Why do my eyes itch?
Reasons why a child scratches his eyes include:
- teething,
- foreign body entering the eye,
- dacryocystitis,
- conjunctivitis,
- demodicosis
The baby may rub his eyes when moving from a dark room into a brightly lit room.
Sometimes a child rubs his eyes due to a bad habit. Such children need to be weaned off it by transferring their attention to another activity, otherwise they can get an infection in the eye.
Itching may be caused by the use of certain medications (in this case, you should consult your pediatrician - they may have to be discontinued).
Possible causes of itchy eyes in a child
It is impossible to miss the appearance of problems in a baby: the baby becomes restless and irritable. Individual symptoms will more clearly indicate the cause of this condition. In particular, itchy eyes usually suggest a local problem rather than a systemic disease.
Pathological
The most common cause of itchy eyes is the activation of pathogens due to infection. The diagnosis can be made very differently (depending on the location of the inflammatory process):
- conjunctivitis;
- blepharitis;
- uveitis;
- blockage of tear ducts.
Typically, this causes swelling of the tissues of the organ of vision, redness of the whites of the eyes, and increased lacrimation.
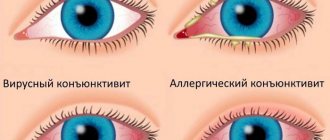
Itchy eyes can also be a sign of allergies. The child’s body is quite weak and does not always adequately perceive the surrounding world, particles of which may be allergens. Especially often, such manifestations appear in the autumn-summer period, as well as after the appearance of new dishes on the menu.
The child may have systemic diseases such as ARVI or influenza. Itching, lacrimation and discomfort may well be part of the overall clinical picture.
Not related to diseases
Very often, the reason why a baby’s eye itches is that a foreign body – a speck or grain of sand – gets into it. Unlike adults, children do not always keep their hands clean, and they then rub their faces with the same hands, including touching the mucous membrane of the eyeball. The consequence of this is irritation, discomfort and itching.
A provocateur of this condition can be eye fatigue. This is especially true for preschool and school-age children who like to spend time in front of a monitor screen or gadgets (phones, tablets). This modern trend is leading to earlier onset of vision problems. Fatigue in the eyes and itching indicate the body’s inability to recover, and it needs a break.
Causes of problems in infants
If the baby begins to show anxiety and rub his eyes, then there is a high probability that the cause is the growth of new teeth. If you look into your baby's mouth, you will see swollen gums - a harbinger of the imminent appearance of teeth. There are special products that, when applied to the gums, reduce pain and cool the tissue. The baby forgets about the pain and feels good again.
However, it is still worth sharing your concerns with your pediatrician, because it is very easy to miss the symptoms of serious diseases.
Foreign body in the eye
Accompanied by redness. You can try to get the mote yourself:
- 1. Wash your hands thoroughly with soap.
- 2. Examine the conjunctiva of the lower eyelid. To make the child look up, his attention is attracted by a rattle, and at this time the eyelid is gently pulled down.
- 3. Remove a speck or eyelash using a dry cotton swab or a cotton swab moistened with a solution of strong tea. If this happens during a walk, you can use the corner of a clean handkerchief.
- 4. Repeat the procedure with the upper eyelid.
- 5. After removing the foreign body, wash the eyes with plenty of clean water or a solution of strong tea.
To prevent infection, it is recommended to use drops - a solution of chloramphenicol or Albucid. If the parents were unable to get the foreign body, then you need to contact an ophthalmologist.
Prevention of eye diseases in children
It is probably already clear that the basis for the prevention of infectious diseases is hygiene, cleanliness and lack of contact with sick children .
The child should regularly consume vitamins in the form of fruits and apples or pharmaceutical preparations.
Teach children from an early age not to rub their eyes with dirty hands and not to play in dusty places outside.
If an allergy is detected, try with the help of a doctor to identify and remove the allergen from the child or carry out appropriate treatment.
To prevent more severe cases, the child should be regularly examined by an ophthalmologist .
Dacryocystitis
Represents inflammation of the lacrimal sac caused by narrowing or blockage of the lacrimal duct. Usually it is accompanied not only by itching, but also pain.
For treatment, newborns are given a special light massage to eliminate blockage of the duct. Use antibacterial drops and ointments as prescribed by a doctor.
Dr. E. O. Komarovsky believes that it is impossible to cure the disease with drops alone, and recommends regular massage. The technique proposed by the specialist is as follows:
- 1. Wash your hands, trim your nails if necessary.
- 2. Lubricate your finger with baby cream.
- 3. Clean the child’s eyes with a cotton pad soaked in a furatsilin solution.
- 4. Place the baby on a flat surface.
- 5. Use your finger to feel the dense lacrimal sac located between the corner of the eye and the eyebrow.
- 6. Apply light pressure from the eye to the nose (5-10 repetitions). This will clear the blockage and cause the membrane to rupture.
- 7. Apply drops to your eyes (as prescribed by your doctor).
Watery and itchy eyes: advice from traditional medicine
As a first “self-help”, if the cause of the itching is known (overwork, dust, burn of the mucous membrane), until the patient reaches the doctor, and, sometimes, as an addition to the already prescribed treatment, you can use traditional medicine.
We still have recipes from our grandmothers from childhood - decoctions and infusions of various medicinal herbs. They help in some cases quickly, and, most importantly, safely, if the eyes of an adult or even a child are watery and itchy.
In first place are chamomile and calendula, which can be called a panacea for various inflammatory processes, including watery eyes and itchy eyes. Decoctions and lotions with chamomile and calendula give a very good anti-inflammatory effect. They should be used repeatedly throughout the day, carefully rinsing the eyes.
There are several other herbs that also have a strong anti-inflammatory effect - plantain, cornflower, calendula and cumin. This will enhance the healing effect, and recovery will come faster. Herbs and lotions made from them can also be used if a child’s eyes itch and the reason is clear (dust or grains of sand, dirty hands, etc.).
Another very accessible recipe from the home archive: compresses made from warm tea leaves. If you do this procedure 4-5 times a day, then after a while the long-awaited effect will occur: your eyes do not water, do not itch, and do not hurt. You can use tea bags for this purpose.
A potato mask is very effective at home. The potatoes need to be grated and applied to the eyes on a thin layer of gauze for an hour. On this day, it is advisable to give your eyes a break from reading, cosmetics, TV, and computer. If it is not possible to quickly make such a mask, you can apply a couple of potato circles to your tired eyes and lie with them for 20 minutes.
When your eyes are tired from reading for a long time, watching the monitor, watery, itchy and sore, a decoction of millet is useful. Brew two tablespoons of millet in a liter of boiling water and simmer over low heat for ten minutes. The eyes are washed with a warm decoction in the evening, and before going to bed, it is applied as a lotion to the eyes for five to seven minutes.
Dill seeds also have a good effect on lacrimation. They are poured with cold water (proportions: 1 tablespoon of seeds to 2 glasses of water), boiled and left for several hours. In the evening, lotions are made with warm infusion for ten minutes.
Lily of the valley infusion lotions are also very effective. A glass of boiling water is poured into one teaspoon of dry lily of the valley mixture; infuse for half an hour.
If the inflammation has gone far and pus appears, it is recommended to wash the eyes with boric acid or furatsilin three times a day. And at night, apply a mask of fresh cottage cheese (wrapped in gauze).
As you can see, traditional medicine knows a wide variety of time-tested recipes, from which there is plenty to choose. They are suitable not only for adults, but also for children whose eyes are watery and itchy, since the plants used are completely safe.
Conjunctivitis
If the eyes are red and the baby constantly scratches them, conjunctivitis is possible - inflammation of the mucous membrane. Can be viral, bacterial, allergic.
In a baby
Many people believe that the disease does not occur in infants, but often it develops in newborns with a reduced level of immunity.
Premature babies are at risk. The reasons for the development of conjunctivitis are very diverse. Depending on them, gonococcal, chlamydial and viral forms of the disease are distinguished. The bacterial staphylococcal form is rare in newborns.
Gonococcal
Non-compliance with the hygienic regime in the obstetric hospital cannot be excluded as a reason. Babies develop gonoblenorrhea or gonococcal conjunctivitis, which appears on the 2-3rd day after birth, since infection occurs during childbirth. This is a very dangerous form of the disease that leads to loss of vision. In addition to itching, the situation is accompanied by severe swelling and redness of the eyelids.
The form is treated with sulfonamides and broad-spectrum antibiotics. In maternity hospitals, it is mandatory to prevent the disease by washing the eyes with furatsilin and instilling a solution of sodium sulfacyl.
Sulfacyl sodium itself can cause itching and conjunctivitis.
Chlamydial
Infants can develop chlamydial conjunctivitis when pathogenic microorganisms are transmitted from the mother during childbirth. Usually occurs on the 14th day from birth, less often – a month later. Films form on the lower eyelid, which can be easily removed. The disease is manifested not only by itching. Sometimes it causes complications in the ears in the form of otitis media, and other inflammatory processes develop. Signs of general intoxication are also possible - fever, headaches. This infection is treated with antibiotics.
Viral
Viral conjunctivitis is often caused by the herpes simplex virus. This form usually affects one eye and lasts a long time, but is sluggish. The eyes itch and blisters appear on the eyelids. Adenoviral infection is less common in infants, but it also leads to conjunctivitis. Then other signs of ARVI appear.
The child has a fever and a stuffy nose. In such cases, antiviral drugs are prescribed, for example Viferon. The eyes are washed with antiseptic solutions, sage infusion (1 tablespoon per glass of boiling water, be sure to strain before use).
In preschoolers
Bacterial and allergic forms of pathology are common in preschool children.
Bacterial
The bacterial form of conjunctivitis is typical for children aged 2-7 years. The incubation period of the disease is 1-3 days. The main causative agent of the bacterial form is Staphylococcus aureus. Both eyes are involved in the inflammatory process - the baby constantly rubs them. They turn red, purulent discharge and crusts appear in the inner corners.
In such cases, the doctor prescribes rinsing with an antiseptic solution, drops based on broad-spectrum antibiotics, for example, furatsilin.
Antibiotics are selected depending on the age of the child. Tobrex drops or preparations based on chloramphenicol solution are effective. At first, the frequency of instillation will be maximum, 6-8 times a day, then it decreases. Treatment usually takes 2 weeks.
Allergic
Allergic conjunctivitis in preschool children is caused by contact with pet hair or pollen, or a reaction to food. A distinctive feature is that the baby sneezes often. In order to get rid of the problem, you need to eliminate the allergen. Therefore, treatment involves following a hypoallergenic diet, when chocolate, citrus fruits, eggs, cow's milk, and seafood are removed from the diet.
The child is prescribed age-appropriate antihistamines. Fenistil drops can be given as early as two months of age. As for itching, it is eliminated with the help of drops based on sodium cromoglycate.
Treatment
Treatment of red eyes should be comprehensive and based on the overall clinical picture. So, if redness is accompanied by the release of purulent contents, there is a high probability that antibiotic therapy is necessary. In this case, parents should definitely seek help from a specialist.
At an appointment with an ophthalmologist, he will ask for complaints, collect a history of life and illness, and also conduct a number of necessary laboratory and instrumental studies:
- ophthalmoscopy, which examines the vessels of the fundus;
- tonometry allows you to measure intraocular pressure to exclude glaucoma;
- microbiological examination of purulent discharge to determine the pathogen;
- biomicroscopy is used to detect pathology.
ATTENTION! Do not neglect to contact a specialist if your child’s eyes are red, especially if it is accompanied by itching, swelling and irritation.
First aid
In acute conditions, first aid consists of limiting the child from the source that caused the redness of the eyes. Also, the eyes should be treated with saline solution or rinsed with boiled water.
The next step is to immediately seek medical help, especially in cases where redness of the eyes is also accompanied by severe pain and swelling.
Alarming symptoms that parents and doctors should pay attention to are the following:
- herpetic rash;
- sharp pain when pressing on the eye;
- reduced visual acuity, blurred vision;
- the child complains of spots in front of his eyes;
- erosions and ulcerative lesions of the cornea;
- the appearance of nausea and vomiting;
- purulent discharge;
- increased sensitivity to light;
- lacrimation;
- increased intraocular pressure.
How to properly treat your eyes if you get a foreign object
If irritating substances or foreign objects get into the eyes, it will be enough to simply rinse the child’s eyes with boiled water and pat dry with a towel.
To do this, if you are at home, pour clean water into a small glass and bring it to your face so that your eye is immersed in this water. After which you need to blink several times. If possible, it is better to pour 0.9% saline solution instead of water.
If you encounter such a problem on the street, wait until increased lacrimation begins and the foreign body is removed along with the tear fluid. If this does not happen, bend the upper eyelid up or the lower eyelid down and remove the speck with a clean scarf or a handy piece of cloth.
ATTENTION! Under no circumstances should you use products that irritate the mucous membranes.
If symptoms do not improve after rinsing the eyes, and your child continues to experience redness, swelling, pain, and itching, consult a doctor immediately.
Medicines
If inflammation of the mucous membrane was caused by pathogenic microorganisms, drug therapy is necessary. Typically, it involves the use of broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs in the form of ointments or eye drops. This group of medications is prescribed by the attending physician, who will conduct the necessary research and select the required doses.
The most common medications are listed below:
| A drug | Indications for use | Mechanism of action, effects |
| Albucid – 20% drops | Inflammatory infectious diseases affecting the organ of vision | Antibacterial effect due to the active substance of the drug - sulfacetamide. |
| Vitabact | Conjunctivitis | Anti-inflammatory agent with antibacterial effect. The active substance is piclosidine (an antiseptic drug). |
| Levomycetin | Group of ophthalmological diseases (conjunctivitis) | Antibacterial effect |
| Torbex | Infectious inflammatory processes localized in the eye area (uveitis, blepharitis, conjunctivitis) | Antibacterial effect |
| Bacitracin/neomycin | Acute blepharitis | Bactericidal effect |
In addition to antibacterial drugs, your doctor may prescribe other groups of medications:
- antihistamines for allergic reactions;
- antiviral (if the causative agent is the herpes virus);
- drops that moisturize the eyeball are indicated for dry eyes;
- antihypertensive medications for increased intraocular pressure (glaucoma);
- in some cases, the doctor may also prescribe glucocorticosteroids;
- neurotrophic agents to improve the functioning of the visual organ.
Surgical treatment may be required if the tear duct is blocked and neoplasms are detected.
Folk recipes
Traditional medicine methods include:
- for dacryocystitis - massage of the lacrimal sac;
- herbal lotions;
- use of tea leaves;
- Ice compresses to relieve swelling and irritation.
Therapy with various foods:
- cucumber, slices of which are applied to the eyes closed for no more than 5 minutes;
- chop the potatoes on a fine grater and squeeze out the juice, in which you then need to moisten a cotton pad and apply it to your eyes;
- Heat the milk, soak a cotton pad in it and apply it to your eyes for no more than 10 minutes.
Useful video
Causes of red eyes in children and how to treat the pathology?