Description of the technique
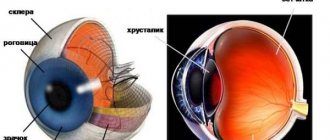
Corneal pachymetry is a type of study that allows you to assess the condition of the corneal layer of the eye. The cornea is the outer shell (from the outside) of a convex shape. In a healthy person, it is completely transparent, which explains its ability to transmit streams of light to the lens and retina of the eye. But an increase in its thickness or thinning causes distortion of the displayed images, which reduces the acuity of visual perception.
A pachymeter is used to measure the thickness of the cornea. This allows you to identify areas with pathological changes, which makes it possible to choose the right treatment method. In addition, the pachymetry method provides the doctor with information after surgical therapy has been performed (assessing how successful the operation was).
Pachymetry – determination of corneal thickness. Standards, price, results
Pachymetry is an ophthalmological examination that determines the thickness of the cornea of the eye. There are two methods of implementation - touch and non-contact, both are non-invasive, painless, require no preparation and take only a few minutes. This examination is carried out mainly in cases of suspected glaucoma and keratoconus, and costs several tens of zlotys.
Indications and contraindications
The study is prescribed when the ophthalmologist, based on clinical signs, suspects the presence of diseases associated with thickening or thinning of the corneal layer.
{banner_gorizontalnyy}
Indications for pachymetry to confirm the diagnosis are:
- Corneal edema
. This pathological condition is accompanied by deformation and thickening of the corneal layer. The study allows you to identify altered areas. The patient complains of hazy organs in front of the audience, tearing and redness of the white part of the organs of vision. - Ulcers of the superficial layer of the cornea
. Pathological formations in the form of a depression in the tissues of the cornea. They are a consequence of inflammatory processes. During the study, areas with a thinned membrane are distinguished. The procedure allows you to assess the depth of the ulcerative lesion. For this type of pathology, the characteristic symptoms are burning and pain. - Dystrophic processes
. They combine hereditary diseases with disruption of the process of renewal of the corneal layer of the eye. Pathologies are manifested by excessive tissue formation, clouding and the presence of ulcers. - Glaucoma
. With this disease, intraocular pressure increases. To measure its parameters, a special device equipped with weights is used, but the thickness of the cornea is not taken into account, which causes an incorrect diagnosis. Therefore, in this case, pachymetry is considered as an informational type of research. - Keratoconus
. The pathology is accompanied by a characteristic protrusion of the cornea with a decrease in its thickness. When choosing surgical therapy, it is necessary to determine the thickness of the cornea in order to determine the depth of the incision without puncturing it all the way through. - Preparation for surgical therapy
. The method is especially relevant for corneal transplantation. In this case, the ophthalmologist needs to know its thickness. - Assessment of the condition in the postoperative period
. The information obtained during pachymetry allows one to assess how well the donor tissue has taken root during transplantation and determine the risk of possible complications.
Despite the relative safety of the procedure, pachymetry is not performed for the following reasons:
- if the patient has an inadequate psyche;
- in case of perforation of the cornea (there is a danger of introduction of pathogenic microflora);
- if purulent-inflammatory processes are diagnosed;
- cases where local anesthesia causes allergies.
Contraindications
Diagnosis is not carried out for patients with corneal injuries if the person arrives for examination under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
Also, the procedure is contraindicated in patients with a serious mental disorder and diseases of the visual analyzer, which are accompanied by the formation of purulent contents. The latter include:
- conjunctivitis;
- herpes of the organs of vision;
- fungal keratitis;
- ulcer;
- dacryocystitis;
- blepharitis;
- stye or chalazion.
Types of pachymetry
Different devices are used to determine the thickness of the cornea. Accordingly, the following types of research are distinguished:
- Optical pachymetry
. The procedure is performed using a slit lamp. The technique was first used 50 years ago, but despite its simplicity, it has retained its relevance due to its information content. The essence of the technique is that a light flux is directed through a slit. It passes through special lenses (located in parallel), due to which the corneal layer is measured. - Diagnostic procedure using ultrasound
. It is a contact type of examination, since the ultrasound sensor is located on the surface of the eye. The examination is carried out after applying local anesthesia. It allows you to reduce the sensitivity of nerve endings and the frequency of involuntary blinking movements of the eyelids. Anesthesia is administered 6 minutes before the start of the study. The ophthalmologist makes tangential movements with the sensor of the device on the surface of the eye, after which the measurements are reflected on the display monitor. The structure of the tissue and its pathological (thickened or thinned) areas can be determined by reflected sound waves, which are recorded by the device. - Computer Assisted Research
. The procedure involves the use of a special tomograph apparatus, which scans the eyeball through examination (in the infrared range). The examination is completed within 10 minutes. In this case, special clamps are applied to the head to ensure its immobility. The working part of the device approaches the visual organ under study, after which the cornea or other structures of the eye are scanned.
{banner_horizontalnyy2}
Indications for pachymetry
Glaucoma is a common pathology affecting millions of people. It can lead to complete loss of visual perception if timely assistance is not provided. Several studies have confirmed that TR is an important parameter of disease progression. Patients with a TR of 550 µm or less are 3 times more likely to develop glaucoma. This indicates the initial stage of development of the disease.
Pachymetry is an important diagnostic procedure for the preoperative monitoring of a patient who will undergo refractive surgery with an excimer laser. The result of the diagnosis, combined with the degree of visual impairment to be corrected, determines the choice of refraction method to be followed during surgery. If the thickness is insufficient, LASIK and Z-LASIK (PRK is used) methods are usually chosen.
The diagnostic test is also indicated for swelling of the transparent outer membrane of the eye with deformation, ulcerative tissue lesions that are the result of an infectious or inflammatory disease. Pachymetry is performed for corneal dystrophy, which is inherited.
Pachymetry technique
The diagnostic study is performed taking into account the following algorithm of actions:
1.
Before the examination, you must remove contact lenses. Women need to remove decorative cosmetics.
2.
Depending on the type of examination, the patient is seated in a special chair or on a couch.
3.
During the contact type of examination, drops with an anesthetic effect are injected into the eyes. Most often this is a 0.3% Dicaine solution. With its help, discomfort is eliminated and tearing is reduced.
4.
When the device's sensor comes into contact with the surface of the corneal layer, the parameters of the thickness of the eye tissues are measured.
5.
When using ultrasound diagnostics or a tomograph, the data is displayed on the monitor.
6.
At the end of the procedure, the eyes are instilled with antibacterial drugs (Albucid or Tsipromed). This will prevent the penetration of pathogenic microflora into the internal structures of the eyeball.
Pachymetry video
Zolotorevsky Kirill Andreevich tells how the examination is carried out and what is the norm:
Author's rating
Author of the article
Alexandrova O.M.
Articles written
2031
about the author
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale!
( 2 ratings, average: 3.00 out of 5)
If you have any questions or want to share your opinion or experience, write a comment below.
Decoding the results
The results of the study are considered normal if their indicator is within the following limits:
- the central part of the corneal layer should be in the range from 0.49 to 0.56 millimeters;
- the thickness of the cornea in women is within 0.551 mm (in men 0.542);
- in elderly people, the corneal layer becomes thinner and amounts to 0.44 millimeters;
- in childhood, the minimum thickness should be 0.44 mm;
- the maximum thickness in the limbus area should not exceed 0.9 mm.
Any deviation of the parameters by 0.6 mm will indicate the presence of ocular pathology.
Interpretation of pachymetry results
The results of the study include data on the thickness of the corneal layer in different areas. The range of normal corneal thickness is from 410 to 625 microns. The average is 515 microns. At the edges, the readings can be up to 1200 microns.
It is important to understand that the thickness of the cornea is an individual indicator, which depends on the anatomical structure of the eye - however, it should not go beyond the above-mentioned range. Surprisingly, but true: based on statistical data, the fair sex has a thicker cornea than men, approximately 9 microns.
Comparing the research results and normal indicators, the doctor draws conclusions about the condition of the cornea and makes a diagnosis or prescribes additional diagnostics.
Complications
Good tolerability and absence of adverse reactions are the main advantages of optical and computer pachymetry. This is explained by the fact that during the procedure there is no contact with the surface of the eye.
Diagnostics using ultrasound involves contacting the sensor with the corneal layer of the eye. Therefore, after the procedure, hyperemia (slight redness), excessive tear production and a sensation reminiscent of the presence of a foreign body may occur. These effects are temporary and usually disappear within a day. However, in some cases, if disinfection rules are not followed, pathogenic microflora can penetrate into the eye, which leads to inflammation (conjunctivitis).
To prevent the development of complications for several days, the ophthalmologist prescribes drops with an anti-inflammatory effect (Sulfacyl sodium or Tsipromed).
Eye pachymetry has a number of advantages, it has a small number of contraindications, and it does not require special training. Therefore, if necessary, it can be performed at the first visit to the ophthalmologist.
What is non-contact pachymetry?
The second method for measuring corneal thickness is non-contact pachymetry. What does the examination look like? To make it, a laser pachymeter is used, which measures not only the central point of the cornea, but also its entire surface, creating a map of its thickness.
Advantages of non-contact pachymetry:
- no contact with the measuring device guarantees complete safety (does not cause irritation, infection, etc.),
- no discomfort during the examination,
- no need for anesthesia,
- measurement accuracy,
- the ability to simultaneously examine the entire structure of the anterior part of the eye (for example, the depth of the anterior chamber).
However, non-contact pachymetry has two disadvantages:
- price (higher than in the case of tactile pachymetry),
- accessibility (in offices there are more ultrasound machines than laser tomographs).
About
Computer pachymetry
Computerized assessment of corneal thickness can be done using optical coherence tomography. The essence of the procedure is quite simple. It consists in the fact that the eyes are “translated” and “examined” using infrared radiation. Special sensors record the nature of the reflection of infrared rays from various structures of the eyeball. After computer processing is completed, the doctor receives an accurate and detailed image of the area being examined.
Apparatus for computer pachymetry
The procedure will be as follows. First, the patient must come to the doctor's office and sit in front of the tomograph. The chin and forehead are fixed using clamps. If this is not done, the results shown by the device may be inaccurate. Then the doctor brings the working part of the device closer to the eye and scans the cornea. Usually the duration of this procedure does not exceed 3-10 minutes. Once completed, the patient can go home.
Optical pachymetry
The technology appeared quite a long time ago. It was first used to study corneal thickness more than 50 years ago. Today, the technology is no less popular and all thanks to its simplicity. The essence of the method is simple and consists in using a slit lamp and special lenses. The slit lamp is a kind of microscope. The lamp allows you to shine a strip of light onto the patient's eye, and then you can examine the structures visible in it under high magnification. To perform pachymetry, two additional lenses are installed on the lamp.
Principle of optical pachymetry
This procedure is as follows. First, the patient comes to the ophthalmologist's office and sits down at the table. Then he must place his chin on a special stand, and press his forehead against the fixing arch. During the examination, the patient must remain motionless, as this may affect the results obtained.
After installing the slit lamp, a beam of light will be directed into the patient's eye. The thickness of the cornea is measured using special lenses that are mounted on a lamp and positioned parallel to each other. One lens is fixed, and the second will be movable. By rotating a special handle, the doctor will change the angle of the movable lens, resulting in a change in the nature of the light rays that pass through the cornea. Based on this, the specialist measures its thickness in various areas.