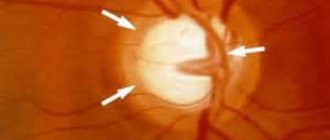
Indications for laser treatment of glaucoma
Therapy is carried out only with the consent of the patient and the treating doctor, who gives a referral after undergoing a full examination. The main indications for surgical intervention to reduce intraocular pressure are:
- narrowing of the peripheral field of vision;
- worsening of acuity;
- high IOP that cannot be controlled with medications;
- allergy to antihypertensive drugs.
Laser treatment is not performed for infectious, inflammatory and fungal diseases. It will not be performed on a patient with a cold, flu or fever.
Laser cyclocoagulation
Laser cyclocoagulation
is a surgical intervention aimed at reducing intraocular pressure by reducing the production of aqueous humor.
This method is used in the treatment of refractory glaucoma, pain syndrome at the terminal stage of the disease, long-term reactive syndrome after surgical interventions on the organ of vision.
The technique is based on partial destruction of the ciliary body and coagulation of the blood vessels supplying it. In this case, 20-25 laser coagulates are applied transconjunctivally, 3-5 mm in a circle from the limbus at 270-300°.
After laser cyclocoagulation, a persistent decrease in intraocular pressure occurs. In the postoperative period, the development of infectious complications, hemorrhage in the anterior chamber of the eye, detachment of the choroid, and hypotension is possible.
Laser cyclocoagulation
is a surgical intervention aimed at reducing intraocular pressure by reducing the production of aqueous humor.
This method is used in the treatment of refractory glaucoma, pain syndrome at the terminal stage of the disease, long-term reactive syndrome after surgical interventions on the organ of vision.
The technique is based on partial destruction of the ciliary body and coagulation of the blood vessels supplying it. In this case, 20-25 laser coagulates are applied transconjunctivally, 3-5 mm in a circle from the limbus at 270-300°.
After laser cyclocoagulation, a persistent decrease in intraocular pressure occurs. In the postoperative period, the development of infectious complications, hemorrhage in the anterior chamber of the eye, detachment of the choroid, and hypotension is possible.
Laser cyclocoagulation is a minimally invasive technique that is based on laser exposure to the ciliary body and its processes in order to achieve a hypotensive and analgesic effect.
The first experience of cyclodestructive surgical intervention dates back to 1936, when the German scientist A. Vogt developed a method of penetrating diathermocoagulation of the ciliary body. Scientists R. Smize and M.
Stein modernized the technique, proposing the use of ruby and neodymium lasers for the purpose of laser cyclocoagulation. Modern modifications involve the use of diode and YAG lasers.
Despite the long-term use of the method in ophthalmology, it still remains relevant, and due to constant improvement, high-tech. Along with trabeculoplasty, laser cyclocoagulation is used in the treatment of patients with glaucoma and is the method of choice in the terminal stages of the disease.
Compared to the YAG laser, diode laser exposure has been proven to be more effective and safe. To perform surgery via the transscleral or transpupillary route, special equipment and a team of qualified ophthalmic surgeons are required.
The endoscopic method of laser cyclocoagulation is also carried out using special equipment.
Indications and contraindications
Laser cyclocoagulation is used in ophthalmology to reduce intraocular pressure in patients with glaucoma resistant to other treatment methods. Indications for the use of this technique are the terminal stages of the disease with severe pain.
Surgical intervention is used to relieve long-term reactive syndrome after operations.
Laser cyclocoagulation is a highly effective treatment method for patients with angle-closure glaucoma caused by organic synechial blockade of the anterior chamber angle. The effectiveness of this technique in the treatment of patients with glaucomatous optic neuropathy has been proven.
Laser cyclocoagulation has limitations for use in patients with high intraocular pressure, therefore, at the stage of preoperative preparation, conservative treatment is not canceled.
Preparation for cyclocoagulation
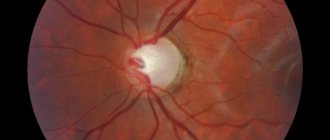
Before the operation, the ophthalmologist conducts an external examination, computer refractometry and biomicroscopy of the eye, and determines visual acuity. In the preoperative period, it is necessary to assess the condition of the inner lining of the eyeball and the optic nerve head using ophthalmoscopy.
If necessary, additional optical coherence tomography, B-mode ultrasound and automated perimetry are performed. Every day for a week before laser cyclocoagulation, the doctor measures intraocular pressure using non-contact tonometry.
Types of laser therapy
Main types of treatment:
- ALT. The most common type of laser surgery performed for open-angle glaucoma is argon laser trabeculoplasty (ALT). The goal of the surgery is to help fluid drain, reducing intraocular pressure, which can cause damage to the optic nerve and loss of vision. Cost - up to 55,000 rubles.
- Cyclophotocoagulation is recommended for patients with refractory glaucoma to reduce the secretion of aqueous humor and lower IOP by lasering the secretory epithelium of the ciliary body. Performed on patients with persistently elevated eye pressure. The procedure is outpatient. The price is high due to the use of new and improved equipment.
- The selective method is less traumatic for the eye than argon laser trabeculoplasty (ALT). SLT is a safe and effective procedure with minimal complications. It is performed on patients to reduce intraocular pressure. It is called selective because the laser used during the procedure has minimal thermal energy absorption and is absorbed only by selected pigmented tissue in the eye. Advantages - affects only specific pigmented cells, stimulates the body's mechanism to increase fluid outflow, reduces IOP by 30%, takes a few minutes and is performed on an outpatient basis. Cost - 43–90 thousand rubles.
- During a laser peripheral iridotomy, a laser makes 1 or 2 small holes through the iris (the colored part of the eye). This gives the fluid that normally circulates in the eye an alternative path to the corner where the fluid drains from the eye. The procedure is performed in a few minutes on an outpatient basis in a surgery center. Price - from 1500 rub.
Recovery and postoperative period
The effectiveness of surgical treatment largely depends on the patient’s compliance with the doctor’s instructions and recommendations in the postoperative period. Its duration varies from 5 days to several months, depending on the complexity of the manipulation, the health characteristics and age of the patient. Basic rules for quick recovery:
- For several hours after surgery, you need to wear a blindfold, use sunglasses and anti-glare computer glasses;
- For 10 days, avoid cosmetics, use of the pool and sauna. It is necessary to greatly limit washing and hair washing;
- You should minimize eye strain and avoid watching videos or reading for 10-14 days;
- stop drinking alcohol, fried and salty foods;
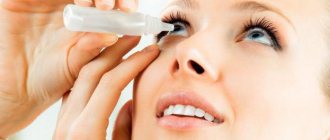
- carry out instillations on time. After surgery, antibacterial drops, NSAIDs and antibiotics are always prescribed.
Visual functions are normalized within 2-3 days from the date of the procedure. If fogginess persists and visual acuity is greatly reduced, or there are other complications, you should consult your doctor as soon as possible.
Advantages and disadvantages
Laser treatment is successful, with minimal trauma and a minimum of postoperative complications. Patients can repeat the procedure. All techniques involve creating an artificial tunnel for fluid outflow, thinning or expanding it. Therapy allows you to stabilize IOP and eliminate the constant use of medications.
We recommend reading: Glaucoma and the computer
The disadvantages of the procedures include:
- development of inflammation;
- damage to the lens;
- fusion at the site of impact of the impulse;
- instability of the effect.
Indications for surgery
The advisability of prescribing laser treatment for glaucoma is determined by ophthalmologists. They recommend it if taking medications does not provide relief or the medications are contraindicated for the patient. Often this method can harmoniously complement conservative therapy and reduce the number of medications taken.
The following types of glaucoma can be corrected with laser:
- open-angle (as well as its primary, pigment, pseudoexfoliative varieties);
- closed angle;
- juvenile (youth);
- secondary (traumatic or inflammatory).
The best results of the procedure are shown in chronic forms of the disease. In acute glaucoma, they are less effective; vision correction with their help is best carried out without an exacerbation. Also, treatment outcomes in young people are usually worse than in older age groups.
It is impossible to restore an already acquired vision defect using a laser - this method is intended only to slow down the development of glaucoma. The incidence of disease relapse is reduced in 80% of patients, but only if procedures were started before the late stages of the disease.
For people whose glaucoma is in the early stages of development, laser treatment is preferable to surgery. In their case, eye surgery can cause side effects that are as serious as the disease itself.
How is the operation performed?
Argon laser trabeculoplasty
How to prepare for the procedure:
- do not wear makeup;
- follow the doctor's instructions (do not use blood thinning medications, do not smoke, do not consume alcohol or nicotine 2-3 days before the procedure);
- plan your trip home in advance.
The operation is performed in the ophthalmologist's office. Before the procedure, the doctor will numb the patient's eye. The doctor will open the patient's organ of vision wide, the patient will see several short flashes of light and feel some discomfort.
The laser beam is directed at the drainage channel of the eye or trabecular meshwork, it opens it, helping the fluid to drain. Thus, intraocular pressure decreases sharply.
The procedure takes less than 10 minutes, and you can return home the same day of surgery. At the end of the operation, the surgeon administers medicated eye drops to prevent the initial increase in intraocular pressure.
Cyclophotocoagulation
The modern method of treating glaucoma is non-invasive. This method gives hope for restoring vision to patients who have not been helped by other techniques.
Method of conducting CFC:
- An anesthetic is instilled into the eyes.
- An eyelid expander is inserted to prevent the patient from blinking during surgery.
- A laser diode with a diameter of a fraction of a millimeter is directed into the ciliary body, which undergoes coagulation. During manipulation, the capillaries close. Due to this action, the pressure decreases because the ciliary body secretes less fluid.
The procedure takes 20-30 minutes and requires the use of drops to reduce post-operative inflammation. Most patients experience minimal postoperative pain. Cyclophotocoagulation is often combined with an injection of a painkiller (chlorpromazine) behind the eyeball.
Since no incisions are made, there are no postoperative restrictions. The patient is given an eye patch, with which he is forced to walk for the first 24 hours.
CFC is repeated if IOP has not returned to normal after the first procedure.
Selective laser trabeculoplasty
Stages of the procedure:
- An anesthetic is instilled into the eye several times.
- The visual organ is opened wide, laser radiation is supplied through a special microscope, the pulses of which are directed to the desired points of the drainage system.
IOP does not decrease immediately. The effect of the operation begins after 2–3 days. It is recommended that you continue to use eye drops during this time. After the procedure, regular examination by an ophthalmologist will be required.
Peripheral iridotomy
The procedure is performed while sitting in front of a slit lamp, similar to an eye examination. A temporary contact lens is placed in the eye for a few minutes to help focus the laser beam. Anesthetic drops are used. The process takes up to 10 minutes. During the procedure, the patient does not feel anything; some describe minor pain.
The laser creates an opening in the peripheral zone of the iris, the angle of the anterior chamber expands, and the outflow of fluid through the trabecula improves. After removing the lens, my vision is blurry for about an hour.
We recommend reading: Treatment of glaucoma at home
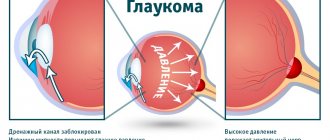
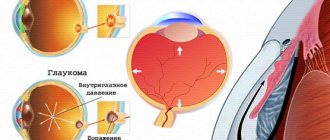
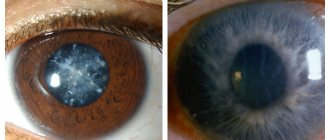
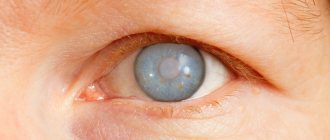
Glaucoma
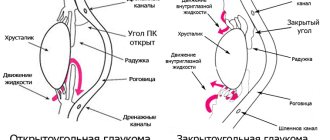
Glaucoma is a chronic eye pathology characterized by increased intraocular pressure, the development of optical neuropathy and visual impairment. Clinically, glaucoma is manifested by narrowing of the visual fields, pain, pain and a feeling of heaviness in the eyes, blurred vision, deterioration of twilight vision, and in severe cases, blindness. Diagnosis of glaucoma includes perimetry, tonometry and tonography, gonioscopy, optical coherence tomography, laser retinotomography. Treatment of glaucoma requires the use of anti-glaucoma drops, the use of laser surgery methods (iridotomy (iridectomy) and trabeculoplasty) or anti-glaucomatous operations (trabeculectomy, sclerectomy, iridectomy, iridocycloretraction, etc.). Open angle glaucoma
Open-angle glaucoma develops more often after 40 years of age. The hereditary factor has a certain significance. Glaucoma affects 1.5-3% of the population.
Symptoms and course:
The onset of the disease is gradual. Heaviness in the eyes appears, periodic blurring of vision, rainbow circles around light sources, over time the field of vision becomes narrower, its sharpness worsens, and pain in the temples and brow ridges may bother you.
Recognition:
Complaints allow one to suspect a disease, but unfortunately, there are cases when a patient goes to the hospital with an already blind eye. The main diagnostic method remains measuring intraocular pressure. Glaucoma causes narrowing of peripheral vision. Examination of the iris and fundus provides more information. Atrophy processes develop in the iris, pigment is washed out, and the optic disc turns pale. Modern methods make it possible to suspect glaucoma in the early stages - topography, examination of the central visual field, and examination of the anterior chamber angle are used.
Treatment:
Intraocular pressure should be below 26-27 mmHg when measured with a 10 g weight according to Maklakov. Conservative therapy: instill drops that narrow the pupil - 1-6% pilocarpine solution; reducing the secretion of intraocular fluid - 0.25-0.5% optimol, arutimol, timolol maleate, 0.125-0.5% clonidine, 0.1% adrenaline. If there is no effect, laser or microsurgical treatment is recommended.
Angle-closure glaucoma
Angle-closure glaucoma occurs differently. Its main clinical manifestation is an acute attack of glaucoma. A sharp pain appears in the eye, vision is reduced to light perception, the eye is hyperemic, there may be nausea, vomiting, headache, sometimes the pain radiates to the heart area, the floor of the scapula, and the abdominal area.
Recognition:
During an acute attack, intraocular pressure rises to 60 mmHg. However, the patient's condition can simulate an attack of angina, acute abdomen, food poisoning, or cerebrovascular accident.
Treatment:
Instill 6% pilocarpine every 15 minutes for an hour; prescription of diuretics - diacarb, furosemide; intramuscular and intravenous - Lasix; inside - glycerol, Epsom salt; distraction therapy - hot foot and hand baths, mustard plasters on the back of the head and calves, leeches on the temple. In the future, laser or surgical treatment.
General approach to glaucoma
There are three main approaches to the treatment of glaucoma: conservative (medication), surgical and laser. The choice of treatment tactics is determined by the type of glaucoma.
The goals of drug treatment of glaucoma are to reduce IOP, improve blood supply to the intraocular part of the optic nerve, and normalize metabolism in the tissues of the eye. Antiglaucoma drops according to their action are divided into three large groups:
Drugs that improve the outflow of intraocular fluid: miotics (pilocarpine, carbachol); sympathomimetics (epiphrine, dipivefrine); prostaglandins F2 alpha - xalatan, travatan).
Agents that inhibit the production of intrauterine fluid: selective and non-selective ß-blockers (betaxolol, betoptik, timolol, etc.); a- and beta-blockers (proxodolol).
Combined action drugs (fotil, cosopt, normoglaucon, etc.).
When an acute attack of angle-closure glaucoma develops, an immediate reduction in IOP is required. First aid begins with instillation of a miotic - 1% pilocarpine solution according to the scheme and timolol solution, prescription of diuretics (diacarb, furosemide). Simultaneously with drug therapy, distracting measures are carried out - cupping, mustard plasters, leeches on the temporal region (hirudotherapy), hot foot baths. To remove the developed block and restore the outflow of the intraocular fluid, it is necessary to perform laser iridectomy (iridotomy) or basal iridectomy surgically.
The methods of laser surgery for glaucoma are quite numerous. They differ in the type of laser used (argon, neodymium, diode, etc.), the method of action (coagulation, destruction), the object of influence (iris, trabecula), indications for the procedure, etc. In laser surgery for glaucoma, laser iridotomy and iridectomy, laser iridoplasty, laser trabeculoplasty, laser goniopuncture. For severe degrees of glaucoma, laser cyclocoagulation can be performed.
Antiglaucomatous operations have not lost their relevance in ophthalmology. Among fistulizing (penetrating) operations for glaucoma, the most common are trabeculectomy and trabeculotomy. Non-fistulizing interventions include non-penetrating deep sclerectomy. Operations such as iridocycloretraction, iridectomy, etc. are aimed at normalizing the circulation of intraocular fluid. In order to reduce the production of intraocular fluid in glaucoma, cyclocryocoagulation is performed.
Patient reviews
Larisa: I cannot but agree that laser surgery is the only alternative option. I used eye drops for a long time, but my IOP continued to rise. After cleaning the ducts through which the fluid flows, everything returned to normal. If necessary, I will agree to surgery again.
Olga: Glaucoma was recently discovered and drops were prescribed. But they warned that the disease cannot be stopped, only surgery will help. They read reviews about laser treatment, I plan to do it in the coming year.
Karina: I am diagnosed with diabetes, I undergo examinations by an ophthalmologist every six months, because my vision is deteriorating greatly. So the government ophthalmologist missed my glaucoma. The disease was discovered at the second stage, when I turned to a private ophthalmologist. The operation was performed and the outflow was restored. I'm afraid I'll have to do it again, but it's better than constantly dripping drops.
Laser treatment of glaucoma
Glaucoma surgery has undoubted success, however, it becomes obvious that no matter how great the achievements in the technique of micromanipulation, no matter how small the cutting blade is, even the maximum potential of its capabilities is incommensurate with the task of correcting the pathology of the microstructures of the thinnest filtering zone. eyes. In this regard, the question inevitably arises about searching for ways of “knifeless” microsurgery for glaucoma.
A unique opportunity for this is a laser beam, with which you can perform operations on the membranes and inside the eye without opening its cavity, i.e. without cutting the wall. Laser surgery for glaucoma is performed using a medical laser. The laser beam can be focused into a pinpoint light spot, which plays the role of a “laser needle” or “laser knife”.
LASER TREATMENT OF GLAUCOMA IS PAINLESS, DURABLE AND IS CARRIED OUT ON AN OUTPATIENT BASIS, ALLOWING YOU TO AVOID SURGICAL INTERVENTION ON THE EYEBALL.
Treatment of glaucoma with a laser, unlike surgery, does not require general anesthesia and can be performed on an outpatient basis with a minimum duration of postoperative release from work. Since laser surgery for glaucoma is performed without opening the eye, it is not accompanied by the complications that can arise during and after antiglaucomatous microsurgical operations. Laser treatment of glaucoma has a very significant advantage - restoration of the outflow of intraocular fluid (IOH) through natural channels.