Electrophysiological testing of the visual organs is a series of procedures used to study the functioning of the optic nerve, retina, and visual areas in the cerebral cortex. The methods are based on recording visual reactions to specific stimuli and are highly informative.
EPI is contraindicated if pathological activity of the nervous system is observed, accompanied by attacks of epilepsy. The procedure cannot be performed if there are pathological processes on the skin at the examination site, severe angina or hypertension. The examination is not performed on patients with pacemakers.
Indications for EPI
EPI has a wide range of indications:
- genetic diseases of the retina (pathological genes are identified);
- pathological childbirth complicated by fetal hypoxia/hypotrophy and prematurity;
- congenital anomalies of the development of visual systems;
- optic nerve atrophy;
- amblyopia of any degree;
- herpetic keratitis (will show signs of damage to retinal ganglion cells and optic nerve fibers);
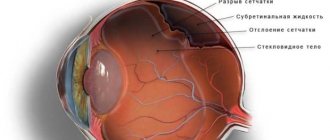
- contusions of the eyeball;
- metallosis;
- congenital or acquired myopia;
- demyelinating diseases of the nervous system;
- opaque optical media (vitreous fibrosis, hemophthalmos, hyphema, traumatic cataract).
An electrophysiological procedure is carried out when the visual analyzer is injured, to determine the functioning of the retina and optic nerve. The procedure is performed for unexpected vision loss, including psychiatric disorders.
Types of EPI
EPI of the visual organs includes 4 types of studies:
- Electrooculography (EOG) is a diagnostic method that allows you to determine the difference in potentials when the eyeballs move.
- Electroretinography (ERG) is based on graphic recording of the activity of retinal cells, which occurs against the background of light irritation.
- Multifocal electroretinography (MERG). Using this research, a three-dimensional map is built. Based on the results obtained, doctors determine the light sensitivity of the central part of the retina, which is the most important part of the fundus of the eye. Detects small areas of damage to the central part of the retina.
- Method of visually evoked potentials (VEP). The study involves identifying visual pathways all the way from the retina to the visual cortex. Used for multiple sclerosis, ocular hypertension, diabetes, optic tract tumors. VEP is the best method for detecting retinal functionality.
Types of procedure
There are 4 types of eye EPI.
- Electrooculography. This method allows you to record changes in the constant potential of the corneal-retinal area of the eye during lateral movement. EOG depends on the degree of preservation of the pigment epithelium. Changes in the electrooculogram indicate the presence of diseases that are localized in Bruch's membrane, the choriocapillaris layer of the retina, as well as in the pigment epithelium.
- Electroretinography. The method allows you to obtain a graphic image of the electrical activity of the retina, which occurs in response to light stimulation. The ERG shows the activity of most cells in the retina, which depends on the number of healthy neurons and photoreceptors. Each layer of cells is displayed separately on the electroretinogram as a curve graph. By assessing the cells' response to certain stimuli, the doctor determines how these groups of cells function.
- Multifocal electroretinography method. MERG builds a three-dimensional map showing the light sensitivity of the most important area of the retina in terms of functionality - the central one. In addition, the method detects small lesions in this area of the retina.
- Visually evoked potentials. EEP is the reaction of the optic nerves of the cortex in the occipital region of the brain to light stimulation of the eyes (cortical fields 17–19 according to Brodmann). The above potentials are recorded in the form of an electroencephalogram, which demonstrates the functional state of the visual analyzer sections. That is why EPI examination of the eyes using the EVP method plays an important role in the topical diagnosis of developing pathology. The stimulus can be flashes or structured stimuli (alternating black and white cells of different sizes), which depends on the visual acuity of the subject and the objectives of the study.
An ophthalmologist and a doctor-researcher who uses EPI eye examination work closely with each other to set the task and decide on the type of examination and choose early or differential diagnosis. The electrophysiologist selects a research plan to obtain an answer from those retinal cells that are involved in pathological processes. EPI of the eyes gives objective results, being decisive in making a diagnosis.
Preparation for the procedure
You need to prepare for the procedure. Before conducting an electrophysiological study, you need to wash your hair the day before. Do not use hairsprays, gels or other chemicals. Immediately before the procedure, remove your earrings and braid your hair so that there is a parting at the back of your head.
If you have a refractive error (myopia, farsightedness, astigmatism), take contact lenses or glasses with you. For SCL and LCL, bring a container and disinfectant solution with you.
When performing the visual evoked potential method, the day before the procedure, stop taking vascular drugs and tranquilizers. These medications distort the results; the VEP will have to be repeated.
Contraindications for endoEPI
- acute infectious diseases,
- acute myocardial infarction,
- unstable angina for 4 weeks,
- chronic heart failure III-IV f.k. according to NYHA,
- left ventricular aneurysm with thrombus,
- blood clots in the cavities of the heart,
- cardiac mechanical prostheses of the left chambers of the heart with access from the left.
When performing endoEPI, the incidence of complications does not exceed 1%. In order to prevent the latter, all necessary measures are taken at all stages of diagnosis and treatment.
The X-ray endovascular diagnostics and treatment room provides diagnosis and treatment of all types of arrhythmias (brady- and tachyarrhythmias). The department carries out operations within the framework of the state program for the provision of high-tech medical care (HTMC). This type of medical care is provided according to quotas allocated by the Russian Ministry of Health. Patients can also be operated on on a self-supporting basis, taking into account the cost approved by the Clinic.
How does EFI work?
Before the ERG, the patient undergoes dark adaptation for 20 minutes. Then the work of all retinal cells is examined. The doctor gives bright flash stimuli to which the cells begin to respond. Then drops are instilled to dilate the pupil and oscillatory potentials are examined.
After this, the eyes are illuminated for 10 minutes and measurements are taken again. This procedure measures the action of photoreceptors.
Method of conducting EOG:
- Electrodes are placed on opposite corners of the eye;
- the patient must rotate the eyeballs in different directions;
- installed electrodes read information.
The procedure does not take more than 7 seconds. Does not cause discomfort. There are no strict standards for the time of electrooculography; if necessary, the doctor repeats the examination.
The visual evoked potential method is the sum response of large populations of neurons in the visual cortex. The results of the study are provided in the form of an electroencephalogram.
The manipulation is painless. It is even performed on newborns. It does not contain manipulations associated with the penetration of foreign objects inside. Method:
- the doctor applies several electrodes to the head;
- one eye is closed with an occluder or shield;
- the doctor tells you what needs to be done during the study.
Sometimes you need to close both eyes. Using this method, the prognosis of visual impairment in pathological conditions such as optic nerve injury, diabetes, and glaucoma is determined.
Multifocal electroretinography is performed in a similar way to ERG. The research is rarely carried out because it is at the stage of study and testing. Only scientists who are developing this research can conduct it. Multifocal electroretinography is not used in ophthalmology clinics.
What is electrical stimulation of the eye muscles?
One of the effective physiotherapeutic procedures performed by experts in the field of modern ophthalmology is electrical stimulation of the eyes in children and adults. This manipulation is carried out using a special device - an electrical stimulator. It delivers pulsed current to specific areas of the visual organs. Thus, the effect on the muscles of the eyelid and oculomotor system helps to increase their tone and improve the process of neuromuscular communication. This has a positive effect on conjugate eye movements in cases of strabismus and ptosis (lifting of the eyelid).
Electrical stimulation of the eyes can be carried out to activate nerve cells in the occipital part of the cerebral cortex, where the visual analyzer is located. In this case, the current is applied to the sensory apparatus: the retina or optic nerve. It has been scientifically proven that such manipulation awakens neurons that are in a state of sleep (parabiosis), due to which they create stronger feedback. In addition, exposure to a weak electric current triggers restoration processes in the tissue cells of the organs of vision due to stimulation of a complex of energy and biochemical processes.
Electrical stimulation of the eyes improves the function of cell membranes by increasing the synthesis of collagen and protein. This helps to increase their transport function and improve the “nutrition” of cells. At the same time, local and regional blood flow is activated, which further accelerates metabolism.
Current stimulation at the level of the retina is carried out with the aim of activating its functionally depressed elements (cones and rods) and improving energy metabolism. In turn, exposure at the level of the optic nerve improves the conduction of nerve fibers by changing the activity of neurons in the posterior cortex of the brain. Electrical stimulation of the ciliary muscle increases the accuracy of focusing images on the retina. In addition, the procedure has a positive effect on the thalamic and hypothalamic structures of the brain (subcortical centers).
- The impact of weak pulse current is carried out:
- On the muscles of the eyelid and oculomotor system;
- On the retina;
- On the optic nerve.
- Performing electrical stimulation of the eyes
The procedure is quite simple, quick and painless. However, it requires additional examination of the patient in order to determine the localization of the impact and other individual parameters.
Electrical stimulation of the eye muscles, retina and optic nerve is carried out using a special ophthalmological device that delivers a weak pulse current. One sensor of the electrical stimulator is fixed on the patient’s hand, and the second is put on a finger and applied to the eyelid of a closed eye for 10-15 minutes. After this, it is necessary to apply the manipulator to the second eye and repeat the procedure. As a rule, a course of physiotherapy is required for the treatment and prevention of visual pathologies. Manipulations are carried out daily for 7-10 days.
For maximum effectiveness, treatment cycles should be repeated 3-4 times throughout the year. In some cases, patients are shown one-time eye stimulation with current.
The procedure contributes to:
- Improving visual acuity, including peripheral;
- Improving the tone of the extraocular muscles;
- Expanding the accommodation reserve;
- Improving the conductivity of nerve fibers in the visual analyzer;
- Improving blood flow and stimulating the metabolism of cell membranes;
- Reducing eye fatigue;
- Normalization of fluid circulation in the eyeball and intraocular pressure.