Often after childbirth, mothers discover strabismus in children, the causes and treatment of which E. Komarovsky recommends identifying and prescribing only after the first 4-6 months of life. Strabismus in newborns is a normal physiological phenomenon; in the first months of life it should not cause alarm. But if the child’s eyes continue to work inconsistently, the strabismus must be treated - and the sooner the better.
Why do newborns cross their eyes?
When a newborn's eyes wander in different directions, it can alarm even an experienced mother. Strabismus in infants can be of two types:
- Functional. This condition is not a pathology. During intrauterine development, the child had no need to focus his gaze, so his eyeball muscles are not trained. The centers of the brain that control eye movement reach a level of sufficient development by 3-4 months. Until this age, the pupils of infants act uncoordinated and can move horizontally, only mastering vertical movement. The skull of newborns has a peculiarity: its right and left halves form an angle, so from the outside it seems that it is squinting. Functional strabismus disappears by the first six months of life.
- Persistent strabismus - strabismus, heterotropia. The visual axes of both eyes are unable to connect to one point, and the eyes always look in different directions. If a baby has this pathology from birth, it is in vain to expect that strabismus will go away by 4-6 months of life. Persistent strabismus occurs in 2% of newborns; it is due to the following reasons:
- oxygen starvation of the fetus during pregnancy and childbirth leads to disruption of the visual centers of the brain;
- infectious diseases of the mother, especially in the first trimester of pregnancy;
- complications after infections suffered by the newborn itself;
- congenital brain diseases (cerebral palsy, Down's disease, etc.);
- severe fear, other mental or physical trauma;
- hereditary factor.
Authoritative pediatrician E. Komarovsky warns: if after 6 months the child’s strabismus does not go away, he must be taken to an ophthalmologist.
Advanced strabismus complicates the process of developing binocular vision; the baby’s brain will form compensatory reflexes, the strengthening of which will complicate treatment. A decrease in visual acuity is inevitable.
Strabismus in children under one year of age can be recognized by the following signs:
- The baby's gaze cannot concentrate on one point.
- No synchronous eye movement.
- In bright light, one eye closes or moves to the side.
- The baby turns his head to see the object with one eye.
- The child bumps into surrounding objects, because... Poorly assesses spatial depth.
The baby crosses his eyes Komarovsky
Often after childbirth, mothers discover strabismus in children, the causes and treatment of which E. Komarovsky recommends identifying and prescribing only after the first 4-6 months of life.
Strabismus in newborns is a normal physiological phenomenon; in the first months of life it should not cause alarm.
But if the child’s eyes continue to work inconsistently, the strabismus must be treated - and the sooner the better.
Why do newborns cross their eyes?
When a newborn's eyes wander in different directions, it can alarm even an experienced mother. Strabismus in infants can be of two types:
- Functional. This condition is not a pathology. During intrauterine development, the child had no need to focus his gaze, so his eyeball muscles are not trained. The centers of the brain that control eye movement reach a level of sufficient development by 3-4 months. Until this age, the pupils of infants act uncoordinated and can move horizontally, only mastering vertical movement. The skull of newborns has a peculiarity: its right and left halves form an angle, so from the outside it seems that it is squinting. Functional strabismus disappears by the first six months of life.
- Persistent strabismus - strabismus, heterotropia. The visual axes of both eyes are unable to connect to one point, and the eyes always look in different directions. If a baby has this pathology from birth, it is in vain to expect that strabismus will go away by 4-6 months of life. Persistent strabismus occurs in 2% of newborns; it is due to the following reasons:
- oxygen starvation of the fetus during pregnancy and childbirth leads to disruption of the visual centers of the brain;
- infectious diseases of the mother, especially in the first trimester of pregnancy;
- complications after infections suffered by the newborn itself;
- congenital brain diseases (cerebral palsy, Down's disease, etc.);
- severe fear, other mental or physical trauma;
- hereditary factor.
Authoritative pediatrician E. Komarovsky warns: if after 6 months the child’s strabismus does not go away, he must be taken to an ophthalmologist.
Advanced strabismus complicates the process of developing binocular vision; the baby’s brain will form compensatory reflexes, the strengthening of which will complicate treatment. A decrease in visual acuity is inevitable.
Strabismus in children under one year of age can be recognized by the following signs:
- The baby's gaze cannot concentrate on one point.
- No synchronous eye movement.
- In bright light, one eye closes or moves to the side.
- The baby turns his head to see the object with one eye.
- The child bumps into surrounding objects, because... Poorly assesses spatial depth.
Causes and types of strabismus
True strabismus is not always a congenital pathology. During the first 3 years, when binocular (3D) vision is actively developing, the following reasons lead to the appearance of an asymmetrical gaze:
- congenital farsightedness or myopia - the difference in refraction between the right and left eyes;
- diseases of the central nervous system: cerebral palsy, brain tumor, etc.;
- severe stress: bruise, fright, vaccination, acute respiratory viral infection or other viral disease.
Normal operation of both eyes produces two images; the visual analyzer combines them into one and forms a three-dimensional image. With strabismus, the images fail to connect and the brain ignores what the squinting eye sees.
His visual acuity gradually decreases, lazy eye syndrome may develop, he stops moving and perceiving objects. The child develops a flat image of the world.
Established pathology is difficult to correct, so it is important to start treatment on time.
If there are cases of hereditary strabismus in the family, parents should regularly check the child's vision in the first three years.
Dr. Komarovsky emphasizes that in the period up to 3 years, any injury can provoke heterotropia, and at this time, hidden strabismus, invisible in a newborn, progresses. Therefore, visits to the ophthalmologist should be mandatory at 2, 6, 12 months, and then once a year until school age.
In total, there are about 25 types of strabismus, the formation mechanism of each of them is different, and, therefore, the treatment methods are different. Based on the displacement of the visual axes, 4 types of strabismus are distinguished.
- esotropia - convergent strabismus, when the eyes converge on the bridge of the nose, this deviation occurs with congenital farsightedness;
- exotropia - divergent position of the eyes, when the ocular axes are shifted towards the temples, this type is characteristic of myopia;
- vertical heterotropia - displacement of the visual axis up or down.
Development of the disease
There are two different mechanisms for the development of strabismus.
- A concomitant form of strabismus, when refraction (refraction of rays) is impaired in one or both eyes. It is hereditary and manifests itself in childhood. It is treated with glasses and lenses if accommodation – vision focusing – is impaired. If there is organic damage to the optical media, corneal surgery or lens replacement is necessary.
- Paralytic form. The work of the eye deviates from normal fixation due to paresis of one or more muscles. Eye movement is limited to one direction; a glance in this direction is accompanied by a characteristic turn of the head. Paralysis of the eye muscles is most often an acquired pathology (trauma, severe stress, brain damage). Restoring normal eye movement function occurs through physical therapy and subsequent surgery to correct the paralyzed muscle.
As you can see, different forms of strabismus require their own treatment methods.
Dr. Komarovsky warns that self-treatment of strabismus with folk remedies can be harmful if the mechanism of its occurrence is unknown. Only an ophthalmologist can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment.
Modern methods of treating strabismus
The concomitant type of strabismus is treated for 2-3 years. The image on the retina is corrected using lenses and special glasses. Occlusion is used to correct low vision in the squinting eye (amblyopia).
The healthy eye is switched off from the act of vision (atropine and special stickers on the eye - occluders are used for this).
In this regard, Komarovsky advises sending a child with strabismus to specialized kindergartens, where all children are treated using this method, and there is no discomfort in communication. We list other treatment methods:
- synaptophore exercises – training of the eye muscles and nerve centers responsible for binocular vision;
- amblyopanorama – treatment with moving blinding fields, can be used from infancy;
- computer-based treatment using special game programs, used for children 3-4 years old and older;
- the Rucheek device trains the accommodative work of the eye muscles;
- virtual 3D glasses for the formation of three-dimensional vision;
- restorative procedures: acupressure, vitamin therapy.
The unfriendly (paralytic) type of strabismus is treated in 2 stages:
- Conservative treatment: gymnastics of the eye muscles; exercises to eliminate duality; physiotherapy (electrophoresis, reflexology, etc.).
- Surgery consists of shortening or weakening the eye muscle that deviates the eye from proper fixation. It is carried out using computer modeling using high-frequency radio wave technology.
A successful result in the treatment of strabismus is possible with timely seeking help from a specialist, with sufficient patience and persistence in following all the recommendations of the ophthalmologist.
Source: https://vmassazh.ru/info/mladenec-kosit-glazami-komarovskij/
Causes and types of strabismus
True strabismus is not always a congenital pathology. During the first 3 years, when binocular (3D) vision is actively developing, the following reasons lead to the appearance of an asymmetrical gaze:
- congenital farsightedness or myopia - the difference in refraction between the right and left eyes;
- diseases of the central nervous system: cerebral palsy, brain tumor, etc.;
- severe stress: bruise, fright, vaccination, acute respiratory viral infection or other viral disease.
Normal operation of both eyes produces two images; the visual analyzer combines them into one and forms a three-dimensional image. With strabismus, the images fail to connect and the brain ignores what the squinting eye sees. His visual acuity gradually decreases, lazy eye syndrome may develop, he stops moving and perceiving objects. The child develops a flat image of the world. Established pathology is difficult to correct, so it is important to start treatment on time.
If there are cases of hereditary strabismus in the family, parents should regularly check the child's vision in the first three years.
Dr. Komarovsky emphasizes that in the period up to 3 years, any injury can provoke heterotropia, and at this time, hidden strabismus, invisible in a newborn, progresses. Therefore, visits to the ophthalmologist should be mandatory at 2, 6, 12
months, and then once a year until school age.
In total, there are about 25 types of strabismus, the formation mechanism of each of them is different, and, therefore, the treatment methods are different. Based on the displacement of the visual axes, 4 types of strabismus are distinguished.
- esotropia - convergent strabismus, when the eyes converge on the bridge of the nose, this deviation occurs with congenital farsightedness;
- exotropia - divergent position of the eyes, when the ocular axes are shifted towards the temples, this type is characteristic of myopia;
- vertical heterotropia - displacement of the visual axis up or down.
A few words about strabismus in children
Very often, newborn babies experience minor or severe strabismus, which is why many parents begin to sound the alarm. As for heterotropia in infants, Komarovsky calls this a completely natural phenomenon.
The fact is that in the first months of life there is an active development of eye motor skills and babies are not yet able to master it. Both symmetrical parts of the face are slightly shifted, so they cannot take the correct position. As a rule, after a few months the correct position of the eyes is restored and the strabismus disappears. Every day the child masters the skills of proper eye coordination, measuring distance, etc.
According to the pediatrician, strabismus up to 4-6 months is not a cause for concern, but if it does not go away after six months, you should seek ophthalmological help to eliminate the problem.
Dr. Komarovsky insists that parents should carefully monitor the behavior and vision of their beloved child in order to be able to detect the problem in a timely manner and prevent its progression. Speaking about existing visual impairments in a child, Komarovsky strongly recommends sending children with heterotropia to specialized preschool institutions.
You may be interested in: What is convergent strabismus in a child and how to cure it?
Modern methods of treating strabismus
The concomitant type of strabismus is treated for 2-3 years. The image on the retina is corrected using lenses and special glasses. Occlusion is used to correct low vision in the squinting eye (amblyopia). The healthy eye is switched off from the act of vision (atropine and special stickers on the eye - occluders are used for this). In this regard, Komarovsky advises sending a child with strabismus to specialized kindergartens, where all children are treated using this method, and there is no discomfort in communication. We list other treatment methods:
synaptophore exercises – training of the eye muscles and nerve centers responsible for binocular vision;- amblyopanorama – treatment with moving blinding fields, can be used from infancy;
- computer-based treatment using special game programs, used for children 3-4 years old and older;
- the Rucheek device trains the accommodative work of the eye muscles;
- virtual 3D glasses for the formation of three-dimensional vision;
- restorative procedures: acupressure, vitamin therapy.
The unfriendly (paralytic) type of strabismus is treated in 2 stages:
- Conservative treatment: gymnastics of the eye muscles; exercises to eliminate duality; physiotherapy (electrophoresis, reflexology, etc.).
- Surgery consists of shortening or weakening the eye muscle that deviates the eye from proper fixation. It is carried out using computer modeling using high-frequency radio wave technology.
A successful result in the treatment of strabismus is possible with timely seeking help from a specialist, with sufficient patience and persistence in following all the recommendations of the ophthalmologist.
Having returned from the maternity hospital with their child, over time, parents may notice strabismus in the newborn, expressed to one degree or another. By paying attention to this issue at an early stage and taking it under control, you can be sure that the baby’s defect will become less noticeable or disappear completely.
Causes and types
The most common type of strabismus (strabismus) in infants is physiological. It is precisely explained by the peculiarities of the eyes of newborn babies. Underdevelopment and weakness of the eye muscles leads to the fact that a newborn either squints his eyes towards the bridge of his nose, or they diverge towards his temples. More often, this form of strabismus occurs in premature babies.
The next common form of strabismus is imaginary. It is associated with the characteristics of the body:
- asymmetrical eye sockets;
- structural features of the facial skull;
- fold of skin at the corner of the eye.
Less common is the congenital form of the disease. The cause of congenital strabismus in children is heredity. If parents have such a defect, there is a high probability that the baby will also develop strabismus. It is impossible to determine this in the first three months of life, since this period is accompanied by physiological strabismus in newborns.
Even less often, such visual impairment occurs against the background of any disease. The main causes of the pathological condition of newborns are:
- intrauterine viral infections - measles, rubella, CMV;
- toxic damage to areas of the fetal brain responsible for the functioning of the eye muscles;
- birth injury;
- meningitis or encephalitis;
- parasites in the medulla;
- traumatic brain injury;
- brain tumor.
Congenital and pathological strabismus is called true. There are two forms of it:
- converging - the newborn squints his eyes towards the inner corner;
- divergent – there is a divergence of the eyeballs towards the temples.
This type of strabismus is called concomitant, since both eyeballs change their position. If the deviation is one-sided, they speak of paralytic strabismus.
How does strabismus manifest in a newborn?
As soon as a child is born, he is not immediately adapted to external environmental conditions. This applies to all sense organs, which are not fully developed and gradually return to normal as the baby grows. Regarding vision, in some newborns you can notice that the eyes do not obey their owner and spontaneously move apart or are reduced to the bridge of the nose, and this process can occur discordantly, and not synchronously.
Strabismus (strabismus) accounts for 2 to 3.5% of the total number of pathologies of the visual organs (more than 10 million patients).
With strabismus, the eyes of a newborn from time to time move apart to the sides, then converge towards the bridge of the nose, and in turn
At the beginning of life, a child has a lot to learn, including how to fully control his body. Taking control of eye movements is as important as developing dexterity and precision in hand movements. However, to fully see is a paramount task, since he receives 90% of the information about the world around the child through vision. Controlling the movement of the eyeball, focusing your gaze on a specific object, observing the actions of others simultaneously with both eyes - not every newborn is able to immediately master such complex work.
How quickly can a child master the skill of eye movement control? The so-called functional strabismus disappears by 3–4 months of the baby’s life. It is believed that by this moment the baby should learn to focus his gaze and concentrate it on the object of interest. Before this period, strabismus is normal and does not require treatment.
A baby in the first months of life is still learning to fix his gaze - he tries to focus it on the rattle for a few seconds, and then his eyes get tired, and one of them moves to the side
If strabismus has not gone away by the age of six months, you should definitely show the child to an ophthalmologist, since this pathology can negatively affect the formation of vision for the rest of his life.
Video: Dr. Komarovsky’s opinion on strabismus
The baby has a squint...
Is it possible to completely cure strabismus?
It is possible to quickly and permanently rid a child of strabismus. To do this, you just need to see the symptoms in a timely manner and contact an ophthalmologist to decide on further actions.
Depending on the type of strabismus and the severity of the situation, the doctor may suggest the following treatment methods:
- Special gymnastics for the eyes (diploptics).
- Vision correction using optics.
- Procedures using devices.
- Pleoptics are techniques that are used to normalize the functions of the yellow spots of the retina.
- Surgical intervention.
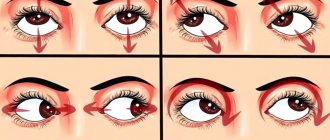
The most common method is special exercises for the eyes. This is especially true for young children and conditions in which the disease is not advanced.
Examples of exercises for children at the initial stage of strabismus
Exercises are performed under certain conditions.
Very often, newborn babies experience minor or severe strabismus, which is why many parents begin to sound the alarm. As for heterotropia in infants, Komarovsky calls this a completely natural phenomenon.
The fact is that in the first months of life there is an active development of eye motor skills and babies are not yet able to master it. Both symmetrical parts of the face are slightly shifted, so they cannot take the correct position. As a rule, after a few months the correct position of the eyes is restored and the strabismus disappears. Every day the child masters the skills of proper eye coordination, measuring distance, etc.
According to the pediatrician, strabismus up to 4-6 months is not a cause for concern, but if it does not go away after six months, you should seek ophthalmological help to eliminate the problem.
Dr. Komarovsky insists that parents should carefully monitor the behavior and vision of their beloved child in order to be able to detect the problem in a timely manner and prevent its progression. Speaking about existing visual impairments in a child, Komarovsky strongly recommends sending children with heterotropia to specialized preschool institutions.
You may be interested in: What is convergent strabismus in a child and how to cure it?
Komarovsky advises performing eye exercises for strabismus while wearing glasses, otherwise it will not be possible to achieve a high therapeutic effect.
During classes, the child should be in good health and mood. It is advisable to perform 2-3 20-minute approaches per day. I bring to your attention the most effective exercises for strengthening the eye muscles and eliminating strabismus in babies under one year of age:
- Bring the index finger of your outstretched hand closer and further away from your baby's nose. Make sure he watches the finger movement carefully.
- Take a tennis ball and hit it against the wall. The child will watch how the ball approaches and moves away, due to which vision will be aligned.
- The youngest children will benefit from activities with a rattle. To do this, one eye should be tied with a bandage and a bright toy should be held in front of the baby’s face. The child's task is to carefully observe the rattle without moving his head. Manipulations are first carried out with one eye, then with the other. To maintain your child’s interest, it is advisable to use different toys during the exercise.
The video asks whether strabismus is a cosmetic defect or is it still a disease? The doctor replies that this disease affects the psychological and social state, so it’s most likely like 2 in 1.
This condition may be congenital, or may appear after the birth of the child. In any case, I advise you to seek effective treatment methods individually from an ophthalmologist.
The human eye is a very fragile, but the most informative analyzer. With its help, we receive a huge amount of information from the world around us.
The visual centers are in close relationship with each other and have a strong influence on the activity of all functions and systems of the body: motor and vestibular, digestive and sexual. The first year of a child’s life is extremely important for the formation and development of vision, when his eyes and body are easily exposed to harmful internal and external influences.
A pathology in the condition of the visual organs, characterized by a displacement of the ocular axes, is called strabismus. If the ocular axes are shifted towards the bridge of the nose, such strabismus is called convergent. That is, the eyes seem to gather in a bunch. One eye can also squint; it is located with the pupil closer to the nose, or two eyes in turn: first one, then the other. There are many other types of strabismus, temporary or permanent.
Eye injuries or improperly developed eye muscles cause strabismus. A child’s vision requires special attention between two and three years, when at this time they develop the ability to simultaneously clearly see the image of an object with both eyes, that is, binocular vision.
Impaired binocular vision leads to strabismus. The causes of its development may be infectious diseases and hereditary factors, mental problems and brain injuries.
If the ocular axes are shifted towards the temples, such strabismus is called divergent. It can be constant or periodic. The permanent is divided into congenital, sensory and secondary.
Periodicity can be of the following types: basic, weakness of convergence, excess of divergence.
READ MORE: Why does a child sleep with his eyes slightly open?
Congenital divergent strabismus appears from birth and is treated mainly surgically. With sensory divergent strabismus, doctors try to initially eliminate the cause of vision loss; if this is not possible, then they use surgical methods. Secondary strabismus can also be corrected with surgery.
Periodic divergent strabismus appears at the age of two. For such a diagnosis, correction with glasses and surgical treatment are used for up to five years.
To treat strabismus, a set of special exercises, drug therapy, or surgery are used.
In early childhood, strabismus is treated with special glasses or a patch that is placed on the dominant eye, thereby stimulating the visual function of the second eye. Also, in addition to glasses and bandages, children are given a course of special exercises for both eyes.
Parents must take control of this process and, if they strictly follow all the instructions of the attending physician, strabismus in the child can be overcome.
Traditional methods of treatment also suggest using bandages, and recommend removing bright toys and flashy objects from children and their cribs. You should also ensure that the baby maintains a calm mental state, do not allow sudden movements and actions in the immediate vicinity of him, and do not bring various objects too close to his nose.
1. Heredity.
3. Neuromuscular diseases (myasthenia gravis, multiple sclerosis).
5. Severe refractive errors (farsightedness, myopia, high-grade astigmatism)
Examination of a child with strabismus
The doctors directed their (and my) attention to the fact that the child had torticollis when, at the time set by nature, he was unable to “hold his head.” Before this circumstance, nothing was noticeable.
Although, with our prematurity, we regularly and regularly visited all specialists. And when the pathology was noticed by would-be specialists, it was already visible even to the layman’s eye: the baby’s torticollis was obvious.
We solved the problem, and you can too. We hope that this publication will help you take the necessary measures on time.
True, up to 6 months the baby has every right to mow. But if strabismus persists after this period, the child squints, turns or tilts his head when talking, it is worth consulting a pediatric ophthalmologist. It will help you figure out what the problem is, because there are more than 20 types of strabismus.
IN SEARCH OF A DIAGNOSIS
The next visit to the ophthalmologist took place when Max was already more than 2 years old. The doctor recommended acupuncture. I had already made an appointment, but my ardor was cooled by a friend: “Do you really think that the baby will withstand treatment that not every adult likes?” “It won’t last,” I agreed, sighing.
By the end of the first week of a baby’s life, you can independently diagnose the pathology in question. To do this, you need to take a rattle and remove it from the child’s eyes at different distances, moving it from side to side. Carefully monitor the reaction of the child's eyes when observing a moving object and draw a conclusion about how mobile the baby's pupils are.
In newborns, the gaze may be discoordinated until 3-4 months; after this age, both eyes become aligned. In some cases, in children with a wide bridge of the nose, strabismus may be apparent. You should consult a doctor and sound the alarm only if, after 4 months of life, the child’s eyes do not look at the same point most of the time.
If a child's eyes run in different directions, parents should look at things straight and rush to the ophthalmologist.
When Maxim was born, he closed one eye slightly, which is why his gaze seemed stern and distrustful. I soon noticed that my son sometimes squints, especially when looking at objects at close range. However, the pediatrician said that such strabismus occurs in many infants and usually goes away after six months, when they learn to control the movement of the eye muscles.
After six months, the strabismus did not disappear, and we went to the ophthalmologist. They didn’t find anything wrong with Max, the doctor advised him to do eye exercises: move a bright rattle in front of the child’s face so that he would follow it. I’ll be honest: I didn’t have enough patience or time for this.
Measles, scarlet fever, influenza and other infections can cause strabismus. Therefore, when your baby is sick, be sure to make sure that he does not overstrain his eyesight.
2. Prematurity with weight less than 2 kg.
4. Congenital anomalies of the development of the eyes and eye muscles.
6. Tumors of the nervous system or the eyes themselves.
7. Cataract.
8. Injuries and infections.
9. Systemic diseases (for example, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis).
Particular attention should be paid to vision in children at risk, since they have a very high likelihood of developing strabismus.
Torticollis is not a happy diagnosis, but it is fixable.
Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye is called conjunctivitis. Komarovsky says that conjunctivitis in children is a common phenomenon.
Since there are many different reasons that contribute to the development of the disease, they must first be identified. And only then plan treatment therapy.
Newborn babies require special attention. Due to weak immunity, their health is at risk, because illness can cause serious consequences.
Of course, at home you will not be able to make an accurate diagnosis, but you will be able to determine the degree of probability of vision pathology in your child.
How to treat strabismus in children? Treatment of the disease is possible conservative (therapeutic) and surgical.
Therapeutic treatment of strabismus must be complex and long-term. In addition, start it as early as possible.
Main stages of conservative treatment:
- diagnosis of the disease with mandatory identification of the circumstances of strabismus
- early optical vision correction (selection of glasses or soft contact lenses)
- treatment of amblyopia (increasing visual acuity of the eyes)
- diploptic and orthoptic treatment (development of binocular vision)
- consolidation of results
- development of stereoscopic vision
Only if therapeutic treatment is ineffective should one resort to surgical interventions.
The optimal age for performing surgeries to correct strabismus in children is 4-5 years of age. Only at this age is the baby able to do all the necessary orthoptic exercises after the operation.
But in the presence of congenital strabismus, characterized by a huge angle of deviation, surgical intervention can be performed at an earlier date.
Today, two types of operations for strabismus are used in medical practice. The first type is aimed at weakening the tense oculomotor muscle, which can be achieved by cutting the muscle, partial excision of muscle fibers, or muscle plastic surgery.
The second type is aimed at strengthening a weakened muscle, which can be achieved by excision of a section of muscle followed by fixation of the shortened muscle, shortening the muscle, or moving the site of fixation of the corresponding muscle.
READ MORE: Is it possible to have children after an inguinal hernia?
It should be noted that quite often during the operation, doctors have to resort to a combination of the listed types of surgery. If it is not known why the desired result was not achieved at the end of the operation, a secondary operation may be scheduled after 6-8 months.
It is noted that the operation in the first stages allows to get rid of a cosmetic defect, which greatly traumatizes the child’s psyche, while the restoration of visual functions takes a longer period of time.
In addition, in many cases, at the end of the operation, the development of a specific complication is noted, which manifests itself in the form of hypercorrection of vision, which is the result of errors in calculations.
Hypercorrection can develop both immediately after the operation and in the long term. Overcorrection is corrected by repeated surgery.
What is scleroplasty and in what cases is its use most effective, you can determine from this article.
Causes
Strabismus can be either a congenital or acquired pathology resulting from a complicated pregnancy or delivery. So, the cause of strabismus in infants can be:
- weak eye muscles are the main cause of physiological strabismus in newborns;
- difficult birth (including hypoxia or asphyxia of the child during delivery);
- infections suffered by the mother during pregnancy;
- fetal hypoxia while in the womb;
- the child has a neurological pathology (for example, increased intracranial pressure);
- congenital abnormalities of the motor muscles of the eye;
- genetic inheritance of strabismus from parents or close relatives;
- congenital pathologies of one eye against the background of a second healthy organ of vision:
- myopia;
- farsightedness;
- astigmatism (impaired shape of the eye lens);
- cataracts, corneal opacity;
- optic nerve diseases, etc.
Video: ophthalmologist Irina Kogut about childhood strabismus and its causes
Why does a newborn's eyes cross?
Strabismus is medically called strabismus. This disease often occurs in newborns. This is primarily due to weakness of the eye muscles.
They have not yet learned to keep up with the movement of the eyeball, so sometimes the eyes can look in different directions or, on the contrary, converge on the bridge of the nose. In some cases, only one eye may squint, while the other looks straight.
Uncoordinated actions of the visual organs can lead to horror for young parents. However, you shouldn't worry too much about this. Strabismus in newborns is a normal physiological process. Over time, the eye muscles will strengthen, and the baby will learn to control the movement of the eyeballs and focus on one object, just like adults.
It’s worse if the baby’s strabismus does not go away by the age of one year. This may already be a consequence of various diseases that the mother suffered during pregnancy or infectious diseases, and they affected the baby himself. Another reason may be the presence of inflammatory processes in newborns. This causes a strong blow to the immune system and leads to various problems, including with the eyes.
Parents themselves can also cause illness in a child if they do not care for him properly. Do not hang toys over the crib too close to the baby's head.
Symptoms of strabismus
Usually strabismus manifests itself already in the first days of a child’s life. Obvious symptoms of strabismus in a newborn:
- the baby is unable to direct both eyes to one place at once;
- in bright light or in the sun, the child closes one eye or squints it;
- the baby's pupils move in different directions;
- the baby tries to tilt his head to look at the object that interests him;
- the newborn squints his eyes.
In addition, strabismus is detected with a simple test, establishing the reaction of the baby’s eyes to the movement of a colorful object (for example, a bright, tinkling rattle), which is moved left and right, forward and backward, and also vertically. If strabismus is present, the child's eyes eventually stop moving in the direction of the toy.
To test for strabismus, you will need a bright rattle or any other richly colored toy.
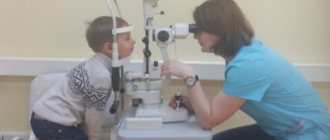
Usually, by the age of one month, all children are routinely examined by an ophthalmologist, performing this simple test during an appointment, thanks to which the doctor assesses the level of mobility of each eye.
Often, parents cannot independently determine the presence of minor visual impairments in a young child. Visiting a specialist at an early age is mandatory to diagnose possible pathologies.
A symptom of physiological strabismus is diverging eyes, in this case the axis of vision is shifted to the temples. Convergent strabismus at such an early age can sometimes indicate the course of independent diseases: cerebral palsy, Down syndrome and pathologies of brain development (microcephaly and other anomalies).
Video: physiological strabismus in a baby
Strabismus in newborns
If strabismus is detected in newborns - when does it go away, how to treat it? Such questions are often asked by parents whose children were born with strabismus. As a rule, mothers begin to sound the alarm, but in fact, this defect is easy to correct after birth. Moreover, most often strabismus goes away on its own. But it is still necessary to show the baby to an ophthalmologist, as complications may arise in the form of other ophthalmological diseases.
The main causes of strabismus in newborns
When a person is inside the womb, his body adapts precisely to such conditions. But when a child is born, he needs a new adaptation, this time to our world. It is difficult for any organ to immediately adjust, and even more so for the eyes. The eye muscles are not yet fully formed and do not have the necessary strength. Therefore, in the first days of life, the eyes squint a little. However, there are other causes of strabismus in newborns:
- Complicated childbirth and pregnancy. The fact is that the entire system of the longitudinal brain fasciculus, located behind, is responsible for the synchronous functionality of the eyeballs. If during pregnancy there is hypoxia of the unborn child, weakened microcirculation or other pathological disorders, then microscopic hemorrhage occurs, which disrupts the synchronous functioning of the eyes. If the baby was born for this reason, then parents should prepare for surgery. Because this type of pathology does not respond to conservative treatment methods.
- Another reason is infection of the mother during pregnancy. These can be such simple diseases as acute respiratory viral infections, influenza, acute respiratory infections, measles, scarlet fever, diphtheria, etc.
- A stressful situation for an infant also leads to the development of strabismus. But the disease is most often temporary and manifests itself only during crying or hysteria.
- Presence of ophthalmological pathologies.
- Cerebral palsy, hydrocephalus.
- Infectious diseases - ARVI, influenza, measles, scarlet fever, rubella, diphtheria.
- Injury to the visual organ.
- Genetic predisposition.
Types of strabismus in an infant
IMPORTANT! When will strabismus in a newborn go away? This is probably the most important and worrying question for parents. In fact, strabismus is considered normal up to six months. If it does not go away during this period, then it is important to conduct a more thorough examination of the visual organs by an ophthalmologist.
The main types of strabismus in infants include the following:
- Depending on the time of development, the pathology can be congenital or acquired.
- Stability of manifestation: constant and periodic appearance.
- Degree of involvement: intermittent, unilateral and monolateral.
- Type of deviation: vertical and horizontal. The vertical type of strabismus is characterized by an upward or downward displacement. The horizontal type can be converging (the eyes are shifted towards the bridge of the nose), divergent (the eyes are turned towards the temples) and mixed.
- Development mechanism: accommodative, non-accommodative and partially accommodative.
What to do?
When parents discover strabismus in their newborns, they should immediately contact an ophthalmologist. Next, it is important to visit this specialist every two months. And only after reaching 6 months will the doctor be able to accurately diagnose and identify the type of disease. For six months, parents must independently stimulate the functioning of the eye muscle system. To do this, you need to give your baby only bright and large toys. It is very important to hang rattles above the generally accepted height so that visual concentration is correct. It is advisable to do gymnastics with your newborn every day. These can be simple but effective exercises. The child needs to be in a reclining position. Mom should pick up a bright toy and move it from one side to the other. At the same time, the baby will follow the movement of the object and exercise his eyes, which leads to strengthening of the eye muscles. Then the toy must be moved up and down. If the baby does not respond to the object, then take a toy with sound.
Strabismus in newborns: when does it go away?
Immediately after birth, the baby's eyes cannot fixate the gaze, but the first fixation is noted after a week of life. But it is also short-lived, so at this age it is almost impossible to make an accurate diagnosis. If only the slanting is very pronounced. The child begins to steadily fix his gaze with both eyes at the same time only after a month or a month and a half. But by six months he should be able to distinguish objects and fix his gaze on them synchronously. That is why this age is considered the maximum for making an accurate diagnosis.
When strabismus in newborns goes away - Komarovsky, as an experienced pediatrician, largely agrees with the opinion of his colleagues. Because this physiological feature is characteristic of infants due to the unformed muscular system of the eyes. The point is also that in the first month and a half, babies can only see in the horizontal direction. And only after that vertical vision develops. If this does not happen, then binocular vision is impaired. Therefore, Komarovsky believes that up to six months it is necessary to be especially attentive to the reactions of the child’s eyes.
Rules for the treatment of strabismus in newborns
There is no point in treating strabismus in newborns up to six months. But it is important to carry out certain manipulations during this period. Firstly, it is necessary to create conditions for the normal development of the visual apparatus. This involves good lighting in the room, placing toys at a certain distance and allowing the child to play with large toys. If the baby has other ophthalmological abnormalities, they must be treated in a timely manner. Since strabismus can occur against the background of a stressful situation, parents should avoid them. Namely, you cannot make sharp and excessively loud sounds, appear in front of the child suddenly, and so on. In a word, fear must not be allowed.
False and true strabismus
A child’s eyes hurt - possible reasons, how you can help your baby
False strabismus is most often observed in infants. The impression of slanted eyes occurs due to the fact that the eyes are set close to the bridge of the nose, or the facial skull has a special structure. The most important reason is the immaturity of the central nervous system, which cannot sufficiently control the child’s eye movements. This condition goes away on its own as the baby grows (usually by six months the eyes are completely level).
True strabismus is diagnosed at 5-6 months of age based on the results of a medical examination.
Imaginary strabismus
Need for therapy
If there is a slight deviation from the norm in children, parents may not pay significant attention to this problem. However, you should know that ignoring even the slightest strabismus in the future is fraught with consequences such as:
- stop in the development of a squinting eye;
- difficulties in eliminating the defect due to the habit of the eye being in the wrong position;
- development of amblyopia - “lazy eye”;
- decreased vision.
In addition to a defect in appearance, strabismus can cause deterioration of vision in the squinting eye
The reason for the deterioration of visual perception lies in the high adaptability of the child’s brain. Unable to compare the image from the healthy and squinting eye, the brain begins to receive and process information only from the eye that is functioning correctly. This causes gradual loss of vision in the affected eye due to its detachment from the transmission of images and visual images.
Treatment of strabismus
As mentioned above, with functional strabismus the child does not need therapy. However, the true disease must be treated, and as soon as possible. A special sign that helps to identify pathology of the organ of vision at an early age is a decrease in the mobility of the squinting eye or its complete absence, and if the optic nerve is damaged, the occurrence of pupil dilation and drooping of the eyelid.
Even if the disease is congenital, if therapy is started in a timely manner, it can be successfully treated. Unfortunately, all effective medical methods are applicable to children from the age of two. Therefore, you can only work with kids at home. Doctors recommend playing with infants games with focusing vision (with a rattle or ball, which are located at the optimal distance from the eyes - 40 cm) and other exercises that promote the full range of movements of the organ of vision (provoke the pupils to draw circles and figure eights, lead the baby to engage in extreme upper and lower positions of the eye). You need to start doing the exercises gradually, with two reactions a day, and by six months reach ten reactions.
If a congenital disease is confirmed and a strabismus angle is greater than 15 0, surgical intervention is often required. However, such treatment is allowed only from the age of three, and the optimal age would be to reach the age of 4–5 years, when the child is able to perform the set of orthoptic exercises prescribed after the operation.
Surgery to eliminate strabismus is prescribed in cases where other therapeutic measures do not help and the duration of treatment is more than a year.
At an early age, other methods of therapy are applicable, for example, if amblyopia is detected in an infant, he is prescribed treatment using the occlusion method (artificial closure of the healthy eye to improve the performance of the other).
The so-called direct occlusion method implies that the child’s healthy eye is switched off from work for a certain time.
Occlusion is possible in one of several types as prescribed by the treating specialist:
- straight - with the healthy eye closed;
- reverse - with closing the squinting eye;
- alternating - in this case, alternating closing of the eyes occurs.
The duration of exclusion of the eye from visual work depends on the complexity of the problem. Occlusion can be either temporary or permanent. Treatment of amblyopia using modern hardware methods is prescribed to children at an older age, but this method is not indicated for infants.
For children with vision problems, massage of the collar area is recommended, which helps improve blood supply to the brain and has a positive effect on the functioning of the visual organs. Only a specialist with a medical education can perform such a massage on newborns. Typically, the child is prescribed a ten-day course of massage, followed by its repetition after 6 months.
Among other things, if a baby has strabismus, it is important in the first months of his life (especially up to six months) to pay attention to supporting full breastfeeding, without early supplementary feeding with formula and introducing complementary foods. Mother's milk contains all the necessary elements for the development of the baby's vision.
A newborn's eyes squint: is this normal, reasons, advice from Dr. Komarovsky
Having returned from the maternity hospital with their child, over time, parents may notice strabismus in the newborn, expressed to one degree or another. By paying attention to this issue at an early stage and taking it under control, you can be sure that the baby’s defect will become less noticeable or disappear completely.
How does strabismus manifest in a newborn?
As soon as a child is born, he is not immediately adapted to external environmental conditions. This applies to all sense organs, which are not fully developed and gradually return to normal as the baby grows.
Regarding vision, in some newborns you can notice that the eyes do not obey their owner and spontaneously move apart or are reduced to the bridge of the nose, and this process can occur discordantly, and not synchronously.
Strabismus (strabismus) accounts for 2 to 3.5% of the total number of pathologies of the visual organs (more than 10 million patients).
With strabismus, the eyes of a newborn from time to time move apart to the sides, then converge towards the bridge of the nose, and in turn
At the beginning of life, a child has a lot to learn, including how to fully control his body. Taking control of eye movements is as important as developing dexterity and precision in hand movements.
However, to fully see is a paramount task, since he receives 90% of the information about the world around the child through vision.
Controlling the movement of the eyeball, focusing your gaze on a specific object, observing the actions of others simultaneously with both eyes - not every newborn is able to immediately master such complex work.
How quickly can a child master the skill of eye movement control? The so-called functional strabismus disappears by 3–4 months of the baby’s life. It is believed that by this moment the baby should learn to focus his gaze and concentrate it on the object of interest. Before this period, strabismus is normal and does not require treatment.
A baby in the first months of life is still learning to fix his gaze - he tries to focus it on the rattle for a few seconds, and then his eyes get tired, and one of them moves to the side
If strabismus has not gone away by the age of six months, you should definitely show the child to an ophthalmologist, since this pathology can negatively affect the formation of vision for the rest of his life.
Causes
Strabismus can be either a congenital or acquired pathology resulting from a complicated pregnancy or delivery. So, the cause of strabismus in infants can be:
- weak eye muscles are the main cause of physiological strabismus in newborns;
- difficult birth (including hypoxia or asphyxia of the child during delivery);
- infections suffered by the mother during pregnancy;
- fetal hypoxia while in the womb;
- the child has a neurological pathology (for example, increased intracranial pressure);
- congenital abnormalities of the motor muscles of the eye;
- genetic inheritance of strabismus from parents or close relatives;
- congenital pathologies of one eye against the background of a second healthy organ of vision: myopia;
- farsightedness;
- astigmatism (impaired shape of the eye lens);
- cataracts, corneal opacity;
- optic nerve diseases, etc.
Symptoms of strabismus
Usually strabismus manifests itself already in the first days of a child’s life. Obvious symptoms of strabismus in a newborn:
- the baby is unable to direct both eyes to one place at once;
- in bright light or in the sun, the child closes one eye or squints it;
- the baby's pupils move in different directions;
- the baby tries to tilt his head to look at the object that interests him;
- the newborn squints his eyes.
In addition, strabismus is detected with a simple test, establishing the reaction of the baby’s eyes to the movement of a colorful object (for example, a bright, tinkling rattle), which is moved left and right, forward and backward, and also vertically. If strabismus is present, the child's eyes eventually stop moving in the direction of the toy.
To test for strabismus, you will need a bright rattle or any other richly colored toy.
Usually, by the age of one month, all children are routinely examined by an ophthalmologist, performing this simple test during an appointment, thanks to which the doctor assesses the level of mobility of each eye.
Often, parents cannot independently determine the presence of minor visual impairments in a young child. Visiting a specialist at an early age is mandatory to diagnose possible pathologies.
A symptom of physiological strabismus is diverging eyes, in this case the axis of vision is shifted to the temples. Convergent strabismus at such an early age can sometimes indicate the course of independent diseases: cerebral palsy, Down syndrome and pathologies of brain development (microcephaly and other anomalies).
Depending on the direction of deviation, strabismus can be vertical (displacement upward or downward), horizontal (deviation of the eye towards the temple or bridge of the nose) and mixed
Need for therapy
If there is a slight deviation from the norm in children, parents may not pay significant attention to this problem. However, you should know that ignoring even the slightest strabismus in the future is fraught with consequences such as:
- stop in the development of a squinting eye;
- difficulties in eliminating the defect due to the habit of the eye being in the wrong position;
- development of amblyopia - “lazy eye”;
- decreased vision.
In addition to a defect in appearance, strabismus can cause deterioration of vision in the squinting eye
The reason for the deterioration of visual perception lies in the high adaptability of the child’s brain. Unable to compare the image from the healthy and squinting eye, the brain begins to receive and process information only from the eye that is functioning correctly. This causes gradual loss of vision in the affected eye due to its detachment from the transmission of images and visual images.
Treatment of strabismus
As mentioned above, with functional strabismus the child does not need therapy. However, the true disease must be treated, and as soon as possible.
A special sign that helps to identify pathology of the organ of vision at an early age is a decrease in the mobility of the squinting eye or its complete absence, and if the optic nerve is damaged, the occurrence of pupil dilation and drooping of the eyelid.
Even if the disease is congenital, if therapy is started in a timely manner, it can be successfully treated. Unfortunately, all effective medical methods are applicable to children from the age of two. Therefore, you can only work with kids at home.
Doctors recommend playing with infants games with focusing vision (with a rattle or ball, which are located at the optimal distance from the eyes - 40 cm) and other exercises that promote the full range of movements of the organ of vision (provoke the pupils to draw circles and figure eights, lead the baby to engage in extreme upper and lower positions of the eye).
You need to start doing the exercises gradually, with two reactions a day, and by six months reach ten reactions.
If a congenital disease is confirmed and the presence of a strabismus angle greater than 150, surgical intervention is often required. However, such treatment is allowed only from the age of three, and the optimal age would be to reach the age of 4–5 years, when the child is able to perform the set of orthoptic exercises prescribed after the operation.
Surgery to eliminate strabismus is prescribed in cases where other therapeutic measures do not help and the duration of treatment is more than a year.
At an early age, other methods of therapy are applicable, for example, if amblyopia is detected in an infant, he is prescribed treatment using the occlusion method (artificial closure of the healthy eye to improve the performance of the other).
The so-called direct occlusion method implies that the child’s healthy eye is switched off from work for a certain time.
Occlusion is possible in one of several types as prescribed by the treating specialist:
- straight - with the healthy eye closed;
- reverse - with closing the squinting eye;
- alternating - in this case, alternating closing of the eyes occurs.
The duration of exclusion of the eye from visual work depends on the complexity of the problem. Occlusion can be either temporary or permanent. Treatment of amblyopia using modern hardware methods is prescribed to children at an older age, but this method is not indicated for infants.
For children with vision problems, massage of the collar area is recommended, which helps improve blood supply to the brain and has a positive effect on the functioning of the visual organs. Only a specialist with a medical education can perform such a massage on newborns. Typically, the child is prescribed a ten-day course of massage, followed by its repetition after 6 months.
Among other things, if a baby has strabismus, it is important in the first months of his life (especially up to six months) to pay attention to supporting full breastfeeding, without early supplementary feeding with formula and introducing complementary foods. Mother's milk contains all the necessary elements for the development of the baby's vision.
Diagnostics
The simplest diagnosis can be done at home. You need to ask someone to attract the baby’s attention with a toy and cover his eye with a piece of thick cardboard. Then close the second eye, carefully watching the first. The position of the first eye should not change - the child should continue to look at the toy. The same thing needs to be observed with the second eye. If the position has not moved. There's no reason to worry.
In medical institutions, diagnosis will be difficult and take a lot of time. First of all, the doctor will check your visual acuity. The procedure is carried out first without the use of corrective lenses, and then with them. Now computer technology can be used for this procedure. They identify problems more accurately.
It is necessary to determine the amount of movement, the angle of squint and the position of the eyes. It is also necessary to examine the anterior segment, the conducting media of the eye, and the fundus. It is necessary to determine the refraction of the child’s eyes. This procedure is done on narrow and wide pupils. The next step will be a binocular vision examination.
How to select contact lenses, see this article.
After receiving all the data and consulting with an ophthalmologist, you can begin treatment.
Under no circumstances should you self-medicate. This will only harm your child!
Preventive measures
If strabismus develops due to pathologies of the visual organs, such as amblyopia, there are no preventive measures. Parents need to undergo medical examinations recommended by the pediatrician on time, so that in the event of eye problems, the ophthalmologist can detect the problem as early as possible and prescribe treatment.
To prevent other causes that cause the development of true strabismus, during the period of bearing a child, the expectant mother must adhere to the following rules:
- minimize any possible exposure to toxic substances;
- get rid of existing bad habits;
- lead a healthy lifestyle with proper physical activity and diet;
- treat infections that occur during pregnancy in a timely manner;
- support the body's defenses and strengthen the immune system.
After the birth of the baby, the prevention of strabismus is facilitated by activities and games with the child, stimulating the work of the eye muscles. It is necessary to purchase large toys of bright colors for the baby, which are hung above the crib at a distance of no less than 40 and no more than 50 cm. By looking at them, the child learns to focus his gaze and strengthens the eye muscles. At the same time, you should not forget to regularly change places of toys or objects.
For prevention or when diagnosing friendly strabismus, toys must be hung on both sides so that the baby does not move his eyes to his nose, trying to see a bright object.
It is not recommended to place a newborn in front of loud household appliances, including a TV. With low visual acuity and myopia, infants have well-developed hearing and try to look for the source of sound with their eyes, provoking overexcitation of the nervous system.
And it is also important to pay attention to lighting: during the daytime, the child should receive maximum natural light, and in the evening, while the baby is awake, there should be soft diffused light from several sources in the room. Toys for small children should not be glowing or flashing, as this causes irritation of the retina and overstimulation of the nervous system.
Normally, the physiological strabismus of infants should go away by 3–4 months of life. Do not forget that the presence of strabismus is not only a cosmetic defect. This is both a violation of the visual process and a deterioration in the ability to perceive the surrounding world in volume. By approaching the issue of childhood strabismus with full responsibility, parents will ensure their child has good vision and an attractive appearance in the future.
Strabismus in children is a topic for a very serious conversation, but only after the child is six months old. Before this, some “slanting” in babies may be quite normal, and therefore parents should not worry unnecessarily.
If after 6 months the baby apparently “mows,” then treatment should be started as soon as possible, according to the famous pediatrician Evgeniy Komarovsky.
He tells moms and dads about what childhood strabismus can be like and how to treat it.
When will strabismus in newborns go away: temporarily or permanently?
Running eyes in the first weeks and sometimes months of a baby’s life are a normal phenomenon. Because of its occurrence, it is impossible to say that the baby has persistent strabismus, since this symptom is observed at this age in all children.
It appears due to imperfect functioning of some systems of their body. So, if a child is not even six months old, then his eyeball muscles are still in the development stage, as well as the brain system of the longitudinal fasciculus, which affects their movement. As soon as they are fully formed, strabismus will no longer be observed in the infant.
What can cause a child's vision to deteriorate?
The following reasons may influence the development of strabismus in an infant:
- injuries he received during childbirth;
- infectious diseases of the brain;
- close proximity of toys and rattles in front of the baby’s face;
- a complication that arose due to the lack of treatment for farsightedness, astigmatism and myopia;
- genetic predisposition;
- extreme mental or physical stress;
- congenital diseases such as Down syndrome, cerebral palsy, as well as brain tumors or microcephaly;
- inflammatory, tumor or vascular changes in the eye muscles;
- infectious diseases suffered by the mother while carrying the baby;
- injuries he received after childbirth.
Also, strabismus can develop in a baby if during pregnancy the mother was repeatedly kept in the perinatal center for preservation due to fetal hypoxia or due to blood flow disorders. It can also occur if she was tormented by toxicosis throughout the entire period of bearing a child.
Visual signs of a problem developing
Dangerous or not? Find out more about conjunctival cysts here.
Strabismus does not go away on its own. He definitely needs to be treated. Therefore, if you find any symptoms indicating it, you should consult an ophthalmologist.
All these factors can affect the development of those parts of the baby’s brain that are responsible for the functioning of the eye muscles. Complicated childbirth can cause microscopic hemorrhages in the brain, which can also cause visual impairment.
Causes of temporary strabismus:
- fright;
- bright light;
- stress.
If strabismus does not go away by one year, you should go to the doctor.
When the inflammation has “gone” too far, treatment is iridocyclitis.
When does imaginary strabismus go away?
If the baby has functional, and not persistent strabismus, then six months after birth his eyes will no longer diverge in different directions. In the first few months, the baby will learn to control his eye muscles, which he did not need to do in his tummy.
It is precisely because of their insufficient development and lack of training that he is unable to initially focus his gaze on objects. Instead, the eyes either scatter in different directions or converge together towards the bridge of the nose.
Types of strabismus (photo)
Proper care for contact vision correction products - which lens solution is best to choose.
Is this a serious disease? What does E. Komarovsky think about this?
The famous pediatrician, like other doctors, believes that strabismus in infancy is not a pathology, but a normal phenomenon. He always explains this to the mothers who contact him.
A working method to restore vision! You will throw your glasses in the trash in just 3 days...
Restoring vision. Real life story.
He also tells them that in the first 4-8 weeks after birth, their babies’ eyes can only run from side to side, that is, horizontally. After 1-2 months they will begin to master the vertical direction. By 4-6 months, babies should stop squinting their eyes.
Read how keratopathy occurs and is treated here.
E. Komarovsky urges all parents, when identifying strabismus in a six-month-old baby, not to try to treat it themselves. Only an experienced specialist should prescribe therapy.
The best remedy for fighting cataracts is Catarax eye drops.
Close proximity of toys is harmful to vision
Methods for treating demodicosis of the eyes in humans are described in detail in the article.
What to do if it doesn’t go on time
If, 6 months after birth, the baby’s eyes continue to move, it means he has persistent strabismus. The sooner parents turn to an ophthalmologist and begin treatment for this pathology in the baby, the greater the chance of restoring his vision.
Treatment methods:
- Reflexology, which is acupressure. During it, the specialist influences the nerve centers, the function of which is to establish consistency in the functioning of the oculomotor muscles. With complex treatment, this technique helps to get rid of strabismus and increase visual acuity. It can also help keep your eye muscles toned.
- Electrophoresis. Thanks to this procedure, muscles relax and nerve conduction improves.
- Pleoptics. The essence of this technique is to cover the healthy eye with a bandage in order to activate the work of the second one.
- Osteopathic treatment. Using his hands, the specialist influences the fluids and structures of the patient’s body, due to which the eye muscles are toned, tissues are relaxed, and the passage of nerve impulses is improved.
- Wearing glasses.
- If the pathology in a child was noticed only after he reached 2 years of age, then surgical intervention can help eliminate it. During this procedure, the doctor truncates the long eye muscle, which improves vision. At the same time, the child’s eyes stop squinting.
- Orthopedic therapy. Exercises are carried out either on orthopedic simulators or at a laptop according to certain programs. The technique is used to eliminate strabismus in children who are already 4 years old.
An important diagnostic method in ophthalmology is keratometry.
Don't stop your baby from growing up healthy
When the central area falls out of the field of vision - treatment for macular degeneration of the retina.
Why do babies mow?
Dr. Komarovsky encourages parents to remain calm and prudent when assessing childhood strabismus. If we are talking about a baby who has just recently been born, then the reasons can be quite physiological: the muscles that hold the eyeball and allow you to focus your gaze on a certain point are very weak in newborns, because inside the mother’s womb this function is not required for the baby’s eyes. These muscles will become stronger by about 3-4 months, and before that the baby can “mow” as he pleases - to the right, to the left, in different directions.
There is such a thing as pseudosquint, which also applies to children. The skull of newborns has structural features; its two halves meet at a slight angle, and therefore visually an adult examining the baby may get the impression that the baby has strabismus.
If strabismus does not go away after six months, the reason may already lie in a disease called persistent strabismus; with this pathology, focusing the eyes is difficult, which is why the baby looks in different directions. Such strabismus, unlike physiological strabismus, does not disappear after six months or later as the eye muscles become stronger.
Persistent strabismus in a child can be a consequence of a previous pathology - often caused by hypoxic changes during the period of gestation and birth, if oxygen starvation caused damage to the visual centers of the brain, acute infectious diseases of the mother during pregnancy, severe infections suffered by the baby himself, cerebral palsy , Down syndrome.
Komarovsky also emphasizes that there is a hereditary reason, and the baby could have inherited the unusual look from his parents.
In any case, after six months of “mowing” the baby, according to Evgeniy Olegovich, it is worth showing it to an ophthalmologist.
Treatment: how to correct strabismus in children under one year old
In the first months of a child’s development, the eyes must adapt and “tune in” to the binocular stereoscopic perception of the surrounding world, and the visual-analytical eye must process and correctly interpret the visual information coming from the eyes. As mentioned above, at this stage various deviations and observed anomalies are possible, but normally they are not persistent and gradually go away. However, in order not to miss really serious problems with developing vision, periodic ophthalmological examinations are prescribed, among other mandatory examinations and consultations. Any baby, regardless of the presence or absence of obvious pathology, must visit a pediatric ophthalmologist three times during the first year of life:
- at the age of 1 month - to monitor the correct structure and development of the visual organs;
- at the age of 6 months - to control a number of optical characteristics, such as refraction (refraction of light), pupil response to light, etc.;
- at the age of 12 months - to monitor the dynamics of eye development.
You should know and understand that strabismus, no matter what the reasons it is caused (heredity, neuropathology, etc.), at this stage of medical development can be successfully cured or, at least, corrected. The key factor in this regard is early diagnosis and timely intervention: with every missed year and even month, the chances of therapeutic success decrease. If true strabismus is diagnosed (as opposed to imaginary, transient, sporadic), treatment may require constant wearing of glasses with an occluder (opaque one glass) or contact lenses with “training”, excess diopters, and a long course of exercises will definitely be prescribed, - both at home and using special equipment in a medical facility. There are many therapeutic and corrective approaches; the specific strategy is chosen by the doctor strictly individually, but in any case, parents will need remarkable patience and perseverance. The result is certainly worth it: any chance to restore the child to normal vision should be taken.
How to determine if a child has a disorder?
This pathology is quite simple to self-diagnose, and parents can easily notice the characteristic signs and symptoms of visual impairment:
- the child, despite the age of six months, cannot focus his gaze on one point (to check, you can use a small bright object that is interesting to the child);
- eye movement when tracking a moving object is not synchronous;
- if you shine a flashlight into a toddler’s eyes, one eye closes or generally “floats” to the side;
- to look at a toy that interests him, the child is forced to turn his head towards the object;
- the baby does not estimate the distance to objects, often bumps into it or cannot reach out and touch it because he is reaching for an object that is too far away.
Formation of the eyes
Eyes begin to form at 8-10 weeks of embryonic development. Pathologies that arise in the fetus while in the womb are quite difficult or almost impossible to eliminate.
In the womb, the baby can distinguish between light and dark and also demonstrates visual reflexes. Due to the lack of bright light, he gets used to constant darkness. After birth, the baby needs time to adapt to new conditions. Color and object vision begins to develop before the age of 3 weeks.
At 2 months, the child can already keep his eyes on large and bright objects. Closer to six months, the baby develops a stereoscopic type of vision, which implies unhindered fixation on objects. The baby's eyeballs are constantly growing, and the optic nerve is developing.
Symptoms and classification
Doctors distinguish several types of strabismus in children.
According to the time of origin, congenital and acquired strabismus are distinguished. According to the stability of the deviation, strabismus is not uncommon constant and periodic. Based on involvement in the pathological process, unilateral and intermittent strabismus are distinguished.
And according to the type of deviation, strabismus in children is often convergent (the eye is directed towards the bridge of the nose), vertical (the deviation of the eye is downward or upward), divergent (the eye is directed towards the temple) and mixed.
In addition, there is the so-called concomitant strabismus, which is further divided into non-accommodative, partially accommodative and accommodative.
Non-accommodative and partially accommodative strabismus in children develops in the first or second year of life. Under such conditions, in addition, optical vision correction rarely leads to a complete restoration of the normal position of the eyeballs, for this reason it is necessary to resort to surgical treatment.
READ MORE: The child has bruises on his legs below the knees for no reason
Accommodative strabismus in children develops at the age of two or three years, since it is at this time that the child begins to actively look at objects, paintings, pictures, and begins to draw independently.
From time to time, this type of strabismus is observed in the first year of life, which is typical for weakened children. The circumstance of accommodative strabismus lies in the presence of farsightedness, astigmatism or myopia (moderate or high degree).
Separately, there is the so-called paralytic strabismus, which is a consequence of damage to the corresponding nerve or muscle, as a result of which the movement of the eyeball towards the affected muscle is absent or limited. Such strabismus is manifested by impaired binocular vision and double vision.
Causes of pathology
True strabismus in children is not always congenital, and during the first three years of life, as binocular vision develops and develops, certain deviations may occur. Strabismus can accompany farsightedness or myopia, diseases of the central nervous system, and brain tumors. A child can develop strabismus after injuries, a blow to the head, or a traumatic brain injury.
The danger, as Evgeny Komarovsky says, lies in the fact that visual acuity gradually decreases in the squinting eye, and the child’s picture of the world is formed flat. If you hesitate and do nothing for treatment and correction, then over time the pathology will become less amenable to therapy.
If parents know that there were people in their family with strabismus or other problems with the organs of vision, it is important to show the child to an ophthalmologist regularly. Therefore, the Ministry of Health of Russia has established a certain sequence of medical examinations by an eye doctor: at 1, 3, 6 months, and then at a year, 2 years, 3 years, and so on until school age.
There are many types of childhood strabismus, and therefore the treatment of one type will differ from the treatment of another, and only a doctor of the appropriate profile can understand this.
Causes of strabismus in newborns
The cause of the disease can be one or more:
- Genetic factor. The chances that a child will have strabismus increase if one of the adults has suffered from this disease.
- Strabismus can be caused by various ophthalmological problems: cataracts, myopia, farsightedness. Strabismus also causes advanced conjunctivitis or stye on the eye.
- After children have suffered from infectious diseases - most often scarlet fever or diphtheria.
- Neurological problems or somatic diseases.
- In infants and newborns, a common cause of strabismus is the mother's problematic pregnancy (both physiological and psychological problems). This also includes fetal hypoxia.
- Difficult birth in which the newborn suffered serious eye or head injuries, accidental damage to the eyes or skull.
- Stressful situations: fears.
Strabismus in children is one of the few pathologies that can be recognized without the help of a specialist. Strabismus (heterotropism, strabismus) is characterized by asymmetry of both or one eye relative to the central axis and the inability to focus on a specific object.
The disease is most common in children 2–3 years old, since at this age the friendly functioning of the eyes is formed. Strabismus often occurs in newborns, but it is temporary and goes away.
Strabismus is not only a cosmetic defect, but also a dangerous pathology. A squinting eye sees worse and develops poorly. If strabismus is not corrected before age 7, the strain on the healthy eye will increase and vision will deteriorate.
Strabismus is a position of the eyes in which the visual axes do not converge on the object in question. Outwardly, this is manifested by the fact that the eye deviates in one direction or another (to the right or left, less often up or down, and various combined options are also found).
If the eye is brought to the nose, the strabismus is called convergent (more common), and if it is brought to the temple - divergent. One eye or both may squint.
Most often, parents turn to a pediatric ophthalmologist after noticing that the child’s eyes are looking “wrong.” Strabismus is not just a problem of appearance.
The effect of strabismus is a consequence of disturbances in perception and the conduction of visual information throughout the child’s visual system.
This pathology in infants is inextricably linked with weakness of the eye muscle. The most common causes of strabismus in newborns are:
injuries and infectious diseases of the brain; changes in the eye muscles of an inflammatory, vascular and tumor nature; untimely treatment of myopia, astigmatism, farsightedness; congenital diseases and birth injuries; increased physical and mental stress; placing children's toys too close to the baby's face.
Heredity also quite often causes the development of strabismus in newborns. If one of the parents has this pathology, then there is a high probability that their child will inherit the disease. Sometimes strabismus manifests itself as a symptom of other congenital diseases or as a result of illnesses suffered by the baby’s mother during pregnancy.
Having met a child with strabismus, many parents involuntarily begin to examine the eyes of their children.
Incorrect eye position can be an independent pathology or a symptom of a neurological disease. It can be detected at birth (congenital) or appear later (acquired).
Contents: [hide]
Enough tests have been developed to help determine strabismus in children under one year of age, but the reasons can be completely different. A child who has just been born cannot yet fix his gaze and look with both eyes. This is due to insufficient development of the nervous system. Sometimes a newborn's eyes may deviate in different directions.
This is an intermittent phenomenon that should subside by six months. In order to develop the skill of eye control, it will take a short period of time, approximately equal to a month of the baby’s life.
Treatment: pediatrician's opinion
Before raising the question of the advisability of a particular treatment, or the accuracy of the prescriptions, the child must undergo a full examination by an ophthalmologist, according to Evgeny Komarovsky. Everything will depend on exactly how the baby developed strabismus, whether it is congenital or acquired.
If we are talking about concomitant strabismus, in which refraction is impaired and light rays are not refracted equally, then we talk about a hereditary pathology. It usually becomes obvious in childhood. Therefore, a lot depends on timely correction.
Treatment can be based on wearing glasses, lenses, occlusion. If there are organic lesions, the child will be prescribed surgical treatment. In the paralytic form of the disease, one or more eye muscles are affected. This is usually an acquired form of the disease, in which it is possible to restore the functions of the eye muscles with the help of physiotherapy followed by surgery.
Treating a child on your own or trying to correct pathological vision using folk remedies or alternative medicine methods is criminal, according to Komarovsky. Moreover, medicine is ready to offer many treatment methods that will be quite effective and successful.
Concomitant disorder usually requires treatment for 2-4 years. Evgeniy Komarovsky calls the method of wearing occlusive dressings a very effective method. According to the decision of the ophthalmologist, corrective exercises can be used with the projection of images onto the retina using lenses or special glasses.
Wearing occlusive dressings can be associated with inconvenience - the child may be embarrassed, restrained, or refuse to attend kindergarten because of ridicule from peers. Therefore, Evgeny Komarovsky sees an excellent solution: send the child to a specialized kindergarten, which is attended by children with vision problems. There will be no one to be embarrassed there, and no one will laugh at a boy or girl wearing glasses or an occlusive eye patch.
Treatment of strabismus is an activity that will require a lot of strength and patience from parents, as well as discipline. The child may be prescribed classes on special ophthalmic simulators to normalize the functioning of the eye muscles; he may have to attend correction classes on an amblyopanorama (the therapeutic effect is achieved due to moving light fields).
Children over 3 years old may be recommended to play special computer games under the supervision of a physician; in some cases, three-dimensional vision glasses are used for training.
Parents should also pay special attention to strengthening children’s immunity - strengthening the child, doing gymnastics with him, making sure that the child walks more in the fresh air and eats less harmful fast food.
Alternating strabismus (convergent) and divergent strabismus are treated taking into account the individual angle of deviation from the norm.
medical reviewer, psychosomatics specialist, mother of 4 children
Doctor Komarovsky about strabismus in children under one year old
Strabismus in children is a topic for a very serious conversation, but only after the child is six months old. Before this, some “slanting” in babies may be quite normal, and therefore parents should not worry unnecessarily.
If after 6 months the baby apparently “mows,” then treatment should be started as soon as possible, according to the famous pediatrician Evgeniy Komarovsky.
He tells moms and dads about what childhood strabismus can be like and how to treat it.
Why do babies mow?
Dr. Komarovsky encourages parents to remain calm and prudent when assessing childhood strabismus.
If we are talking about a baby who has just recently been born, then the reasons can be quite physiological: the muscles that hold the eyeball and allow you to focus your gaze on a certain point are very weak in newborns, because inside the mother’s womb this function is not required for the baby’s eyes. These muscles will become stronger by about 3-4 months, and before that the baby can “mow” as he pleases - to the right, to the left, in different directions.
There is such a thing as pseudosquint, which also applies to children. The skull of newborns has structural features; its two halves meet at a slight angle, and therefore visually an adult examining the baby may get the impression that the baby has strabismus.
If strabismus does not go away after six months, the reason may already lie in a disease called persistent strabismus; with this pathology, focusing the eyes is difficult, which is why the baby looks in different directions. Such strabismus, unlike physiological strabismus, does not disappear after six months or later as the eye muscles become stronger.
Persistent strabismus in a child can be a consequence of a previous pathology - often caused by hypoxic changes during the period of gestation and birth, if oxygen starvation caused damage to the visual centers of the brain, acute infectious diseases of the mother during pregnancy, severe infections suffered by the baby himself, cerebral palsy , Down syndrome.
Komarovsky also emphasizes that there is a hereditary reason, and the baby could have inherited the unusual look from his parents.
In any case, after six months of “mowing” the baby, according to Evgeniy Olegovich, it is worth showing it to an ophthalmologist.
How to determine if a child has a disorder?
This pathology is quite simple to self-diagnose, and parents can easily notice the characteristic signs and symptoms of visual impairment:
- the child, despite the age of six months, cannot focus his gaze on one point (to check, you can use a small bright object that is interesting to the child);
- eye movement when tracking a moving object is not synchronous;
- if you shine a flashlight into a toddler’s eyes, one eye closes or generally “floats” to the side;
- to look at a toy that interests him, the child is forced to turn his head towards the object;
- the baby does not estimate the distance to objects, often bumps into it or cannot reach out and touch it because he is reaching for an object that is too far away.
Causes of pathology
True strabismus in children is not always congenital, and during the first three years of life, as binocular vision develops and develops, certain deviations may occur.
Strabismus can accompany farsightedness or myopia, diseases of the central nervous system, and brain tumors.
A child can develop strabismus after injuries, a blow to the head, or a traumatic brain injury.
The danger, as Evgeny Komarovsky says, lies in the fact that visual acuity gradually decreases in the squinting eye, and the child’s picture of the world is formed flat. If you hesitate and do nothing for treatment and correction, then over time the pathology will become less amenable to therapy.
If parents know that there were people in their family with strabismus or other problems with the organs of vision, it is important to show the child to an ophthalmologist regularly. Therefore, the Ministry of Health of Russia has established a certain sequence of medical examinations by an eye doctor: at 1, 3, 6 months, and then at a year, 2 years, 3 years, and so on until school age.
There are many types of childhood strabismus, and therefore the treatment of one type will differ from the treatment of another, and only a doctor of the appropriate profile can understand this.
Treatment: pediatrician's opinion
Before raising the question of the advisability of a particular treatment, or the accuracy of the prescriptions, the child must undergo a full examination by an ophthalmologist, according to Evgeny Komarovsky. Everything will depend on exactly how the baby developed strabismus, whether it is congenital or acquired.
If we are talking about concomitant strabismus, in which refraction is impaired and light rays are not refracted equally, then we talk about a hereditary pathology. It usually becomes obvious in childhood. Therefore, a lot depends on timely correction.
Treatment can be based on wearing glasses, lenses, occlusion. If there are organic lesions, the child will be prescribed surgical treatment.
In the paralytic form of the disease, one or more eye muscles are affected.
This is usually an acquired form of the disease, in which it is possible to restore the functions of the eye muscles with the help of physiotherapy followed by surgery.
Treating a child on your own or trying to correct pathological vision using folk remedies or alternative medicine methods is criminal, according to Komarovsky. Moreover, medicine is ready to offer many treatment methods that will be quite effective and successful.
Concomitant disorder usually requires treatment for 2-4 years. Evgeniy Komarovsky calls the method of wearing occlusive dressings a very effective method. According to the decision of the ophthalmologist, corrective exercises can be used with the projection of images onto the retina using lenses or special glasses.
Wearing occlusive dressings can be associated with inconvenience - the child may be embarrassed, restrained, or refuse to attend kindergarten because of ridicule from peers.
Therefore, Evgeny Komarovsky sees an excellent solution: send the child to a specialized kindergarten, which is attended by children with vision problems.
There will be no one to be embarrassed there, and no one will laugh at a boy or girl wearing glasses or an occlusive eye patch.
Treatment of strabismus is an activity that will require a lot of strength and patience from parents, as well as discipline. The child may be prescribed classes on special ophthalmic simulators to normalize the functioning of the eye muscles; he may have to attend correction classes on an amblyopanorama (the therapeutic effect is achieved due to moving light fields).
Children over 3 years old may be recommended to play special computer games under the supervision of a physician; in some cases, three-dimensional vision glasses are used for training.
Parents should also pay special attention to strengthening children’s immunity - strengthening the child, doing gymnastics with him, making sure that the child walks more in the fresh air and eats less harmful fast food.
Alternating strabismus (convergent) and divergent strabismus are treated taking into account the individual angle of deviation from the norm.
Treatment
Optical correction
- Sidorenko vacuum glasses;
- glasses with prismatic lenses;
- innovative glasses with red and blue filters;
- glasses using Fresnel prisms.
Fresnel prisms should only be attached to glasses by an ophthalmologist; you should not do this yourself.
Pleoptics
- electrical stimulation (to improve metabolic processes);
- laser stimulation (to stimulate the retina);
- magnetic stimulation (to improve blood circulation in the organs of vision);
- light-color stimulation (stimulation of the eyes with light flux).
Folk remedies
- Boiling water is poured into a glass.
- Next, 10 g of plant root is added to it.
- The mixture is infused for half an hour.
- The resulting product is filtered.
- Take the decoction four times a day, a quarter glass, 30 minutes before meals.
- A handful of pine needles are poured with 200 ml of boiling water.
- The product is infused for an hour and filtered.
- The finished product is taken in the amount of one tablespoon 15 minutes before breakfast. The course of therapy with its help is not limited in time.
- Boil a liter of water.
- Pour one hundred grams of plant fruits into boiling water.
- Cook the drug for 15 minutes over low heat.
- The broth should be allowed to brew for five hours.
- You can drink this tea several times a day 30 minutes before meals.
Prevention of childhood strabismus
Among the main preventive measures that will help avoid the development of strabismus are:
- regular and timely examination of the child by an ophthalmologist;
- protecting women's health during pregnancy;
- avoidance of stressful situations;
- timely treatment of diseases that can cause strabismus (measles, scarlet fever, diphtheria, etc.).
Strabismus is a common phenomenon in childhood. In many cases, this condition is normal, but pathological disorders are no less common. That is why it is important to undergo regular examinations by a pediatric ophthalmologist - it is better to be on the safe side than to treat an advanced disease later. Treatment at home cannot be done.