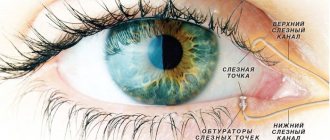
Why does mucus occur?
The causes of mucus in the eyes vary. This is usually associated with:
- with eye diseases;
- allergies to cosmetics, eye creams, food;
- severe strain on the visual organs.
White mucus in the eyes occurs when there is excess dust. It accumulates and is removed during sleep. Mucus in the eyes causes discomfort, but timely measures will quickly eliminate it.
Possible ailments
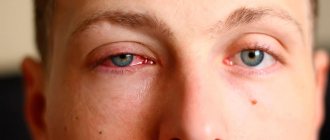
The nature of the mucus in the eyes can determine eye disease. If white discharge periodically occurs in the morning, but there are no symptoms of inflammation, then this is normal. With the regular appearance of mucus and the presence of other complaints, there may be ophthalmological ailments:
- If white mucus comes out of the eyes, this may be a symptom of viral diseases. For example, this happens with viral conjunctivitis. Still white, stretchy mucus is released from the eyes after an acute respiratory viral infection. Redness of the mucous membrane and sclera, lacrimation, photophobia, swelling, and cold symptoms also appear. When the virus occurs, first one visual organ is damaged, and then the second.
- Mucus in the eyes also appears with dry eye syndrome. Dryness and fatigue of the visual organ occur. Appears after long hours of hard work at the computer or with small objects.
- Liquid discharge is considered a symptom of allergies. Usually both eyes are affected. With this phenomenon, severe itching occurs. There is redness of the eyelids and swelling. When the allergen is eliminated, the symptoms subside.
- Liquid transparent discharge occurs from dust and foreign bodies. This is a protective reaction of the body. In this case, it is necessary to remove foreign particles mechanically.
- Yellow, profuse discharge occurs due to inflammation of the lacrimal sac - dacryocystitis. The mucus is thick and abundant. It intensifies when massaging the affected area.
- The appearance of greenish or yellowish foamy discharge is associated with blepharitis - inflammation of the eyelid. This disease causes itching, peeling, and swelling of the eyelids. The discharge is sticky, occurs in the morning, and sticks the eyelashes together. They create dense scales and crusts.
- Thick yellow, green discharge is a symptom of inflammation that appears when white blood cells accumulate. It occurs with bacterial conjunctivitis, viral and fungal infections of the cornea, trachoma, and barley opening. Dense crusts also form, which are difficult to remove. A film appears on the eye, interfering with the clarity of vision. There is redness, swelling, lacrimation, photophobia. In difficult cases, pain in the eyes, headache, and high fever are observed.
- Thread-like discharge appears with filamentous keratitis. This disease occurs when the function of the lacrimal glands is reduced. Dryness, burning, thread-like discharge, and redness of the sclera occur. This causes dystrophic changes in the cornea.
Why does mucus come out of the eyes and accumulate in the corner? The reason is the anatomical structure of the organ of vision. The corner is slightly recessed in the orbit compared to other structures. Therefore, liquid secretions flow there most easily. There is an outlet for the nasolacrimal duct. With its inflammation, pus comes out in the corner.
Discharge from the eyes of a child
Young children are not able to describe their complaints, so parents have to take a closer look at the health of their child. If the baby begins to actively rub his eyes, this should alert you. Typically, the appearance of discharge is preceded by swelling and redness. Current formations with inflamed eyelids and a yellow crust indicate the addition of an infectious process.
The following symptoms may indicate the presence of eye diseases in a child:
- refusal of food;
- restless sleep;
- frequent blinking;
- irritability, moodiness;
- increased sensitivity to bright light;
- eyelid hyperemia;
- tearfulness;
- blurred vision;
- swelling in the area of the bridge of the nose;
- yellow or white discharge in the corners of the eyes;
- stinging, burning and pain in the eyes;
- Stretching mucus from the eyes.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with About the eyes of Mirzakarim Sanakulovich Norbekov
In what situations should you immediately contact a specialist? Let's look at four main reasons:
- yellow discharge;
- swelling and redness of the eyelids;
- crust formation;
- the pain becomes constant.
In children
Discharge from the eyes in newborns appears due to dacryocystitis. The cause is obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct, which is associated with its underdevelopment. The baby experiences redness, swelling, and yellow discharge. The child becomes capricious and rubs his eyelids.
For treatment, massage of the lacrimal sac, rinsing with antiseptics, and topical antibiotics are used. If this is ineffective, the nasolacrimal duct is washed with a probe.
In children, discharge from the eyes appears due to bacterial and viral infection. In the first case, the mucus will be yellowish, and in the second, whitish. The child usually cries, becomes lethargic, and scratches his eyes. Treatment is performed by washing with antiseptics, and local antibacterial drugs are prescribed (for bacterial infection). If there are crusts, they are soaked before removal to prevent damage to the skin.
It is normal to have a small amount of white content after sleep. The baby's body protects the eyes from microparticles. Treatment in this case is not required.
Diseases that provoke discharge
- Blepharitis is a chronic inflammatory process of the edges of the eyelids, which occurs against the background of infection by Staphylococcus aureus.
- Conjunctivitis is an inflammatory process of the outer membrane of the organ of vision (conjunctiva), which can have different etiologies.
- Ophthalmoherpes.
- Keratitis of fungal etiology.
- Corneal ulcer.
- Dacryocystitis is an inflammatory process in the lacrimal sac, from which green or yellow pus is released.
- Chalazion or Stye.
- Dry eye syndrome is a pathological process that develops due to insufficient tear production.
Often, the cause of pathological discharge from the eye in an adult is infection of an organ that has been weakened after surgery during rehabilitation. Inappropriately sized or dirty contact lenses can also cause this symptom. In some people, discharge appears after accidental chemical exposure or UV irradiation, as well as due to prolonged work at the computer.
Associated symptoms
In addition to the appearance of discharge from the eyes, other signs are likely to be present:
- blurred vision;
- burning sensation in the eyes;
- itching in the eyes and eyelids;
- severe drying of mucous membranes;
- pain in the eyes;
- profuse lacrimation;
- hyperemia of the sclera and skin of the eyelids;
- photophobia.
Sometimes, with eye discharge, symptoms of general malaise, fever, coughing, and sneezing occur. There may be body pain, rhinitis. Such symptoms occur with bacterial and viral infections.
Causes and mechanisms
If pathological exudate accumulates in the eyes, then with a high degree of probability the development of inflammatory disorders can be assumed. They can be provoked by bacteria, viruses and even parasites (Demodex). But there are also allergic origins of changes. The organ of vision has a rather complex structure, but most often the discharge appears when structures directly adjacent to the eyeball are damaged - the conjunctival sac, eyelids, lacrimal ducts. Therefore, it is necessary to exclude the possibility of the following conditions:
Local changes become both an independent disease and a sign of general disorders. Quite often they appear during a cold, and hypothermia and decreased immunity are predisposing factors. The danger of inflammatory pathology is that the infection can spread to the eye itself, which will lead to a deterioration in its function. The diseases occur not only in adults, but are also typical for children. Therefore, it is especially important to identify the cause of changes in time. Early diagnosis greatly facilitates further treatment and increases its effectiveness.
Any symptoms require analysis and detail. First, the doctor interviews the patient to identify complaints and find out how the disease began and progressed. When examining discharge from the eyes, one should note their characteristics. The main characteristics of the symptom include:
- Color: white, yellow, greenish.
- Type: mucous, purulent.
- Consistency: liquid, viscous, thick.
- Volume: abundant or scanty.
- Frequency of occurrence: in the morning or throughout the day.
- Provoking factors: rubbing the eyes, pressing on the lacrimal sac.
At the same time, a physical examination is carried out, which includes inspection and palpation. This allows us to establish objective signs of pathology. The complex creates a general picture of the disease, allowing a preliminary conclusion to be made.
If the eyes are running, then diagnosing the problem begins with finding out all the symptoms that are present in the patient.
Conjunctivitis
Inflammation of the conjunctival mucosa is the most common cause of eye discharge. Based on the type of pathology and its origin, the symptoms may have some differences. The most common signs of conjunctivitis are:
- Sensation of a foreign body, cutting.
- Redness of the eye.
- Swelling of the mucous membrane and eyelids.
- Tearing.
With bacterial inflammation, purulent discharge appears, which mainly collects after sleep. Due to the viscous and cloudy secretion, the eyelids stick together and plaque forms on them. First, one eye is affected, but due to poor hygiene, the infection spreads to the second.
Quite often, conjunctivitis appears to be a sign of a general respiratory disease. A viral infection is characterized by signs of general intoxication: fever, weakness, malaise, body aches. A runny nose occurs, and patients are bothered by a sore throat and cough.
Conjunctivitis with adenoviral infection is a sign that allows you to distinguish it from other colds. It can occur immediately or after some time from the beginning. The discharge is often scanty, enlarged follicles are visible on the mucous membrane, and sometimes a filmy coating forms. Inflammatory phenomena in the eye persist even after the temperature normalizes.
Small mucous discharge also appears in the allergic form of conjunctivitis. But in this case, severe redness and swelling of the eyelids, burning and itching in the eyes come to the fore. The addition of secondary bacterial flora leads to suppuration of the exudate, the mucus becomes white-yellow or greenish.
In addition to viral infections, conjunctivitis can be one of the manifestations of Reiter's syndrome. This is a condition caused by chlamydia. It is characterized by damage to the urethra, mucous membrane of the eyes and joints. Conjunctivitis is often combined with keratitis, iridocyclitis, and uveitis. Its manifestations can be scanty, but concomitant urethritis and arthritis are unlikely to go unnoticed.
When the eyelids become inflamed, viscous fluid may also be released from the eyes. But most often this is observed with demodectic blepharitis, which occurs due to tick-borne infestation. The outer edge of the eyelids itches a lot, especially in the morning, and sometimes the itching becomes almost unbearable. Stinging occurs in the eyes, sticky secretions collect, which stick together the eyelashes, further transforming into scales and crusts. The eyelids thicken and turn red. The disease has a chronic course; demodicosis can also affect other areas of the face: eyebrows, smooth skin.
Dacryocystitis
In cases where sticky fluid flows from the eye, it is necessary to think about a disease such as dacryocystitis. It occurs due to obstruction of the lacrimal canal (with ARVI, rhinosinusitis, nasal polyps, congenital anomalies, after injuries). Tears stagnate in the bag, which leads to the addition of secondary flora and the development of an inflammatory reaction. The secretion turns from transparent to cloudy mucopurulent.
The clinical picture of dacryocystitis is quite typical. The main symptoms of the disease include:
- Severe lacrimation.
- Swelling below the inner corner of the eye.
- When pressed, pathological exudate is released from the lacrimal openings.
The acute process is characterized by more striking signs. The skin turns sharply red, the swelling becomes painful, the eyelids are swollen, and the palpebral fissure does not close completely. Swelling may spread to the cheek and nose. Patients complain of pain in the orbital region, fever and other signs of intoxication. And after a certain time, a fluctuation forms in the center of the swelling, then pus breaks through the fistula outward or into the nasal cavity. The danger is that phlegmon of the orbit may form.
Discharge of pus from the eyes during dacryocystitis is a fairly characteristic sign, which, in combination with other symptoms, suggests a diagnosis.
Therapy
Mucus from the eyes of children and adults is removed with a cotton pad. It needs to be moistened in an antiseptic solution (“Furacilin”) and the pus removed in the direction from the outer part of the angle to the inner. Each eye is cleaned with a separate disk. This is first aid before going to a specialist.
To treat mucus in the eyes, the doctor may prescribe antibacterial, antiviral, antiallergic, anti-inflammatory, moisturizing drops and ointments. Rinsing with antiseptic solutions (Furacilin, a weak solution of potassium permanganate) is effective. In severe cases, glucocorticosteroids are prescribed intravenously.
The doctor prescribes medications based on the reason:
- Preparations with antibacterial action. These are Floxal drops and Tetracycline ointment.
- Antiviral agents - Acyclovir ointment, Ophthalmoferon drops.
- Medicines with antiallergic properties - Allergodil drops.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs - Indocollir drops.
- Moisturizing with a regenerating effect - Visin drops.
- Glucocorticosteroids - Prednisolone.
For dacryocystitis, massage of the lacrimal sac is effective. It improves the outflow of stagnant pus. Sometimes it is necessary to insert a probe to remove pus and rinse the lacrimal sac. The frequency of administration and duration of treatment are prescribed by an ophthalmologist after examination.
Treatment of eye diseases
There is no single approach to the treatment of this disease; it is the ophthalmologist who must decide what measures to take. Typically, antiallergic measures or removal of a foreign body from the eye, if any, are required.
In the case of conjunctivitis of infectious origin, such discharge appears only at the initial stage of development of the disease, after which it acquires a yellowish tint, which indicates the presence of pus. In this case, the treatment approach is based on identifying the type of pathogen. As a rule, they prescribe:
- Drops and ointments based on antibiotics: drops - Floxal, Tsipromed, Levomycetin, ointments - Erythromycin, Hydrocortisone, Tetracycline.
- Antiviral agents are selected individually based on the identified pathogen. Among the most common are Oftalmoferon, Acyclovir, Okoferon.
- Anti-inflammatory drops - Diclofenac, Diklo F, Nevanak, Zinc Sulfate, etc.
- Antiallergenic drugs – Opatanol, Olopatadine, Allergodil, Vizalergol. Floxal is used in the treatment of white discharge from the eyes
To treat barley, ointments are mostly used, because The drops did not work well due to the specific nature of their application to the damaged structure. Drops can only be used in the case of complex therapy for the treatment of meibomitis and chalazion.
As for the treatment of dacryocystitis in children, in this case we will not give recommendations, because in its drug therapy an exclusively individual approach is practiced, depending on the developmental characteristics of the child’s visual system and nasopharynx.
The treatment regimen is prescribed by an ophthalmologist taking into account the pathogen, stage of the disease, and the presence of complications. Almost all eye diseases require local treatment with medicinal solutions, compresses, and ointments. If eye diseases accompany diseases of the ear, nose, throat, or respiratory tract, then it is imperative to cure them, otherwise a relapse will occur. In such cases, an integrated approach is effective.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Pro-Visio eye tablets, use analogues
When a viral bacterial infection is associated, drops containing antibiotics (ciprofloxacin, chloramphenicol) are prescribed. To treat allergic eye diseases, you cannot do without topical antihistamines (drops, ointments) and tablets.
Eliminate discomfort and improve vision using lotions with a remedy such as a decoction of eyebright or mistletoe, as well as cornflower. You can also use chamomile, birch leaf, plantain, caraway, nettle, oak bark, yarrow, celandine, calendula (twice a day for ten days) or applications of carrots, cucumber, cabbage, dill, celery, aloe juice and Kalanchoe.
When barley appears at the beginning of the disease, you need to wipe the eyelid (or keep a soaked napkin on the sore spot until dry) with any alcohol-based cosmetic (eau de toilette, cologne) or apply heated (wrapped in cloth) flax seeds, sand, mustard (dry). Compresses made from raspberry, apple, currant, and cherry leaves (each plant separately) are effective. Drink the same decoction as tea for a long time.
For any eye disease, you should definitely go to a specialist, because otherwise you can simply lose your sight. You should not engage in self-diagnosis, especially since sometimes the cause can be quite difficult to identify, and a comprehensive examination is required. After this, the ophthalmologist will prescribe adequate therapy.
If you or your child has purulent discharge in the corner of the eye, accompanied by pain, redness of the eyeball, increased tearing, etc., you need to go to an ophthalmologist. Only he will be able to establish the exact reason why pus appears from the eyes.
Self-medication is very dangerous, as it can lead to serious problems, including complete loss of vision. Therefore, if the eye festers and waters, you must immediately go to the doctor. Only correctly selected and timely treatment will quickly get rid of suppuration and prevent the occurrence of complications against it.
Treatment of adults and children includes comprehensive measures to combat ophthalmological disorders. To determine the root cause, the pathological secretion is taken for analysis. Before going to a specialized facility, treat your eye. Soak a cotton swab with an antiseptic solution and wipe from the outer edge to the inner corner.
Depending on the underlying disease, antiviral or antibacterial agents are prescribed. In some cases, the use of systemic drugs may be necessary.
To treat allergic conjunctivitis, it is extremely important to determine the substance to which the body is hypersensitive and to eliminate contact with the allergen. Next, antihistamines are prescribed, as well as rinsing with solutions based on medicinal decoctions.
Viral conjunctivitis is treated with antiviral drops and ointments, as well as means to boost immunity. Pathological processes caused by exposure to fungal infections require an integrated approach to treatment. As a rule, this is a long and systematic struggle.
Traditional methods can only be used after a doctor’s permission, otherwise they may harm you. At home, you can prepare compresses and rinsing solutions yourself:
- prepare a regular aqueous solution based on table salt. You only need one pinch of salt, which is diluted in a tablespoon of warm boiled water;
- Use chamomile and calendula infusion as a rinse. Three tablespoons of dry raw materials are diluted in a glass of water. After the solution has cooled, it should be filtered. The resulting decoction can be used as a lotion;
- You can also use black tea leaves. It is used both in the form of lotions and for rinsing.
As they say, a hundred grams of prevention is better than a kilogram of cure.
The following tips will help you prevent the development of eye diseases:
- undergo preventive examinations with an ophthalmologist;
- You should use clean tap water as a wash;
- do not use other people’s decorative cosmetics;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- If possible, avoid contact with substances that can cause an allergic reaction;
- treat somatic diseases in a timely manner;
- if the quality of vision decreases, wear glasses;
- Do not select contact lenses yourself, entrust this choice to a specialist.
Yellow and brownish discharge from the eyes is a reason to use effective antimicrobial medications for topical use. The doctor will prescribe the medicine and the amount of administration during the day (drops or gel). It is optimal to use eye baths with an antiseptic solution before this to remove purulent discharge.
In the absence of an inflammatory reaction, the ophthalmologist will recommend standard antiallergic measures, detect and remove the foreign body, and give advice on optimal hygiene of the periorbital area. In case of excessive tearing, it is necessary to conduct a full examination to identify the root cause and get rid of the unpleasant problem.
The presence of discharge from the palpebral fissure is a good reason to visit a doctor: only a specialist, after an examination and hardware examination, will be able to make an accurate diagnosis and help cope with the pathological condition. It is strictly unacceptable to self-medicate using folk remedies, especially if problems arise in a child.
Complications and prognosis
The prognosis is positive. Timely treatment allows for quick results. The effect is noticeable within a few days. If therapy is chosen incorrectly or treatment is not performed, this leads to complications.
Eye discharge impairs visual acuity and allows infection to penetrate into the deep structures of the eyes. The negative consequence is cataracts and blindness. The most severe complication is panophthalmitis. This is a severe inflammation of the eye. It may require removal of the visual organ.
Eye protection
Although you need to get the “sunlight vitamin” for health, ultraviolet radiation can lead to various eye diseases. Cataracts often appear in older people. Therefore, when outdoors, it is important to protect your eyes from harmful UV rays with a wide-brimmed hat or sunglasses that block harmful UV light. If you have glaucoma associated with increased pressure in the eyeball, you should not wear dark glasses.
When working with carpentry tools, you must wear safety glasses. You should not ignore this rule, since failure to comply with it can lead to various eye problems.
When playing sports (basketball, baseball, tennis, hockey) you need protective glasses.
Eye problems occur when the air conditioner is running. Low humidity causes dryness. You need to use special drops that moisturize your eyes. You can also place a humidifier.
Prevention
Preventative measures must be taken. Then there will be no suppuration in the eyes:
- You should lead a healthy lifestyle: eat right, ensure good sleep.
- You need to properly care for your lenses and follow the recommendations for their use.
- Be sure to wash your face in the morning and evening.
- It is important to remove makeup before going to bed.
- Cosmetics and hygiene products must be individual.
- A protective mask (goggles) must be used in production.
- You should regularly perform eye exercises.
Preventive measures are very simple. It is necessary to follow them so that unpleasant discharge does not occur again. And if mucus does appear, then you need to use effective means to eliminate it.
Source
Therapeutic measures and prevention
To get rid of discharge, the doctor prescribes certain procedures to the patient, based on the nature of the discharge and the reason that caused it. Some manipulations need to be carried out in a hospital, while others can be carried out at home. If the discharge is severe, your doctor may prescribe antibacterial medications in the form of eye drops or oral medications to relieve symptoms.
Methods for eliminating eye discharge at home consist of using a sponge moistened with warm water, which is applied to the eye to soften the sticky eyelids. For women, it is important to promptly remove old eye makeup, which is one of the main causes of eye infection.
Caring for contact lenses, as well as replacing them, should be carried out strictly according to the advice of the attending physician. The lens case also needs to be changed regularly to a newer one. Traces of fat from the eyelids can be washed off very well with baby shampoos or other detergents. Avoid sharing personal hygiene products (towels, washcloths, etc.).