Causes
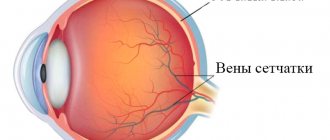
The retina consists of 10 layers, thanks to which the visual image is formed. Retinoschisis is a pathology in which retinal separation occurs. As the disorder develops, fluid begins to accumulate between the layers of the retina, which separates the retina, causing vision problems. The development of the problem occurs due to circulatory disorders, which is provoked by:
- the presence of hereditary and congenital diseases;
- degenerative pathologies of the retina;
- problems with the vascular system;
- the presence of eye injuries;
- other eye diseases;
- the presence of farsightedness or myopia;
- development of malignant tumors.
What is herpes on the eye
Ophthalmoherpes is an infectious disease provoked by increased activity of the herpes virus, where eye tissues and mucous membranes are involved in the pathological process. The disease is congenital or acquired, but in any case, in the presence of a primary infection, urgent treatment with conservative methods is required. Herpes under the eye itself is not dangerous; the real threat to health is dangerous complications such as keratitis with subsequent loss of visual acuity and potential blindness.
Classification
Retinoschisis in medicine is usually divided into the following stages:
- The first stage - limited detachment of several layers of the retina occurs. The resulting fluid accumulates around the altered vessels.
- The second stage is the gradual development of delamination. However, there is no particular difference between the affected and healthy retina. Small cystic degenerations appear;
- The third stage - large cystic formations begin to appear between the layers of the retina. Stripes also form, which subsequently provoke retinal ruptures and contribute to complete retinal detachment. In this case, such a lesion is formed over a fairly large area.
Symptoms
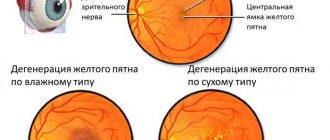
Degenerative retinoschisis is characterized by an asymptomatic course. The disorder is most often diagnosed accidentally during the next visit to a specialist, since damage to the outer plexiform layer occurs. Also, most of the area is covered with small cystic changes in the layers.
In the hereditary form of retinoschisis, the first diagnosis occurs between the ages of 7 and 9 years. The pathology primarily affects the macular area, causing visual acuity to decrease. Large oval cystic formations begin to form, causing detachment. Secondary retinoschisis manifests itself as a complication of various eye problems.
The symptoms of retinossis completely depend on the type of underlying disease.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic methods for retinoschisis are determined by a specialist. First of all, a test is performed to determine visual acuity, after which the border of peripheral vision is diagnosed and ophthalmoscopy is performed. Additionally, there may be a need for an electrophysiological study, which will determine how well the retina is performing its functions. Optical coherence tomography helps determine how badly the retinal structure is damaged.
In cases of genetic origin of pathology, it may be necessary to study heredity. To do this, molecular genetic tests can be performed to identify predisposition to the disease. All this contributes to the differential diagnosis of the existing disorder.
Treatment
Retinoschisis can be treated with medications and surgery. With conservative treatment, as a rule, drugs are prescribed that accelerate blood flow and metabolic processes, preventing the retina from delaminating. For this we use:
- B vitamins – Milgamma, Riboflavin, Thiamine chloride;
- vitamin E – Aevit, Alpha-Tocopherol acetate;
- drugs with antiplatelet action - Pentoxifylline, Trental;
- angioprotectors – Nicergoline, Thiotriazoline.
Laser correction can be used to stop existing retinal dissection. Using laser coagulation, adhesions are made between the layers of the retina. A laser beam is used to solder the healthy part of the retina to the damaged areas around the circumference.
In the final stages of pathology, when there are ruptures and detachments, surgery is used. This treatment includes 2 types of operations:
- removal of the vitreous;
- scleral filling.
In some cases, after surgery, there may be a need for additional laser correction to enhance the result obtained.
Therapeutic measures
It is impossible to completely eliminate eye pathology with subsequent restoration of vision. However, with the help of medications, physiotherapy and surgical methods, it is possible to stop destructive changes and slow down their development.
Medicines
Medicinal influence involves the use of a complex of drugs from various directions. Most often it consists of the following groups:
- Drugs that prevent the formation of blood clots. Among them are Aspirin, Ticlopidine, Clopidogrel.
- Means for strengthening the walls of blood vessels and capillaries, toning them up and maintaining elasticity: Ascorutin, vitamin and mineral supplements. They are also necessary to nourish tissues and prevent further destruction.
- Biological regulators. The most commonly used drug is Retinolamine. It is necessary to restore vascular permeability and regulate the functioning of photoreceptors.
- Angioprotectors and antispasmodics: Drotaverine, Actovegin. Drugs are necessary to protect blood vessels and capillaries from extensive damage and further development of the disease.
Additionally, injections can be used against edema, as well as against hematomas during hemorrhages. To reduce symptoms, it is also necessary to prescribe eye drops that improve metabolic processes.
Physiotherapy and surgery
In difficult cases, laser coagulation is used to treat peripheral retinal dystrophy, as well as reduce its consequences and manifestations. Using a laser, the doctor makes so-called adhesions, which prevent further development of destructive changes and destruction of the inner membrane. The mechanism of action of the intervention is based on a local increase in temperature, which results in blood and soft tissue coagulation. The procedure is practically painless, but requires a recovery phase, during which it is necessary to systematically take preventive medications. Avoidance of physical activity and proper rest are also recommended. With the correct operation and recovery period, it is possible to completely stop the disease and stop its further progression.
Complications
In the absence of timely treatment, the disease develops into severe forms that lead to complete blindness. It is difficult to choose the right therapy for the congenital form of the disease, since it provokes hemorrhages in the retina. When the disease provokes retinal dissection, not only violations of its integrity arise, but also problems with the normal performance of its functions.
With severe damage to the retina, signs of complications such as loss of orientation in space with insufficiently strong lighting may occur. The quality of vision is significantly reduced, as a result of which a person can become completely blind. Retinoschisis can also provoke complications, such as:
- retinal tears;
- retinal detachment;
- development of hemorrhage in the eyeball.
Congenital retinoschisis (x-linked pathology)
Congenital retinoschisis is an inherited genetic mutation linked to the X chromosome. Since boys lack a section of the chromosome that duplicates the female X chromosome, this disease, like color blindness, occurs only in them. Girls are often carriers of this gene and can pass it on to inheritance. Congenital retinoschisis is quite rare (approximately one boy in fifteen thousand newborns).
Most often, this pathology manifests itself by the age of ten, but there are examples of diagnosis in early infancy.
Typically, congenital retinoschisis affects both eyes, which have a symmetrical pattern. Without medical intervention, there is a progressive decrease in vision, which, as a rule, ends in complete blindness.
Forecast
Depending on the different forms of retinoschisis, the prognosis for the development of the disease may differ:
- with a hereditary form - a high risk of vision loss;
- in the degenerative form there is a low risk of cure;
- in the secondary form, the result directly depends on the course of the underlying disease - the root cause.
In order not to cause the risk of complications after surgery for retinoschisis, you should limit sports and other strength activities, and lifting heavy objects is prohibited. The specialist prepares a dietary plan that should be followed.
For a positive prognosis, it is necessary to follow all the specialist’s recommendations during the rehabilitation period and continue treatment until visual functions are completely restored.
What does such a salary entail: responsibility of the employee and the employer
Employers who pay their employees gray or black wages, if there is evidence after an audit, the Tax Service or the Labor Safety Inspectorate may be charged with violating the following legislation:
- Art. 123 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation: failure by a tax agent to fulfill the obligation to withhold taxes entails a fine of 20% of the personal income tax amount for the period during which he was supposed to transfer money to the budget;
- Art. 15.11 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation: the fine for violating accounting requirements reaches 20,000 rubles. Disqualification is also provided for a period of up to 2 years;
- Art. 199.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, which provides for not only fines but also imprisonment for failure to fulfill the duties of a tax agent.
For employees, deliberately concealing the receipt of black or gray salaries is also fraught with adverse consequences, ranging from receiving a minimum pension in the future, and ending with the mandatory declaration of personal income tax if payment evasion has been detected. What you have to do in this case:
Prevention
For the purpose of prevention, the following recommendations must be followed:
- Avoid eye strain. Provide mandatory rest for the visual organs.
- Protect eyes from harmful effects.
- Perform gymnastic exercises for the eyes.
- Increase the amount of vegetables and fruits, vitamins and microelements consumed.
- Include drugs and foods containing vitamins A, E and B in your diet. Also increase the amount of zinc in the body.
In any case, you should follow all the recommendations of a specialist to prevent deterioration in the quality of vision. You can save your vision by identifying the pathology in time and starting to treat it.