The human retina contains nerve endings: rods and cones.
They have pigments that can capture different colors. These include blue, green, and red filters.
When they are combined, many shades are formed that a person perceives. For some people, these parameters are violated. Patients may be blind to one or more colors. It is important to diagnose the pathology in time, since their lifestyle with color weakness is limited.
Causes of color blindness
In the retina of the human eye (retina) there are color-sensitive receptors - cones and rods, containing various protein pigments. Several types of cones are responsible for color perception of vision. The first captures green light - light waves with a length of about 535 nm (nanometers), the second - waves of 553-558 nm (red), the third captures blue color (wavelength 425 nm). The presence and normal functioning of all three types of receptors indicates that the person does not suffer from color blindness.
A decrease or absence of pigment in the cones (this may be one of them or several) manifests itself as a deviation in color perception.
The pathology is transmitted genetically through the X chromosome from mother to son. For a male child to develop this vision deviation, a mutation of one chromosome with the color blindness gene, passed on to him by his mother, is enough. The girl inherits color blindness through her father's lineage - from his mother or grandmother.
This explains the statistics: up to 8% of men and only 0.5% of women suffer from the disease. Hereditary color blindness, with rare exceptions, affects both eyes and does not progress throughout life.
A person receives the acquired form of this disease due to damage to the retina or optic nerve; it can be caused by pathologies of the organs of vision and the central nervous system.
For example, with cataracts, clouding of the lens occurs, light rays have difficulty penetrating the optical system of the eyeball, and as a result, photoreceptors begin to perceive colors worse.
If the optic nerve is damaged, against the background of a general deterioration of all functions of the eye, the condition of the cones may remain normal, but color perception worsens.
A malfunction associated with the transmission of nerve impulses on the way to photoreceptors can provoke Parkinson's disease, cancer, and stroke.
The photoreceptors of the organs of vision can be affected to varying degrees: sometimes one eye after damage can perceive colors better than the other.
Acquired color blindness can also be caused by drug intoxication (not often), head trauma, ultraviolet radiation burns, or macular degeneration, a disease associated with insufficient blood supply to the retina. It occurs equally in men and women.
Note! A person with color blindness may not know about it for years. Thus, John Dalton himself, the English scientist who first described this vision defect, did not suspect until he was 27 years old that he could not distinguish shades of red. And since his brothers and sister received the same diagnosis, Dalton made an assumption about the hereditary form of this visual feature.
Sources of protanopia
In most cases, color blindness, namely its form - protanopia, has a hereditary etiology, that is, it is inherited from one of the parents. At the same time, during the prenatal period, the cone apparatus of the retina, which is responsible for the perception of colors from the outside, is deformed.
The retina contains 3 cones endowed with their own light-sensitive pigment. Each cone is responsible for color perception of different wavelengths of light. Thus, waves with a length of 570 nm are perceived as red, 544 nm – green, 443 nm – blue. If any cone is damaged, the perception of the corresponding color is impaired. When several flasks are involved in the pathological process, the outside world for a person becomes almost black and white.
More rarely, color blindness occurs due to exposure to another provoking factor on the body. In this case, protanopia is diagnosed as a secondary disease, which often develops against the background of other retinal pathologies and diseases of the optic nerve.
So, possible sources of protanopia can be called:
- concomitant development of age-related macular degeneration;
- formation of diabetic retinopathy;
- the occurrence of retinitis pigmentosa or cataracts;
- brain injury;
- development of a tumor in the brain;
- ultraviolet exposure to the retina;
- medications that a person takes (intoxication with chemical compounds).
Of course, this list of reasons is not exhaustive, because each organism is individual and can react differently to external stimuli.
Classification of color blindness
Congenital color blindness is classified into the following types.
Achromasia – there is no color vision, a person can only distinguish shades of gray. It occurs very rarely, in 0.2% of cases.
Monochromasia - a person perceives only one color. Often accompanied by painful sensitivity of the eyes to light (photophobia) and nystagmus, a pathology expressed in frequent involuntary movements of the eyeballs.
Dichromasia - the eyes distinguish between two colors. There are the following types of dichromasy:
- protanopia – the color red is not perceived (the most common type);
- deuteranopia – a person cannot distinguish the color green;
- tritanopia is the rarest form of the disease, there is no perception of blue-violet colors, twilight vision disappears (the ability of the visual organ to work in low light conditions).
Trichromasia – all three primary colors (blue, green, red) are perceived. There are normal (meaning the absence of the disease) and abnormal trichromasia - in this case, difficulties arise in the perception of not the colors themselves, but their shades.
Anomalous trichromasia is divided into types of weakened perception of color shades:
- protanomaly - red;
- deuteranomaly – green;
- tritanomaly - blue.
The following types of acquired color blindness :
- Xanthopsia - a person sees the world around him in yellow shades. The reasons for the deviation may include previous jaundice, atherosclerosis, and drug intoxication.
- Erythropsia - surrounding objects are perceived in red hues, typical for patients with retinal diseases.
- Trianotopia - the color blue is not perceived; it is characteristic mainly of people suffering from night blindness (hemeralopia) - poor vision at dusk.
Symptoms (signs) of color blindness
Since the disease does not affect visual acuity, it is recognized only by signs of impairment in the perception of various colors. The severity of the pathology is of great importance. In the case of a mild color anomaly, this is often discovered only after passing a medical commission.
For example, red color can be perceived as gray or yellow, blue as pink or purple, etc., depending on the type of pathology. Identifying this vision feature can affect the choice of profession and employment. Colors that a colorblind person cannot distinguish appear to him as gray.
The acquired type of color blindness, in addition to the inability to distinguish colors and shades, may be accompanied by photophobia, lacrimation and pain in the eyes, signs of nystagmus - frequent movements, involuntary twitching of the eyeballs.
Symptoms in children
By about three years of age, a child’s color scheme is considered to be formed, therefore, starting from this age, parents can independently determine the signs of color blindness. Children in whom this pathology can be traced through the maternal line require special attention.
One of the easiest ways is to watch your child color pictures. He already knows that the grass is green, but when drawing it, he constantly takes a pencil of a different color - for example, brown. A child with signs of the disease may paint the sky green rather than blue.
Another simple test. You need to put any two objects in front of the baby (let, say, it be balls), but one of them must be gray or black, the second - any bright color. Children with normal vision will immediately gravitate towards the second one; if there is a pathology in color vision, the child, as a rule, begins to think, and it is clear that he chooses an object at random.
Children do not complain about pathology; they cannot compare normal vision with pathological one. If a child confuses one color with another, for example, considers white to be light pink, this can already be considered a reason to consult a specialist.
Impact on professional activities
The ability to distinguish colors is important for drivers, sailors, pilots, doctors and representatives of some other professions. There are sad statistics of disasters that occurred due to the fact that the person at fault was color blind. But at the same time, in most European countries, protanopes and deuteranopes are allowed to drive a car - it is believed that they distinguish red from green by the location of the traffic light signal. But in Turkey and Romania, and since 2012 in Russia, driver’s licenses are not issued to colorblind people.
Jun 27, 2017Anastasia Tabalina
Diagnosis of color blindness
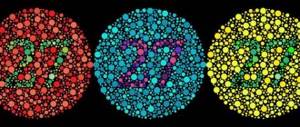
The most common types of diagnostics of congenital color blindness are the Ishihara (Ishihara) test and Rabkin’s polychromatic tables. Both methods involve the use of drawings where numbers, geometric shapes or chains of different configurations are depicted in multi-colored circles.
The background of the figure that the subject must identify differs little from the general background of the picture, so color-blind people are not able to notice these small changes in the color scheme; often they only see the background. The number and color of figures correctly identified by a person will indicate either the absence of pathology, or will tell about the degree and type of color blindness.
For children, similar tables are used, only with other images - a square, a circle, or other simple figures or symbols.
Along with the tables, congenital color blindness is detected using an anomaloscope - a device for determining color vision disorders, identifying its type and nature.
Since the acquired form of color blindness can be accompanied by disturbances in other parameters of vision and often provokes the development of organic changes in the eyeball, additional methods are used to diagnose this type of pathology.
These include:
- tonometry – determination of intraocular pressure;
- ophthalmoscopy – examination of the fundus of the eye, assessment of the condition of the retina, optic nerve head, and fundus vessels;
- perimetry - study of the visual field using special devices - perimeters;
- refractometry is a study based on determining the index (coefficient) of refraction (refraction) and some of its functions;
- biomicroscopy is a non-contact diagnosis of diseases of the eye, its environment and structure using a slit lamp.
Experts advise patients with acquired color blindness to be examined by an ophthalmologist at least once a year.
Treatment of color blindness
There are no effective therapeutic methods for treating congenital color blindness. If there are minor deviations in color perception, the doctor may prescribe you to wear glasses or contact lenses with special light filters. But many experts consider this technique controversial, since it is not always effective.
Acquired color blindness has its own characteristics: it can be accompanied by progressive deterioration, the appearance of color blindness in one eye.
If color blindness has developed against the background of glaucoma or cataracts, the problem of color blindness is solved by surgical intervention that eliminates these diseases. After surgery, to avoid complications, you should be regularly examined by an ophthalmologist.
Note! Since it is believed that color blindness does not have a major impact on the quality of life, disability for this type of pathology is not assigned, with the exception of monochromasia (complete color blindness).
Treatment of protanopia
An acquired disease, that is, secondary, is amenable to therapeutic treatment. For example, if protanopia is caused by ultraviolet exposure to the retina, it is necessary to exclude such a provoking factor, after which vision will return to normal.
Sometimes doctors practice a method of correcting congenital color blindness, such as treatment with special glasses. If the degree of pathological changes is insignificant, ordinary darkened glasses are also suitable, because the eyes see better in dim light. If a certain cone is completely absent, it is not advisable to treat protanopia, since restoring normal color vision is no longer possible. Only a well-qualified specialist can prescribe treatment or correction of protanopia.
What treatment is required for the acquired form of the disease is determined taking into account the cause of its occurrence. Age-related changes in the eyes cannot be corrected. The natural disturbance of color perception processes cannot be restored by any drug or therapeutic procedure. In some cases, replacing the lens helps restore vision, but not completely.
Important! If protanopia is caused by trauma, the prognosis for treatment depends on how badly the macula (retina) is damaged.
Implications for colorblind people
The consequences of this type of pathology include restrictions associated with the choice of work. Colorblind people are not allowed to drive commercial vehicles, and for medical reasons they cannot become military personnel, chemists, or pilots. And representatives of these and a number of other responsible professions are forced to regularly undergo color blindness tests.
The degree and type of color blindness are of great importance. If it is incurable, a person has no choice but to come to terms with the diagnosis and build his life taking into account these visual features.
An overview of life with color deficiency
If color weakness is detected, the patient is diagnosed. The degree of violation is revealed. If he does not perceive red or green tint, driving a vehicle is prohibited. You can get a license if the violation is caused by a primary disease.
It is necessary to first treat it and undergo repeated diagnostic tests to identify the patient's condition.
It is also not recommended for such patients to work in medicine, in an enterprise with harmful chemicals, or with moving mechanisms. If the work involves recognizing different colors, it is also prohibited.
Other activities can be performed if color vision is weak. In this case, the patient must provide a certificate to the employer.
Prevention of color blindness
Using DNA testing, it is possible to identify a gene with a mutation through which color blindness is potentially inherited by the child from the mother. But, firstly, this is an expensive procedure, and secondly, and more importantly, scientists are not yet able to modify the mutated gene to prevent pathology.
If we keep in mind nonspecific preventive measures, then these are consultations with a geneticist when a family is planning the birth of a child. Doctors advise people suffering from diabetes and progressive cataracts to see an ophthalmologist twice a year to prevent complications.
If a defect in color perception is detected in a child, when studying in the lower grades, he should use tables and maps with bright, contrasting colors developed for these cases.