Reasons for the breakup
For a long time, doctors argued that the main reason for the violation of the integrity of the membrane was associated with injuries. But recently it has been established that injuries are only a predisposing factor. In most cases, the rupture is idiopathic. It is impossible to determine the true cause of its occurrence.
Often such disorders are diagnosed in older people. This is associated with degenerative changes. With age, the retina becomes thinner and susceptible to tearing. It may gradually increase in size. Possible causes of damage to the integrity of the macula:
- Injuries. Can occur in patients of any age. Impacts lead to retinal defects.
- Consequences after surgery. In this case, sudden ruptures are diagnosed, which are observed in no more than 1% of patients. Occurs after eye surgery. This may be due to the individual structure of the eyes. Usually the doctor is not to blame for such consequences.
- Retinal detachment. Appears with epiretinal fibrosis. The reason may also be hidden in age-related changes, violations of hydraulic pressure. Detachment leads to tearing of the macula and other areas.
For each patient, the causes of such disorders may be individual. If treatment is not promptly addressed, the proliferation of blood vessels will actively progress. Against this background, hemorrhages may occur. The wet form is more dangerous. Against this background, photoreceptors are destroyed, and vision loss is an irreversible process.
Macular hole of the retina: treatment methods -
A macular hole in the retina can lead to retinal detachment and vision problems. The pathology causes complete loss of vision or can significantly impair visual acuity, which negatively affects the patient’s daily life and professional activities.
Diagnostic methods
Any disease requires special therapy; in order to choose it correctly, you need to make the correct diagnosis. Before sending a patient for examination, the doctor collects anamnesis by asking the patient about symptoms.
But since pain and visual disturbances occur extremely rarely during a rupture, in addition to a visual examination, a number of diagnostic measures are required to help accurately determine the pathology:
- Ophthalmoscopy. Helps analyze the condition of the fundus and identify existing damage;
- Examination of the visual apparatus using a slit lamp;
- Ultrasonography.
Ultrasound is an additional procedure; with its help, the doctor determines in detail the type of damage, the size of the tear and its location.
Therapy for lamellar tears
When diagnosing such a pathology, visual acuity does not decrease as much as with penetrating damage. The main symptom of the disease is a blurred and distorted outline of objects. Previously, enzyme preparations were used to treat the disease, but they were low in effectiveness.
Therefore, lamellar tears today are also treated with surgery. For this purpose, microinvasive vitrectomy is used. It causes minimal visual discomfort, is safe and does not cause pain. Hospitalization of the patient is not required.
After the intervention, it is necessary to walk with your head down for four days so that the injected mixture puts pressure on the tear. This creates optimal conditions for merging the edges. Therapy with medications is also carried out for some time. This will minimize the risk of infection and speed up recovery.
| Vitrectomy is a high-tech operation and requires modern equipment. Unfortunately, it is not available in all government clinics. Therefore, it is not always possible to carry out an intervention using a compulsory medical insurance policy. |
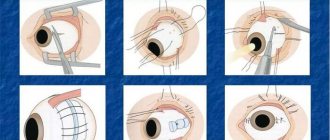
Operation
The essence of the procedure is to create a reliable adhesion between the vascular system of the eye and the retina. Laser coagulation is performed under local anesthesia on an outpatient basis. During the operation, the temperature at the site of the rupture under the influence of rays rises, microscopic burns of the retina are formed, as a result of which fusion of the damaged area is achieved.
Coagulation takes thirty minutes. A strong lens is installed on the patient’s eye, which helps the doctor control the entire process. The operation does not require hospital recovery. On average, laser coagulation costs nine thousand rubles per eye.
The price for vitrectomy is several times higher, it can reach one hundred thousand. During the operation, the damaged vitreous body is removed and silicone oil is injected, which after some time is changed to a saline solution to ensure maximum clarity of vision.
Another type of intervention that is used for retinal tears is pneumatic retinopexy.
After anesthesia, the doctor uses a syringe to inject a small bubble of gas into the vitreous body, which presses the retina to the choroid.
Fourteen days later, the position of the retina is fixed using laser coagulation or cryopexy. This operation is mainly used for superficial damage.
Also, for macular holes, a procedure is used to press in the sclera. During the intervention, a silicone filling is attached to the sclera using sutures and optimal conditions are created for a tight fit to the retina. Cryopexy is used to heal damaged areas.
Actions after surgery
After surgery, an antiseptic bandage is applied to the eye. It should be left overnight and removed the next day under the supervision of a doctor. During surgery, the patient may feel air or gas tamponade entering the eyes, causing a decrease in visual acuity. During the intervention, it will be gradually removed using a special liquid.
| Blurry images of surrounding objects may persist for several days or months, depending on what type of tamponade is used (gas or air). |
After the operation, the patient is left in the hospital for three days. The patient is explained in detail which ointments to use. After discharge, you will be under the doctor's supervision for some time. If any of the following symptoms occur, consult your doctor immediately:
- Severe pain;
- Redness of the eyes;
- Significant drop in visual acuity;
- Ripples or lightning before the eyes;
- Migraine.
Regarding driving after surgery, you should consult your doctor individually.
Folk remedies
“Grandma’s recipes” are not able to eliminate retinal tears, but they will help minimize the manifestation of unpleasant symptoms and speed up the recovery process.
Tinctures made from medicinal herbs (chamomile, sage, elderberry, cornflower) are highly effective. Patients note that decoctions of pine needles helped them well. Regularly use compresses based on calendula, elderberry or fennel.
Introduce into your diet foods that contain a large amount of vitamins and beneficial elements.
Prognosis and prevention
There are no special measures that can prevent retinal tears. Ophthalmologists simply recommend taking better care of your eyesight and using protective equipment when working with hazardous materials.
| A prognosis for the patient's future life and ability to work can be given based on the degree of damage to the organ of vision. If the tear is microscopic, then most often spontaneous regression of the eyeball is observed. |
If such a pathology is detected, it is necessary to regularly visit the ophthalmologist for a preventive examination. Timely detection of the disease and selection of effective therapy will ensure a favorable outcome and minimize the risk of vision loss. Otherwise, the patient faces blindness and disability.
Conclusion
A macular hole in the retina can lead to blindness or cause detachment of the membrane, which partially reduces visual acuity. Treatment of the disease consists of surgery. The operation does not cause pain, and the patient is allowed to go home after a few days. If pathology is detected at an early stage, the prognosis for treatment is favorable.
For more information, watch this video about the causes of macular holes and how to treat them.
Source: https://zdorovoeoko.ru/bolezni/makulyarnyj-razryv-setchatki/
Risk group
The risk group includes patients over 50 years of age. Women are more likely to experience this disease than men. This pathology tends to develop spontaneously and unexpectedly. The following risk factors are also identified:
- blunt eye injuries;
- severe myopia;
- retinal detachment;
- diabetes;
- uveitis
Patients with chronic diseases, diabetes mellitus, should consult an ophthalmologist more often. The pathology is not associated with genetic predisposition. Also, its development is not affected by the state of the environment.
Symptoms
Dry macular degeneration of the retina is accompanied by a slow development of characteristic symptoms. First of all, a person should be concerned about decreased vision when reading. Usually they start turning on brighter lights.
If such symptoms occur, you should immediately consult an ophthalmologist. If this is not done, then vision will gradually become distorted. This negatively affects everyday life.
The disease rarely causes visual hallucinations. Especially in old age. The patient begins to see objects nearby blurry. It could even be relatives with whom the person lives. Sometimes you might think that a loved one has problems not with vision, but with the psyche. Therefore, you should not remain silent and hide such violations, but it is better to immediately consult a doctor.
Sometimes vision can deteriorate rapidly. It is impossible not to notice such manifestations. Spots often appear before the eyes, which significantly affect the usual way of life. Lamellar macular hole is accompanied by the same symptoms.
What to do if you have a retinal tear
Retinal rupture in ophthalmology is considered one of the most severe conditions. Pathological changes in this element of the eye can lead to complete loss of vision, so it is important to respond to the symptoms in a timely manner.
Anatomical structure of the eyeball
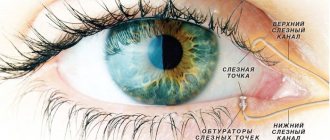
The retina (retina) is the thinnest layer of the eye, which serves to convert light rays into nerve impulses. The retina is called the primary analyzer of the optic nerve. This element of the eye is 0.3-0.6 mm at its thinnest part.
To understand the causes of a retinal tear, you must first understand the anatomy of the eye. The human eyeball has a spherical shape.
Eye shells:
- The outer fibrous membrane consists of the corneal layer and the sclera.
- The middle vascular (choroid) includes the iris, ciliary body and a collection of blood vessels.
- The inner layer is called the retina and is responsible for converting light energy into impulses.
In front of the retina is the vitreous humor, a gel-like substance that fills the chamber of the eye. From the outer shell, impulses are transmitted along the neural circuit to the cerebral cortex. In the area of the optic nerve, the retina connects with nerve fibers.
The retina lines the eyeball and is adjacent to the choroid, from which it receives substances for normal functioning. Therefore, the vessels of the eye are visible through the retina and create a red fundus reflex. The retina is fed from the central artery and vessels from the choroid.
The retina is fixed in only two places: near the optic nerve head and on the dentate line to the equator of the eye. The rest of the retina is held in place by the pressure of the vitreous without fusion.
The macula, or macula, is located in the center of the retina. This region includes the fovea centralis and the fovea, where photoreceptors are concentrated and there are no blood vessels. The dimple helps to perceive colors and provides visual acuity. The macula gives a person the ability to read, and images that are focused in this area are seen clearly.
What causes a retinal tear?
The retina is a very complex structure that includes ten layers. One of the layers contains photoreceptors (rods and cones), which are responsible for daytime and twilight vision. Often, a retinal rupture occurs due to a violation of its structure and surrounding tissues.
Common causes of retinal tears:
- Retinal dystrophy.
This phenomenon leads to the occurrence of holey ruptures. Dystrophic damage to the retina leads to disruption of the integrity of the periphery of the visual analyzer. This can occur for a variety of primary and secondary reasons, not necessarily ophthalmologic. - Fusion of the retina with the vitreous body.
Retinal rupture occurs in areas that cannot withstand sudden movements: when the position of the vitreous body changes, it pulls the retina along with it at the fusion sites. This phenomenon is called valve rupture. - Severe injuries to the eyes or body.
Even in normal eye conditions, the retina can still tear. This occurs during a strong shock when the layer breaks in the area of contact with the jagged line. A blow that can tear a healthy retina is typical for road accidents, falls from great heights, and industrial situations.
When fusion of the vitreous body and the retina occurs in the area of the macula, valve ruptures occur, but in this area they pose a much greater danger. In this case, urgent treatment is required, otherwise the patient may quickly and permanently lose vision.
Symptoms of a retinal tear
The danger of this phenomenon lies in the fact that at first it does not manifest itself at all or gives minor symptoms that are rarely paid attention to. If you have even one mild symptom, you should immediately contact an ophthalmologist.
Signs of a retinal tear:
- Small flashes before the eyes that resemble lightning strikes. The symptom worsens in poor lighting.
- The presence of flickering dark dots, lines and spots.
- Sudden decrease in visual acuity.
- Blurred objects regardless of distance from location.
- Film effect on the eyes.
- The appearance of dark spots that obscure the field of vision.
Usually there is one spot, but it can have different sizes and be located anywhere. The growth of this spot indicates an increase in the gap.
Such symptoms may indicate a retinal tear or even the initial stage of retinal detachment. It is noteworthy that most often discomfort occurs during detachment, since the rupture does not have specific symptoms.
The appearance of a black area in the field of vision indicates that the process of retina peeling has begun. In the blind area, visual cells have already lost the ability to transmit information to the brain. The longer the retina is detached, the less chance there is to restore visual function.
Consequences of retina rupture
The most dangerous consequence of retinal rupture can be considered its detachment. In this case, contact is lost between the retina and the choroid that feeds it. Without connection to the blood vessels, the retina quickly dies, so without immediate treatment, you can become permanently blind.
Retinal scarring can be identified as one of the severe complications of a rupture. This is fraught with contraction of the membrane to the point of the defect, which increases the risk of detachment of healthy areas. If there is a rupture, bleeding often occurs. In this case, a hematoma begins to form, which provokes peeling of the retina along its entire length.
When signs of a retinal tear or detachment occur, you should seek help immediately. Such phenomena require urgent treatment, otherwise vision loss will inevitably occur. When choosing therapy for a rupture, the doctor must take into account the stage and type of pathological process.
Diagnosis of retinal rupture and detachment
Timely diagnosis and treatment of the tear increases the chances of retinal restoration and vision preservation. Old defects are difficult to treat, and even operations are often ineffective.
A retinal tear can be confirmed using ophthalmoscopy, biomicroscopy (examination of the fundus with a slit lamp), sonography and ultrasound of the eyes. After making a diagnosis, the doctor specifies the location of the defect, as well as its size and age. These indicators will determine the treatment method.
Early diagnosis of retinal tears is difficult but is of utmost importance. In the process of examining a patient, the following methods are usually used:
- visometry (measurement of visual acuity);
- ophthalmoscopy (examination of the fundus of the eye);
- perimetry (study of visual fields);
- biomicroscopy (assessment of the anterior segment of the eyeball);
- tonometry (measurement of intraocular pressure);
- definition of entoptic phenomena.
If necessary, also prescribe:
- ultrasound scanning in B-mode;
- laboratory tests.
Ophthalmoscopy should be given importance when diagnosing a rupture. It will show the detachment if it is present and will allow you to assess the extent of the defect, assess the condition of the macula and find the location of the rupture.
It is recommended to combine fundus examination techniques to obtain all the information about the condition of the retina. Repeated fundus examinations allow you to detect a retinal tear and choose a treatment technique.
It is also worth conducting research into entoptic phenomena. They help determine the presence of detachment due to clouding of the lens or vitreous hemorrhage (conditions in which it is impossible to examine the fundus). In these cases, ultrasound in B-mode is also prescribed.
If a detachment is suspected, electrophysiological tests are sometimes prescribed to evaluate the functionality of the retina. Laboratory tests are needed before surgery (blood and urine tests, testing for HIV, hepatitis and syphilis, x-ray of the chest and nose). Before the operation, you must also obtain permission from your physician, dentist, and otolaryngologist.
In case of rapid progression of detachment, emergency hospitalization of the patient is necessary due to the risk of damage to the macular area. Hospitalization does not require all tests, a blood test is sufficient. This increases the risk of complications, but will speed up the operation.
Surgical correction of retinal tear
When a retinal tear is not accompanied by a detachment, laser coagulation is most often recommended to correct the pathology. During surgery, the defective area is isolated and the spread of the tear is blocked, especially to intact areas. Cryosurgical therapy works in a similar way, only the procedure uses low temperatures rather than a high-temperature laser.
If a retinal tear is combined with a detachment, surgical limitation is ineffective, especially when the defect is located in the macula. Complicated damage requires additional pressure on the retina during surgery.
A similar effect can be achieved using vitrectomy. This procedure involves replacing the vitreous with “heavy water”. The substance helps press the retina to the choroid.
A similar procedure is filling the sclera with a silicone sponge.
Patients with a retinal tear, even after treatment, should undergo regular examinations by an ophthalmologist, because this pathology often recurs.
Laser coagulation of the retina
The coagulation procedure is performed for retinal dystrophy, as well as vascular defects that are caused by the development of a tumor. The operation helps prevent retinal detachment and stop fundus dystrophy.
Surgical treatment is the only correct option for retinal rupture. Laser coagulation is an outpatient procedure for which local anesthesia is sufficient. It takes approximately 20 minutes, and after the examination the patient can go home. The operation is safe for people of all ages and does not harm the cardiovascular or other systems.
Treatment involves the use of a laser, which increases the temperature of the tissues and causes them to coagulate (clotting). This principle ensures a bloodless operation.
A high-precision laser is used to treat a retinal tear. It creates adhesions between this and the choroid, and a special lens is inserted into the eye to filter radiation. The progress of the operation is monitored through a microscope.
Advantages of laser coagulation:
- no need to open the eyeball;
- bloodlessness, respectively, prevention of infection;
- local drip anesthesia;
- efficiency;
- fast recovery.
Cryocoagulation of retinal tear
Retinal cryotherapy allows you to create a chorioretinal lesion using low temperatures. The treatment result has similar properties as laser coagulation.
Cricoagulation is performed on an outpatient basis using local drip anesthesia. The procedure is carried out with a cryoapplicator, which allows you to influence oval areas (6 by 2 mm). First, the applicator is immersed in liquid nitrogen (-196°C).
Ultra-low temperatures when operating on the organs of vision provide good penetration. Cryotherapy does not affect muscle fibers and sclera.
Vitrectomy for retinal detachment
Vitrectomy is a microsurgical operation that involves removing the vitreous body of the eyeball. Indications for surgery include the following pathologies: tension, detachment or rupture of the retina, hemorrhage and visual impairment caused by it, the presence of a foreign body, trauma, opacification of the vitreous, proliferative retinopathy.
Vitrectomy involves the gradual removal of the vitreous humor using the finest instruments. After removal of the element, laser endocoagulation of the retina is most often additionally performed.
The doctor removes fibrous and scar tissue, straightens the retina and removes any holes that have formed.
To restore pressure in the eye, a balanced salt solution, gas, or silicone oil is injected in place of the vitreous.
Vitrectomy should only be performed by an experienced ophthalmologist. It is advisable that the doctor specializes in microsurgical treatment of the retina.
Often the operation is performed on an outpatient basis, although sometimes the patient still needs to be hospitalized. The procedure usually takes 1-3 hours under local or general anesthesia. After vitrectomy, it is necessary to hold the head in a certain position for some time, but in general, rehabilitation does not require much effort.
Possible complications:
- increased intraocular pressure;
- prolonged bleeding;
- swelling of the corneal layer;
- relapse of detachment;
- eye infection.
Often, vitrectomy is the only way to preserve vision in case of retinal rupture and detachment. The operation allows you to stop the spread of pathology and even restore visual function in case of tractional detachment. However, this method will only be effective if the defect does not affect the macula and central vision is preserved.
Sources used:
- Microsurgery of the vitreous body and retina: monograph. / Steve Charles, Jorge Calzada, Byron Wood. - M.: MEDpress-inform, 2012.
- Retinal vein occlusions. Etiology, pathogenesis, clinic, diagnosis, treatment / S.N. Tultseva, Yu.S. Astakhov. - Moscow
- D. Hubel. Eye, brain, vision. — ed. A. L. Byzova. - M.: Mir, 1990.
- First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
- Acuvue lenses 43%, 3184 votes3184 votes 43%3184 votes – 43% of all
- Air Optix lenses 17%, 1263 votes1263 votes 17%1263 votes – 17% of all
- Optima lenses 16%, 1202 votes1202 votes 16%1202 votes – 16% of all
- Pure Vision lenses 11%, 847847 11%847 – 11% of all
- Biofinity lenses 6%, 430430 6%430 – 6% of all
- Biotrue lenses 4%, 311311 4%311 – 4% of all
- Clariti lenses 2%, 160160 2%160 – 2% of all
Source: https://BeregiZrenie.ru/rogovitsa-setchatka/razryv-setchatki/
Diagnostics
If these violations are suspected, the doctor conducts a full examination. Initially, the specialist examines the patient’s medical history and excludes the presence of systemic and genetic diseases. A visual inspection is then carried out. In most cases, the patient is registered at the hospital. Then he regularly undergoes scheduled examinations.
Treatment depends on the form of the pathology. Sometimes additional examination by a surgeon may be necessary. After the results are obtained, the treatment method is determined. An effective result can be observed after a course of conjunctival injections. In extreme cases, laser treatment is prescribed.
Since symptoms often appear when the form is already advanced, the patient only then comes to see an ophthalmologist. The disease is detected in a timely manner by chance, during routine and preventive examinations.
Additionally, the following activities are prescribed:
- perimetry;
- special tests and tables;
- ophthalmoscopy;
- optical coherence tomography.
After the results obtained, the doctor can make the correct diagnosis.
Treatment
Treatment will require complex therapy, which requires an individual approach to each patient. In severe cases, surgery is required. It is impossible to get rid of the pathology on your own. During the period of taking medications, the prescribed dosage should be strictly observed.
Treatment with folk remedies in this case is not appropriate.
Vitamins
The patient is prescribed complex vitamins and dietary supplements. They can be in the form of drops or tablets. It is also recommended to adjust the daily diet.
Folk remedies
The use of folk remedies is possible only as complex therapy. Useful plants have anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects. For example: chamomile, St. John's wort. They can be used to prepare solutions that are used to wash the eyes.
Anti-VEGF drugs
These drugs are intended for intravitreal administration. This is a modern method of treating such diseases. Widely used in ophthalmology because it reduces the risk of pathological changes in blood vessels. Medicines are administered by injection. The effect occurs very quickly, and the person may experience an increase in vision. To obtain long-term results, a long course of therapy will be required. Since the procedure is very expensive, not every patient can afford it.
Laser coagulation of the retina
This technique is widely used in ophthalmology. A large number of eye diseases are eliminated using lasers. Prevents the development of hemorrhages and atrophic changes.
It is important to consider that this technique cannot cure the cause of the pathology. Treatment is mainly carried out for the purpose of prevention. In addition, it is often combined with injections and other treatment methods.
Photodynamic therapy
In this case, the doctor prescribes the use of drugs that are sensitive to light radiation. They are usually administered intravenously. In the future, laser treatment will be effective. This technique is quite effective. In some cases, vision can be restored. This type of therapy is quite expensive. Therefore, it is rarely prescribed.
When is surgery needed?
Surgery is prescribed in cases where other methods do not bring the desired result. Main indications: severe bleeding, hemorrhages under the retina. In this case, surgery is the only treatment option.
Macular retinal hole treatment with folk remedies | Portal about traditional medicine
Causes and treatment of macular retinal hole.
A macular hole in the retina occurs due to a lack of vitamins, abnormalities in the development of the eye, as well as after surgery or injury. In this case, a hole appears in the fundus of the eye, more often this happens in the central area and threatens complete or partial loss of vision. This damage disrupts the molecular layer of the macula, which is responsible for color perception.
Treatment of pathology consists of performing surgery.
Reasons for development
The influence of the following factors on the human body can provoke a rupture of the macula of the eye:
The pathology develops against the background of mechanical damage to the eyeball.
- traumatic injury;
- high myopia;
- blood pressure surges;
- stress;
- overwork;
- lack of sleep;
- significant physical activity;
- consequences of surgery;
- inflammatory diseases of the eye;
- congenital anatomical features of the eyeball;
- advanced age;
- smoking;
- alcohol consumption;
- poor nutrition;
- lack of vitamins and microelements;
- exposure to ultraviolet radiation;
- diabetes;
- atherosclerosis;
- angiosclerotic changes;
- increased intraocular pressure.
Damage to the retina occurs when the eyeball is exposed to various factors. Most often, the pathology is caused by injury, the result of unsuccessful surgery, or a lack of vitamins and microelements. A macular hole can also be idiopathic, that is, it occurs for unknown reasons. In children, the disease is caused by congenital structural features of the eye.
Main symptoms
A macular hole in the retina of the eye causes the development of the following clinical signs in a person:
- Pain in the eyes;
- blurred vision;
- changing the contours of objects;
- distortion of the surrounding world;
- inability to perform minor actions;
- inability to read;
- gray spot before the eyes or scotoma area;
- impaired color perception;
- irritability when exposed to bright light;
- lacrimation.
Rupture of the choroid and macula can be completely asymptomatic. In this case, the person does not experience any manifestations of pathology.
During damage, the molecular relationship between different layers and light-sensitive cells is disrupted. The hole in the retina can be through and incomplete.
In this case, the tear is called laminar and affects only a few layers of the macula. In the place where the hole is located, the person loses the ability to see and a dark zone or scotoma appears.
Complications
A through or lamellar retinal tear without the necessary treatment leads to complete loss of vision. Sometimes the pathology provokes loss of a portion of the visual field.
The patient also complains of headache, dizziness and loss of consciousness. In addition, the patient is bothered by the flickering of flies and the appearance of lightning before the eyes.
Retinal tears as a result of trauma are very dangerous, as they can cause massive hemorrhage in the tissue of the eyeball.
How is diagnosis carried out?
You can suspect that a macular hole has formed by the presence in the patient of clinical signs characteristic of this pathology.
In addition, patients are recommended to undergo an ophthalmoscopic examination, with the help of which it is possible to visualize the condition of the fundus of the eye and the formations located on it. It is important to examine the volume of visual fields and perform ultrasound diagnostics of the eyeball.
A comprehensive study shows magnetic resonance and computed tomography. They give a general and biochemical blood test.
Treatment options
The approach to the treatment of macular retinal holes should be comprehensive and include the use of medications, surgical manipulations and traditional methods of influence.
This guarantees a positive effect of treatment and rapid restoration of visual function. Surgery will help cure the pathology.
For this purpose, the method most often used is cryosurgery and photocoagulation, which help to strengthen the edges of torn tissue into the desired place on the fundus and at the same time minimize further damage and scar formation.
Drug treatment is used as symptomatic therapy and is used in the postoperative period. The effectiveness of therapy depends on the speed of assistance, which should be provided in the first hours after a macular hole occurs.
Treatment with drugs
Medications are used to treat the symptoms of a macular hole, but they cannot directly treat the problem.
They are also used in the postoperative period to prevent possible complications and negative effects.
For this purpose, drugs are used that reduce intraocular pressure and improve blood circulation in damaged tissues, which promotes their speedy healing.
Source: https://zdorovyavsem.ru/bolezni/makulyarnyj-razryv-setchatki-glaza-lechenie-narodnymi-sredstvami
Prevention
The main thing is to consult a doctor in a timely manner. Especially when suspicious symptoms develop. Nutrition should also be given importance. Many products provide the body with healthy foods and microelements. This has a positive effect on the acuity and quality of vision. A person is advised to give up bad habits.
The macular hole plays an important role in the visual apparatus. The ability to recognize objects depends on its condition and functionality. Self-medication or untimely therapy leads to irreversible processes. In such cases, it is almost impossible to restore primary visual acuity. If work activity is associated with physical activity or work with chemicals, then the activity should be changed. If you have diabetes, you must strictly follow your doctor's recommendations.