Home / Pulpitis
Back
Published: 06/04/2020
Reading time: 10 min
0
2
- 1 Which is better: tsiprolet or tsipromed?
- 2 What's the difference?
- 3 Respiratory diseases
- 4 The difference between Tsiprolet and Tsipromed
- 5 Side effects: ciprofloxacin
- 6 Indications for use
- 7 Contraindications for use
- 8 Recommendations and instructions for use
- 9 Comparison of the safety of Signicef and Tsiprolet
- 10 Comparison of two medicinal formulations
- 11 Comparison of the effectiveness of ciprofloxacin and ciprolet
- 12 Release form
- 13 Characteristics of ciprolet
- 14 Ciprofloxacin
Which is better: tsiprolet or tsipromed?
It is difficult to determine which drug is best to use on your own. This can only be done by the attending physician, taking into account the characteristics of the patient’s body and the course of the infectious process.
Tsipromed is best used for eye damage from dacteroides, Escherichia coli, staphylococci, Klebsiella, streptococci, spirochetes, legionella and gonococci.
Tsiprolet is recommended to be used if you have:
- keratitis;
- uveitis;
- blepharitis;
- iridocyclitis;
- dacryocystitis;
- endophthalmitis;
- conjunctivitis;
- complicated by the penetration of bacterial flora of a corneal ulcer.
The duration of use, regimen and dosage of the drug used are determined by the attending physician, depending on the severity of the pathological process and the characteristics of the physiological state of the patient’s body.
Tsiprolet or Flemoxin solutab – which is better?
Manufacturer: Astellas (Netherlands)
Release form: tablets
Active ingredient: amoxicillin
Both drugs are broad-spectrum antibiotics. In terms of action, Flemoxin Solutab will be the best, since the drug is quickly and almost completely (93%) absorbed from the stomach into the blood after oral administration.
This is the most commonly used analogue of Tsiprolet for children, prescribed for the treatment of bacterial respiratory infections. It is safe and well tolerated by young patients. The drug is highly effective in the treatment of tonsillitis, tonsillitis, bronchopneumonia, bronchitis, and sinusitis.
Respiratory diseases
Infectious agents that cause diseases of the upper respiratory tract are sensitive to Tsiprolet. These can be staphylococci, streptococci and other harmful microorganisms. They contribute to the occurrence of sore throat, various forms of pharyngitis, laryngitis, sinusitis, and aggravate chronic tonsillitis.
Before prescribing Tsiprolet, the sensitivity of the biological material to this drug is checked. To cure these diseases, it is enough to take antibiotic tablets for a week.
For acute and chronic bronchitis, which occurs in a mild form, Tsiprolet is also used in the form of tablets, but the dosage in this case should be higher.
In order for the therapeutic effect to be better, the antibiotic must be taken on an empty stomach without chewing. It is not advisable to take a drug with it that reduces the acidity of gastric juice. You need to take the tablet with plenty of water.
For severe diseases such as pleurisy, pneumonia, bronchiectasis, and lung abscess, Tsiprolet is used as an injection, administered slowly intravenously twice a day. How long the treatment will last and the dosage of the drug depend on the severity of the disease and the patient’s condition.
The difference between Tsiprolet and Tsipromed
Tsiprolet and Tsipromed are antibacterial drugs belonging to the pharmacological group of fluoroquinolones.
Tsiprolet and Tsipromed are antibacterial drugs belonging to the pharmacological group of fluoroquinolones.
Both drugs have a wide spectrum of action. Medications are recommended for use when eye damage occurs as a result of bacterial infection with Escherichia coli, staphylococci, Klebsiella, streptococci, spirochetes, legionella, gonococci.
Tobrex
These are drops with the active ingredient tobramycin. The substance has a wide spectrum of action and belongs to the group of aminoglycosides. Effective against a large number of microorganisms that cause purulent diseases.
Used to treat:
- streptococcal and staphylococcal eye infections - blepharitis, keratitis and keratoconjunctivitis;
- blepharoconjunctivitis;
- infectious lesions after surgical treatment of the organ of vision.
Tobrex cannot be prescribed if the patient suffers from hypersensitivity to the active substance. Prescribed with caution during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Typically, a doctor will prescribe a medicine only in cases where the benefits of its use are greater than the potential risks. When using Tobrex during lactation, breastfeeding is temporarily stopped.
1 or 2 drops of medication are injected into the conjunctiva. The frequency of administration depends on the degree of infection of the eye. During the acute period of the disease and in severe cases, drops are administered hourly until the patient’s condition stabilizes.
An overdose of Tobrex is impossible. Side effects - nausea or dizziness, photophobia, allergic reactions in the form of redness of the eyelids are extremely rare. The shelf life of the drug is 3 years.
Side effects: ciprofloxacin
Despite the similarity of the drugs, the side effects from taking Ciprofloxacin are somewhat different. As in the case of Tsiprolet, disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system, kidneys and liver, as well as allergic reactions, are possible. But this list is not complete. Taking ciprofloxacin may cause additional problems, including:
- disruptions in the functioning of the cardiovascular system,
- high or low blood pressure,
- decreased functioning of the musculoskeletal system - patients taking Ciprofloxacin for a long time complain of pain in the joints, ligaments and tendons.
Ciprolet is a safer drug, especially for those who have heart problems (for example, patients with hypotension when using Ciprofloxacin become prone to fainting and frequent dizziness).
Deviation from the established treatment course and recommendations of the attending physician, regardless of the drug used, is fraught with the appearance of nausea, vomiting, dizziness, and disorientation in space. If these symptoms are detected, call an ambulance as soon as possible and perform an emergency gastric lavage.
In some cases, after hospitalization, patients are prescribed a course of hemodialysis. Such procedures are also accompanied by an increase in fluid intake, including intravenous infusion of water. The consequences can be very serious, so it is recommended to strictly follow the therapeutic course prescribed by a specialist.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Contraindications for dental implantation
Indications for use
- The antibiotic Tsiprolet is prescribed for various diseases of an infectious-inflammatory nature. It is mainly used for complications arising after acute respiratory viral infections. At the same time, viruses inflame the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract, and this facilitates the penetration of harmful microflora. Tsiprolet helps fight bronchitis and focal pneumonia.
- The antibiotic Tsiprolet is often used to treat inflammatory diseases of the kidneys and bladder. A short course of taking this antibacterial drug can completely cure cystitis and relieve inflammation in the kidneys.
- It is often prescribed for the treatment of gynecological and urological diseases, including sexually transmitted diseases.
- This drug is also very effective in surgery in the treatment of abscesses, boils, phlegmons, carbuncles, mastitis and many other diseases that are accompanied by suppuration of various parts of the body.
- For infectious processes occurring in the area of the nose, throat, ear.
- With inflammation in the abdominal cavity (abscess, peritonitis).
- For infectious diseases of joints and bones.
- For infectious eye diseases. In this case, Tsiprolet drops are prescribed.
- In a hospital setting, Tsiprolet is prescribed after surgery for cholecystitis and pancreatitis as a prophylaxis for purulent complications.
Tsiprolet
The active ingredient in these drops is ciprofloxacin hydrochloride. In ophthalmology it is used for:
- infectious pathologies of the eyes and appendages - blepharitis, conjunctivitis, blepharoconjunctivitis;
- bacterial ulcers of the cornea;
- chronic barley.
This drug is also prescribed for the prevention of purulent-inflammatory complications in the post-traumatic or postoperative period.
Tsiprolet is prohibited from use in case of individual intolerance to the main medicinal substance. Not for use in children, pregnant or lactating women.
Adults receive 1 – 2 drops of Tsiprolet into the conjunctival sac. The frequency of instillation is every 4 hours. In particularly severe cases, instillation is carried out every hour until the patient’s condition stabilizes.
When using eye drops, an overdose is impossible. Side effects such as nausea, vomiting, taste disturbances, and low blood pressure are rare. Drops are stored in dark and dry places for no more than 3 years.
Contraindications for use
Taking antibiotics in the vast majority of cases creates a serious burden on the body, which is why it is necessary to consult a doctor before starting treatment. The use of Ciprolet and Ciprofloxacin is not recommended for the following categories of people:
- pregnant and lactating women,
- patients with intolerance to the components contained in the drugs,
- people suffering from kidney and liver diseases,
- patients under 18 years of age,
- people with mental disorders.
When using such medications, attention should be paid to the condition of the patient’s kidneys and liver, since these organs are used to remove the active components of Ciprolet or Ciprofloxacin from the body.
Patients suffering from a lack of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (related to hereditary pathologies), as well as those who have pseudomembrane colitis, should refrain from taking it - the use of these drugs is contraindicated for them. In addition, patients who have cerebral atherosclerosis, as well as convulsions or epileptic seizures, must undergo a thorough examination in the clinic before using the drug.
The only restriction on the use of the drug, supplied in the form of eye drops, is age: it should not be used in the treatment of children under 12 years of age.
Tsiprolet eye drops
INSTRUCTIONS for the use of the medicinal product for medical use
CIPROLET®
Registration number: P N 012765/01 Trade name of the drug: Ciprolet® International nonproprietary name of the drug: ciprofloxacin. Chemical name: 4-oxo-7-(piperazin-1-yl)-6-fluoro-1-cyclopropyl-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid hydrochloride monohydrate Dosage form: eye drops
Composition 1 ml of solution contains: Active ingredient: ciprofloxacin hydrochloride (equivalent to 3.0 mg of ciprofloxacin) - 3.49 mg/ml. Excipients: disodium edetate 0.50 mg, sodium chloride 9.00 mg, benzalkonium chloride 50% solution 0.0002 ml, hydrochloric acid 0.000034 mg, water for injection up to 1.0 ml.
Description Transparent, colorless or light yellow solution.
Pharmacotherapeutic group: antimicrobial agent, fluoroquinolone.
ATX code: S01AX13
Pharmacological action Pharmacodynamics A broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent, a fluoroquinolone derivative, suppresses bacterial DNA gyrase (topoisomerases II and IV, responsible for the process of supercoiling of chromosomal DNA around nuclear RNA, which is necessary for reading genetic information), disrupts DNA synthesis, growth and division of bacteria; causes pronounced morphological changes (including cell wall and membranes) and rapid death of the bacterial cell. It has a bactericidal effect on gram-negative organisms during the period of rest and division (since it affects not only DNA gyrase, but also causes lysis of the cell wall); it acts on gram-positive microorganisms only during the period of division. Low toxicity for the cells of the macroorganism is explained by the absence of DNA gyrase in them. While taking ciprofloxacin, there is no parallel development of resistance to other antibiotics that do not belong to the group of DNA gyrase inhibitors, which makes it highly effective against bacteria that are resistant, for example, to aminoglycosides, penicillins, cephalosporins, tetracyclines and many other antibiotics. Gram-negative aerobic bacteria are sensitive to ciprofloxacin: enterobacteria (Escherichiacoli, Salmonellaspp., Shigellaspp., Citrobacterspp., Klebsiellaspp., Enterobacterspp., Proteusmirabilis, Proteusvulgaris, Serratiamarcescens, Hafniaalvei, Edwardsiellatarda, Providencia spp., Morganellamorganii, Vibriospp. , Yersiniaspp.), others gram-negative bacteria (Haemophilus spp., Pseudomonasaeruginosa, Moraxellacatarrhalis, Aeromonasspp., Pasteurellamultocida, Plesiomonasshigelloides, Campylobacterjejuni, Neisseriaspp.), some intracellular pathogens - Legionellapneumophila, Brucellaspp., Chlamydiatrachomatis, Listeria monocytogenes, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, My cobacteriumkansasii, Corynebacteriumdiphtheriae; gram-positive aerobic bacteria: Staphylococcus spp. (Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus haemolyticus, Staphylococcus hominis, Staphylococcus saprophyticus), Streptococcus spp. (Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus agalactiae). Most staphylococci resistant to methicillin are also resistant to ciprofloxacin. The sensitivity of Streptococcus pneumoniae, Enterococcus faecalis, Mycobacterium avium (located intracellularly) is moderate (high concentrations are required to suppress them). The following are resistant to the drug: Bacteroides fragilis, Pseudomonas cepacia, Pseudomonas maltophilia, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Clostridium difficile, Nocardia asteroides. Not effective against Treponema pallidum. Resistance develops extremely slowly, since, on the one hand, after the action of ciprofloxacin there are practically no persistent microorganisms left, and on the other hand, bacterial cells do not have enzymes that inactivate it.
Pharmacokinetics The maximum concentration of the drug (Cmax) in plasma when using eye drops is less than 5 ng/ml. The average concentration is below 2.5 ng/ml. After instillation, systemic absorption of the drug is possible. The drug is excreted through the kidneys mainly unchanged (50%) in the form of metabolites (up to 10%), about 15% is excreted through the intestines, and in nursing mothers it passes into breast milk.
Indications for use Local treatment of various infectious diseases of the eye and its appendages caused by bacteria sensitive to the drug: acute and subacute conjunctivitis, blepharoconjunctivitis, blepharitis, bacterial corneal ulcers, bacterial keratitis and keratoconjunctivitis, chronic dacryocystitis and meibomitis. Preoperative prophylaxis in ophthalmic surgery. Treatment of postoperative infectious complications. Treatment and prevention of infectious complications of the eyes after injuries or foreign bodies.
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to ciprofloxacin and other quinolone drugs, viral keratitis, pregnancy, lactation (breastfeeding), children (up to 1 year).
with caution in patients with cerebral atherosclerosis, cerebrovascular accident, and convulsive syndrome.
Method of administration and dosage Locally. For mild and moderately severe infections, instill 1-2 drops into the conjunctival sac of the affected eye every 4 hours, for severe infections - 2 drops every hour. After the condition improves, the dose and frequency of instillations are reduced. For bacterial corneal ulcers: 1 drop every 15 minutes for 6 hours, then 1 drop every 30 minutes during waking hours; on day 2 – 1 drop every hour during waking hours; from days 3 to 14 – 1 drop every 4 hours during waking hours. If after 14 days of therapy epithelialization has not occurred, treatment can be continued.
Side effects Allergic reactions, itching, burning, mild soreness and hyperemia of the conjunctiva, nausea, rarely - swelling of the eyelids, photophobia, lacrimation, sensation of a foreign body in the eyes, unpleasant taste in the mouth immediately after instillation, decreased visual acuity, the appearance of a white crystalline precipitate in patients with corneal ulcer, keratitis, keratopathy, corneal infiltration, development of superinfection.
Overdose There are no data on overdose of the drug when applied topically. If the drug is accidentally taken orally, there are no specific symptoms. Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache, fainting, and anxiety may occur. Treatment: standard emergency measures, adequate fluid intake, acidification of urine to prevent crystalluria.
Interaction When combined with other antimicrobial drugs (beta-lactam antibiotics, aminoglycosides, clindamycin, metronidazole), synergism is usually observed; can be successfully used in combination with azlocillin and ceftazidime for infections caused by Pseudomonas spp.; with mezlocillin, azlocillin and other beta-lactam antibiotics - for streptococcal infections; with isoxazolepenicillins and vancomycin - for staphylococcal infections; with metronidazole and clindamycin - for anaerobic infections. Ciprofloxacin solution is pharmaceutically incompatible with drugs with a pH value of 3-4 that are physically or chemically unstable.
Special instructions Eye drops can only be used topically; the drug cannot be administered subconjunctivally or into the anterior chamber of the eye. When using Tsiprolet® eye drops and other ophthalmic solutions, the interval between their administrations should be at least 5 minutes. During treatment with the drug, wearing contact lenses is not recommended. Patients who temporarily lose clarity of vision after application are not recommended to drive a car or work with complex machinery, or any complex equipment that requires clarity of vision, immediately after instillation of the drug.
Release form: Eye drops 3 mg/ml. 5 ml of the drug in a plastic dropper bottle with a screw cap. 1 bottle is placed in a cardboard box along with instructions for use.
Storage conditions List B. In a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25°C. Do not freeze. Keep out of the reach of children!
Shelf life 2 years. Use the drug within 1 month after opening the bottle. Do not use after the expiration date stated on the packaging.
Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies By prescription.
Manufacturer Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Ltd. Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh, India.
Manufacturing Location Plot No.2, Sudarshanpur Industrial Estate, Bais Godam, Jaipur 302006, SP-918, Phase III, Industrial Estate, Bhiwadi District, Alwar, India.
Address for sending claims: Representative office 115035, Moscow, Ovchinnikovskaya embankment, 20, building 1 tel., 783-29-01; Fax
Recommendations and directions for use
To avoid the risk of side effects and for the most productive treatment, the following rules must be observed when taking Ciprolet and Ciprofloxacin:
- Closely monitor your body - any changes that begin immediately after taking the drug serve as a signal of intolerance. Ciprofloxacin, like any antibiotic, can harm the intestinal microflora and cause dehydration, so for any, even minor, ailments, you should consult a doctor.
- Drawing and sharp pain in the tendons, discomfort when walking are signs that this drug is not suitable for the patient and must be immediately replaced with another drug.
- During therapy using the medications described, it is necessary to ensure a constant flow of fluid into the body. Drinking plenty of clean, still water is the most effective way. Taking liquids enriched with vitamins is also welcome.
- Ciprolet and Ciprofloxacin have a significant effect on the nervous system and cause a decrease in reaction speed. Therefore, during treatment it is better to stop driving a car and other vehicles, and also minimize exposure to the sun.
- Eye drops should never come into contact with the anterior chamber of the eye.
- If the drops irritate the mucous membranes and the effect does not go away for a long time, you must choose another drug.
- The shelf life of the drops from the moment the bottle is opened is 1 month.
- Drop therapy involves avoiding the use of contact lenses.
Comparison of the safety of Signicef and Tsiprolet
The safety of a drug includes many factors.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Methods for removing dental pulp
At the same time, in Signitsef it is quite similar to Tsiprolet. It is important where the drug is metabolized: drugs are excreted from the body either unchanged or in the form of products of their biochemical transformations. Metabolism occurs spontaneously, but most often involves major organs such as the liver, kidneys, lungs, skin, brain and others.
The risk-benefit ratio is when the prescription of a drug is undesirable, but justified under certain conditions and circumstances, with the obligatory observance of caution in use. At the same time, Signicef does not have any risks when used, just like Tsiprolet.
Also, when calculating safety, it is taken into account whether only allergic reactions occur or possible dysfunction of the main organs. In other matters, as well as the reversibility of the consequences of using Signitsef and Tsiprolet.
Comparison of two medicinal formulations
To understand which drug, Ciprofloxacin and Ciprolet, will be more effective, you need to consult your doctor.
There are more common features than differences:
- active substance;
- antibacterial effect;
- dosage forms;
- dosage;
- concentration of the active substance;
- wide range of uses.
Both medications are recommended for a course of combating infections of various forms, including chronic. Tsiprolet therapy looks at its best, due to the fact that the composition is cleared of harmful impurities.
An antimicrobial agent, Cipronate, is produced with the same active ingredient ciprofloxacin. These two drugs are different in their actions and methods of therapy.
In therapeutic complexes, remedies can easily replace each other.
The market supply of Ciprofloxacin includes 2 manufacturers:
- Russia.
- Netherlands (tablets).
Tsiprolet is produced in India. The cost depends on the country of origin: domestic drugs are cheaper.
Comparison of drugs
Both drugs contain antibacterial substances. They are effective in the treatment of eye diseases caused by exposure to microorganisms, and significantly alleviate the patient’s condition within a few days from the start of use.
Tobrex and Tsiprolet have a similar method of application. Both medications also do not cause overdose and extremely rarely have side effects.
The difference between drugs is that they contain different active ingredients. Due to the nature of the action of ciprofloxacin, it is not prescribed during pregnancy. Tobrex can be used by pregnant women if the symptoms of conjunctivitis are associated with a serious deterioration in health.
Comparison of the effectiveness of ciprofloxacin and ciprolet
The effectiveness of Ciprofloxacin is quite similar to Ciprolet - this means that the ability of the drug substance to provide the maximum possible effect is similar.
For example, if the therapeutic effect of Ciprofloxacin is more pronounced, then using Ciprolet even in large doses will not achieve this effect.
Also, the speed of therapy - an indicator of the speed of therapeutic action - is approximately the same for Ciprofloxacin and Ciprolet. And bioavailability, that is, the amount of a drug reaching its site of action in the body, is similar. The higher the bioavailability, the less it will be lost during absorption and use by the body.
Tsiprolet or Amoxiclav – which is better?
Manufacturer: Sandoz (Austria)
Release form: tablets
Active ingredient: amoxicillin, clavulanic acid
Both drugs are broad-spectrum antibiotics. Unlike Tsiprolet, its analogue Amoxiclav is a combined medication with a milder effect and fewer side effects.
It will be the best in the treatment of various bacterial infections in children (sore throat, bronchitis). The medication can be used by both children under 2 years of age and school-age children.
Release form
The pharmaceutical industry produces the antibiotic Tsiprolet in the following forms:
- In the form of a solution for intravenous and intramuscular injections.
- Pills.
- Sterile eye drops.
In what cases are injections indicated:
- Sepsis.
- Adnexitis.
- Severe diseases of the upper respiratory tract.
- Antibacterial therapy after surgery.
- Damage to the arachnoid and serous membranes of the brain by pathogenic microflora.
- Abdominal abscesses.
- Severe pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis.
If the inflammation is mild or moderate in severity, Tsiprolet is prescribed in tablet form. It can be:
- Acute bronchitis.
- Prostatitis, urethritis, cystitis.
- Acute tracheitis.
- Salmonellosis, dysentery, typhoid fever.
- Sinusitis and laryngeal lesions.
- Acute rheumatoid arthritis and arthrosis.
- Lesions of the genitals and larynx as a result of gonorrhea.
- Complicated caries and periodontitis.
- Exacerbation of chronic cholecystitis, bulbitis, cholangitis and duodenitis.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=53f6UV-_AYk
It is advisable to take Tsiprolet in tablet form after meals to achieve greater effect.
Eye drops are prescribed for damage to the mucous membranes of the eyelids and eyes. These may be diseases such as blepharitis and conjunctivitis. In addition, these drops are used after eye surgery to prevent complications. Tsiprolet drops are also prescribed for injuries to the soft tissues of the eye and mucous membranes.
Characteristics of ciprolet
Tsiprolet is produced in three dosage forms: in the form of eye drops, a solution for infusion and in tablet form.
The active component of the drug is ciprofloxacin. In addition to this component, the tablets contain a second active ingredient - tinidazole.
Additional components of the medication in the form of an injection solution and eye drops are the following compounds:
- water for injection;
- disodium edetate;
- hydrochloric acid;
- benzalkonium chloride in the form of a solution;
- sodium chloride.
Tsiprolet tablets contain the following compounds as additional components:
- croscarmellose sodium;
- corn starch;
- sodium carboxymethyl starch (type A);
- MCC;
- colloidal silicon dioxide;
- talc;
- magnesium stearate;
- hypromellose;
- titanium dioxide;
- macrogol 6000;
- dimethicone;
- polysorbate 80;
- sunset yellow dye (E110).
The drug in any form of release has pronounced antiprotozoal and antimicrobial properties.
The mechanism of action of the main active component is manifested in the suppression of DNA gyrase of the bacterial cell, which provokes disturbances in the process of bacterial DNA synthesis, and this leads to a slowdown in the growth and reproduction of the bacterial pathogen. This effect on the bacterial cell provokes its death.
We suggest you read: When wisdom teeth grow and erupt
Tsiprolet tablets are used for drug therapy of diseases and pathological conditions such as:
- Bacterial lesions of the respiratory system: cystic fibrosis, bronchitis, bronchiectasis, pneumonia and tonsillitis.
- Lesions of a bacterial nature in the ENT organs: tonsillitis, pharyngitis, otitis media, mastoiditis, sinusitis and sinusitis.
- Infection of the genitourinary system: salpingitis, cystitis, pyelonephritis, oophoritis, tubular abscess, adnexitis, prostatitis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, chancre, pelvioperitonitis and pyelitis.
- Pathologies of the digestive system: peritonitis, typhoid fever, salmonellosis, intraperitoneal abscesses, yersiniosis, campylobacteriosis, cholera, shigellosis,
- Bacterial lesions of the skin: phlegmon, abscess, burns, infected ulcers, wounds.
- Pathologies of the osteoarticular system caused by bacterial infection: sepsis, septic arthritis and osteomyelitis.
Tsiprolet is used for infections of the genitourinary system.
- Tablet and injection forms of the drug can be used for prophylactic purposes to prevent bacterial infection after surgical interventions.
- Tsiprolet eye drops are prescribed for drug treatment of conjunctivitis, blepharitis, and barley.
- When prescribing the drug, the patient should take into account the following contraindications:
- minority;
- intolerance to the components of the drug;
- pregnancy period;
- lactation period.
The medication should be prescribed with caution when:
- impaired blood circulation in brain tissue;
- atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels;
- presence of epileptic syndrome;
- epilepsy;
- mental disorders;
- severe pathology of the liver and kidneys;
- old age.
During treatment, the patient may experience a whole range of side effects and unwanted reactions.
From the digestive system:
- vomit;
- diarrhea;
- flatulence;
- epigastric pain;
- feeling of nausea;
- bloating;
- cholestatic jaundice;
- decreased appetite;
- hepatonecrosis;
- hepatitis.
On the part of the nervous system, the patient may develop:
- insomnia;
- dizziness;
- anxiety;
- fatigue;
- tremors of the limbs;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- increased sweating;
- hallucinations;
- depression;
- confusion;
- different mental reactions;
- thrombosis of cerebral arteries;
- fainting;
- migraine.
Sense organs may react to the use of Tsiprolet with the following undesirable reactions:
- decreased hearing acuity;
- tinnitus;
- violation of taste perception;
- diplopia.
The patient may develop:
- tachycardia;
- drop in blood pressure;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- anemia;
- granulocytopenia;
- leukocytosis.
Carrying out drug treatment with Tsiprolet can provoke the occurrence of allergic reactions in the form of urticaria, arthralgia, tenosynovitis and arthritis.
If an overdose occurs, increased side effects are observed. To eliminate the pathological condition, gastric lavage and hemodialysis are used.
The drug is dispensed at the pharmacy only after presenting a prescription from the attending physician.
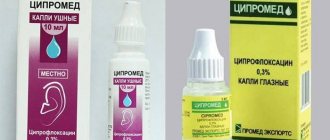
Which medicine is better and more effective: Tsiprolet or Tsipromed
For bacterial infections, antimicrobial agents . This group of drugs includes Tsiprolet and Tsipromed. These drugs are analogues. But they have not only similarities, but also differences that need to be known before starting therapy.
Tsipromed
Tsipromed contains ciprofloxacin as its main component.
The drug is available in two dosage forms:
- Eye drops , which are used to treat infectious and inflammatory diseases of the eye and its appendages. They are prescribed for conjunctivitis, keratitis, anterior uveitis, blepharitis and other eyelid infections, dacryocystitis. They can be used for the treatment and prevention of infectious complications after eye injury or surgery.
- Ear drops , which are used to treat infectious diseases of the ears, such as external, middle and internal otitis, eustachitis. They are recommended for the prevention of otitis during surgery and ear injuries, or removal of a foreign object from the ear canal.
General characteristics
Both drugs contain ciprofloxacin as an active ingredient, to which the following microorganisms are sensitive:
- Escherichia coli.
- Salmonella.
- Shigella.
- Citrobacter.
- Klebsiella.
- Enterobacteriaceae.
- Proteas.
- Morganella morgani.
- Serrations.
- Hafnia.
- Edwardsiella tarda.
- Providence.
- Vibrios.
- Yersinia.
- Haemophilus influenzae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
- Moraxella.
- Aeromonas.
- Neisseria.
- Pasteurella.
- Plesiomonas.
- Campylobacter jeuni.
- Legionella.
- Brucella.
- Listeria monocytogenes.
- Mycobacteria, including tuberculosis.
- Staphylococci.
- Streptococci.
- Corynebacterium diphtheria.
In addition, there are the following similarities between the drugs Tsiprolet and Tsipromed:
- Both drugs are manufactured in India .
- Both drugs can be purchased with a doctor's prescription .
- Both medications should not be prescribed to pregnant women or those who are breastfeeding.
- During treatment with these drugs, you must be careful when driving a car and when working in potentially hazardous work.
- Both drugs can cause allergies .
- Tsiprolet and Tsipromed eye drops can cause burning, itching, pain, redness of the eye mucosa, swelling of the eyelids, photophobia, lacrimation, sensation of a foreign object in the eyes, unpleasant taste in the mouth immediately after instillation, blurred vision, keratitis, keratopathy, spots. or infiltration of the cornea, superinfection. In patients with corneal ulcers, a white crystalline precipitate may appear.
Differences
Tsiprolet and Tsipromed have the following differences:
| Tsiprolet | Tsipromed | |
| Release form | The drug is commercially available in eye drops, solution for infusion, and tablets for oral administration. | The drug is available in the form of ear and eye drops. |
| Use in pediatrics | Eye drops can be used for patients older than 12 months. Tablets and infusions can be prescribed to children over 5 years of age to treat and prevent pulmonary anthrax. They can also be prescribed to patients in this age group suffering from cystic fibrosis to prevent complications caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. | Eye drops are allowed for children over 1 year of age, ear drops are allowed only for patients over 15 years of age. |
| Adverse reactions | Tablets and infusions can cause dizziness, cephalgia, fatigue, insomnia, trembling of certain parts of the body, anxiety, nightmares, peripheral paraalgesia, excessive sweating, intracranial hypertension, depression, hallucinations, migraines, fainting, thrombosis of the cerebral arteries, agitation , disorientation, convulsions, paresthesia, dysesthesia, hypoesthesia, gait disorder, hyperesthesia, peripheral neuropathy and polyneuropathy, perversion of taste and smell, double vision, hearing loss, tinnitus, increased heart rate, prolongation of the QT interval, vasodilatation, hypotension, ventricular arrhythmias, nausea, vomiting, indigestion, abdominal pain, bloating, lack of appetite, inflammation of the pancreas, hepatitis, hepatonecrosis, inhibition of bone marrow hematopoiesis, serum sickness, a decrease in the amount of all formed blood elements, the appearance of blood and protein in the urine, crystalluria, dysuria , polyuria, urinary retention, renal failure, glomerulonephritis, bleeding from the urethra, interstitial nephritis, respiratory failure, joint and muscle pain, arthritis, tendovaginitis, tendon rupture, impotence, muscle hypertonicity, muscle weakness, exacerbation of myasthenia gravis, increased activity of liver enzymes, levels creatinine, bilirubin and sugar, hot flashes, superinfection. Infusions can cause swelling at the injection site. | Ear drops can cause the eardrum to become red and painful. |
What to choose?
Despite the fact that the drugs are complete analogues, they have different release forms and areas of application.
For eye infections, you can use any of these eye drops. For ear diseases, you need to use Tsipromed in the form of ear drops, and for infections of internal organs - Tsiprolet in tablets or infusion solution.
Source: https://vchemraznica.ru/kakoj-medicament-luchshe-i-effektivnee-ciprolet-ili-cipromed/
Ciprofloxacin
Like Tsiprolet, this drug can cause unwanted reactions associated with damage to the nervous system, liver and kidneys. If the patient is allergic to the components of the drug, it will manifest itself in the same way as to other representatives of the fluoroquinolone group. Patients may experience skin redness, itching, rashes, and photosensitivity.
Despite the similarity of side effects, when Ciprofloxacin is administered to patients, other undesirable reactions may also occur:
- associated with damage to the cardiovascular system - increased heart rate, rhythm disturbances, decreased blood pressure;
- damage to the musculoskeletal system - many patients with long-term use of Ciprofloxacin complain of pain in the ligaments, joints, and tendons.
Photo 2. Packaging of Ciprofloxacin in the form of tablets with a dosage of 500 mg. .
Comparing the adverse reactions that may occur when taking these two drugs, we can say that Tsiprolet is safer. This is especially important for patients with diseases of the cardiovascular system - patients with hypotension (low blood pressure) may faint when using Ciprofloxacin, and they will experience severe dizziness.