forms. From this moment on, the symptoms of inflammation begin to decrease. On days 5-7 from the onset of the disease, the barley opens and the purulent contents come out. The skin of the lower eyelid takes a couple of days to heal.
Treatment
You should not try to open a stye or squeeze out its contents yourself, as this can cause the infection to spread, followed by inflammation of the eye socket (cellulitis) or meninges (meningitis), which can be fatal.
As with any inflammatory process, exposure to heat is contraindicated for barley, as this can contribute to the spread of inflammation to nearby tissues and the development of serious complications. The use of warm compresses is contraindicated, as this causes maceration of the skin and also contributes to the spread of the inflammatory process to adjacent tissues with the formation of an abscess.
During treatment, it is better not to use cosmetics; it is forbidden to wear contact lenses.
For the treatment of barley the following is used:
1. In the first few days, before the barley ripens, the swelling is carefully treated with ethyl alcohol or an alcohol solution of brilliant green, iodine, and calendula tincture.
2. Antibacterial drops (Floxal, etc.) or eye ointments, for example, Floxal eye ointment.
A broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent, ofloxacin, from the group of second-generation fluoroquinolones, has proven itself well. It is embedded in the cell walls of bacteria and blocks the work of enzymes responsible for the reproduction of DNA molecules, after which the bacteria lose the ability to reproduce and die. Ofloxacin is the active ingredient of the drug Floxal, which is available in the form of eye ointment and drops and has a pronounced antibacterial effect. For barley, antibacterial ointment is applied to the inflamed area, the characteristic swelling of the eyelid, at least 3 times a day until the symptoms disappear completely, but for at least 5 days even if the symptoms disappeared earlier. For bacterial conjunctivitis (red eye with purulent discharge), drops are instilled 2-4 times a day until symptoms disappear completely, for at least 5 days in a row.
3. If the body temperature is not elevated, the doctor may prescribe UHF to accelerate the ripening of barley.
In the case of a recurrent course of the disease, drugs are used aimed at activating the body's defenses (vitamins, adaptogens, yeast preparations); autohemotherapy is indicated.
Treatment of internal stye
Suitable treatment for internal stye is determined by a specialist - an ophthalmologist. He conducts a preliminary examination and determines the complexity of the disease. For each patient, therapy is selected individually depending on the physiological characteristics of the patient’s body and the nature of the disease.
Often medications are prescribed to treat meibomitis. But additional treatment can be used to speed up recovery.
Use of ointments
Treatment of internal styes on the lower and upper eyelids is often carried out using special ointments. They should be prescribed only by an ophthalmologist according to the indications and course of the disease.
For meibomitis, the following external remedies can be used:
- Tetracycline ointment. This is a safe and effective external remedy, during the use of which no burns are formed on the surface of the mucous membrane and cornea. The ointment is recommended to be used from the first day of detection of the disease until it disappears. Apply to the inner surface of the eyelid 3 times a day;
- Phloxal. This remedy is considered effective and safe, it can be used for meibomitis. The ointment can be used by adults and children;
- Hydrocortisone ointment. The drug is recommended for severe forms. It should be applied as a compress to the eyelid area. It is recommended to use up to three times a day.
Ointments for internal barley
Treatment with drops
Internal styes of the lower and upper eyelids can be treated with eye drops. They can be used additionally together with ointments. Drops eliminate inflammation and have a disinfecting effect.
Particularly popular among drugs in the form of drops for the treatment of meibomitis are:
- Albucid. These are the most affordable drops that help eliminate a number of infectious eye diseases, including internal stye. However, they can cause itching, burning, and increased tearing;
- Tobrex. The product has a direct effect on the area of inflammation. Active substances attack the infection and accelerate the resorption of the abscess;
- Gentamicin. Drops are often prescribed in severe cases when other drugs have not helped eliminate the disease.
Drops for internal stye
Physiotherapy
Various physiotherapeutic procedures help eliminate early forms of internal stye. They can also be used as a supplement in the treatment of advanced internal stye.
The following physiotherapy methods are often used:
- Microwave therapy;
- Irradiation with ultraviolet rays;
- Electrophoresis;
- Dry air shower.
Folk remedies
For internal barley, folk remedies can be used. They help quickly eliminate pain, speed up recovery and improve overall condition. Folk remedies do not have harmful effects and have no contraindications, so they can be used independently without a doctor’s prescription.
The following are considered the most effective:
- Lotions with calendula. Add 1 tablespoon of calendula flowers to a glass of hot water. Let it sit for about an hour. It is recommended to make lotions from the tincture 2-3 times a day. The duration of each session is 15 minutes.
- Aloe. The leaves of the plant must be cut into small pieces and filled with hot water. The mixture is infused for 10 hours. Next, it is applied to the affected area several times a day.
- Applying heated salt. Table salt needs to be heated a little in a frying pan over a fire. Next, it is transferred to cotton fabric and wrapped. After this, it is applied to the sore area and left until it cools completely.
Symptoms
Although the symptoms of blepharitis vary greatly depending on what type of blepharitis a person develops, there are some basic signs of the disease that appear in most cases. Main symptoms of blepharitis:
- redness and characteristic swelling of the eyelids;
- impaired growth of eyelashes or their loss in large quantities;
- heaviness and itching sensations along the edges of the eyelids;
- rapid eye fatigue with little strain on them;
- discomfort and increased lacrimation from bright light.
Other symptoms of different types of blepharitis may vary depending on what type it is. Its simple appearance is characterized by swelling of the edges of the eyelids, dilated ducts of the meibomian glands, redness of the eyes, discharge and accumulation of whitish-gray plaque in the corners of the eyes.
The scaly/seborrheic type, in addition to thickening and redness of the eyelids, is accompanied by the accumulation of epidermal scales and epithelial tissue on their edges, as well as in the area of the eyebrows and hair on the head. The course of the disease may be accompanied by symptoms of blepharitis such as severe lightening of eyelashes or their profuse loss.