Swelling of the upper eyelid is a common phenomenon that can occur as a result of exposure to external or internal negative factors. It can be the only symptom or be accompanied by additional symptoms, occur in one eye or both at the same time. First of all, a swollen eyelid is a serious aesthetic defect, but do not forget that it can serve as a signal of serious problems in the body. For what reasons does swelling of the upper eyelid of one eye occur and how to get rid of the problem?
Swelling of the upper eyelid of one eye - causes and treatment
Why does the upper eyelid swell?
- 9.1 Conservative therapy
- 10.1 Video - Ptosis of the upper eyelid. Exercises
The tendency of the eyelids to edema is due to their anatomical structure - they consist of loose tissue (mainly subcutaneous fat) and a large number of blood vessels . If too much fluid accumulates in the eyelids, swelling occurs quite quickly and can last for several days. The upper part of the eye increases in size, as a result of which the eye shape narrows, the skin acquires a red or bluish tint, as well as an unhealthy shine, and the tissues become dense to the touch.
Anatomical structure of the eyelid
Depending on the reasons that caused the pathology, swelling of the upper eyelid can be inflammatory, non-inflammatory, allergic or traumatic. In each case, it may be accompanied by additional symptoms (itching, pain, increased skin temperature, general symptoms) and requires appropriate treatment.
There are many reasons why the upper eyelid swells
Attention: tissue swelling must be distinguished from a disorder called ptosis, or drooping of the upper eyelid - in the second case, the eyelid does not increase in size and does not turn red, but droops, covering part of the eyeball.
Causes
Pain in the eyeballs is a rather unpleasant symptom that can occur in adults, men and women. Sometimes the symptom is observed in children, but such cases are rare.
There are physiological reasons that provoke pain:
- Nervous disorders of acute and chronic nature.
- Stressful situations associated with family problems or professional difficulties.
- Hypothermia, causing muscle spasms or disruption of nerve impulse conduction.
Eye pain when blinking and pressing may be due to wearing glasses for a long time - Long and regular work at the computer, accompanied by tension in the muscles of the eyeball.
- Being outside in windy weather.
- Entry into the eye of a foreign body of various sizes.
- Violation of personal hygiene rules, rare hand washing and exposure of germs to the mucous membrane of the upper and lower eyelids.
- Wearing contact lenses on a regular basis and violating the technique of their use.
- Overstrain of the muscles of the eyeball and disorders of the optic nerve.
- Congenital anomalies of the development of the visual apparatus.
In addition to pain, the patient may experience a burning sensation and the quality of vision decreases. Additional symptoms largely depend on the underlying cause of the condition.
Inflammatory swelling
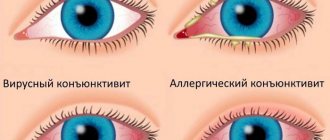
Swelling of one upper eyelid most often occurs with eye diseases, less often with ARVI, sinusitis, sinusitis and other diseases accompanied by an inflammatory process in the nasal sinuses. Distinctive signs of such conditions are itching, tingling and burning sensation, lacrimation, photophobia. Most often, the eyelid swells with barley, conjunctivitis, blepharitis, dacryocystitis, abscesses, phlegmon and erysipelas.
Allergic conjunctivitis in a child
Table. Diseases in which the eyelid swells.
| Disease | Causes and features of the flow |
| Barley | The disease develops as a result of pathogenic microorganisms (most often Staphylococcus aureus) entering the surface of the eye, which causes inflammation of the hair follicle of the eyelashes. A swelling with purulent contents appears in the affected area, the eyelid turns red, swells and hurts when pressed. |
| Conjunctivitis | Inflammatory processes in conjunctivitis develop in the mucous membrane of the eye and are accompanied by redness of the eyeball, a feeling of a foreign body and sand in the eye, photophobia, and the release of clear secretion or pus. |
| Dacryocystitis | The cause of the disease is inflammation of the lacrimal sac, which prevents the normal outflow of fluid. Symptoms include redness, pain and swelling, which are located closer to the inner edge of the eye. |
| Unilateral blepharitis | A severe pathology of a chronic nature, resulting from an inflammatory process of the edges of the eyelids. Signs include swelling of the eyelid (usually at the edges). |
| Infectious and inflammatory diseases (abscess, phlegmon) | Inflammation of the tissues of the eyelids, which usually develop due to a violation of the integrity of the skin and the entry of pathogenic microorganisms into the wound. They are accompanied by severe swelling of the eyelid, impaired mobility, pain, and in severe cases, increased body temperature, headaches, and general weakness. |
Swelling of the eyelid due to inflammation of the nasal sinuses is most often observed in childhood, but can also occur in adults. Patients are concerned about nasal congestion and discharge of purulent contents, headache, a feeling of heaviness in the sinuses, general weakness, fever and chills. This condition requires immediate medical attention as it can cause decreased vision and other serious complications.
Inflammation of the sinuses
Swollen eyelid: how to understand that you need a doctor
What to do if the eyelid above the eye is swollen, and the swelling has become denser and hot to the touch? This is probably phlegmon - an extensive lesion of the eyelids. Consultation with a specialist is required to avoid the spread of inflammation to neighboring tissues.
If swelling appears for no apparent reason, and it is not clear what to do, the best solution would be the help of a specialist. Since the most common cause of swelling is allergies, the doctor, after conducting a test to identify the allergic pathogen, will prescribe a course of treatment.
A sharp increase in body temperature, aching, throbbing pain in the eyelid are frequent accompaniments of this disease. If the temperature cannot be brought down, and the pain constantly intensifies, immediate medical attention is required.
Swelling of the eyes caused by injury. They are easy to diagnose as a bruise is visible on the eyelid. Swelling after injury disappears within the first week, and no doctor’s help is required. But, if in addition to the bruise there is also a painful thickening of the eyelid, then medical care is necessary.
Non-inflammatory swelling of the eyelid
Swelling of the eyelids of a non-inflammatory nature is most often observed in the morning after sleep, and is not accompanied by redness, local fever and severe pain. The skin usually does not appear hot, but pale and cool, sometimes with pronounced vascular network. The reasons that cause this condition include:
- systemic diseases (impaired functioning of the cardiovascular system, kidneys, thyroid gland, digestive tract);
- poor circulation or lymphatic drainage;
- oncological diseases of eye tissue;
- excessive consumption of salty foods;
- poor lifestyle, lack of sleep, eye strain;
- bad habits.
The eyelid may swell due to an unhealthy lifestyle
In some cases, non-inflammatory swelling of the eyelids goes away on their own after normal rest and lifestyle adjustments. If they appear with a certain regularity, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible and determine the cause of the swelling.
Allergic edema
Swelling of allergic origin most often occurs suddenly and is often accompanied by itching, redness and discomfort. Additional symptoms may include nasal congestion, skin rash, and watery eyes. Allergies are caused by food products, hygiene products, household chemicals, cosmetics, as well as plant pollen, animal dander and insect bites.
Allergic swelling of the eyelid
There are two types of allergic swelling of the eyelids - allergic dermatitis and Quincke's edema . With dermatitis, the swelling is not too pronounced, but is always accompanied by redness and itching. Quincke's edema, on the contrary, is quite extensive (sometimes a person cannot even open his eyes), and there are no additional symptoms, but they are the most dangerous for the patient, as they can spread to the respiratory system.
Symptoms of Quincke's edema
Why does the inner corner of the eye hurt?
Before starting therapy, it is necessary to find out why the inner corner of the eye hurts. This problem is not always of an ophthalmological nature. Some diagnoses can be very surprising to the patient. The merit of a quick and correct diagnosis largely lies in the professionalism of the diagnostician.
Migraine
For most people, migraine is a very severe headache that is extremely difficult to treat with medications or any other means. It is caused by a violation of the tone of intracranial vessels, which means that the problem is located much deeper than a standard headache. In addition to headaches, a person complains of photophobia, nausea and vomiting, spasms and increased sensitivity in the eye area. By the way, during a migraine attack, the outer corner of the eye usually hurts, closer to the temples.
This attack can last for several days. The condition is sometimes so severe that a person is unable to carry out ordinary household activities, and even eating food brings enormous difficulties. Any provoking factors can intensify the unpleasant sensations - strong light, noise, strong smell. This causes irritability and nervousness, as well as increased symptoms.
Glaucoma
Increased intraocular pressure (glaucoma) is caused by an increase in fluid levels in the organ of vision. This can happen for a variety of reasons. Untimely treatment leads to rapid visual impairment, loss of visual acuity and even blindness.
This is a very insidious disease, since in the initial stages it is almost asymptomatic. Few people turn to a specialist with pain in the corners of the eyes, but this step on the way to a specialist can save a person’s vision.
Sinusitis
This diagnosis can rival migraine in its popularity. Sinusitis is an inflammation of the sinuses; often, when the infection spreads, it turns into sinusitis. Radiating pain is very typical for this diagnosis. Discomfort may appear in various parts of the face, in particular, the patient may feel pain in the upper jaw and think that his teeth hurt. Since the eyes are located in close proximity, discomfort can easily move to their area. This is facilitated by swelling and increased pressure inherent in the active development of the inflammatory process.
This process is almost always accompanied by an increased temperature of the whole body, and the sinuses in particular. The patient feels the pain more in the corner of the eye closer to the nose. On the outside of the eye, almost no discomfort may be felt.
Neurology
Neuralgia of the facial nerve is a very scary diagnosis. In addition to severe pain, the patient is concerned about damage to the facial muscles, which are noticed by everyone around him. The symptoms here are very variable. In some patients, the clinical picture affects only the eyes (dryness, pain, spasms or lack of sensation in this area). In other patients, disturbances affect parts of the oral cavity, in particular changes in the taste of the front of the tongue.
The disease is complicated by constant relapses, and not always even the most modern treatment gives a good effect.
Ciliary knot syndrome
The inflammatory process in the area of the ciliary ganglion is also called neuralgia of the nasociliary nerve. This disease is also called Charlin's syndrome. This diagnosis is usually secondary, that is, the inflammatory process develops as a result of an existing active infection in adjacent areas. Ciliary ganglion syndrome can develop as a result of sinusitis, caries, stomatitis, trauma, as well as any other bacterial or viral infection in the body (cold).
With this disease, in addition to the traditional lacrimation, redness, and burning in the eye area, the patient also complains of the inability to fully open the eyelids. The eye seems to be constantly squinting. Corneal and conjunctival reflexes are reduced or completely absent. When trying to touch the eye, the patient experiences severe pain because the inflammation has affected the nerve - the most painful tissue of the body.
Traumatic edema
The tissues of the eyelids are very delicate and thin, so any injury can cause bleeding and swelling. As a rule, this situation does not require medical intervention - you just need to maintain eye hygiene and make sure that the wound does not get infected. In women, eyelid swelling is often observed after a tattoo procedure, which involves driving pigment under the skin of the eyelids. If the procedure was carried out correctly, the swelling will subside within a day, but too deep injection of pigment or its poor quality can cause allergies and inflammation.
Eyeball bruise
For reference: in rare cases, swelling is a consequence of the anatomical structure of the eyes - if the membrane between the skin and the fat layer is too thin, any negative impact can cause swelling.
Swelling of the upper eyelid in a child
Swelling of the eyelids in childhood is most often caused by genetic predisposition, allergic reactions or infectious eye diseases (children often have the habit of rubbing their eyes with dirty hands). Allergies and infections require appropriate treatment, and for edema caused by hereditary factors, parents are advised to monitor the child’s drinking regime and daily routine, and also reduce the amount of salt in his diet. In any case, if this symptom appears, you should consult your doctor.
Edema in a child
Diagnostics
There can be many reasons for swelling of the upper eyelid, so anamnesis and the presence of additional symptoms play an important role in making a diagnosis. Diagnosis of ophthalmological diseases, as a rule, does not cause difficulties for specialists, but non-inflammatory edema may require additional examinations and consultation with specialized specialists (cardiologist, nephrologist, endocrinologist, etc.).
Diagnostic features
Non-pathological causes of redness in the corner of the eye in an adult
| There are many reasons for the development of the disease, from ordinary lack of sleep to serious illness. Inflammation can be eliminated only after the root cause of its occurrence has been determined. |
Redness of the corners of the eyes is also caused by physiological factors: stress, heavy lifting, lack of sleep, etc. If purulent discharge is observed, antibacterial treatment is prescribed. In some cases, antibiotics are prescribed. To relieve redness, use Prednisolone and Erythromycin eye drops.
Traditional medicine recipes will help eliminate inflammation:
- Prepare an infusion of chamomile; it copes well with pathogenic microorganisms. Pour boiling water over two tablespoons of dried flowers and let it brew;
- Pour water (500 milliliters) into a couple of tablespoons of dry mint and boil for fifteen minutes. Use for compresses.
In addition to diseases, an unpleasant problem can be caused by an incorrect lifestyle. Modern people cannot imagine themselves without computers; we often sit at them until the very night, straining our eyes. As a result, it is possible to develop dry eye syndrome or computer vision syndrome, which cause redness and burning of the corner of the eye, pain and other unpleasant manifestations, for example, intolerance to sunlight.
There are several types of reasons why this symptom appears:
- Mechanical irritation, for example, from dust, dirt, aerosols, smoke, foreign substances, strong winds, exposure to excessively bright light (for example, welding), prolonged eye strain, injuries;
- Physiological reasons - expansion of the blood vessels of the eye, but without any disruption of its functioning; this can happen with fatigue, drinking alcohol, severe sneezing, physical exertion, eye irritation with contact lenses or glasses if they are incorrectly selected;
- Eye pathologies - can be inflammatory or non-inflammatory in nature;
- Pathological changes in the functioning of other organs - for example, allergic diseases, diabetes mellitus, intoxication with toxic substances, hypertension, etc.
What should not be done for swelling of the eyelids?
In order not to aggravate the situation, the following manipulations should not be performed during swelling of the upper eyelid:
- warm the affected area;
- open the ulcers yourself if they are on the skin;
- lubricate the eyelid with concentrated alcohol solutions, as they can cause irritation or burns.
You cannot open ulcers yourself
In addition, it is not recommended to take antibiotics on your own, regardless of the form of release of the drug - improper use of drugs for oral administration or local treatment can seriously harm the patient.
Video: Swelling of one upper eyelid, causes and signs
Treatment of eyelid swelling
The therapy used for edema of the eyelid depends on the cause of the development of the pathology - to eliminate edema and its cause, conservative therapy, cosmetics and folk remedies are most often used.
Conservative therapy
For infectious processes, patients are prescribed broad-spectrum antibiotics and antiviral agents in the form of tablets, drops and ointments. In the case of allergic edema, antihistamines and anti-inflammatory drugs containing synthetic steroid hormones are used, which eliminate not only swelling, but also itching, redness and discomfort. In addition, with edema of allergic origin, it is important to determine the factor that led to the undesirable reaction of the body and, if possible, eliminate it. Non-inflammatory edema can often be eliminated with proper sleep, reducing fluid and salt intake, and giving up bad habits. If swelling persists, you should consult a doctor and check your kidney function, endocrine and cardiovascular systems.
Using eye drops
Cosmetical tools
If swelling of the eyelids is purely a cosmetic problem, you can use special ointments, creams and masks to relieve swelling. Physiotherapeutic procedures have a good effect - electrical stimulation, mesotherapy, various types of massage (manual, vacuum, roller), which have a beneficial effect on tissues, remove excess fluid and stimulate the outflow of lymph, which helps reduce swelling.
Sometimes swelling can be hidden with cosmetics
For reference: a massage that improves the condition of the eyelids during swelling can be performed at home - you need to gently massage the skin of the upper eyelid with light pressure for 1-2 minutes, and finish the procedure with light tapping.
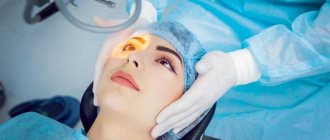
In extreme cases, usually with the formation of so-called blepharochalasis (a fold in the outer part of the eyelid that hangs over the eye), they resort to plastic surgery called blepharoplasty.
Blepharoplasty
Folk remedies
Traditional recipes for combating eyelid swelling involve the use of agents with anti-inflammatory and diuretic effects that draw out excess fluid, improve blood circulation and lymph outflow.
- Parsley . The most common and effective decongestant that can be taken orally, and can also be used to prepare decoctions for lotions and compresses. One of the recipes is as follows: pour a chopped liter of parsley with a liter of water, add 2 tablespoons of sugar and simmer for half an hour over low heat. Drink 100 ml three times a day. To prepare an infusion for compresses, you need to take a bunch of fresh herbs, chop them, steam with a glass of boiling water, and leave for 15 minutes. Soak cotton pads in slightly cooled liquid and apply to eyelids for 10 minutes.
- Flax-seed. Flaxseed has an antibacterial and diuretic effect on the body. Pour 4 teaspoons of seeds into a liter of water, boil for a quarter of an hour, then cool, filter and take half a glass three times a day. The course of treatment is 20 days.
Flax-seed - Chamomile . An infusion of chamomile helps well with allergic and inflammatory swelling - the product soothes the skin, relieves redness and itching. Pour a tablespoon of flowers into a glass of boiling water, leave for half an hour, cool slightly and rinse the affected eye several times a day.
- Birch leaves . Birch leaves are considered one of the best diuretics. Infuse crushed leaves (2 tsp) in a glass of boiling water for 10 minutes, then drink the infusion in an amount of at least 2 glasses per day. The infusion can also be used for lotions - moisten cotton pads in it and apply to the eyes.
As a quick way to relieve swelling, you can apply pieces of ice, slices of fresh cucumber, raw potatoes, or even cold spoons to your eyes after placing them in the freezer for 10 minutes.
Fresh cucumber slices for eyes
Important: diuretics that are used to combat swelling of the eyelids have a number of contraindications - they are prohibited from being taken if you have urolithiasis or cholelithiasis, pregnancy, or breastfeeding.
Video: How to remove swelling from the upper eyelid?
What diseases cause eye pain?
Many people have eye pain due to ophthalmological and systemic diseases. The reason may be in the organs of vision or in other disorders. The choice of specialist and treatment depends on the cause of the pain; in order to identify it, laboratory and instrumental examination methods are prescribed.
There are a number of ophthalmological diseases and conditions that can affect soft tissues, blood vessels, and nerves located in the organs of vision.
They cause acute and chronic pain:
- Increased eye strain. It occurs in people who spend a long time in front of a computer, phone, TV, or tablet. Pain occurs when reading books frequently in poor conditions, for example, in low light.
- Entry of a foreign body. It can penetrate the cornea due to strong winds, sparks from a welding machine, or for other reasons. Acute pain, redness, photophobia, increased sensitivity, and spasm of the eyelids occur.
- Conjunctivitis. It can be of an allergic, bacterial, viral nature. This is a disease in which the conjunctiva of the eye becomes inflamed. Redness, swelling, pain, and photophobia appear. With bacterial conjunctivitis, purulent exudate is released.
- Blepharitis is inflammation of the eyelids. It can develop due to the proliferation of fungi, viruses, bacteria, parasites (eyelash mites). The eyelids swell and an abscess filled with fluid may form under the skin.
- Keratitis is inflammation of the cornea. The inflammatory process begins as a result of mechanical damage, burns, and the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. If the disease lasts a long time, the cornea becomes cloudy and visual acuity decreases.
- Glaucoma is an increase in intraocular pressure due to impaired outflow of secreted fluid. There are anterior and posterior chambers in the eyeball, and fluid constantly circulates inside them. If it accumulates but does not come out, the pressure increases. This can lead to damage to the optic nerve, retinal detachment, and blindness.
- Retinal diseases. They develop due to burns, mechanical damage, and malnutrition through blood vessels. If the retina detaches, the person goes blind.
- Diseases of the optic nerve. Light streams pass through the eyes, hitting the rods and cones of the retina. From them, information in the form of nerve impulses passes through the nerve, entering the brain. The nerve is damaged due to malnutrition through blood vessels, mechanical damage, and infectious and inflammatory processes.
- Strabismus, amblyopia. If both eyes see the picture in front of them incorrectly, this leads to increased strain. As a result, not only your eyes hurt, but also your head.
There are diseases that develop not in the eyes, but in peripheral organs; with their prolonged development, complications arise from the organs of vision, this also leads to pain:
- Diabetes. A large amount of glucose accumulates in the patient’s blood, which is not distributed to the tissues, but binds to cholesterol and forms plaques. They are transported through large and small vessels, including the microcirculation of the eyes. This leads to blockage, severe pain, decreased or complete absence of vision.
- Atherosclerosis. Cholesterol accumulates in the patient’s blood, which spreads through the vessels, clogging their lumen. The mechanism of the disease is the same as for diabetes mellitus.
- Arterial hypertension. Increased pressure puts stress on the endothelium. This leads to rupture of the vessel wall and hemorrhage inside the eyeball. With chronic hypertension, the function of the visual organs decreases, and constant headaches and eye pain occur.
- Ischemic disease. A person experiences spasm of peripheral vessels. If this happens in the eyes, nutrition is disrupted. Gradually, the organs of vision will fail to function. Severe spasm causes severe pain.
- Vasculitis, increased fragility of blood vessels. If the endothelium is fragile, this leads to hemorrhage in any part of the body. Painful sensations appear during spasms, which causes a decrease in vision function.
- Neuropathy. The inflammatory disease can spread to the optic nerve, this is dangerous because it connects to the brain. This causes a decrease in its functionality and constant pain.
For each disease, a separate treatment is determined. Therefore, diagnostics are initially carried out, identifying the nature of pain, decreased vision function and other symptoms.
Prevention of eyelid swelling
To prevent swelling of the eyelids, you should lead a healthy lifestyle, stop smoking and alcoholic beverages, and do not overuse salty, spicy and pickled foods, especially at night. Women should be careful when choosing decorative cosmetics and be sure to wash off makeup before going to bed. In addition, it is important to protect the eyes from the negative effects of external factors (ultraviolet radiation, mechanical damage), treat infectious diseases in a timely manner, and monitor the functioning of the kidneys and cardiovascular system.
Prevention of eyelid swelling
Swelling of the upper eyelid of one eye can be a common cosmetic problem, but in some cases it indicates the development of serious diseases, so you should consult your doctor if this symptom appears.