Discrimination against albinos
In some countries, albinos are often targets of ridicule, persecution and discrimination. In Tanzania, in recent years, more than 20 albinos have become victims of beliefs and superstitions according to which the skin, meat and bones of albinos can be successfully used to treat all sorts of diseases. These rumors are sometimes deliberately spread by local healers. As a result of these superstitions, the lives of many albino Tanzanians are put in daily danger. Rumors about the healing properties of albinos began to gradually spread in neighboring Kenya. In Israel, there was a case of granting asylum to a refugee family from Cote d'Ivoire, in which an albino girl was born.
Classification
The following types of diplopia are known to medicine:
- binocular diplopia - develops in three forms (sensory, motor, mixed), the most common type of pathology;
- monocular diplopia is much less common; monocular diplopia has its own forms of development: refractive, aberration, papillary, retinal.
There is also temporary diplopia, which appears after a head injury or after severe alcohol poisoning. This deviation passes very quickly. There is also a strong-willed one, when a person himself provokes this state.
There are horizontal and vertical diplopia, depending on the plane in which the image splits.
Symptoms and causes of the disease
Unusual, often beautiful appearance, blond hair, fabulously snow-white eyelashes and eyebrows, light eyes and porcelain pale skin - this is all just one side of the coin. Albino adults and children experience many difficulties in everyday life, and it’s not just the sidelong glances of passers-by and the ridicule of peers. Total albinism in humans is always accompanied by visual impairment:
- myopia;
- farsightedness;
- strabismus;
- photophobia.
In the complete absence of tyrosinase, symptoms of the disease can be noticed from birth. The iris of an albino child's eyes is light, almost transparent or light blue. Blood vessels can be seen through it, giving the eyes a red tint. The skin and hair are very light. The body is dry to the touch and the sweat glands have no function
With partial albinism, there is a weakening of the pigmentation of the skin, hair and iris. Often such people are not afraid of light, like their counterparts with complete depigmentation. Their eyes have a hazel, blue, light gray or greenish tint. Vision is reduced. The skin is normally pigmented.
Due to total damage to the skin, albino people often develop the following syndromes and formations throughout their lives:
- hypothyroidism or alopecia (lack of hair);
- hypertrichosis (excessive body hair);
- problems in the functioning of the sweat glands;
- keratoma (benign neoplasm on the skin);
- telangiectasia (dilation of blood vessels in the skin, which causes the appearance of vascular red spots in the form of stars);
- epithelioma (development of formations in the form of ulcers, nodules, plaques, seals);
- actinic cheilitis (inflammation of the skin of the lips, caused by sun rays).
Ocular albinism affects only the organ of vision, without affecting either the skin or hair. HA manifests itself in the following symptoms:
- very low vision;
- uncontrolled movement of the eyeballs;
- strabismus;
- colorless iris;
- pathology of refraction (astigmatism).
Another accompanying symptom of this disease is often infertility.
Depending on the type of albinism, the cause of GCA lies in a congenital pathology in one of the chromosomes of the gene. This may be an anomaly on the fifteenth, eleventh, ninth, rarely fifth chromosome or a malfunction in the P-protein gene, which encodes proteins in the melanosome that take part in amino acid metabolism. The latter disorder is the most common among all types of disease.
How are albinos different from ordinary people?
It has long been the custom that the human race rejects fellow tribesmen who have significant and noticeable differences from the general mass. Moreover, it does not matter what differences they are, expressed in material wealth or physical characteristics. Society calls such individuals “white crows.”
This is exactly how albino people feel. On some continents, such people are considered disabled from birth, and in some states they are deliberately oppressed by their neglect.
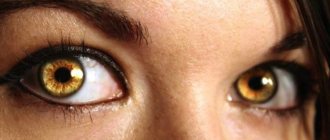
Albino people with red eyes are significantly different from the general mass of humanity.
Their distinctive features are as follows:
- pale, sometimes white skin color;
- colorless hair;
- snow-white eyelashes and eyebrows;
- Red eyes.
Such differences are caused by the partial or absolute absence of a pigment substance such as melanin. The pigment has a complex chemical composition.
It consists of:
- eumelanin;
- pheomelanin;
- allomelanin.
A deficiency of one of the components already causes adjustments to the human genome, and the absence of all three components causes the disease albinism.
Red eyes are not always found in such people; many of them are grey, green or blue.
Pigment deficiency is very dangerous, since human skin and hair are susceptible to the negative effects of ultraviolet radiation, the source of which is the sun's rays. Moreover, the influence from ultraviolet radiation occurs constantly, even in the evening or at night, only to a lesser extent.
Discrimination against albinos
In some countries, albinos are often targets of ridicule, persecution and discrimination. In Tanzania, in recent years, more than 20 albinos have become victims of beliefs and superstitions according to which the skin, meat and bones of albinos can be successfully used to treat all sorts of diseases. These rumors are sometimes deliberately spread by local healers. As a result of these superstitions, the lives of many albino Tanzanians are put in daily danger. Rumors about the healing properties of albinos began to gradually spread in neighboring Kenya. In Israel, there was a case of granting asylum to a refugee family from Cote d'Ivoire, in which an albino girl was born.
Treatment and prognosis for albinism
To date, there is no specific treatment for this disease; only preventive measures have been developed that can improve the patient’s quality of life.
In order to maintain the existing level of visual acuity, mandatory eye protection from sunlight is necessary. This is achieved by wearing special contact lenses or sunglasses. You should avoid exposure to bright sun or protect your skin with special lotions or creams.
If you adhere to all these recommendations, the prognosis for albinism is generally favorable - patients will be able to live a full and long life. At the same time, such patients need regular consultations with an ophthalmologist and dermatologist in order to prevent and timely detect complications such as retinal detachment or skin cancer.
How many years do albino people live, why don’t they live long?
Albinism is a chronic hereditary disease, which is why humanity is confident that such people will not live long. This is partly a correct assumption, since albinos have to protect themselves from negative influences from the outside all their lives and fight diseases that appear against this background many times more often.
The most dangerous disease that most often affects such patients is skin cancer. Pathology develops with strong negative effects of the sun on unprotected skin.
However, knowing about their vulnerable state, many take preventive measures that help them live into old age. Albinos live full lives, create families, get jobs, lead a social lifestyle - and all this brings them joy and gives them strength to continue to fight for their health.
Causes
The deviation in question is a congenital pathology resulting from various genetic abnormalities. The disease can develop in the background with nephrofibrosis, Down syndrome, Apert syndrome, Edwards syndrome, etc. Brain tumors, hernias and clefts can be concomitant abnormalities of this disease.
The main causes of progressive pathology:
- hereditary predisposition provided that close relatives have a similar deviation;
- use of potent medications during pregnancy;
- deviations in fetal development due to the negative impact of an infectious disease suffered by the mother;
- use of drugs, alcohol and other prohibited substances by the mother during pregnancy.
According to statistics, the most common cause of pathology is hereditary predisposition.
What is albinism?
Albinism is the name for a group of inherited conditions that affect the production of melanin.
Melanin is a pigment that colors the skin, hair, and iris (the colored parts of the eyes).
People with albinism may have reduced amounts of melanin or no melanin at all. Symptoms of albinism vary depending on the amount of melanin.
Affected people often have very pale hair, skin and eyes, but some may have brown or red hair and skin that may tan.
People with albinism usually have a number of eye conditions, such as:
- Sensitivity to light, medically known as photophobia. They may feel blinded by bright lights.
- Vision problems such as nearsightedness. They may benefit from glasses, but their vision will usually be impaired even with glasses.
- Involuntary eye movements known as nystagmus.
How common is albinism?
There are several different types of albinism. In most cases, they affect both sexes equally, although there is one type of ocular albinism (mostly affecting the eyes) that is more common in men.
Albinism can affect people of all ethnic groups. Certain types of albinism are more common in different parts of the world. For example, German Pudlak syndrome is very rare in Russia, but affects 1 in 2,700 people in Puerto Rico.
Vision problems
Many children with albinism may appear blind in the first months of life. However, their vision often improves dramatically after a few months. This is known as delayed visual maturation (DVD).
A child with albinism will need regular eye checks and it is very likely that they will need to wear glasses or contact lenses to deal with problems such as:
- myopia;
- farsightedness;
- astigmatism (an eye condition that causes blurred vision);
However, glasses or contact lenses may not completely correct a child's vision problems. They may also need low vision aids such as magnifying lenses, and their vision may be poor even with these aids.
Oculocutaneous
People with this condition have white hair and skin of the same color. The iris of the visual organ completely transmits light, so the sclera acquires a pink or red tint due to translucent vessels. In addition, light hair and skin enhance the contrast of the eyes, so it begins to appear that the latter are red.
Albino people often suffer from light sensitivity and reduced visual acuity. They may also experience nystagmus. With this disease, the eyeballs move chaotically in different directions. Another problem for such people is the harm of ultraviolet radiation to the skin. Albinos are at risk of sunburn due to prolonged exposure to the outdoors.
Types and signs of albinism
Based on the symptoms that characterize the disease, two types of albinism are distinguished. The most common type is oculocutaneous albinism.
With oculocutaneous albinism, there is a lack of pigmentation in the hair, skin and iris of the eyes.
Ocular albinism is characterized by the fact that with normal hair and skin coloring, there is no pigmentation of the iris of the eyes.
Signs of albinism, with the oculocutaneous development of the disease, are light to white, thin and soft hair, soft white skin through which capillaries are easily visible, and light gray eyes. With a mild form of albinism, the hair may darken slightly over the years due to the aging of the body. This form of the disease is characterized by the presence of nystagmus - flickering movement of the eyes, as well as increased photosensitivity (photophobia). Other vision problems are also possible - farsightedness, nearsightedness, astigmatism.
With oculocutaneous albinism, due to the lack of melanin, problems with sunlight arise. Patients should not sunbathe, because... Burns may occur, and in addition, exposure to ultraviolet radiation can cause skin cancer.
Ocular albinism is less common but has significant problems. Hair and skin color with ocular albinism does not differ from the norm.
Signs of albinism in this case are the lack of pigmentation of the iris and impaired ocular coordination. There may be a decrease in the depth of visual perception.
Ocular albinism can be expressed by decreased visual acuity, nystagmus, myopathy, head tremor, and strabismus.
There is an opinion that albinos have red eyes. In fact, everything is not like that. The eyes may even be light brown, but due to the fact that the light is reflected from the retina, there is a feeling of a reddish glow, as when photographing with an electronic flash.
In addition to visual signs, there are tests that determine the type of albinism. This is a hair follicle pigmentation test and a tyrosinase test. The tyrosinase test is more accurate and measures the ability of tyrosinase to convert into melanin.
The causes of albinism must be sought in family hereditary history. There are currently no treatments for albinism. Various medical courses and surgical methods can be carried out, but all of them can only slightly correct the problem. Albinism has no cure.
People suffering from albinism need to take preventive measures. Wear sunglasses, wear long sleeves, cover your legs, and avoid exposure to bright sunlight. Don't sunbathe!
Why do albinos have red eyes and is this always the case?
In a healthy body, the vessels of the iris have a pigment that colors it in different shades. Albinos, due to the complete or partial absence of melanin production, have a transparent membrane, but not red, as everyone is accustomed to believe. The eyes become red due to the translucency of the blood vessels of the eye as a result of light reflection from the thin membrane.
Albino people can only be seen with red eyes if they have type 3 albinism, which is quite rare. With this type, redness is also noted on the hair and skin.
What time of day did the event occur?
The meaning of the sign is interpreted depending on what time of day the dove knocked on the window. The first half of the day, most often, promises positive changes. If a bird decides to knock in the morning while its owners are in bed, unprecedented happiness is expected.
The persistent knocking of a bird after lunch is a bad omen. Night tapping signals a visit from the soul of a recently deceased relative. For a pregnant woman, the knock of a night guest can mean the appearance of the soul of the unborn baby.
Consequences of albinism
Every child requires the attention and help of parents, but an albino child needs special care. It must be constantly protected from exposure to sunlight and eye protection due to photophobia. Then, the mature albino himself should not lose his vigilance and keep his white skin away from ultraviolet radiation, since even in cloudy weather it can turn red and get burned.
Albinism cannot be cured. Today, there are only safety measures and vision correction.
Vision problems force some albino children to study in specialized educational institutions for children with visual impairments and, because of this, to register as a disability group.
Sensitive skin and poor vision - these two problems are the main consequences of a genetic defect. If we look at individual cases, then, in addition to the physical complications of albinism, there are also psychological and emotional problems. They depend on society's acceptance of people who are different from others. Unfortunately, even in the 21st century, discrimination, humiliation and infringement occur in civilized countries. Not to mention East Africa, where white-skinned blacks are hunted.
But, in general, you can live with albinism quite fully and even use your appearance to your advantage. In the modeling business, people who look special are highly valued.
It is very important for albinos themselves not to consider their signs of albinism a disease, but to accept them as a special distinctive feature
Incredible facts
Although people with albinism are often teased or ridiculed, people know little about the condition.
16. In some cultures, albino animals are highly revered. Thus, Native Americans honor white bison as a symbol of strength and good luck, protecting them from attacks.
Signs and symptoms
With oculocutaneous albinism type 1, several vision problems can occur, including involuntary back and forth eye movement (nystagmus), decreased iris pigment (iris transillumination), decreased retinal pigment, and lack of macular development (macula hypoplasia), which leads to abnormal development of the fovea. (the area of the eye responsible for visual acuity), poor visual acuity and abnormal connections in the nerves from the retina to the brain, which causes squinting and reduced depth perception. Visual acuity in humans can range from 20/60 to 20/400, usually depending on the amount of pigment present in the eye. Visual acuity is usually better in people with more melanin pigment.
Oculocutaneous albinism type 2 (OCA 2) is associated with the same vision problems as OCA type 1. People with GCA type 2 have a wide range of skin pigmentation, which depends in part on their genetic background and the mutations present. The hair color is usually not completely white, and some pigment may be present in the skin, but the skin color is usually lighter than that of unaffected relatives. People exposed to prolonged sun exposure may develop pigmented nevi and lentigines. This does not happen with other types of GCA. Reduced skin pigmentation is evident in Africans and African Americans, but skin coloration appears close to normal in other populations with generally lighter pigmentation, but affected individuals do not tan. Brown OCA is a subtype of OCA 2 in which the hair and skin are darker in color. This type of GCA has only been reported in people of African descent. OCA type 2 is associated with mutations in the OCA2 gene, formerly called the P gene.
Oculocutaneous albinism type 3 (OCA 3) was originally described in African populations. Affected individuals have red to reddish-brown skin, red or reddish hair, and brown eyes, and the condition was originally called rufous albinism. OCA type 3 has now been identified in several additional populations, particularly those of Asian origin, including Chinese and Japanese, as well as Asian and Northern European Indians. People of Asian descent have blond hair with light brown eyebrows and lighter skin than their ancestors. Hair and skin pigmentation increases with age. Vision problems are not as severe as with GCA type 1 or GCA type 2. Nystagmus and photophobia may be absent. OCA 3 is associated with mutations in the tyrosinase-related protein 1 (TYRP1) gene.
Oculocutaneous albinism type 4 (OCA 4) is characterized by physical signs similar to OCA 2. Hair color in affected individuals can range from yellow to brown. Visual acuity can vary from 20/30 to 20/400 depending on the amount of pigment present, but is usually in the range of 20/100 to 20/200. After childhood, vision usually stabilizes. OCA type 4 was originally identified in a person of Turkish descent and has been found in Asian populations including Japanese, Koreans and Germans. OCA 4 is associated with mutations in the SLC45A2 gene (formerly called MATP), a membrane-associated transport protein.
Symptoms
According to statistics, 1 in 17-18,000 people worldwide suffer from some type of albinism. Why variety? Yes, because albinism is a heterogeneous disease. In medicine, it is customary to distinguish two large clinical groups of this pathology:
- complete albinism, or oculocutaneous;
- partial albinism, or ocular.
Complete albinism develops in cases where a genetic defect determines the content of melanin in the skin, hair, and visual system. Partial albinism means a lack of melanin only in the visual system. In recent decades, it has become clear that among complete and partial albinism there are several more varieties. Let's look at the main features of some of them.
Complete or oculocutaneous albinism
People with this type of albinism are born with white (milky) skin, white hair and blue irises. This is due to the complete absence of tyrosinase (or when its activity is zero).
Since the iris completely transmits light, the eye itself acquires a reddish or pink tint (due to translucent vessels), which forms the phenomenon of “red eyes”. Due to the complete absence of pigment, the skin of such patients is not able to fight ultraviolet radiation, and a tan does not form. When exposed to sunlight, people with oculocutaneous albinism immediately get burned. That is why they are forced to hide their skin with long sleeves, constantly wear trousers or long skirts, and hats. These albinos have a significantly higher risk of developing skin cancer. The skin remains white throughout life, no pigmentation is formed. There is a tendency to develop spider veins and keratomas. Usually the skin is dry, with low sweat production. Albinos have thin and soft hair.
Eye manifestations include more than just a reddish tint to the eyes. Such people find it difficult to tolerate bright light, so they are characterized by photophobia. Visual acuity is usually reduced (and does not increase with age), and nystagmus is often observed - oscillatory involuntary movements of the eyeballs.
There is a type of oculocutaneous albinism in which tyrosinase is not completely absent, but only partially (or its activity is reduced). In this case, incomplete albinism (albinoidism) develops. Clinically, this is manifested by a change in skin color from white (with a significant decrease in tyrosinase activity) to almost normal (with almost normal enzyme activity). At birth, such people have white skin, reddish eyes, and hair without pigment. However, as people with this type of albinism grow older, their skin darkens (and may tan slightly) and their hair accumulates yellow pigment. The iris is also pigmented: light or dark brown pigmentation appears, sometimes in patches and not completely. An adult with this type of albinism can have any eye color, even dark brown. So, not all albinos have red eyes, as is commonly believed. Freckles and age spots may appear. With this type of albinism, the eyebrows and eyelashes are darker in color than the hair on the head. Visual acuity is reduced, but may increase with age (as the iris darkens).
Another fairly common type of albinism among the African population is rufous oculocutaneous albinism. In this case, a genetic defect causes the production of melanin not black, but brown. Such patients have reddish or light brown skin, and the irises are brownish-blue.
Another interesting type of albinism is also known - temperature-sensitive (heat-dependent). With this type, tyrosinase is not active at body temperatures above 37°C. This leads to the fact that melanin is synthesized in the “cold” parts of the body (hair on the head, arms and legs), but not in the “warm” parts (armpits). Such people at birth have white skin and colorless hair (since the body temperature of infants is above 37°C). After the first year of life, the skin and hair gradually darken. The eyes have a body temperature above 37°C, so pigmentation does not appear in them even over time.
Partial or ocular albinism
This form of albinism has clinical manifestations only in the organ of vision. The skin is normally pigmented and can tan. The hair is normal in both color and structure.
The main eye symptoms for this form of albinism are:
- decreased visual acuity;
- astigmatism;
- strabismus;
- photophobia;
- nystagmus;
- transparent iris (with a gray-blue or light brown tint);
- impaired binocular vision (the ability to see one image with both eyes), amblyopia.
Separately, I would like to note that albinism can be a component of other diseases (for example, Chediak-Higashi syndrome, Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome, and so on). In these cases, there are more severe genetic disorders that affect not only the genes responsible for the synthesis of tyrosinase, which leads to a number of other symptoms (immune disorders, problems with kidneys and cardiac activity, etc.).
Disease prevention
The following tips will help minimize the risk of diplopia:
- Don't abuse alcohol.
- Quit smoking.
- Follow sleep, rest and nutrition schedules.
- Don't forget about daily physical activity.
- Monitor your blood pressure.
If signs of diplopia occur, you should immediately consult a doctor. A split image indicates the development of diseases in the body. You can avoid their consequences if you take the necessary measures in time.
Causes of albinism
Genes are responsible for the color of the skin, hair, eyes, eyebrows and eyelashes. At conception, information about the color of the irises, skin and appendages is stored in the body of each person. As a result of a gene mutation, albinism may develop in the womb. Even a slight mutation causes problems with the coloring pigment responsible for the shade of skin, hair and eyes.
You need to understand that albinism is a congenital disorder, but it can manifest itself gradually. Most often, albinos are born into families where there have been albinos in the family. Often, a gene mutation occurs spontaneously, even if there were no albinos in the family.
Melanin is responsible for the color of the skin, hair and irises. The less melanin in the body's cells, the lighter the skin and hair. Depending on the amount of melanin in the body, people may have different types of the disorder. In the case of a complete absence of coloring pigment, a person is born completely white - an albino.
The enzyme tyrosinase, the activity of which is determined at the genetic level, is responsible for the quantitative production of melanin. Under the influence of the enzyme, melanin begins to form in the irises of the eyes and skin. The pigment, in turn, protects people's skin from ultraviolet radiation through the formation of a tan. The presence of pigment in the eyes allows light to enter only through the pupils, which makes bright lighting and sunlight less harmful to the eyes.
Why are albino people born this way?
Albino people with red eyes, according to modern scientists, are born due to the absence of the enzyme tyrosinase, responsible for the production of the melanin pigment. The disease is considered hereditary, that is, the cause is a genetic disorder. However, even with mutated genes, a person can be born without any abnormalities.
Albinism is a hereditary pathology that manifests itself in a person only if one or both parents are carriers of altered genes, while the parents themselves may not have external differences from ordinary people.
Albinism is an incurable pathology; treatment in this case is aimed at correcting some of the problems caused by the disease. For example, albinos often have vision problems, so therapy is based on correcting this condition.
It is possible to avoid the appearance of an albino child in a family only with careful pregnancy planning. Modern research methods make it possible to undergo a genetic examination, which will determine the presence of mutated genes in potential parents. In addition, before conceiving a child, you can study the “family tree”; perhaps the father or mother previously had albino relatives in the family.
Another assumption for the appearance of mutated genes is a complication after suffering a serious illness.
Types of albinism in humans
Based on the extent of damage to the body, total, incomplete and partial albinism are distinguished:
- Total – observed from birth, manifested by depigmentation, dry skin, hyper- or hypotrichosis, disturbances in the functioning of the sweat glands. Patients often develop keratomas, epitheliomas, cheilitis, sunburn, and telangiectasia. Complications include infertility, strabismus, poor vision, immunodeficiency, and decreased life expectancy. People with the total type suffer from photophobia, horizontal nystagmus, and a red pupil.
- Partial - piebaldism, manifests itself from birth, signs are visible to the naked eye. The type is characterized by achromia, gray strands of hair, spots on the face, legs, and stomach. This variety is called autosomal dominant.
- Incomplete - albinoidism, characterized by hypopigmentation of the hair, iris, and skin. A person with this diagnosis rarely develops photophobia.
Another classification of pathology is based on the location of the lesion:
- Ocular – only the eyes are affected.
- Oculocutaneous albinism - xanthism, the cause is a gene mutation. Signs include damage to the eyes, skin, and lack of pigment.
Oculocutaneous
Cutaneous-ocular albinism is also divided into total, incomplete, and partial types. Total develops with a lack of melanin in the skin, hair and organs of vision. Partial means a deficiency only in the eyes, incomplete - in the eyes and skin, while the hair is normal. The partial oculocutaneous subtype is divided into types:
- The first type is a mutation in the 11th chromosome; patients have milky skin and hair, and blue eyes. With age they become a little darker, the skin does not change.
- The second type is a mutation of the 15th chromosome, the skin is white or light brown, the hair is yellow, red or golden, the eyes are blue-gray or yellowish-brown. This look is typical for desert dwellers, African Americans, and Indians. In the sun, freckles are visible on the skin.
- The third type is a mutation of the 9th chromosome. A rare species in which the skin is reddish-brown and the eyes and hair are red. It affects people in southern Africa.
- The fourth type is extremely rare, a mutation of the 5th chromosome, the symptoms are the same as the second. Residents of southeast Asia are susceptible to it.
The first subtype is temperature-sensitive, which is caused by a mutation in the tyrosinase gene. With it, a person has dark hair on his arms and legs, and white hair under his arms and on his head. With age, the skin gradually becomes pigmented, but the eyes remain blue, but it is impossible to tan.
Ophthalmic
Ocular type albinism affects only the eyes. Such patients have normal skin, slightly paler than their relatives. Manifestations from the eyes:
- reduced visual acuity;
- strabismus;
- transparency of the iris;
- nystagmus.
More often, the ocular type affects men, while women are only carriers. In patients, the pathology is characterized by the fact that the fundus of the eye becomes dirty in color with spots and hypopigmented lines, and the iris is transparent.
How does albinism manifest in humans?
Albinism is a hereditary pathology in which the melanin pigment is absent or present in a small amount in the human body. It is he who is responsible for the color of the skin, hair and iris of the eye.
A common type of disease is ocular-cutaneous albinism. People with this diagnosis usually have completely white skin and hair, which may develop faint pigmentation over time. On the part of the visual system, they have pathological flickering movements of the eyeballs, increased photosensitivity, poor vision, sometimes strabismus and amblyopia.
Another common type of pathology is eye albinism. With this diagnosis, people have hair and skin of the usual color, but the iris of the eye is completely or partially without pigment. The iris of albinos may have a whitish or bluish tint. In certain light, such eyes appear red. People with ocular albinism often have vision problems.
What causes visual problems in people with albinism?
Melanin is the most important pigment that is involved in the visual process. When we perceive a visual image, it passes through the optical media of the eyeball and enters the retina. The retina contains photoreceptors that convert light signals into nerve impulses, which then travel to the brain. These receptors with their tips are immersed in the pigment epithelium of the retina, which, in turn, must absorb all light rays passing through the photoreceptors. Thanks to the absorption of light by the pigment epithelium, we obtain a high-contrast, clear image.
In people with albinism, there is no pigment in the retinal epithelium or there is too little of it to fully absorb light rays. As a result, light passing through the photoreceptors is not absorbed by the pigment epithelium and enters the choroid of the fundus. It begins to be reflected from it in a chaotic manner and again passes through the photoreceptors, which reduces the sharpness and clarity of the image.
If the pigment is also absent in the iris, then it cannot retain part of the light flux. As a result, a large amount of light enters the retina and its focusing is disrupted. This is why people with albinism see worse than those who have normal amounts of melanin in their bodies.
A common pathology in albinos is nystagmus, in which the eyes make uncontrolled oscillations. The disturbance intensifies when a person tries to use as many photoreceptors as possible in looking at a particular object.
Albinos often have one or another refractive error (farsightedness, nearsightedness, astigmatism). According to research, the optical system of the eye can change in such a way as to achieve a clear image on the retina. This explains the change in the optics of the eye towards myopia or farsightedness with albinism.
It is impossible to cure albinism today, but correcting visual impairments is possible and necessary. To do this, you should consult an ophthalmologist.
What kind of vision problems do albinos have?
Albino people with red eyes and others always have some kind of vision problems. This is due to the absence of the same melanin, because it not only gives pigmentation to the iris, but also performs a number of functions. One of them is the absorption and concentration of incoming light. In the absence of substance, the light is scattered, and the picture turns out blurry and low-contrast.
Among the numerous vision problems in albinos, the most common are:
- abnormal sprouting of retinogenic images, which leads to unnatural intersection of nerve fibers;
- decreased quality and visual acuity;
- photophobia, accompanied by pain; sometimes light damages the retina of the eye;
- hypoplasia of foveal tissue;
- myopia or farsightedness.
Against the background of these problems, albinos develop the following diseases:
- nysgam (involuntary movement of the eyeballs);
- optic nerve hypoplasia (underdevelopment);
- amblyopia (decrease in visual acuity);
- astigmatism (change in the spherical shape of the cornea or lens structure).
The absence of pigment, which absorbs a large amount of light, increases light glare and scatters light within the retina. This is why albinos have a highly developed pathological photophobia. The condition is often accompanied by pain and a feeling of severe discomfort. Wearing sunglasses reduces this sensation to some extent.
Albinos people - character: features
Albinos - character
In fact, albinos are no different in character from others. Generally, young people do not like daytime because they are too sensitive to light. Therefore, many people note that they go to bed late at night, because they feel much more comfortable this way. Children often bully peers who are different from them, but this does not prevent them from achieving great success. For the most part, these are kind, cheerful people.
By the way, today the topic of albinism is gaining more and more popularity on the Internet, and some people even deliberately pretend to be such because they like to stand out and be different from everyone else.
What kind of children are born to albinos?
Children whose both parents are carriers of the mutated gene are guaranteed to inherit the albinism gene. Moreover, they themselves may not differ at all from their fellow tribesmen. If only one parent is a carrier of albinism, the likelihood of having an albino child is quite low, but there is still a small percentage.=
A child born without signs of the disease, but having inherited the genome from its parent, subsequently passes it on to its offspring. A couple who has a mutated gene, but without symptoms of the pathology, gives birth to an albino child in 1 case out of 4.