Is it possible to affect visual acuity?
Scientists and doctors of ophthalmology have tried to answer this question for many years in a row.
And in the end, they came to a common decision that through special training it is possible to increase visual acuity by 2-3 times. Of course, it is unlikely that it will be possible to break the record, but the visual apparatus will significantly improve its performance. Exercises for “improving” vision for children are much more effective. Because their visual muscles, like many others, are more elastic than those of adults.
Preventive methods
If the mother or father wears glasses, you should pay attention to the child's vision. Supplement routine examinations at 3,6 and 12 months with home diagnostics.
| By the age of three, you should be tested for myopia, as at this age the risk of detecting the disease increases. |
An adult should rest his eyes both during working hours by changing his occupation, and at night by sleeping for at least 8 hours. Increase the amount of vision-healthy foods in your diet: sea fish, eggs, fruits and berries, legumes.
Don’t forget about age-related changes; when you retire, try to do eye exercises every day. Don't ignore headaches - they often become harbingers of diseases of the visual apparatus.
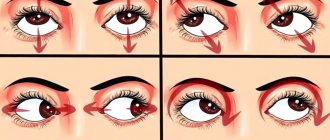
Bates exercises
Help tone muscles, promoting their healthy development. Gymnastics also has a beneficial effect on blood circulation, thereby reducing the risk of stagnation and vascular atrophy. Thus, daily performance of these simple activities reduces the likelihood of increased IOP and the occurrence of diseases of the organs of vision.
In addition, do not forget to perform a light massage with your fingers - from the temple to the nose and back. A “trick” with warm palms will help relieve fatigue: rub your hands, place them on your closed eyelids, slightly bending your fingers into a bowl shape. After a few seconds, you will feel fresh and energized when you open your eyes.
Exercises according to Norbekov
A complex exercise will help you get rid of stress after reading or working with small parts for a long time:
- Close your eyes tightly for a few seconds and open them sharply. Repeat 2-3 times.
- Massage each eyelid in a circle for 30-60 seconds.
- Place three fingers together and use your hands to apply gentle pressure on both eyelids.
The video will also tell you in detail about Norbekov’s technique:
What should a person's ideal vision be like?
The average person on the planet has vision of 1.
This number indicates 100% vision. Normally, such a person can see two points in separate places located at an angle of 1 minute between them. To determine visual acuity in medical terminology, the numbers 0, 1, 1, 2 are used. In one human eye there are over 120 million cells that are sensitive to light. The cerebral cortex deciphers information coming from cells and produces it in various shapes and colors.
The human retina consists of rods and cones. The former are responsible for the ability to see gray color in low light, and the cones are responsible for colored objects and details. Ideal vision is easy to confirm; to do this, you need to visit an ophthalmologist's office. The specialist will ask the person to consider special tables and symbols. It is very important that it is the tables hanging in the doctor’s office that can determine visual acuity, but not pictures from the Internet on the computer that “promise” to give an accurate result.
What is the normal eye pressure for a healthy person? Consider all cases and ages
Intraocular pressure (IOP) is an important diagnostic indicator that allows you to indirectly determine the presence of various ophthalmological diseases.
With the development of various pathological processes, this indicator may increase or decrease, deviating from the established average statistical norm.
Below we will analyze in detail what normal eye pressure should be in a healthy person at different ages.
You can read more about the symptoms and causes of this disease here.
What is eye pressure?
Intraocular pressure refers to the amount of tone that occurs between the membrane of the eyeball and its internal contents.
Also, fluid can accumulate in the organs of vision, which leads to an increase in the indicator, and this can lead to such an additional problem as deformation of the vessels through which the fluid is transported.
There are three types of such violations:
- In case of transient disorders, destabilization of IOP is short-term, and it is restored without the need for treatment within a short period.
- With labile disorders, short-term pressure surges are also observed, which go away on their own, but the processes are regular.
- If the excess of the norm is constant and does not go away, they speak of a stable type of pathology.
Such jumps can be dangerous, especially if there is a decrease in IOP.
In such rare cases, which can be caused by injuries, infectious and endocrine diseases, dry eye syndrome may appear.
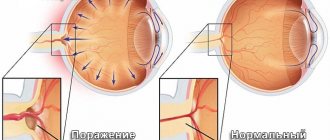
If the indicator increases, which is diagnosed more often, in the absence of treatment, compression of the optic nerve may occur, which subsequently is fraught with its atrophy.
Changes in pressure in the organs of vision require immediate intervention by specialists and timely treatment.
Normal eye pressure in adults and everything you need to know about it
Intraocular pressure (or ocular tone) is measured in millimeters of mercury.
During the day, such values may change, but if they do not go beyond the designated limits, there is no reason to consult a doctor.
How is IOP measured?
There are several ways to take measurements.
The first of them, named after Professor Maklakov, has been used by ophthalmologists for over a century.
During this procedure, a special medical weight is placed on the cornea of the eye, previously treated with an anesthetic.
For details about all methods of measuring IOP, read a separate article: how to measure intraocular pressure.
It leaves a small dent or imprint on the shell of the eye, which the ophthalmologist subsequently deciphers.
The second method is pneumotonometry, in which pressure is exerted not by a load, but under the influence of a jet of compressed air. Unlike the Maklakov method, this is a less accurate method.
Modern specialists prefer more accurate modern diagnostics using an electron diffraction scanner to these two methods, which involves non-contact measurement.
During this procedure, the production of intraocular fluid is artificially stimulated, after which its outflow is also artificially accelerated.
This method allows you to quickly establish the most accurate results and determine the presence of pathological disorders.
Norms of eye pressure for different ages and in different cases
In most cases, in adults, the norm of intraocular pressure remains unchanged for people of any age, and this indicator can mainly change in case of some ophthalmological diseases.
40 years
The average value for people aged 40 years and older is considered to be from 10 to 23 millimeters of mercury.
With such indicators, all metabolic and tear-forming processes proceed in a normal natural mode.
This indicator of fundus pressure is the same for men, women and children, although in a child the indicator rarely approaches 20 units.
50-60 years
At the age of 50-60 years, intraocular pressure increases slightly, but this is normal, and an indicator of 23-25 units is not considered pathological and does not require intervention, although this is already a signal that a person may develop glaucoma and other inflammatory processes, so after Fifty years of age requires an ophthalmological examination every six months.
For people aged 70 years and older, a figure of 23-26 units is considered normal.
What is normal eye pressure for glaucoma?
Ocular pressure readings change dramatically when glaucoma occurs.
This disease can occur in one of four degrees of severity, which determines how much the indicator will increase:
- At the initial stage of the disease, IOP can fluctuate from normal to 4-5 units higher. Usually the pressure does not exceed 27 millimeters of mercury.
- In severe glaucoma, the value can be from 27 to 32 units.
- At a deep stage, the pressure rises to 33 millimeters of mercury.
- When IOP exceeds 33 units, they already speak of the final stage of glaucoma.
Intraocular pressure is measured during any routine ophthalmological examination, since based on these numbers, a specialist can draw conclusions about the presence of certain ophthalmic defects, even if they do not show any symptoms.
Useful video
In the video you will see clearly what IOP is:
The older a person is, the more often he needs to undergo examinations and be attentive to increasing IOP. Sometimes this is the only hint of diseases that need to be treated as early as possible.
More than once in our lives we hear the phrases “one hundred percent vision”, “and I have -2”, but do we know what they really mean? Why in some cases is one considered the best indicator, but in others +1 is already a deviation from the norm? And yet, what kind of vision is considered normal?
What tables are used to test visual acuity?
Today, there are several types of special tables that make it easier for a doctor to determine how well or poorly a person sees.
- Golovin table. This option consists of identical rings. They have holes in different parts of the “body”. The specialist points out to the patient the rings that the person must examine; the patient must sit at a distance of 5 meters from the table.
- Snellen chart. It is used mainly in English-speaking countries. This table consists of 11 rows. The very first line contains one large letter. In each subsequent line, the size of the letters decreases, and their number in the row increases.
- Orlova's table. It is used to test visual acuity in children. Here, instead of rings or letters, icons in the form of animals and plants are used. Vision is considered normal when a child sees the tenth line, sitting at a distance of 5 meters from the table.
- Sivtsev's table. This is the most common type of perfect vision test. This table consists of letters of the Russian alphabet arranged in 12 lines. In the top line the letters are large, the lower they are, the smaller they are. Ideal vision 0 is when a person manages to recognize letters from the tenth line from a 5-meter distance.
What vision is considered normal?
Many people believe that normal vision is a sense. In fact, they are practically right, since vision is officially considered to be a kind of sensory perception or sensation.
Doctors believe that vision is the ability to perceive colors, light, see the location of objects or objects from a long or close distance, which represent entire images or images.
Humans and almost all animals have optical vision, but there are other types of perception of the surrounding world, among which we can distinguish, for example, ultrasonic sensations, which are characteristic of bats.
The human eye, like many other human organs, is susceptible to various kinds of diseases and defects due to the incorrect performance of a number of certain functions. All this can be directly related to diet, bad habits, hostile characteristics and many other factors that can affect vision deterioration.
Deviations in the functioning of the visual apparatus
The most common visual impairment is myopia. In medicine it is called myopia. This disease is characterized by a person’s ability to see only objects, objects and parts that are nearby. He can't see them from a distance. Also characteristic of myopia is an enlargement of the eyeball. This pathology can be either acquired or acquired during childbirth, that is, congenital. The main symptoms of myopia:
- poor distant vision;
- while the near remains normal;
- When viewed, objects may merge into one object and the image may be distorted.
There are cases when a person develops false myopia, in which case drug treatment can help.
Another pathology in the functioning of the visual apparatus is hypermetropia. This disease is characterized by perfect distance vision and poor near vision. The main symptoms of hypermetropia:
- seeing objects as if in a fog;
- sometimes it is possible to develop strabismus;
- eyes get tired quickly;
Hypermetropia can be functional, normal or pathological.
Visual deviations
The human eye is a delicate and sensitive instrument. Good vision is achieved with its help only if all its components work perfectly, and this does not happen in all cases. There are many abnormalities, often insignificant at first glance, that can cause decreased vision or even blindness.
The most common among them:
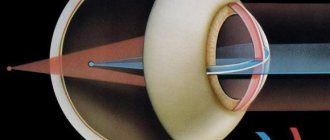
- Farsightedness. The eyeball is somewhat shorter than it should be, because the light rays that pass through it are focused not on the retina, but as if behind it. In mild stages, it is compensated by curvature of the lens - more noticeable than normal. In severe cases, it is not compensated for and prevents a person from perceiving nearby objects. Develops in children, most often as a result of congenital pathologies. Once eye development is complete, it does not progress. No treatment is required; the patient is prescribed glasses and that’s it.
- Age-related farsightedness. Over time, the lens, which must move and change its thickness in order for a person to see clearly at any distance, becomes less mobile. This is a natural part of its development, and it enters the hardening stage immediately after it finishes forming (that is, around high school). But the effect becomes noticeable only at forty-five, and then not in all people. It is treated in the same way as normal farsightedness - with the help of glasses that need to be worn to see up close.
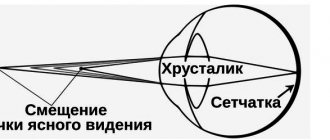
- False myopia. It develops if a person for a long time does not properly use those eye muscles that are responsible for the movements of the lens. They gradually stop serving and the lens becomes fixed in one position, in which the image is focused not on the retina, but in front of it. Such myopia tends to turn into true myopia if it is not treated. It is treated with the help of gymnastics, which tone the muscles.
- True myopia. It develops if the eyeball grows in length (this happens if the eye tries to compensate for the effects of false myopia or suffers from constant strain due to attempts to look at nearby objects closely and constantly). If the provoking factor is removed, it usually stops. There is no treatment that is 100% effective, but decreased visual acuity is usually compensated by wearing glasses. Even if a person is already at a difficult stage and cannot focus on anything at all, glasses lenses correct this deficiency.
- Astigmatism. Distortion of the shape of the cornea or lens. Normally, it is present in all people - there are no people whose eyeballs are perfectly round. But in severe cases it can greatly influence how much a person sees. It is treated in the same way as other disorders in this group - with the help of glasses that help the light focus on the desired point.
- Colorblindness. It occurs more often in men than in women; it does not affect visual acuity, but does affect its quality. The mechanism of operation is very simple: in the human eye there are cones that are sensitive to three primary colors. If sensitivity to one, two or all three colors decreases, a person loses color vision completely or partially, and ceases to perceive certain colors of the spectrum. Not all colorblind people are allowed to drive, they are not accepted into the army and similar fields. The disease is detected quite early using special scales. Color blindness is incurable.
Vision can deteriorate not only due to physical abnormalities that do not cause pain, but also due to serious illnesses - and without treatment, it can even lead to blindness. The most common of these diseases are:
- Cataract. Clouding of the lens, in which it stops transmitting light, which should be concentrated on the retina. As a result, vision gradually decreases. In severe stages, the patient ceases to distinguish between darkness and light, and eventually becomes completely blind. The treatment is surgical - the lens is replaced with a thin lens.
- Glaucoma. Due to increased intraocular pressure, the tissues of the eye suffer - the vessels are compressed, blood flows through them poorly, oxygen starvation begins, followed by degradation. Treatment is initially conservative (to improve the patency of blood vessels and remove the cause of the pressure), in acute attacks, when the pressure needs to be reduced quickly, surgical treatment.
- Retinopathy. It works on approximately the same principle as glaucoma, but the vessels are damaged due to problems not related to pressure. For example, due to diabetes, atherosclerosis, constant smoking, thrombosis, stroke. Without access to air, eye tissue degrades. The main treatment is to get rid of the cause or put it into remission. In some cases, it is simply impossible to save vision.
Even the best vision usually deteriorates due to aging changes in the tissues of the eye - the lens becomes cloudy, blood vessels suffer, and a person develops signs of farsightedness, myopia and future blindness.
In some cases, medicine cannot reverse the process and make vision 100% again, but it can “freeze” the disease and find a way to compensate for its consequences.
The best way to preserve your vision is to have an annual eye exam!
What is astigmatism?
An equally complex disease of the visual system is astigmatism. It is often combined with myopia and hypermetropia. Astigmatism is characterized by a violation of the sphericity of the lens and cornea. This pathology can be congenital or acquired. Congenital astigmatism is often diagnosed in childhood, and in adulthood it does not affect visual acuity in any way. But this is only in cases where the sharpness is not higher than half a diopter. When the pathology has more than one diopter, this indicates that vision is deteriorating. The visual system needs urgent treatment. Acquired astigmatism often results from scarring of the cornea.
What is the norm
It has been established that visual acuity is considered to be the norm - 100% or V = 1.0, the refraction of the eye is 0, the normal IOP is 22-24 mm Hg.
The norm is considered to be a combination of indicators of refraction and acuity; pressure in this case refers to third-party assessment factors, but in some cases plays a significant role, because primarily affects the clarity of vision.
Why acuity and refraction are key:
- Refraction is the position of the focal point relative to the retina. The optical system of the eye consists of the lens, vitreous body, cornea and aqueous body. The incoming beam passes through each refractive medium in turn and reaches the macula - a small spot on the back wall of the eye, consisting of nerve endings, cones responsible for color perception, and blood vessels. The reflected beam projects an image and transmits it to the visual analyzer in the brain. And as a result, we see the image, and how well it enters the analyzer is the work of refraction. During the normal functioning of the totality of all systems, the focal point is on the surface of the retina, and this is called emmetropia (indicators are equal to 0). Refraction is measured in Diopters.
- Visual acuity is the ability of the human eye to perceive two points at a minimum distance between them. Simply put, this indicator determines the quality of the reproduced picture in the brain. The difference between refraction is that acuity does not have an exact mathematical model of calculation, unlike refraction. All designations for visual acuity are conditional and vary depending on the individuality of the organism.
Visual acuity is determined using tables, while refraction is measured linearly, that is, in fact, the length of the position of the focal point is measured in centimeters/meters. If vision abnormalities are detected, the strength of the curvature of the cornea, the degree of image distortion are determined, and one or a combination of the diseases listed below are diagnosed.
Keratometry measures the radius of curvature of the cornea to assess corneal astigmatism. This type of astigmatism is the most serious, although astigmatism at the level of the back of the cornea and the anterior and posterior surfaces of the lens is equally important, which in many cases is minimal.
What is ideal vision for children?
The eyes are a paired organ that is formed before the age of 18. Vision, in turn, can be stable, but it can also change throughout a person’s life. Children from birth to the first year of life experience the development of their visual system.
After birth, only an experienced specialist can check the pupil's reaction to light. By the age of one year, children begin to distinguish familiar objects well. Distinguish them from each other by shape and color. After the age of two years, a small person begins to see everything more perfectly and learn to distinguish the distance between objects. When a child goes to kindergarten, the load on the visual system increases. To maintain the child’s ideal vision during this period, it is necessary to take breaks between eye strains, giving them a rest.
What is minus
Ophthalmologists like to use the concepts of plus and minus to indicate visual acuity. Myopia is a so-called disadvantage, and let's see why.
The task of contact correction devices is to correctly disperse light rays, shifting the focus to the retina where it should be. As a result, normal image clarity returns. Since the diopters of lenses prescribed for myopic changes produce a concave glass shape with a scattering effect, designated “-,” myopia is called minus vision.
Clinical picture
Symptoms of myopia include:
- Reduced clarity of vision of distant objects;
- Merging pictures;
- Good near vision function.
The stronger the degree of myopia, the worse a person sees at a distance. If the minus is high, the patient distinguishes objects only near his nose - correction tools are required for distance. The degree of distortion of visual function can vary - from slight blurred vision to complete distortion of the picture. Double vision and distortion of the display of objects are characteristic not of myopia itself, but of its combination with astigmatism.
Interesting features of the physiology of vision
These are real facts that not every person knows about;
- In ancient times, people tested visual acuity in this way: they looked at the sky at night, found the Big Dipper, then looked at a small star in the handle of a bucket. This was evidence that the visual apparatus was working normally.
- The weight of one human eye is approximately 7 g and its diameter is 24 mm.
- Carrots can improve vision. This is absolutely true, vitamin A, which is found in this vegetable, helps maintain the full functioning of the visual apparatus.
- More than 90% of people in the world are born with blue-gray eyes. Closer to the second year of life, the eye color is formed, which will remain forever.
- Green eyes are the rarest in the world. Only 2% of people have this iris color.
- The lightest-eyed nations are considered to be the Poles, Swedes, and Finns, and the darkest-eyed are the Turks and Portuguese.
- For 1% of people on the planet, the color of the iris of one eye is different from the color of the other. Such people tend to have unusually high intelligence and can be very talented.
- Men blink twice as fast as women.
- It is impossible to sneeze without closing your eyes.