Visual acuity is checked at every visit to the ophthalmologist; this study is called visometry. Decreased visual acuity can occur as a result of injury, disease, refractive error, or neurological disorder.
Visual acuity is determined by the ability to distinguish between two separate points at the smallest angle. In nome, the angle is one minute, which corresponds to visual acuity of 1.0. Sometimes during the examination, the doctor establishes a higher visual acuity, which can reach 1.5 or 2.0.
To calculate this indicator, scientist Donders proposed a formula: V=d/D. In this equation, V corresponds to visual acuity, D is the distance from which the patient can identify elements of the optotype at an angle of 1 minute, and d is the distance at which the patient is able to recognize this sign.
To determine visual acuity, ophthalmologists around the world use the visometry method. In this case, the patient must identify special objects called optotypes. In the construction of these objects, a number of principles are used: a certain ratio of the width of the object to its element is 5 to 1. Typically, for visometry, tables of Sivtsev-Golovin (consists of Cyrillic letters), Snellen (consists of Latin letters), Landolt (consists of semi-rings) are used. Tables are also used separately to determine near visual acuity. To carry out visometry in patients with a pronounced decrease in visual function, as well as to clarify the diagnosis if malingering and aggravation are suspected, you can use the tables of B.L. Pole, as well as objective techniques (optokinetic nystagmus, preferential gaze, visual evoked potentials).
For young children, bright spherical objects of various sizes are used that contrast with the surrounding environment. In older children, vision is checked by showing Orlova or Aleinokova tables, in which the optotypes are recognizable objects (airplane, car, etc.).
Visometry is carried out both without optical correction and with it. In the first case, the doctor receives the result of relative visual acuity, and in the second - absolute. Relative visual acuity is not a constant value and depends on external factors, including lighting level, degree of fatigue, etc.
The examination results are expressed in the form of simple or decimal fractions (depending on the traditions of the ophthalmological school). Thus, in the CIS countries and Germany, visual acuity is calculated in decimal fractions, and in other countries - in simple fractions. When calculating in simple fractions, the numerators include the distance to the optotype. In some cases it is expressed in feet (20), in others – in meters (6). The denominator is the distance from which an eye with normal vision should see this optotype. That is, in different countries the norm for visometry will look like 1.0, 6/6 or 20/20.
Often, to simplify perception, the doctor converts fractions into percentages, that is, visual acuity of 0.5 corresponds to 50%. This is not correct, since the dependence in this case is not linear, but logarithmic. That is, the patient practically does not feel a decrease in visual acuity from 1 to 0.9, while a decrease from 0.2 to 0.1 is much more noticeable.
According to WHO, low vision is defined as a decrease in visual acuity of less than 0.3 (6/18 or 20/60), but more than 0.1. This term is also used if there is a narrowing of the field of view of less than 20 degrees from the point of fixation for the better seeing eye. Blindness implies a decrease in visual acuity of less than 0.05 or a narrowing of the visual field of less than 10 degrees.
Most ophthalmologists also use the term practical blindness. This corresponds to loss of performance, limitation in self-care and movement. In Europe and the USA, this term is used if there is a decrease in visual acuity of less than 0.1 (or a narrowing of less than 20 degrees), which cannot be corrected.
Visual acuity
Visual acuity is the ability of the eye to distinguish the smallest details of an observed object. Even ancient Greek healers, trying to determine the quality of vision, suggested their patients to see the stars in the constellation Ursa Major.
Ideal 100% vision is the ability of the eye to distinguish individual points at a distance of 1.45 mm (ophthalmologists call this segment 1 arc minute of vision) from 5 meters. This is the same vision of 1.0 or “one”.
The reasons why the eye loses the ability to see clearly can be divided into 3 groups:
1. Refractive errors
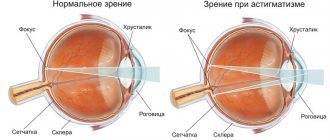
– or the loss of the lens’s ability to focus the eye on an object of interest depending on the distance to it. This may be myopia or farsightedness, which occurs due to age and excessive visual load. Refractive error is the most common cause of visual impairment
2. Lens clouding
– for example, after an eye injury, with age-related cataracts or high blood sugar levels in diabetics.
3. Diseases of the retina and optic nerve
– in these cases, the eye normally focuses the image and conducts light, but the entry (“projection”) of the image into the visual fields of the brain is impaired due to problems with the conductive pathways.
Indications for visometry
- Preventive examination and medical examination
. Nowadays, a huge number of people constantly work with a computer, exposing their eyesight to excessive stress. Bright blue light “forcibly” dilates the pupil and causes spasm of the extraocular muscles, and an incorrect distance to the monitor, lack of a break to rest the eyes and neglect of visual gymnastics only worsens the situation. Timely prescription of glasses will slow down the decline in vision and restore comfort to life. - The appearance of vision complaints.
Deterioration of vision near and far, blurred vision, the need to squint, difficulty reading, double vision and even constant headaches - all this is a reason to visit an ophthalmologist and signals that the ability to focus the lens may be impaired. - Observation during ongoing vision correction
. Wearing glasses or soft contact lenses, even properly fitted ones, does not guarantee that your current acuity will be maintained forever. Age, degenerative processes and many other reasons can affect the conductive media of the eye, continuing to further reduce vision. Therefore, it is important to visit an ophthalmologist periodically. In such cases, visometry is carried out with correction to ensure that vision close to “unity” is achieved and maintained with these glasses or lenses.
{banner_horizontalnyy}
Contraindications
There are practically none. Visometry is absolutely safe and can be performed on both adults and children.
However, you need to understand that the organ of vision is sensitive to any changes in the body, so the results may be inaccurate in the following cases:
- during colds and infectious diseases, especially with the presence of conjunctivitis, lacrimation, irritation of the eyelids and cornea
- crisis course of hypertension - due to spasm of blood vessels in the fundus, blurred vision and the appearance of “floaters” before the eyes are possible. In this case, it is better to wait until the pressure stabilizes
- after a recent injury or concussion, as well as after a stroke. For these diseases, it is very important to immediately examine the fundus and retinal vessels, but it is better to postpone the determination of acuity for 1-2 months
- alcohol and other types of intoxication, which may prevent you from strictly following the doctor’s instructions.
No special preparation is required for the examination; the procedure is performed without restrictions at any examination by an ophthalmologist.
Price
Visometry can be performed as a separate study, or can be part of a comprehensive eye diagnostics.
- Determination of visual acuity with maximum correction - 700 rubles.
- Comprehensive diagnostic examination (visometry, biomicroscopy, autorefractometry, small-pupil ophthalmoscopy, pneumotonometry) - 3,500 .
- Extended comprehensive diagnostic examination (visometry, biomicroscopy, autorefractometry, ophthalmoscopy with a narrow pupil, pneumotonometry, fundus examination with a dilated pupil, OST) - 5,500 rubles.
Above is the price for diagnostic services at our ophthalmology center at the time of publication of the material. You can find out the exact cost of services and make an appointment by calling the numbers listed on our website.
Visometry technique
Determination of visual acuity using the visometry method is based on a person’s ability to distinguish specially selected symbols (or optotypes) of various sizes from a fixed distance.
Simply put, the doctor points to the symbols on the poster (vision chart) and asks to name them.
For diagnostic accuracy, the method has been standardized and must be performed in accordance with a number of conditions:
- Distance to the vision table is 5 meters (in Europe and the USA the definition of vision is 6 m)
- Room illumination of at least 700 lux
- Acuity is assessed first on the right eye, then on the left. The second eye is covered with a special shield or palm. After examining each eye separately, both eyes are diagnosed simultaneously (binocularly)
- Using universal vision tables with the same set of optotypes.
There are various modifications of vision testing tables, but in general it is always a poster with lines of letters or symbols, the height and width of which decreases from top to bottom. The color of optotypes is almost always black. In Russia, a domestic version is used - the Sivtsev-Golovin table, in which 7 letters of the Russian alphabet (Ш, М, Н, У, Б, И, К) are arranged in 12 rows. Each subsequent line contains letters of a smaller size and corresponds to a certain severity - 0.1, 0.2, etc. The ability to correctly see all the characters on line 10 means having a visual acuity of 1.0 (or 100%).
During the check, you are given the “right to make mistakes” - for example, you can make a mistake in one character from lines 4 to 6 and 2 times in lines from 7 to 10, which will not affect the result. But from lines 1 to 3, a mistake cannot be made “with impunity.”
People who are able to see lines 11 and 12 have vision exceeding 100% - 1.2 or even 1.5.
This also happens. Most often this is a genetic feature - a high density of visual elements of the retina in the ocular area. There are also other options for optotype sets:
- The Snellen table was proposed back in 1862, and consists of 11 rows of letters of the Latin alphabet, and is used in Europe and the USA.
- Landolt optotypes - the use of rings with breaks on one side. A random set of rings is used in cases where malingering is detected. Thus, when passing the driver's commission, there are occasionally cases of memorizing letters
- Tables by Orlova or Aleynikova - are used mainly for children, and instead of letters they contain simple, generally understandable symbols (typewriter, Christmas tree, etc.)
{banner_gorizontalnyy2}
Minor changes were made to the methodology with the advent of the opportunity to use modern projectors instead of vision tables in ophthalmology rooms.
Devices displaying optotypes can be calibrated to distances of less than 5 meters, with the optotypes being proportionally reduced in size. Therefore, you should not be surprised if in a small office visometry is carried out from a shorter distance.
Insignia for determining visual acuity
Landolt Ring
A black ring with a gap that can be placed in 4 (top, bottom, right and left) or 8 (add four diagonal positions) positions. In 1909, at the International Congress of Ophthalmology in Naples, the ring was adopted as the standard sign for determining visual acuity.
Snellen hook
The letter “Ш”, which is located in 4 positions in the table, when the free edges are facing left, right, down or up. If the middle strip in “W” is shortened, then in this case the symbol is called a Pflueger hook.
How to measure vision in children
The baby's first meeting with an ophthalmologist usually takes place at the age of 1 month. At this age, the visual system has not yet been formed, and determining absolutely accurate readings of acuity is not only technically impossible, but also unnecessary. As a rule, the doctor limits himself to diagnosing the ability to fix gaze - using a large bright ball, slowly moving it in front of the eyes.
Interestingly, in infancy, periodic convergent strabismus and farsightedness of up to 4-5 diopters are considered normal.
But at the age of 1 year, it is necessary to evaluate visual acuity, since disorders identified at this stage of development without treatment can greatly impair visual acuity in the future.
To determine visual acuity from 1 year to 3 years, siascopy is performed (literally this translates as “observation of shadows”). Directing a beam of light into the child's pupil, the doctor observes the presence of shadows in the fundus through a special ruler with lenses of different diopters. As soon as it is possible to select the required curvature of the lens, the shadow on the fundus will disappear, since the light beam will no longer be refracted.
The method is fundamentally similar to visometry, but in the case of skiascopy, the doctor is not guided by the patient’s own answers, but visually evaluates the passage of light through the lens and its accommodation (the ability to accept the curvature necessary for clear vision). The size of the lens that is necessary to neutralize shadows is an indicator of refractive error.
To direct the baby's gaze in the right direction - above the doctor's ear - a small bright ringing toy is often used. Such an examination is simple, very informative, carried out without expensive equipment, but requires accuracy and speed, as well as significant manual dexterity from the doctor, because babies quickly get tired and can begin to be capricious and resist. The results largely depend on the experience and skill of the doctor.
For children who are already 3-4 years old, they use the classic method of visometry - identifying symbols from a distance of 5 meters. On a poster for children (in Russia these are usually tables by Orlova or Aleinikova), instead of letters, simple symbols well known to children are depicted - a mushroom, a teapot, a car, an elephant, etc. Children at this age do not yet know letters, but they distinguish well-known objects well and can already name them. Before the examination, the doctor and the baby will look at the table closely and agree on what to call each symbol. Autorefractometry can also be used for children over 3 years of age.
An autorefractometer is a special device that performs computer diagnostics of the eye to determine the ability to focus on an object. During the study, you need to look into the eyepieces of the device, where a glowing picture will be shown (most often it is a house in a field). The eye will automatically “adjust” the clarity of the image, and the device will detect the path of reflection of light rays from the picture to the retina and back, and automatically calculate the approximate visual acuity.
The focal length and ability to project an image onto the retina is determined by the length of the eye and the thickness of the lens.
In children, due to their age, the size of the eye is small and the image is projected behind the retina, that is, young children are always farsighted and this is normal. Normal acuity values for age:
- 3 years – 0.6-0.9
- 4 years – 0.7-1.0
- 5 years – 0.8 – 1.0
- 6 years and older – 0.9 -1.0
As the baby grows, the size of the eyeball also increases, so that in most cases, visual impairment goes away on its own. Vision reaches one at about 5-7 years.
Objective methods of visometry
Objective methods for determining visual acuity can be used in children when malingering and aggravation are suspected, to clarify the cause of vision loss, that is, in cases where standard visometry is not suitable.
Optokinetic nystagmus method
In this case, special objects are used that have a periodic structure, for example, a chessboard or a lattice. The subject is shown this object in motion, and the doctor observes the nystagmus of the patient's eyes. If the patient is able to distinguish the structures of an object, then his eyes make involuntary and rhythmic movements. Visual acuity is determined by the size of the minimum object that causes nystagmus.
Visual evoked potential method
In this case, the examination does not depend on eye movement, but the patient must be attentive. At the same time, electrical potentials that are formed in the cells of the occipital region of the brain in response to visual stimuli are recorded. The subject is shown a field with black and white cells that change places with a given frequency. In this case, the cells gradually decrease in size. Those cells that lead to oscillations on the EEG that coincide with the reversal of colors are considered minimally distinguishable.
Forced selective vision method
The preferred gaze test is based on the fact that a person, in particular a child, prefers to look not at homogeneous objects, but at structured ones. In this case, two test objects are placed in front of the subject’s eyes. One of them is uniformly colored gray, and the second is represented by vertical stripes. Typically the test is performed using Keeler cards. If the child is able to distinguish between them, then he prefers to look at the brighter object, which is represented by a grid. Assessing visual function requires not only eye movements, but also head and neck movements. In this regard, if it is impossible to perform the test, we may be talking about a violation of the oculomotor function, and not at all about problems with the primary sensory system.
Decoding the results
Paying tribute to established traditions, the results obtained are usually described in Latin. The words and symbols in the conclusion mean the following:
Visus – vision OD – oculus dexter – right eye OS – oculus sinister – left eye Sph – spherical component, with a “+” sign means myopia, with a “-” sign farsightedness.
As a result, the sum of the refraction of the eye itself and the lens for correction should ideally be 100% or 1.0
Examples:
- The entry VisusOS = 0.4 means that when testing vision in the left eye, the person recognized 4 lines correctly and vision is 40% of normal.
- The entry VisusOD/OS = 0.2/0.7 means that vision in the right eye is reduced to 20%, and in the left to 70% of normal.
- The entry VisusOD = 0.3 Sph - 1.5 means that vision in the right eye is 30% and myopia is 1.5 diopters.
- Recording ODsph +1.75 means the need for correction in the right eye with a spherical lens with an optical power of 1.75 diopters.