Yellow spots on the white membrane of the eyeball indicate pathological conditions or disturbances in the functioning of internal organs.
Atypical manifestations worry a person.
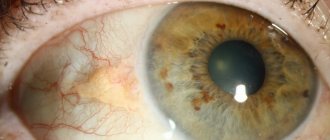
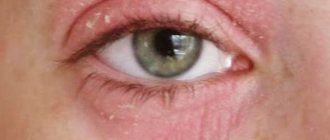
Orange spots at a young age are unlikely to pose a threat to health and visual perception, but it may be a symptom of a disease that leads to complete blindness. Therefore, it is important to know why it appears and how it is treated.
We recommend reading: Red spot on the white of the eyes
Causes
Yellow spots on the tunica albuginea are a manifestation of Gospel disease. This pathology develops due to a violation of bilirubin metabolism in the body.
Common reasons:
- malignant tumors in the liver;
- obesity;
- cirrhosis;
- anemia;
- cholelithiasis;
- inflammatory pathologies of the liver.
If the yellowish spot is a general cause, you need to contact a specialized specialist. This sign indicates serious disorders in the body that require immediate treatment.
The second group of reasons are specific pathological conditions that lead to the formation of orange spots on the tunica albuginea. The following pathologies cause this symptom:
- A pinguecula is a yellow formation that is often found on the conjunctiva in elderly patients. Appears on both sides of the cornea. This is a sign of aging of the conjunctiva. Manifested by irritation, dry eye syndrome, redness.
- Pterygium or pterygoid hymen is a dystrophic pathology characterized by the formation of a fold of the connective membrane. The hymen grows in the inner corner and looks like a yellow triangular spot. Pterygium is manifested by redness, itching, swelling, and a feeling of a foreign body.
- A connective membrane cyst is a formation that has formed in the area of the outer membrane. This is a thin-walled seal with exudate. It may be yellowish in color and appear as a raised spot.
- A nevus is a benign formation consisting of an accumulation of melanocytes. These are moles or birthmarks that are yellow or brown in color.
- Horner-Trantas spots appear due to allergic reactions. These are small grains formed on the albumen. The cause is conjunctivitis and allergic keratitis.
- Leukoma is a disease that appears as a white spot on the cornea, sometimes manifesting as a yellow formation. Formed due to cicatricial changes after inflammation or ulceration.
Lutein and zeaxanthin
The macula is yellow because it contains two types of pigments (zeaxanthin and lutein). They are also present in large quantities in yellow, orange, and green vegetables (corn, cauliflower, spinach). These pigments perform a protective function and help prevent aggressive effects on the photoreceptors of the retina. Since these substances are natural antioxidants and absorb harmful rays in the blue spectrum, ultraviolet damage to the surface of photoreceptors is reduced.
With age, the amount of pigment substances in the macula decreases, which may be one of the causes of retinal damage and the development of serious ophthalmological diseases, in particular age-related macular degeneration.
Symptoms
A yellow formation near the pupil is almost never associated with pathologies of the optical system. But it is a sign of a progressive disease. Accordingly, the symptoms will be different, depending on the cause of its appearance.
Progressive eye pathologies cause:
- doubling of objects;
- pain syndrome;
- unbearable itching;
- mucous and purulent discharge;
- sensitivity to bright light.
In the case where the orange spot is a sign of problems with internal organs, the clinical picture of the disease is supplemented by an increase in body temperature, poor appetite, asthenopia, trembling and the occurrence of a gag reflex.
Table. Signs depending on the cause
| Name of pathology | Clinical picture |
| Cirrhosis | icteric discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes; skin and eye itching; abdominal pain on the right; weakness; swelling of the legs, arms and face (especially the eyes). |
| Anemia | pallor; sticking on the lips; asthenia; dry mucous membranes; taste disturbance. |
| Hepatitis | increased body temperature; yellowness with a greenish tint to the skin and tunica albuginea; dry conjunctiva; itching; lethargy; insomnia; sweetish odor from the mouth. |
| Gallstones | feeling of heaviness; nausea; sharp pain; light stool; change in color of the skin and sclera. |
| Leukoma | corneal clouding; deterioration in the quality of vision; complete blindness or partial loss of visual perception; increased intraocular pressure; disruption of fluid outflow. |
Photo
Symptoms of diseases of the macula
When the macula area is damaged, central vision is primarily impaired. Typically, patients complain of a spot that covers the central area of the visual field. Patients may experience:
- A disorder of central vision, in which image contrast, brightness, and color saturation decrease.
- Metamorphopsia, that is, the curvature of lines in objects.
- Changing the size of objects, in which they can either decrease or increase. This sign is associated with changes in the density of cone photoreceptors.
Diagnostics
It is impossible to make a diagnosis after a visual examination; even an experienced ophthalmologist will not be able to immediately determine the cause of the macular spot. The patient will need to undergo a series of tests:
- First, the ophthalmologist collects the patient's medical history. Finds out what symptoms are bothering you, except for the detected yellow spot near the pupil.
- Performs palpation if there is a history of liver disease.
- Biomicroscopy makes it possible to study the structure of the eye, detect damage to the cornea, cataracts, inflammatory disease or degenerative changes in the optic nerve.
- Ultrasound and computed tomography allow you to examine the internal organs located in the abdominal cavity. Performed if hepatitis, cirrhosis, or stones in the gallbladder are suspected.
Laboratory tests are performed to confirm jaundice and anemia. The patient is given a referral to donate blood, urine and feces. With their help, the level of hemoglobin and bile pigment is determined.
Rods and cones
The foveal zone is the most sensitive area of the retina of the eyeball, which provides the ability to distinguish fine details as well as colors. In other words, the formation of central vision occurs due to the fovea. This function is performed by special photoreceptors called cones. It is in the foveal zone that the greatest concentration of these photoreceptors is observed. Another type of receptors are rods, which are located mainly in the peripheral zone of the retina. They provide peripheral vision, which includes twilight vision, visual field, and light perception. The anatomical features of the structure of the macula lead to the fact that it provides vision with high resolution:
- There are no vessels in this zone that could prevent light photons from reaching the surface of the photoreceptors. This in some cases worsens perception.
- Secondly, in the area of the macula there is a high concentration of cones, which push aside the other layers of the retina. As a result, almost all light rays that enter the eye through the pupillary opening are focused on the surface of the photoreceptors.
- In addition, the cone cells themselves have direct contact with other cellular elements. Each cone has one ganglion cell and one bipolar cell. Due to this, there is a clear transmission of the formed image to the higher located central structures along the fibers of the optic nerve.
In the peripheral zone of the retina there is no such clear transmission, since there is only one bipolar cell for several rod photoreceptors. For several bipolar neurons there is one ganglion cell. As a result, the peripheral region of the retina cannot form a clear image, but is able to distinguish even minor light rays, since the summation of irritations occurs. This quality is especially well developed in animals.
Treatment
After determining the cause that caused the formation of a yellow spot on the tunica albuginea, treatment is prescribed. You can remove the yellowish halo after getting rid of the cause.
Methods of therapy:
- For jaundice, phototherapy is prescribed until bilirubin is completely destroyed. They take Karsil and Hofitol. In severe cases of the disease, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed. Treatment takes place in a hospital setting.
- In case of cirrhosis, it is important to follow a diet and take diuretics. Glucocorticoid hormones and antiviral treatment will help slow the course of the disease. Additionally, medications are prescribed that reduce pressure in the collar area and plasmapheresis (the procedure allows you to purify the blood and reduce jaundice).
- If the cause of the macula is anemia, therapy will be based on taking medications containing iron, folic acid and vitamin B12. A blood transfusion is prescribed.
- If there are stones in the gall bladder, they are dissolved with special preparations. Diuretics are prescribed to help small stones pass out quickly in the urine. In this case, extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy is performed. If the stones are large, surgery is performed, then medications are prescribed for rapid recovery.
- Leukoma is treated with surgery. Keratoplasty and keratoprosthesis are mainly performed.
- Pinguecula is treated with medications that relieve discomfort. These are moisturizing drops. If you have pinguecula, it is not advisable to wear contact lenses until it is completely cured. Anti-inflammatory and antibacterial medications are prescribed. If the patient is concerned about aesthetic discomfort, surgery is performed to remove the stain.
- Pterygium is treated surgically. It is advisable to carry out the operation in the early stages of development. Treatment with traditional methods is ineffective and can aggravate the course of the pathology.
- The nevus is removed using surgical removal or a laser beam. The latter method is used more often because it is painless and the rehabilitation period is reduced.
- Conjunctival cysts are treated with conservative and surgical methods. Glucocorticosteroids are prescribed, then trichloroacetic acid is injected into the cavity, which has a sclerosing effect.
The structure of the eye and the blind spot
I was going to show you interesting pictures from a foreign site: how people with eye diseases (glaucoma, cataracts, etc.) see. But first we need to talk about the structure of the eye
, otherwise it will be completely unclear. However, all this is taught at school.
Briefly, the structure and operation of the eye can be described as follows: a stream of light containing information about an object hits the cornea
, then
passes
the anterior chamber the pupil
, then through
the lens
and
vitreous body
, and is projected onto
the retina
, the light-sensitive nerve cells of which convert optical information into electrical impulses and send them along the optic nerve to the brain. Having received this encoded signal, the brain processes it and turns it into perception. As a result, a person sees objects as they are.
Next, you will be convinced that a person sees not with his eyes, but with his brain using his eyes
.
Cornea
The cornea is the transparent membrane that covers the front of the eye. It has a spherical shape and is completely transparent. Rays of light falling on the eye first pass through the cornea, which strongly refracts them. The cornea borders the opaque outer layer of the eye - the sclera.
(tunica albuginea).
Anterior chamber of the eye and iris
After the cornea, the light beam passes through the anterior chamber of the eye
- the space between the cornea and the iris, filled with a colorless transparent liquid.
Its depth is on average 3 millimeters. The back wall of the anterior chamber is the iris
(iris), which is responsible for the color of the eyes (if the color is blue, it means there are few pigment cells in it, if it is brown, it means a lot).
In the center of the iris there is a round hole - the pupil
.
[Increased intraocular pressure leads to glaucoma]
Pupil
When examining the eye, the pupil appears black to us. Thanks to the muscles in the iris, the pupil can change its width: narrow in the light and widen in the dark. It's like a camera aperture
, which automatically narrows and protects the eye from entering a large amount of light in bright light and expands in low light, helping the eye to catch even weak light rays.
Lens
After passing through the pupil, the light beam hits the lens. It is easy to imagine - it is a lenticular body, reminiscent of an ordinary magnifying glass
.
Light can pass freely through the lens, but at the same time it is refracted in the same way as, according to the laws of physics, a light ray passing through a prism is refracted, i.e. it is deflected towards the base. The lens has an extremely interesting feature: with the help of ligaments and muscles around it, it can change its curvature
, which in turn changes the degree of refraction. This property of the lens to change its curvature is very important for the visual act.
Lentils
. The lens has approximately the same shape.
[Cloudiness of the lens is called a cataract]
Vitreous body
After the lens, light passes through the vitreous body
, filling the entire cavity of the eyeball. The vitreous body consists of thin fibers, between which there is a colorless transparent liquid with high viscosity; this liquid resembles molten glass. This is where its name comes from - the vitreous body. Participates in intraocular metabolism.
Retina
The retina consists of 10 layers, where there are photoreceptor cells
(they are sensitive to light) and
nerve cells
.
Photoreceptors in the retina are divided into two types: cones
and
rods
. In these cells, the energy of light (photons) is converted into electrical energy of the nervous tissue, i.e. photochemical reaction.
Sticks
They have high photosensitivity and allow you to see in poor lighting (
twilight
and
black-and-white
vision), they are also responsible for
peripheral vision
.
Cones, on the contrary, require more light for their work, but they are the ones that allow you to see small details (responsible for central and color vision
).
The largest concentration of cones is located in the macula
(more about it below), which is responsible for the highest visual acuity.
To remember faster:
- AT NIGHT it is more convenient to walk with a STICK.
- DURING THE DAY, laboratory assistants work with CONES.
The retina is adjacent to the choroid, but in many areas it is loose. This is where it tends to flake off.
for various retinal diseases.
[The retina is damaged by diabetes, hypertension and other diseases]
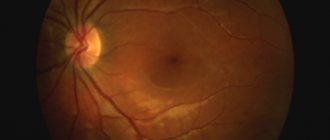
Yellow spot
Yellow spot
is a tiny, yellowish area
near the fovea
(center of the retina) and is located near the optical axis of the eye. This is the area of greatest visual acuity, the same “center of vision” that we usually point at an object.
Notice the yellow
and
blind spot
.
Optic nerve and brain
Optic nerve
passes from each eye into the cranial cavity.
Here the optic fibers travel a long and complex path (with decussations
) and ultimately end in the occipital cortex.
This area is the highest visual center
, in which a visual image is recreated that exactly corresponds to the object in question.
Blind spot
The place where the optic nerve exits the eye is called the blind spot
. There are no rods or cones here, so a person cannot see with this place. Why don't we notice the missing piece of the picture? The answer is simple. We look with both eyes, so the brain receives information for the blind spot area from the second eye. In any case, the brain “completes” the picture so that we do not see defects.
The blind spot of the eye was discovered by the French physicist Edme Mariotte
in 1668 (remember the school Boyle-Mariotte law for an ideal gas?) He used his discovery for the original entertainment of the courtiers of King
Louis XIV
. Marriott placed two spectators opposite each other and asked them to look with one eye at a certain point on the side, then it seemed to each that his counterpart had no head. The head fell into the sector of the blind spot of the looking eye.
Try to find it yourself
"blind spot" and you.
- Close your left eye and look at the letter “O” at a distance of 30-50 cm
. The letter "X" will disappear. - Close your right eye and look at the "X". The letter "O" will disappear.
- By bringing your eyes closer to the monitor and moving it away, you will be able to observe the disappearance and appearance of the corresponding letter, the projection of which will fall on the area of the blind spot.
Other optical illusions can be seen here and here.
Prevention
To prevent yellow spots from appearing on the sclera, you must initially protect your eyes. Preventive measures are as follows:
- an active lifestyle and proper nutrition (especially for patients suffering from liver diseases);
- combining long work with a little rest for the eyes;
- correct use of contact vision correction products (regular cleaning and changing of lenses in accordance with the wearing period);
- moisturizing mucous membranes when working in the sun, in a dusty room or in an air-conditioned room.
It is important to protect the visual organs from direct ultraviolet radiation, dust and wind using protective glasses. Taking vitamin complexes and healthy sleep for 8 hours will reduce the likelihood of certain diseases that lead to the formation of a yellow spot on the white of the eye.
What is it, causes
A pinguecula is a yellow spot of any shape, most often it is localized next to the pupil on the side of the bridge of the nose. An ophthalmological examination does not show any abnormalities, therefore in medical practice this phenomenon is usually associated with the aging process of the conjunctiva. Macula can also develop in young children, and this can happen for a variety of reasons.
Diagnostic measures
A specialist may suspect the occurrence of degeneration when examining an elderly patient complaining of decreased vision. Special drops are used to dilate the pupils. Thanks to this manipulation, the back of the eye becomes accessible for inspection. The Amsler test is also used in the diagnostic process - a sheet with a grid and a black dot in the middle. If, when examining the central mark, the cell lines appear curved (distorted), this may indicate pathology.
Types of degeneration
Aging leads to such changes in this part of the organ.
This pathology occurs in the human retina more often during aging and is associated with a violation of the condition of rods and cones, as well as a decrease in their number. In this case, the patient’s central vision is impaired, but peripheral vision remains the same. This disease rarely occurs in young people and its development is caused by a lack of vitamins and minerals. Nutrients essential to the eye include antioxidants, vitamins A, E and C, and zinc.
What is important is the reduction in the macula zone of zeaxanthin and lutein, protective substances from exposure to ultraviolet rays of the sun. Exposure to certain viruses, such as cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr, can cause macular degeneration. When pathology appears, a person complains of blurred vision, the appearance of distortions when looking at straight lines, and the inability to see details. There may be a dark dot in the field of view.
Return to contents
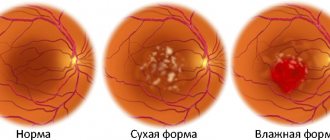
Wet macular degeneration
It is neovascular macular degeneration, which is caused by the proliferation of blood vessels in the thickness of the central fossa. This helps to reduce the number of rods and cones with their replacement by arterial plexuses, which are not able to capture and distinguish light rays. This type of disease is quite rare, but is extremely malignant and often leads to complete loss of central vision. Mostly young people suffer. Ophthalmoscopically, foci of hemorrhage and areas with scars on the surface are observed in the area of the optic fovea.
Return to contents
Dry dystrophy
Atrophic changes in this area of the organ contribute to a decrease in visual acuity.
It consists of macular atrophy and the gradual death of rods and cones, which leads to slow regression of vision and the inability of patients to see objects in the center of the visual field. Light-sensitive cells die due to insufficient supply of vitamins or microelements, as well as due to age-related involution. This process is quite slow and rarely leads to complete loss of vision, but only worsens it. As a result of atrophic processes in dry macular degeneration, drusen or areas where rods and cones are absent appear.
Return to contents
Hidden variety
It develops in the process of neovascularization and increased growth of blood vessels in the area of the macula. But with this type, minimal visual impairment is observed. Central vision is completely preserved and the patient does not experience discomfort when reading. Ophthalmoscopic examination reveals minor foci of hemorrhage and abnormal choroid plexuses without scarring of the retinal tissue.
Return to contents
Homeopathic treatment
To eliminate unpleasant symptoms and moisturize the conjunctiva , the following drugs are used:
- Fagopyrum (Fagopyrum) drug reduces itching in the eyes , eliminates inflammation, swelling and redness.
- Heracleum sphondylium improves the condition of mucous membranes and skin, relieves inflammation.
- Senega is effective for swelling, neoplasms in the eye , clouding of the cornea, photophobia.
- Euphrasia relieves unpleasant symptoms in the eye area, eliminates the feeling of dust and sand under the eyelid .
- Causticum prevents the formation of nodules, compactions, and eliminates dry mucous membranes . This drug cannot be combined with the homeopathic remedy Phosphorus .
- Silica acts on foci of chronic inflammation, on connective tissue, mucous membranes, reduces pain and itching in the acute period of the disease , reduces swelling, congestion, and improves the condition of patients with photophobia.
- To prevent dryness , fatigue and inflammation of the eyes, a complex homeopathic preparation has been developed - Similasan drops containing harmless mineral and herbal components.
- Conium has an antitumor effect, promotes the resorption of inflammation, and is indicated in the presence of compactions , including painful ones.
Important! Conium should be taken with caution in patients with hypotension.
Despite the availability of homeopathic remedies, treatment must be prescribed by a specialist , based on the patient’s lifestyle, temperament, and stage of the disease.
How are they treated?
Therapy for macular dystrophy, which is associated with age, is effective, since the disease is incurable. A positive effect is achieved by using photodynamic therapy, which helps slow down the atrophic processes of photosensitive cells. It is important to change your lifestyle, get rid of bad habits and normalize your diet so that it contains healthy vegetables and fruits that contain vitamins.
Medications that help improve the patient’s condition are vitamin-mineral complexes rich in carotenes and zinc.
Return to contents
Macular degeneration: treatment
As practice shows, in most cases no therapeutic measures are carried out. Some patients, however, with a dry form of the pathology are prescribed low-intensity, or threshold, laser exposure. Its essence is to remove drusen (specific yellowish deposits) using moderate doses of radiation. Until recently, for the wet form of pathology, the method of photodynamic therapy using the Visudin agent was used. The drug is administered to the patient intravenously. From the systemic bloodstream, the drug is selectively absorbed exclusively by newly formed regional vessels. Thus, Visudin has virtually no effect on the pigment epithelium in the retina. Along with the use of the drug, a laser therapy session is performed. The procedure is carried out under computer control. Low-intensity radiation is directed to the area of the neovascular membrane (a fiber optic device is used for this). Pathologically dangerous vessels become empty and begin to stick together. As a result, hemorrhages stop. As practice shows, the therapeutic effect lasts for 1-1.5 years.