Anomalous trichromasia is a color vision disorder characterized by decreased perception of one of the three primary colors - red, green, blue.
The ability to distinguish them decreases, but does not disappear completely.
The disease is congenital. It is believed that this condition develops due to a slight deficiency of one or another pigment. A person perceives all three primary colors, but in the wrong proportion.
Symptoms of abnormal trichromasia
The clinical picture of the disease is based on loss of sensitivity to three primary colors. The perception of one cone is impaired or it is completely absent. Normally, 3 cones function, making it possible to see blue, green and red normally.
With anomalous trichromasia, a violation occurs in one of them, which is why a person perceives colors incorrectly. For example, green appears yellow, orange appears dirty green, blue appears almost white, and purple appears dark green.
The disease is considered hereditary and cannot be acquired. There are three degrees of impaired color vision:
- A - the most severe, the patient distinguishes only 2 primary colors (this means that 1 visual pigment is missing in the retina);
- B - average;
- C - a person distinguishes shades almost normally.
People with anomalous trichromasia have impaired twilight vision. In 80% of cases, the acuity of visual perception decreases, the eyes get tired faster. In 60% of cases, increased sensitivity to light appears and in 50% - diplopia.
What is color blindness?
Since this disease belongs to one of the types of color blindness, it is worth initially understanding what kind of disease it is. Colorblind people are people who do not perceive color balance correctly. In such patients, color vision is impaired.
What is color vision?
Color vision or color vision function is the ability of the retina to perceive and distinguish primary colors, the wavelength of which is 400-700 nm.
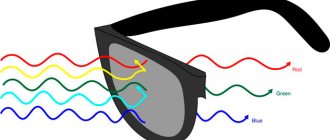
The eye perceives colors through three types of cones, each of which has one or another characteristic. These three cones differentiate the brightness, saturation and hue of the supplied light stream. All this depends on the length of the light flux, its richness and radiation intensity.
Colorblind people are people who do not perceive color balance correctly.
Types of color blindness
Many people believe that color blindness is a disease that is inherited and can manifest itself completely differently in each family member. But scientists have proven that various forms of this disease can also be acquired. There are 4 types of color blindness, namely:
- abnormal trichromasia;
- dichromasia;
- monochromasia;
- achromasia;
Each type has its own specifics, symptoms and methods of improving vision for this disease. And if, with monochromasia and achromasia, people practically or completely do not distinguish colors, then in the first 2 cases everything is not so advanced.
With dichromasia, patients cannot see the difference between colors such as green, yellow, orange and red. But with trichromasia, a person is able to distinguish primary colors, but in certain cases this perception may be impaired.
Varieties of trichromasia
Protanomaly
This is a form of abnormal trichromatism, manifested in insufficient sensitivity to red tones. The development of the disease is due to the absence of erythrolab retina in the cones.
Erythrolab is a photoreceptor sensitive to the yellow-red part of the spectrum. Part of iodopsin. It is most sensitive to long-wave radiation.
If perception is not severely impaired, a person will not even know about the presence of protanomaly until he comes for an examination.
The disease develops due to a gene mutation. A photopigment that absorbs green color is inserted into L-opsin (absorbs red color). Therefore, the properties of the latter are violated, the colors are mixed, and a person does not perceive red shades.
Deuteranomaly
This is a form of color vision disorder that is characterized by weakness in the perception of the color green. Deuteranomaly occurs in 1% of the population, in most cases it is found in men.
Scientists have found that the disease is transmitted through the maternal line. Women are carriers of the defective gene, but the disease themselves does not manifest itself. There is a malfunction in the gene code. The disease is associated with a recessive X chromosome.
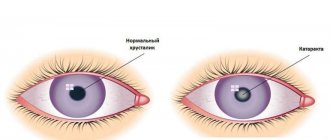
Deuteranomaly can develop as a result of serious trauma with damage to the lens, diabetes, glaucoma and cataracts. Color perception is also affected by taking certain medications.
Green color is produced by M-cones located in the retina of the eye. The light wavelength is average. With deuteranomaly, they lack pigment, which allows them to highlight the colors of the middle part of the spectrum.
With this color vision disorder, swamp-yellow shades predominate. Red color is replaced by blue and brown.
Tritanomaly
This type of abnormal trichromasia is less common. Tritanomaly is characterized by a decreased ability to perceive blue light. Patients with this disease are called tritanopes.
Blue cones have the greatest sensitivity to short-wave radiation. The disease develops due to the lack of photoreceptors, which are responsible for the perception of blue color.
Instead of purple and blue, a person sees gray. There are no other signs. Visual acuity is normal unless there are concomitant diseases that worsen it.
Why are not all colors visible to the eye?
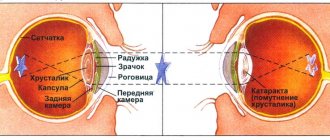
In the central part of the human retina there are color-sensitive receptors - cones (nerve endings). Each three types of cones have their own color-sensitive pigment of protein origin.
One pigment color reacts to red, another to green, and a third to blue.
In a person with normal vision, all 3 pigments are present in the cone. Color blindness is usually passed on from mother to son. 8% of men and 0.4% suffer from it to one degree or another . The acquired form develops due to injuries to the retina and clouding of the lens.
Diagnostics
Anomalous trichromasia is most often a congenital disease, so many people do not even suspect that they have it because they initially see the wrong colors. The pathology is discovered at the next preventive examination, by chance.
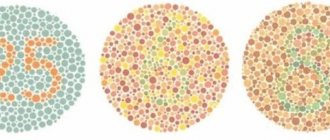
Rabkin tables are used to test color perception. They depict numbers consisting of circles of a certain color, and the background is a different one. The person must say what numbers or figures are drawn.
With normal color vision, a person will quickly name the numbers depicted. Patients with anomalous trichromasia find it difficult to determine which symbol is indicated; they focus their eyes for a long time and peer into the picture.
The second diagnostic method is the Ishihara test. It was developed by a Japanese ophthalmologist. The Ishihara test is similar to the Rabkin table, only the pictures show only numbers. There are pictures that don't have numbers on them. People with abnormal trichromasia may see them.
The last diagnostic method is the Farnsworth shade test. It contains 4 stands with different shades. A total of 85 removable chips. The task of the person undergoing diagnostics is to arrange the color chips in accordance with the spectral progression. The color should change smoothly.
Farnsworth-Munsell FM100 Hue is solved in 4 steps. Persons with normal color vision will solve the test, while those with abnormal trichromasia will get confused in the shades.
There are 2 more ways of diagnosing. The polychromatic tables of Schaaf and Stilling are used.
Requirements for different categories
Regardless of the categories, driving a car with a color vision disorder is prohibited.
It is not allowed to drive a car if the citizen being examined suffers from glaucoma, retinal detachment, severe cataracts, or optic nerve atrophy. It is impossible to drive a car if less than 3 months have passed since vision correction surgery.
The ban applies if there is a significant decrease in visual acuity. To obtain a category “A”-BE license, you can obtain a license if your visual acuity is at least 0.6 and 0.2 for different eyes.
You can drive a car if you have one eye, but if the visual acuity of the second is no less 0.8%.
A complete ban on driving a car applies when the angle of view (world) is narrowed by more than 20% . You cannot drive if the diopter of glasses or lenses is less than 8 units .
Treatment
Anomalous trichromasia is a genetic disorder. Therefore, there are practically no treatment options. The pathology has not been treated recently.
Now scientists have developed an innovative method of therapy that involves identifying the missing element of the retina and then introducing it into the retina. The treatment is still being tested and is under development.
Not every ophthalmology clinic provides such treatment. It's hard to find which doctors are willing to take risks. In most cases, treatment is carried out as a study. Patients are carefully examined and monitored after insertion of the missing retinal photoreceptor.
Do colorblind people get driver's licenses?
Colorblind people are not issued a driver's license, but only if doctors were able to accurately diagnose this pathology and write about it in the appropriate medical report.
Color blindness test
For verification, special polychromatic tables are used. Accurate results can be obtained using high-quality equipment.
If the disease is diagnosed at an early stage, obtaining a medical certificate for driving is possible.
This is possible when replacing a driver's license. Other certificates that indicate the neglect and progression of the disease will not be accepted.
For verification, the tabular forms of Rabkin and Ishihara are used.
They are numbers, figures and circles that are arranged in the form of a chain. All circles are presented with almost the same brightness. The set consists of 27 tables. If a person cannot determine the color of a picture, it appears uniform to him.
People who are not colorblind can easily determine the number, color of the figures and circles, as well as the numbers represented.
Incorrect answers do not mean that the person is sick. Insufficiently good lighting may affect the health of the person being examined.
To obtain accurate results, the patient is seated in a room with natural light. A man sits with his back to the window. The patient should calm down and relax. Then the ophthalmologist shows the subject a picture at a distance of 1 m for about 15 seconds .
This method allows you to determine color blindness with minimal error.
Experts do not recommend going to see a doctor if you have a fever or headaches.
You cannot be checked by an ophthalmologist if a person has obvious mental disorders and other diseases that prevent him from adequately assessing the situation.
The liability for driving with an expired license is described in the article: fine for an expired driver's license. Not sure if a driver's license is a form of identification? Read about it here.
Where and how to go
You can take the test at the district (municipal) clinic. To do this, you can contact your doctor directly or see a specialist by appointment. There are no specific requirements for the patient. It is enough to appear on time for an appointment with a specialist and undergo the appropriate medical procedure.
It is possible to take the test online.
To do this, you need to go to the profile sites and take the test. However, such procedures are not of an official nature, but are rather aimed at colorblind people independently identifying their pathology before applying for a medical certificate.
Price
If the test is carried out in a municipal clinic, as part of a routine medical examination, then you can take it under the compulsory medical insurance policy. The average cost of taking the test in private medical institutions is 800-2 thousand rubles.
Anomalous trichromasia – what is it, causes, diagnosis, treatment – About the eyes
Vision is considered one of the most important and necessary functions of the human body. And those who have it are truly happy.
But due to the deterioration of the environment in recent years, various disorders of the visual apparatus are occurring more and more often. This article will discuss a disease such as anomalous trichromasia.
You will learn what it is, what are the symptoms of the disease, causes, treatment and diagnostic methods.
What is color blindness?
Since this disease belongs to one of the types of color blindness, it is worth initially understanding what kind of disease it is. Colorblind people are people who do not perceive color balance correctly. In such patients, color vision is impaired.
What is color vision?
Color vision or color vision function is the ability of the retina to perceive and distinguish primary colors, the wavelength of which is 400-700 nm.
The eye perceives colors through three types of cones, each of which has one or another characteristic. These three cones differentiate the brightness, saturation and hue of the supplied light stream. All this depends on the length of the light flux, its richness and radiation intensity.
Colorblind people are people who do not perceive color balance correctly.
Types of color blindness
Many people believe that color blindness is a disease that is inherited and can manifest itself completely differently in each family member. But scientists have proven that various forms of this disease can also be acquired. There are 4 types of color blindness, namely:
- abnormal trichromasia;
- dichromasia;
- monochromasia;
- achromasia;
Each type has its own specifics, symptoms and methods of improving vision for this disease. And if, with monochromasia and achromasia, people practically or completely do not distinguish colors, then in the first 2 cases everything is not so advanced.
With dichromasia, patients cannot see the difference between colors such as green, yellow, orange and red. But with trichromasia, a person is able to distinguish primary colors, but in certain cases this perception may be impaired.
Types of trichromasia
Trichromasia itself is not a disease; on the contrary, normal trichromasia is considered an ideal option for the perception of color balance. That is, normal trichromatic vision is when the 3 cones of the eye function correctly and the 3 primary colors are perceived normally. An anomalous trichromat is considered a deviation.
Normal trichromatic vision differs from abnormal vision in that in normal vision the 3 cones of the eye function correctly and the 3 primary colors are perceived normally.
What is anomalous trichromasia and its symptoms
Anomalous trichromasia is the partial perception of three primary colors. In this case, as a rule, the work of one cone is disrupted or is absent altogether. In turn, this disease is also divided into subtypes, namely:
- Protanopia (in this case, a person partially does not perceive the color red).
- Deuteranopia (this subtype involves incomplete perception of the color green).
- Tritanopia (when the blue color is partially lost from perception).
It is worth saying that it is anomalous trichromasia that is considered a hereditary disorder and cannot be acquired.
Also, this disease is classified not only by type, but also by degree, in case a person exhibits protanopia or deuteranopia. There are three degrees of the disease:
- Grade A (considered the most severe, as it is close to a disease such as dichromasia (when a person distinguishes 2 colors)).
- Grade B (moderate degree of impairment).
- Grade C (the smallest manifestation of pathology, considered almost normal perception of all three primary colors).
Diagnosis of abnormal trichromasia
This disease, like other vision anomalies, is diagnosed using banal checks using tables. Color discrimination disorders can be studied using multicolor tests and pigment tables created on the principle of polychromaticity.
People with anomalous trichromasia are not considered disabled or retarded.
These include polychromatic tables
- Stilling;
- Ishihira;
- Shaafa;
- Fletcher-Gamblin;
- Rabkina;
The essence of these tables is that they have printed figures, numbers, letters, signs in the form of circles, which have the same color, but different shades (brightness, saturation), while the background has a completely opposite color. People who have a deviation from the norm find it very difficult or not at all to see the applied drawing.
An important condition for diagnostics is good daylight, and the patient must be at least 1 meter away from the table.
There are also other methods for diagnosing this anomaly. For example, operating rooms. One of them is examination with an anomaloscope. The device calculates color discrimination thresholds in conventional units, and the doctor compares them with the norm. This diagnostic method can detect disturbances in the perception of red and green colors.
Treatment of abnormal trichromasia
If we talk about methods of treating this disease, it is worth noting that it is genetic. Therefore, there are very few methods of therapy. And not all clinics are able to provide this treatment.
As a rule, the solution is to study the missing elements in the retina and their subsequent introduction there. But this method is still at the development stage, so it is not considered effective.
But there is no point in despair, because people with anomalous trichromasia are not considered disabled or inferior. They also have the right to education, work, and rest.
There are only a small number of exceptions for such patients. They cannot work in a certain number of industries where perfect vision is important, serve in the army and be a driver.
But the important thing is that such restrictions are only necessary for categories A and B in a given disease.
The main thing is to always remember that all anomalies and deviations in the body do not make you disabled or somehow “different”. You are the same person as everyone else - alive and happy.
Jul 9, 2017Anastasia Tabalina
Source:
Trichromasia - causes, varieties and symptoms
› Features of vision
Trichromasia is normal human vision in which the organ of vision recognizes shades of all three primary colors. Such people are called trichromats.
Kinds
We can highlight:
- normal;
- abnormal trichromasia.
Dichromasia and driver's license
Despite these significant differences in incidence, women are asymptomatic carriers of the mutant gene and can pass it on to their children.
With normal color vision, a person is able to distinguish all primary colors. This is called normal trichomasia. That is, people who do not suffer from color vision disorders are normal trichomates.
With congenital anomalies of color perception, problems arise with distinguishing color radiation.
Moreover, all congenital pathologies of this type can be divided into three groups: anomaly in the perception of red color (protan defect), blue color (tritan defect), green color (deuter defect).
If color perception of only one of the primary colors is impaired (usually the green, less often the red range), then abnormal color perception as a whole occurs. This is due to abnormal color mixing. Depending on the degree of disturbance in color perception, they are distinguished: anomalous trichromasia, monochromasia, dichromasia.
If a person is able to distinguish only two primary colors, then this condition is called dichromasia; with complete color blindness, when the patient perceives the world in black and white shades, the pathology is called monochromasia.
Disruption of all pigment layers is quite rare. Much more often, anomalies occur in the functioning of one of the three layers of pigment cells, that is, dichromasia develops.
Such patients (dichromats) have a peculiar color perception, but they can only find out about this with a special test.
Dichromasia was first described by a physician and scientist named Dalton, and the most common color vision disorder (color blindness) was named after him.
If color perception of only one of the primary colors is impaired (usually the green, less often the red range), then abnormal color perception as a whole occurs.
Diagnosis of dichromasia
To study the patient’s complex color perception, the doctor resorts to special multicolor (polychromatic) tables. Much less often, diagnostics are carried out using spectral anomaloscopes. The number of tests that have been created to identify abnormal color vision reaches several dozen.
During the experiment, tables are shown to the potential patient. The doctor notes the number of correct answers, noting the color zone. As a result of the examination, it is possible to determine the degree of anomaly and the severity of the color vision deficiency.
Source: https://4hospital.ru/veki/anomalnaya-trihromaziya-chto-eto-prichiny-diagnostika-lechenie.html