Heterochromia
The second name for the pathology is piebaldism. It develops when there is an uneven distribution of melatonin in the iris of one or both eyes, or when there is an excess (deficiency) of it. Color variations depend on which shade of pigment is present in increased or decreased concentration. It can be brown, yellow or blue.
This condition is not considered a deviation or disease. The most it can cause is psychological discomfort. Because different eye colors do not always look mysterious and attractive. At the same time, heterochromia does not in any way affect the visual function.
| There is no reason to worry. Contacting a doctor is required only if the deviation is associated with eye pathologies. |
Heterochromia of the eyes: how to get sick?
Modern society treats heterochromia as a certain feature that gives the owner of eyes of different colors a magical look. The creators of anime and computer games who give their characters heterochromia are trying to emphasize their mystery. Perhaps this is why the fashion for multi-colored eyes arose.
Many people deliberately try to change their eye color to achieve the effect of heterochromia. In this case, you can use multi-colored lenses. It is impossible to become infected or intentionally become ill with heterochromia .
Thus, if a person has eyes of different colors, then this phenomenon is not considered dangerous to health. The cause of heterochromia can be either a hereditary factor or various diseases. Thanks to the emerging fashion for eyes of different colors, many people specifically wear contact lenses that differ from each other in shade.
Heterochromia types
The phenomenon is classified into several types:
- Simple. It occurs most often and is diagnosed from the first days of a child’s birth. A characteristic manifestation of heterochromia of this type: one eye is green (blue, gray), and the second is necessarily colored brown. In addition to the genetic factor, Horner's syndrome, accompanied by weakness of the cervical bundle of nerves, can influence the occurrence of the phenomenon;
- Complicated. The main prerequisite for the development of the deviation is Fuchs syndrome. It is accompanied by severe inflammation in the upper layers of the iris and sclera. The disease affects one eye. At the same time, the patient complains of a decrease in visual acuity. Due to the saturation of the eye with lymphatic compounds, the shade of the iris becomes lighter. It is difficult to identify the disease; it is practically impossible to treat;
- Acquired. Neoplasms, inflammatory processes, injuries, swelling - these factors can provoke heterochromia. Overuse of medications can change the shade of the iris.
According to the shape and localization of the “colored spot,” the phenomenon is divided into the following types:
- Full. A person has different eye colors. Moreover, from an anatomical and aesthetic point of view, each eye is correct. Most often, brown and blue colors live in the “neighborhood”;
- Partial (sector). One eye is painted in different shades. The iris is divided into halves, quarters, or has wavy edges. The phenomenon is caused by the uneven distribution of pigment during the formation of color, which lasts during the first six months of life. Partial heterochromia lasts up to about two years, then the condition returns to normal;
- Central. The most common form, characterized by a change in the color of the iris of one eye. It has virtually no effect on a person’s appearance. In some cases, the shade is located around the pupil in rings. This creates a rainbow effect when two areas of different shades are combined in one organ of vision. In this case, the second eye is painted in one color;
- Metallic. A unique form of heterochromia. Usually develops as a result of damage from copper or bronze scale. The phenomenon is also provoked by the entry of metal filings into the eye, which penetrate the upper layer of the iris or protein membrane. If scale is left in a humid environment for a long time, it oxidizes and forms pigment. As a result, the iris takes on a light green or rusty green color. After removing the scale, the color does not change.
Return to contents
Hair heterochromia
This is when there is uneven hair color on the body.
That is, hair in different parts of the body may differ from each other. It is considered normal for pubic and armpit hair to be darker than the rest, and facial hair (beard, mustache and eyebrows) also differ in shade. Another case is when there are pieces of sharply different colors. For example: light strands on black hair (on the head), the color of the eyelashes of one eye is different from the color of the other.
Learn also about Anabolism and Atavism.
Heterochromia causes
Most often, heterochromia of the eyes is caused by a genetic predisposition, but it can manifest itself with the development of illnesses or damage to the organ of vision.
- Waardenburg syndrome. Uneven pigmentation of the upper layer of the iris;
- Neurofibromatosis. Stopping the distribution of melanin;
- Inflammatory processes of a non-critical type in one of the organs of vision;
- Violation of the integrity of the iris;
- Glaucoma therapy or its presence in the membrane;
- Getting a foreign body into the eye;
- Heredity;
- Hemorrhage into the tunica albuginea or eyeball.
Reasons for different eye colors
Researchers still cannot give an exact answer to the question of why heterochromia occurs. The most common theory is that it is simply a quirk of individual development, an unusual natural phenomenon. However, the following reasons for this feature are distinguished:
- A congenital or simple form of heterochromia is when a person’s eyes are of different colors, and no other visual disturbances are observed. This is a fairly rare form of anomaly. Heterochromia may not manifest itself immediately, but during the first two years of a child’s life.
- Complicated heterochromia - often appears against the background of Fuchs syndrome. This pathology is characterized by damage to one eye, while heterochromia is mild or absent. The cause may also be more dangerous conditions, for example, the development of a tumor process. At the same time, the person will make other complaints;
- Acquired form - discoloration occurred due to trauma, inflammation, tumor, irrational use of eye drops. A change in color can occur, for example, after a tiny particle of any metal gets into the eye. Because of this, the iris becomes greenish, blue, brown or rusty.
The most common cause of heterochromia, not associated with any diseases or injuries, is wearing colored contact lenses. The modern ophthalmological market is represented by a variety of lenses that can change not only the color of the iris, but the shape of the pupil.
Who may experience
Heterochromia is diagnosed in one person out of a hundred, and most often the disease is detected in girls. Doctors cannot determine why this happens. There are no anatomical or physiological prerequisites for this.
If the phenomenon manifests itself in the stronger half of humanity, then it takes on unimaginable and interesting forms.
Modern youth do not always accept “God’s gift” positively and try in every way to correct it. There are several popular methods for adjusting the iris shade:
- Colored contact lenses. The best option. The main thing is to wear and store them correctly;
- Eye drops. The color changes a few months after starting medication. The iris darkens. However, long-term use is not recommended, since in this case the nutrition of the organ of vision is disrupted;
- Laser correction. The procedure is expensive and has an irreversible effect. In addition, surgery can lead to diplopia and photophobia;
- Implantation of the graft. The procedure is very harmful to health and has a huge price (about eight thousand dollars). Can lead to the development of glaucoma, cataracts and blindness.
General recommendations when buying an apartment
Of course, the best advice is to contact a real estate agency or realtor and suffer yourself.
Even if you resort to the services of specialists, and even more so if you decide to act independently, you should pay attention to the following:
- Carefully check the real estate documents. It is better to refuse the purchase if the sale occurs by proxy.
- Clarify the number of owners and registered persons, whether there are utility debts or encumbrances. Is the apartment mortgaged?
- The desire to sell quickly and profitably can lead to misleading the potential buyer. Therefore, the rule applies: “Trust, but verify.” There must be documentary evidence of the words.
When a suitable apartment is found and the deal is on the way, a number of other questions arise: how to buy an apartment with a mortgage and not be left with nothing? Find a good offer and hope that the seller will wait for the mortgage to be issued? What if she is not approved? Or run to the bank, apply for a loan, and then look for an option?
It is to resolve such issues that there is a preliminary agreement for the purchase and sale of an apartment under a Sberbank mortgage. The process steps are as follows:
- searching for a suitable deal;
- signing a preliminary agreement for the purchase and sale of an apartment encumbered with a mortgage;
- mortgage loan approval;
- signing the main purchase and sale agreement;
- registration of transfer of ownership rights;
- settlement with the seller.
Diagnosis and treatment
Heterochromia cannot be considered a disease. But it is important to find out the reasons for its occurrence; for this, detailed diagnostics are carried out. The examination includes a number of procedures:
- Biomicroscopy. Performed using a slit lamp. Helps to analyze in detail the primary layer of the iris and detect a foreign body or injury;
- Ophthalmoscopy. The procedure makes it possible to study the circulatory system of the organ of vision and the retina. When diagnosing there is no direct contact with the eye, the doctor uses a special lens;
- Electrophysiological examination. Assess the condition of the pupil and lens. Gives a primary opinion about the amount of pigment in the iris. The organ of vision is subjected to a targeted electric current in a thousandth of power;
- Campimetry. Identifying the eye's reaction to different lighting and color. For diagnostics, a white screen is used, where markers appear in a chaotic manner. They differ in color, their brightness increases or decreases. During this period, the doctor examines the reaction of the iris and pupil using a lens. Eyes that differ in color react differently to the picture of the surrounding world;
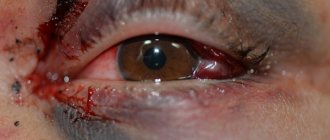
- Ultrasound of the organ of vision. It is carried out in the presence of mechanical damage to the face.
| If, in addition to changes in the color of the iris, there are no abnormalities and visual function is normal, then therapy is not required. If the cause of heterochromia is hidden in injury or ophthalmic diseases, the doctor prescribes steroid medications. |
If clouding of the lens is detected, which cannot be eliminated with medications, vitrectomy is performed. This is an operation that involves complete or partial removal of the vitreous body. If the shade has changed due to the penetration of metal filings, then the foreign object is removed and medications are selected to normalize the color.
In difficult situations, antibacterial or anti-inflammatory drugs are used. Return to contents
Treatment
- If the cause is Fuchs syndrome, a vitrectomy is performed—removal of scar, blood, or abnormal tissue from the vitreous of the eye, which is replaced with a balanced salt solution and silicone oil/gases.
- If there is metallosis, the foreign body is removed. For inflammation, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs are indicated. It should be noted that even if the irritants are eliminated, the color of the iris may not be restored.
- In people with congenital heterochromia, this anomaly will remain in any case. Only medical intervention will help, namely laser correction or implantation. If this is an acquired phenomenon, you can get rid of it over time, however, not in all situations.
- If heterochromia began to appear as a result of using drugs with the hormone prostaglandin, the solution to the problem is simple and logical - consult a doctor so that he can help you choose other medications for the eyes.
Video:
Related articles:
- Myopia: treatment, symptoms, degrees, causes
- Retinal dystrophy - what is it?
- Scleritis: symptoms and treatment, photos, causes
- Ophthalmoplegia
Heterochromia and human character
There are no personalities without flaws. People with different eyes are no exception. The main character flaw is selfishness. This trait explains the extremes in their behavior. They withdraw into themselves or consider the phenomenon a significant drawback. Other owners of different eyes try to emphasize their uniqueness by any means and strive to be the center of attention. However, this does not prevent them from having a large number of friends with whom they like to spend their free time.
Multi-colored eyes are characteristic of touchy individuals, so when talking to them, be extremely careful in your statements. They know how to forgive, but they will remember the offense for a long time. Such people do not understand hints and do not know how to make them themselves; heterochromes say everything they think to their face. This causes them difficulties in everyday life and professional activities.
Individuals with different eyes are patient and prefer to work in places where perseverance is required. These people are also characterized by the fact that they never complain. Low salary? No problem, we'll get over it! Didn't work out well with your colleagues? And this is not a problem, we can handle it!
Heterochromes usually experience resentment alone, but can share difficulties with loved ones. Creative individuals have a lot of talents. People with different eyes sing, dance, draw, write poetry. They love holidays, parties, visiting and receiving friends at home.
In general, odd-eyed individuals are extraordinary and interesting, so they definitely shouldn’t feel complex about their appearance. They are loyal to those close to them and will always lend a helping hand; they make great friends.
Do I need treatment?
As a rule, no pathological changes occur in the functioning of the eyeball, and different pigmentation does not affect visual acuity. The perception of colors, shapes and sizes of surrounding objects is not impaired. However, not all patients with heterochromia are ready to accept their unique appearance as a given and try to get rid of this unwanted feature. The easiest way to do this is with .
Despite the fact that it makes no sense to treat the disease, there are cases when surgical intervention is simply necessary. For example, if the cause of the disease is siderosis and chalcosis (deposition of metal salts in the tissues of the iris and lens), then an operation is performed to restore the true color of the eyes, as a result of which the causes of this disease are eliminated.
If heterochromia is caused by any disease, other symptoms are noted, and appropriate treatment is carried out. This could be hormonal therapy with steroids, laser treatment, or other types of surgery. The choice of a specific treatment method is made by the doctor based on the diagnosis and individual characteristics of the patient.
And if, with a congenital disorder, the color of the iris in both eyes never becomes the same, then in the case of acquired heterochromia, the original color of the iris can be restored.
Have you ever met people with different colored eyes? One look at such a person makes you stop your gaze on him, arousing great interest. The combination of brown and blue eyes is impossible not to notice. Nature has endowed such people with a special charm, however, there are only one percent of them in the world. Why is the iris of the eye different colors in one person? We will try to explain this to you.
In science, this phenomenon is called heterochromia. It is explained either by the presence of an excess or, conversely, a deficiency of a pigment called melanin. The most important thing you need to know is that different eye colors are not a disease, but just a gift of nature.
There are also two states of heterochromia. If the irises of the eyes have different colors, then this is complete heterochromia. Partial heterochromia is caused by a two-color iris of one of the human eyes. However, partial heterochromia is extremely rare. In addition, different-colored eyes in a person can be an acquired phenomenon, due to a head injury or after recovery from a serious illness.
Nowadays, science explains this phenomenon, and people with different-colored eyes live peacefully. In the old days, this caused fear. It was believed that multi-colored eyes were a sign of dark forces and such people were avoided. Today, a person with different colored eyes is always the center of everyone's attention. Psychologists have even compiled a special psychological portrait for people with this phenomenon. As a rule, these are sincere, brave and sometimes unpredictable people. Since childhood, feeling different, they are always the center of attention and surround themselves with only a small circle of friends. Maximalists by nature, they always strive to be the first in everything.
“Mosaic People,” as they are called, often use colored lenses to hide their phenomenon from strangers
Excessive attention can sometimes be tiring, which may be why they hide their individuality. The average person, on the contrary, is jealous of the mosaics
After all, being different from others is a reason for pride.
If you find an error, select a piece of text containing it and press Shift + E
or, in order to inform us!
Why does my breath smell?
Heterochromia in animals
Representatives of the fauna have multi-colored eyes much more often than humans. The phenomenon can be observed in pets (dogs, cats), horses, cows, etc. Most often, the anomaly is observed in animals with snow-white skin. Heterochromia is common in dog breeds such as huskies. In horses, when the phenomenon develops, one eye is colored white or blue, the other is brown. Another important point: multi-colored irises in most cases appear in animals that have a piebald color.
Different eye colors
Eye color depends on the blood supply to the vessels of the iris and the amount of pigment it contains. This pupil-thin diaphragm is located in front of the lens and behind the cornea. The color of the pigment may indicate a disease in the body. For example, with liver disease, the iris becomes yellow or brown. The natural color of pigments depends on genes and race. It can also be a characteristic feature of a particular nationality. There are only three colors of pigment. These are brown, blue and yellow. The mixing of these pigments in the blood vessels determines the color of the eyes. For example, mixing blue and yellow gives a green color.
Different eye colors
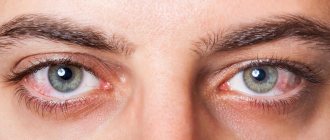
Sometimes there is an excess or deficiency of melanin in the iris. Then a phenomenon called heterochromia is possible, the manifestation of which is different eye colors. This condition occurs in both humans and animals. Most often, the color of one eye is brown and the other blue. But still, each person has his own, unique form of heterochromia. Such people look mysterious and unusual, standing out from the crowd.
Heterochromia happens:
1. Complete, when the colors of the irises of the eyes are different.
2. Partial, in which one pupil combines two colors.
Different colored eyes in cats are no longer surprising. This phenomenon is familiar to us. Eyes of different colors are much less common in people. Heterochromia can be congenital, resulting from an excess or deficiency of melanin. But there is also an acquired condition as a result of injury, in people with tumors or glaucoma.
From a psychological point of view, people with different eye colors are considered extraordinary, unpredictable and fearless. However, they exhibit pronounced egocentrism. Demanding a lot of attention to their personality, they love to be alone with themselves. As a result, they have a very narrow circle of close people.
Women with different eye colors always strive for perfection. They love to enjoy their appearance, considering it ideal. Possessing a delicate taste, they are fond of poetry, music, dancing and are great optimists.
People with different eye colors lead a measured lifestyle. Bright events happen quite rarely for them. But this does not cause disappointment. Thanks to their inexhaustible imagination and remarkable organizational skills, they can always arrange a holiday for themselves.
Women with different eye colors are always looking for their unique and unique one. And only with him will they be wise and wonderful housewives, creating such comfort and coziness in the house that one can only envy the husband. But at the same time, these women will never forget to carefully monitor their appearance.
Such ladies have a natural addiction to alcohol. But due to their wisdom, they will easily overcome this craving. But once they try smoking, they are unlikely to be able to quit.
When communicating with people with different eye colors, do not forget that they are very capricious and stubborn. It is unlikely that you will be able to emerge victorious in an argument with them. They can even be rude in their desire to prove that they are right.
When communicating with such people, you need to choose your words carefully. They will quickly forgive, but the resentment will remain for a long time.
Heterochromia should not be perceived as a disease or mutation. Different eye colors do not affect your health in any way. A person with heterochromia perceives the colors of the surrounding world absolutely normally and sees like an ordinary person.
Should you worry if you have heterochromia?
Of course, heterochromia is an anomaly, but its presence does not necessarily mean the presence of hidden health problems. However, there is evidence that heterochromia may accompany some hereditary diseases. One example of such diseases is Waardenburg syndrome, in which children develop the following clinical signs: congenital hearing loss of varying degrees, gray hair above the forehead and heterochromia. Another example is a disease such as neurofibromatosis, which affects many organs and even entire systems. Externally, it is accompanied by the presence on the skin of many coffee-milky spots, neurofibromas and pigmented hamartomas of the iris (Bream nodules).3 Experts recommend that not only children, but also adults with congenital or acquired heterochromia undergo an annual medical examination.4 If you notice a sudden change in color irises, the appearance of heterochromia, this may be due to health conditions. In this case, you should consult an ophthalmologist who will conduct a thorough examination and identify any problems.5
Treatment of conditions caused by heterochromia
When the anomaly is acquired and not present in the eyes from birth, extensive diagnostics are required. An examination is necessary to establish the cause that caused the development of imperfection (or advantage).
Treatment for different eye colors is aimed at combating the underlying disease that contributed to the occurrence of this problem. In some situations, a complex of medications is used; in other clinical cases, surgical intervention will be required.
Only a specialist can most accurately determine the need for therapy. You should not use any methods to change your eye color on your own.
Therapeutic treatment
Therapeutic treatment is necessary in cases where the anomaly is caused by various infectious diseases. In this case, the specialist prescribes various medicinal drops to relieve the patient of the underlying cause. Antibiotics, glucocorticosteroids, and topical ointments are used.
Surgery
Surgical intervention is indicated for severe health conditions that provoke the occurrence of heterochromia. The question of the advisability of surgical treatment is decided by a specialist after all diagnostic measures have been completed.
In what situations is surgery indicated:
- the presence of a malignant neoplasm;
- progressive cataracts, causing color changes and clouding of the pupil and iris;
- a sharp decrease in visual acuity;
- entry of a foreign body into the area of the visual organs.
Most often, eye surgeries are minimally invasive. Manipulations are carried out using a laser or other non-contact types of equipment. This allows you to significantly shorten the rehabilitation period, as well as reduce the risks of possible postoperative complications.
Symptoms and manifestations of heterochromia
Heterochromia occurs in both humans and animals. It does not pose any particular danger, but may indicate the development of a certain pathology. Therefore, people with such a defect are recommended to undergo regular preventive examinations. As you know, people with different eyes are quite rare - they are only 1% of the planet's population. The main symptom of heterochromia is a partial or complete discrepancy between the color of one eye and the other. This is due to different pigmentation of the iris of the visual organs.
Reasons for development
The cause of the development of pathology is a lack of melanin or oversaturation of the visual organ with this substance. As a rule, this phenomenon is associated with a genetic predisposition. The color of the iris is determined by the level of melanin and its distribution. The development of the color range of the iris begins with the birth of a person, but the final shade of the eyes is established only after 1-2 years. With a high concentration of melanin, the eyes become dark, with a low concentration they become lighter.
In some cases, the pigment substance is distributed unevenly, which leads to the appearance of heterochromia. This process is entirely determined by nature and it is almost impossible to change the shade of your eyes on your own. Most often, this phenomenon is encountered by girls who subsequently experience difficulties in choosing cosmetics.
The disease can be either genetic or acquired in nature, when heterochromia arose as a result of a deterioration in the general condition of the body or injury. In fact, the pathology does not pose a danger to the organs of vision, since a person sees well. There are also the following reasons for the appearance of multi-colored eyes:
- hemorrhage;
- neurofibromatosis;
- heredity;
- iris atrophy;
- glaucoma;
- disease siderosis;
- inflammatory process;
- cancer tumor;
- Waardenburg syndrome;
- the use of medications (eye drops) that enhance melanin generation;
- foreign object in the eye.
Is heterochromia curable?
If heterochromia occurs as a result of pathology, it requires treatment; only congenital heterochromia is safe.
After diagnosing and establishing the cause of heterochromia, the ophthalmologist prescribes treatment. The types depend on the severity of the anomaly:
- Laser correction is a surgical operation. Modern and effective treatment. The method is safe. The recovery period is minimal.
- Steroid therapy is a group of drugs. Used in the treatment of a number of diseases of the organs of vision. Steroids destroy enzymes in the eye fluid and change the amount of outflow.
- Vitrectomy is an ophthalmological operation. Prescribed when treatment with steroids fails. Consists of complete or partial excision of the vitreous substance.
- A surgical operation is performed in cases of a sharp decrease in visual acuity and progressive cataracts.
In society, people with unusual eyes are treated with genuine interest and kindness. Different colors of irises do not spoil, but on the contrary, complement the external beauty of a person.
Why does heterochromia appear?
So, why can a person’s eyes be different colors? The main reasons, as well as prerequisites for the development of this phenomenon, include:
- heredity;
- various types of injuries, for example, the entry of foreign objects into the organs of vision. Such injuries may cause the eyes to darken. And if, say, the gray/blue iris is damaged, then it may eventually turn brown or green;
Why do people's eyes have different colors?
- Fuchs syndrome. It is characterized by developing inflammatory processes in the tissues of the organs of vision. Other signs include blurred vision, as well as complete/partial loss of vision;
- side effects of some drugs used to treat glaucoma;
- neurofibromatosis.
Fuchs syndrome
Note! In most cases, it is hereditary heterochromia that is observed. Therefore, if the phenomenon was identified in one of the parents, then with a probability of more than 50% the child will have it (to a lesser or greater extent).
Depending on the cause, heterochromia can be simple, complicated or acquired. The acquired form is when the color of the eye changes after the use of glaucoma medications or due to injury. In addition, this can appear after copper or iron gets into the eyes - in the first case, the phenomenon is called chalcosis, and in the second - siderosis.
Central heterochromia
Complicated heterochromia develops due to Fuchs syndrome, although it is quite difficult to diagnose it in some cases, because the eye does not always undergo significant changes. Although there are additional signs that determine the complicated form of the phenomenon:
- blurred vision;
- the appearance of precipitates (these are floating white formations in the eye);
- dystrophic changes in the iris;
- cataract.
As for simple heterochromia , it develops without any diseases; A simple congenital form is often detected, most clearly manifested in children under 2 years of age.
Heterochromia in children
Although the reasons may be different, not entirely normal - for example, Horner's or Waardenburg's syndrome.
Video: Why do people have different colored eyes?
Variety of shapes
Heterochromia is classified according to various parameters.
Heterochromia comes in different forms
Table. Classification according to the nature of coloring.
| Options | Description |
| Full | Each eye has its own color, different from the other. The iris is completely painted in it. The most common options are contrasting - brown and blue. |
| Sectoral | The pupil is colored in sectors of different colors. Color shades are arranged segmentally. There may be a change in only one or both eyes in different variations. Shades of coloring are usually contrasting. |
| Central | The iris of the eye has several multi-colored circles coming from the center. These rings are each painted a different color. |
This applies mainly to congenital forms. As for acquired forms, they arise as a result of diseases or other pathologies that somehow affect the iris.
- Simple, damage to both eyes by a color effect without pathological changes in the visual organ. Occurs less frequently than others. In the presence of congenital vulnerability and weakening of the sympathetic nerve, defective visual deviations are possible.
- In Fuchs syndrome, which causes uveitis (an inflammation process in the uvea of the eye), it is complicated, affecting one eye. The color difference may be subtle, barely noticeable.
- The consequences of matallose, expressed in the development of siderosis, when iron particles enter the eye.
- This is also a result of metallosis, expressed in the development of chalcosis, when copper gets into the eye.
- An abnormality that begins as a result of trauma.
- Dynamic development of the inflammatory process.
- Violations of the rules for the use of eye contact medications, in particular for the treatment of glaucoma.
- Neurofibromatosis.
- Neuroblastoma.
- Atrophy of the iris, accompanied by a decrease in color.
- Melanoma.
Iris melanoma
What is heterochromia
Central heterochromia
With this type of anomaly, the color changes only in the area of the pupil, usually in both eyes at the same time. It looks like this. The circle outlined directly next to the pupil is dark in color, usually brown. The next, larger circle or several circles are painted in lighter, sometimes contrasting shades.
Central heterochromia
Central heterochromia should not be a reason to look for eye diseases or develop anxiety associated with this condition, but it is still worth seeing an ophthalmologist. Especially if the effect is fresh and pronounced.
Etiology
Since heterochromia is not a disease, in most cases there is no need to worry about its manifestations. It usually does not pose any risks to health or visual acuity. The person continues to see with the same clarity, especially if the anomaly was acquired from birth. But when it appears as a result of injury, foreign material, or after an illness, the process can manifest itself not only as staining of the iris, but also as clouding of the lens and other visual pathologies that require treatment.
Heterochromia in a man
How does this phenomenon occur, what is the process and when is medical intervention necessary? If we use medical terms, the anomaly is explained by the depletion of the iris stroma, the occurrence of a lack of pigment, the cause of which in the congenital version is trophic disorders. If an anomaly occurs in the acquired status, the clinical picture is as follows.
Can eye color change in case of severe injury?
Simple form
Changes in the iris are minor if nerve weakness is absent or mild. With congenital paresis, the picture changes dramatically, the color changes immediately and significantly, Claude-Bernard-Horner syndrome occurs:
- not only the color of the eyes changes, but also the color of the skin;
- the pupil narrows;
- the palpebral fissure becomes narrower (ptosis is formed);
- the upper eyelid droops;
- the apple moves in its orbit;
- sweating disappears on the side where the eye is affected.
Claude-Bernard-Horner syndrome
Complicated form
In the presence of Fuchs cyclitis and the heterochromia that arises against its background, the following signs are observed:
- cloudiness of the lens of varying degrees;
- fixed points on the frame of the lens are white;
- iris dystrophy;
- cortical cataract in progression;
- precipitates.
Heterochromic Fuchs cyclite
Forms of metallose
If the patient has any form of metallosis, siderosis or chalcosis, changes in the eye are as follows:
- bright nature of the severity of pigmentation;
- shades of color from blue-green to rusty brown.
Siderosis