Dacryocystitis is an inflammatory or purulent-inflammatory lesion of the lacrimal sac. The tear duct, which carries secretions from the lacrimal sac to the mucous membrane of the eye, is quite thin. If for any reason there is an obstacle to the removal of secretions, stagnation occurs in the lacrimal gland.
Stenosis or blockage (full or partial) of the duct leads to the development of inflammatory processes. In places of stagnation, swelling, redness occurs and a favorable environment for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms is formed.
This disease is treated by an ophthalmologist; in some cases, the patient requires consultation with an ENT doctor.
Types of dacryocystitis
According to the severity of the process, dacryocystitis can be divided into 2 types:
- Acute dacryocystitis. It occurs when the lacrimal canaliculus is completely blocked and pathogens get inside; it can be accompanied by purulent processes and high fever.
- Chronic dacryocystitis. Occurs when the canal is partially or incompletely blocked, as well as when there is a pathology in the structure of the lacrimal ducts. It has more vague symptoms, often limited to swelling and discomfort without sharp pain. The chronic form, despite less severe pain, can be more dangerous than the acute form, since the likelihood of complications is high.
According to the mechanisms of occurrence, dacryocystitis is divided into the following types:
- viral – occurs as a result of pathogenic viruses entering the duct;
- bacterial - when there is stagnation in the lacrimal sac, it becomes vulnerable to bacteria;
- chlamydial (parasitic) – accumulations of chlamydia or other single-celled parasitic organisms can cause a blockage;
- traumatic - with a traumatic injury, the nasolacrimal duct may be damaged, or swelling after injury leads to pinching of it;
- allergic - swelling due to allergies can also compress the lacrimal canal;
- congenital - the newborn may have a clogged or insufficiently open lacrimal canal.
Women are more susceptible to the disease. This is due, firstly, to the smaller structure of the ducts. And secondly, when decorative cosmetics get into them, which causes blockage and allergic swelling.
Dacryocystitis in newborns
During intrauterine development in the fetus, the nasolacrimal duct is closed by a special membrane, which breaks through during childbirth or resolves itself shortly before birth. In some babies, the membrane remains on one or both sides after birth, leading to difficulty in tearing and inflammation of the lacrimal sac.
Characteristic symptoms
With dacryocystitis of newborns, the nasolacrimal ducts are blocked by a film. Immediately after the baby is born, he inhales, which causes the film to rupture, which ensures the proper functioning of the lacrimal apparatus. If the film does not break, this leads to the development of the disease.
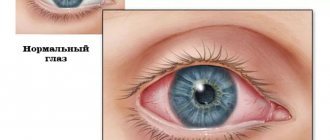
When pathology occurs, excessive tearing is observed. But the baby does not cry. Young patients are also diagnosed with red eyes. In pathology, the addition of an infectious process is often diagnosed. That is why after several days there is a discharge of purulent contents from the lacrimal canal.
During the course of the disease, swelling is observed in the area of the lacrimal sac. When pressure is applied to the lacrimal sac, fluid or pus is released. In young children, the pathological process is accompanied by pain in the lacrimal sac, so they cry constantly. Untimely treatment of the pathology can cause frequent headaches. Some children were diagnosed with an increase in body temperature during the course of the disease.
The symptoms of dacryocystitis are pronounced, which makes it possible to diagnose it in a timely manner.
Causes of the disease
For newborns and infants, common factors in the development of the disease are:
- too narrow nasolacrimal duct;
- partial fusion of the nasolacrimal canal or preservation of the membrane in it;
- plugs that have not resolved after intrauterine development;
- complete overgrowth of the duct (extremely rare).
In adults, the most common causes of darkyocystitis are:
- diseases of the nasopharynx, such as sinusitis, sinusitis, nasal polyposis, allergic or catarrhal rhinitis;
- nasal injuries that lead to rupture of the canal or blockage due to pressure on it from traumatic edema;
- eyelid injuries leading to blockage of the secretion of the lacrimal glands;
- foreign bodies (sand, dust, cosmetic residues) getting into the duct;
- viral or bacterial infections can be both the cause of blockage and its consequence;
- infectious skin lesions around the eyes;
- hypothermia, leading to thickening of the tear secretion and blockage of the canal;
- prolonged exposure to high temperatures and dryness, which leads to drying out and blockage of the canal.
Constant exposure to certain risk factors can lead to chronic dacryocystitis. Possible influence of external factors, such as working in hazardous conditions. The structural features of the lacrimal ducts can also cause partial blockage and the occurrence of chronic dacryocystitis.
Risk group
Dacryocystitis is a fairly common disease that can occur in any person. However, for some groups of the population the risk is higher.
These include people:
- prone to allergic reactions, especially during “seasonal allergies”;
- with a chronic decrease in immunity, including in the autumn-winter period;
- patients with diabetes mellitus;
- having chronic nasal diseases or ophthalmological diseases;
- working in hazardous or dusty industries;
- women who abuse decorative cosmetics.
What drops are prescribed for the treatment of dacryocystitis?
The reasons for this condition may be:
- narrowing of the nasolacrimal canal or its blockage;
- inflammation in the nasal cavity or sinuses, which are located near the nose;
- inflammation of the bones in the skull surrounding the lacrimal sac.
The results of this process are the retention of the outflow of tear fluid, the development of a pathogenic environment, inflammation of the mucous membrane in the bag, which causes complications of a purulent-septic nature, meningitis, and brain abscess. This disease is dangerous for both newborns and adults.
Therefore, treatment should begin at the moment the disease is diagnosed. An integrated approach to the treatment of the disease is due to the fact that dacryocystitis can cause quite serious complications. Of the medications used in treatment, drops and antibiotics are most often used.
You can only use medications that are prescribed by your doctor. The drops should help flush out the pus that accumulates throughout the day and stop the growth of bacteria and the spread of harmful microorganisms.
List of titles
Drops should effectively fight the disease, so doctors prescribe the following drugs:
- Gentamicin;
- Tobrex;
- Levomycetin;
- Furacilin;
- Vitabact;
- Vigamox;
- Oftaquix;
- Ciprofloxacin;
- Oftalmoferon.
Symptoms of dacryocystitis
The acute purulent form of the disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Swelling of the eyelid and around the eye, narrowing of the palpebral fissure. The eye looks half closed.
- An inflammatory swelling in the area of the lacrimal sac, which can be very painful and hard.
- Pain in the eye area and its orbit.
- Fever, intoxication of the body.
- An abscess that usually opens to the outside with purulent contents leaking out.
In the acute form, the symptoms are expressed both visually and by sensations.
The chronic form of the disease has more vague symptoms:
- excessive tearing;
- swelling of the eyelid is not as pronounced as in the acute form;
- tumor of the lacrimal sac is present, but not so pronounced.
Despite its less painful course, the chronic form is even more dangerous due to its consequences for the eye. Chronic disruption of healthy tear production leads to inflammatory damage to the conjunctiva (the mucous membrane of the eye). The symptoms of chronic dacryocystitis may be similar to conjunctivitis. But dacryocystitis usually affects one eye, and conjunctivitis affects both.
In newborns, dacryocystitis manifests itself as:
- constant lacrimation;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- purulent discharge from the eyes instead of tears.
This is very dangerous for infants, as complications can arise both for the eyes and nasopharynx, and for the brain.
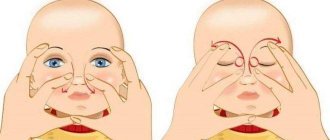
How to properly massage the nasolacrimal duct in a newborn baby:
- First, mom needs to wash her hands! The newborn’s body is still very weak, since it has not acquired its own immunity, having become accustomed to hiding behind the mother’s protection inside the womb. Therefore, any infection is easily caught by the baby and transformed into a new disease.
- Mom's nails should be cut short!!!!
- Use a cotton pad to remove all discharge and crusts that have formed after sleep; or use a warm solution of furatsilin 1 to 5,000 (1 tablet per glass of boiled warm water, you need to prepare a new solution every day). After soaking a cotton swab in it, you need to lightly touch it to remove the purulent discharge towards the nose.
- Also, before the massage, it is necessary to toilet the nose. To do this, you need to drip drops based on sea water into both nasal passages, then remove all the boogers using cotton wool. Only now, when the eyes and nose are clean, can the massage begin.
- It is done by softly touching the pad of the index finger in the direction from the inner corner of the eye, located near the nose, moving strictly from top to bottom. The movements should be jerky, but the finger should not slide over the baby’s skin, it should remain in place! Pressure is created inside, which breaks through the embryonic film. 6-10 up and down movements are enough. Attention! You need to massage the tear ducts strictly, from top to bottom!!!
- This massage should be done at least 5-6 times a day for at least two weeks, before feeding. It is best to start massage when the baby is crying. At this moment, the tubules are tense, so the breakthrough of the film will be painless. But the older the child gets, the more painful the film is torn. After 3-7 days, the film will resolve or break through, and there will be no consequences from dacryocystitis.
After the massage, and not instead of it, you need to instill drops with disinfectant properties (those prescribed by the doctor!). Instill without touching the tip of the pipette/tube to your eyelids and face, this will keep the drops sterile!!! If the massage does not have a positive effect within 14 days, then you need to see an ophthalmologist to decide on further treatment. The earlier treatment is started, the higher the effectiveness and the sooner the cure.
Complications
Ignoring symptoms and delaying treatment can lead to quite serious complications:
- an extensive abscess is formed, which can turn into phlegmon;
- the visual function of the eye is impaired as a result of drying out of the conjunctiva and purulent discharge from the tear ducts;
- purulent inflammatory processes in the eye threaten complications that are dangerous for the brain - up to meningitis and encephalitis;
Many people do not like to see doctors. But dacryocystitis is not a disease that will “resolve on its own.” Its consequences can be quite harmful; patients should be careful and conscientiously follow the recommendations of their doctor to avoid complications.
Phloxal
Floxal is an antibacterial eye drop of the fluoroquinolone group for use in ophthalmology. They are a yellowish solution.
Compound
Active ingredient: ofloxacin.
Additional components: benzalkonium chloride, sodium chloride, hydrochloric acid, sodium hydroxide, water for injection.
Pharmacology
A widely used medicine against pathogenic microbes. Has a bactericidal effect. Actively used for inflammatory processes in the visual apparatus. Prevents the spread and reproduction of harmful microorganisms.
Pharmacokinetics
When used topically, the necessary concentration of the product occurs in the soft tissues of the eye.
Indications for use
The medicine is actively used if inflammation of the lacrimal canal is observed. Recommended for the following pathological conditions:
- Dacryocystitis;
- Blepharitis;
- Conjunctivitis;
- Barley;
- Keratitis;
- Ulcer in the corneal area;
- Infectious diseases that are caused by the penetration of chlamydia.
Drops for dacryocystitis are prescribed to prevent inflammatory processes after eye surgery, as well as for damage to the eyeball of various types. For the treatment of pathologies that have formed after surgery on the eyeball or as a result of its injury. Eye drops for dacryocystitis are approved for use in newborns.
Method of use
If the therapy method involves the use of several eye drops, the interval between their use should be at least five minutes. Use in conjunction with Floxal ointment is allowed. In this case, the drops are applied first.
The dosage and course of administration are prescribed by the attending physician, individually for each patient. As a rule, the dose is as follows: one drop of the drug must be instilled into the affected eye three to four times a day. The duration of therapy should not exceed two weeks. You cannot prescribe the dosage yourself without consulting a treating specialist.
Contraindications
Use is not recommended in case of individual intolerance to the components. Cannot be used by pregnant women or while breastfeeding.
Review
The drug gives effective results for dacryocystitis in adults, children and newborns. For infants, drops must be used very carefully. Since they are still an antibiotic. But you must admit that it is better to treat the disease at its initial stages than to treat more severe complications later.
Diagnostics
For a specialized specialist (ophthalmologist), making a diagnosis is not a problem, since most of the signs are visible visually. But to clarify the diagnosis, determine the causes and select treatment, additional studies are carried out:
- the patency of the lacrimal ducts is determined - a dye is injected into the eye, which, if patency, enters the nasal cavity;
- probing the nasolacrimal duct to assess the extent of its damage;
- conducting eye biomicroscopy;
- instillation (fluorescein) test;
- Vesta color test;
- passive nasolacrimal test;
- microbiological examination - culture of secretions from the lacrimal canal;
- X-ray examination using special substances injected into the nasolacrimal canal;
- examination of the nose and sinuses;
The doctor may prescribe one or more additional research methods if necessary.
When diagnosing, it is important not only to establish the fact of the disease, but also to determine the causes and select the most effective treatment methods.
Treatment
The use of drops against dacryocystitis for newborns should be carried out in strict accordance with the scheme developed by the doctor. That is why it is recommended to consult an ophthalmologist before using a certain medicine. In most cases, to treat the disease in newborns, drops should be used throughout the day. In the evening, ointment is placed in the lacrimal sac. Thanks to this treatment regimen, the inflammatory process is combated.
Before using eye drops, it is recommended to rinse the eyes of infants. In this case, special solutions are used that have an antibacterial effect. To ensure the highest therapeutic effect, anti-inflammatory drugs must be used simultaneously with the drops. In this case, hormonal medications, antibiotics, and paracetamol are prescribed. To avoid injuring the child with tablets, the doctor selects drops that are made on the basis of an antibiotic. If the child is less than a year old, he is recommended to use Tobrex or Vigamox. At older ages, treatment is carried out with Oftavix. Treatment with Gentamicin or Levomycin can be carried out without age restrictions. Newborn children are strictly prohibited from using Ciprofloxacin in their eyes.
Attention! Antibacterial drops for dacryocystitis are prescribed if the child has purulent discharge.
Treatment of dacryocystitis in infants should be carried out in strict accordance with the doctor’s recommendations, which will eliminate the possibility of complications.
Treatment of dacryocystitis
To eliminate the disease and prevent complications, comprehensive treatment is carried out, which includes:
- ingestion of antibacterial and immunostimulating drugs;
- topical preparations, mainly in the form of ointments, emulsions;
- physiotherapeutic effects - UHF lamps, warming up;
- special massage, which is carried out up to 5-7 times a day, to open the lacrimal duct and remove the contents of the lacrimal sac;
- opening the abscess, washing and treating with antiseptic agents;
- formation of a new channel if necessary, if it itself has not recovered.
In the case of chronic dacryocystitis, it is possible to use a surgical method - widening the duct and forming the nasolacrimal duct. If the cause of the chronic form is deformation of the new cavity as a result of trauma, the help of a maxillofacial surgeon is required.
The following methods are used to treat newborns and infants:
- probing of the nasolacrimal duct - used if the prenatal membrane itself has not resolved;
- washing the eyes with special solutions;
- massage to squeeze out contents from the nasolacrimal ducts. Often, massage effectively removes the membrane that interferes with the outflow of tears;
If conservative methods do not help after three months of age, surgical intervention is possible to open the nasolacrimal duct.
In case of dacryocystitis, it is very important to exclude mechanical irritation of the eyeball. If the patient has vision problems and wears contact lenses, it is necessary to abandon them for the duration of treatment and use glasses. Contact lenses irritate the already damaged mucous membrane of the eye, which can lead to a purulent process on the conjunctiva and injury.
What drops are used?
Homeopathic
For dacryocystitis, the main component of treatment is eye drops, which are selected by the ophthalmologist individually for each patient, depending on the nature of the disease. To speed up recovery, oral administration of medications, in particular homeopathic ones, is also recommended.
Among the effective drugs that promote the smooth passage of tear fluid through the eye tract are homeopathic remedies. Although they have not passed clinical trials, they also continue to be in great demand among the majority of patients with dacryocystitis. The homeopathic drug Argentum Nitricum, which is sold in the form of granules for oral administration, is highly effective. The dosage is selected individually depending on the age of the patient, for example, for children the most common dose is 1 granule dissolved in 1 tsp, three or four times a day for a month. Another homeopathic medicine that is effective for dacryocystitis is “Silicea terra”.
Anti-inflammatory
Topical Indocollir anti-inflammatory drops are non-toxic and therefore do not affect the gastrointestinal tract.
Doctor of Ophthalmological Sciences V.V. Doroshenko, together with many other scientists, has proven the incomparable benefits of anti-inflammatory medications for dacryocystitis. Since this disease is accompanied by inflammation and, as a consequence, pain, local redness of the dermis around the eyes and mucous membrane, it is advisable to use anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve the accompanying symptoms and the source of inflammation.
And most often, ophthalmologists prescribe eye drops “Diclofenac”, “Diclo F”, “Indocollir”. Such medications act directly on the eyeball, without having a toxic effect on the gastrointestinal tract, as other forms of anti-inflammatory drugs do. If dacryocystitis occurs in a chronic form, then it is important to use drops with glucocorticoids, which have a stronger and more persistent anti-inflammatory effect.
Antibiotics
An equally important part of the treatment of dacryocystitis is the use of antibiotics, both systemically and locally. Vitabact is considered the most effective drug for external use with pronounced antimicrobial properties. Its components quickly penetrate into the inflammatory focus with a bacterial infection, practically without being absorbed into the conjunctiva, which minimizes the risk of developing negative effects during long-term therapy. The antibacterial drug Tobrex also shows excellent results in the treatment of dacryocystitis. These eye drops fight most pathogenic microorganisms and, apart from an allergic reaction, do not show any side symptoms.
Albucid eye drops can also cope with an ophthalmological problem, but due to their irritating effect on the mucous membrane, it is not recommended to be prescribed in childhood. A unique drug based on protein silver “Protargol” also has antimicrobial activity and is therefore often used against dacryocystitis.
Prevention
In order to eliminate the possibility of dacryocystitis from your life, the following conditions should be observed:
- promptly and completely cure diseases of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses, such as sinusitis, rhinitis or nasal polyposis;
- avoid traumatic effects on the nasal area and eyes;
- in case of injury, consult a doctor to eliminate the consequences;
- avoid harmful conditions such as dusty environments or exposure to harmful substances;
- when working in hazardous conditions (construction, chemical production), use protective equipment - special glasses and respirators;
- avoid extreme temperatures (hypothermia or dry heat) for long periods of time;
In order to avoid the development of the disease, if you notice one or more symptoms, you should definitely consult a doctor.