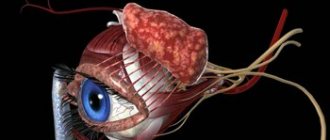
The eyes are friction organs that perceive not only surrounding objects, but also color.
This function is performed by the retina, which contains nerve endings that transmit information to the brain.
If any structures along the path of light transmission are disrupted, a person stops perceiving 1, 2 or completely all colors. The disorder can be congenital or acquired. For diagnosis, consult an ophthalmologist, conduct research, and use treatment if possible.
Clinical picture
Color vision disorders can be congenital or acquired.
Anomalies of color vision, which are acquired in nature, are observed in pathologies of the retina, optic nerve, central nervous system, poisoning, and intoxication. They are manifested by a violation of the perception of the three primary colors and are accompanied by various visual impairments. These disorders usually change their nature during the course of the disease and during its treatment, while congenital disorders cannot be corrected. Typically, congenital disorders depend on the weakening or complete loss of function, usually of one of the components. This vision is called dichromasia. Pathology of color perception can be inherited. According to the classification of Chris and Nagel, the following types of color vision are distinguished:
- normal trichromasia;
- abnormal trichromasia;
- dichromasia;
- monochromasia;
Anomalous trichromasia is in turn divided into protanomaly, deuteranomaly, and tritanomaly. Dichromasia is divided into protanopia (partial red color blindness), deuteranopia (partial green color blindness), tritanopia (partial blue or violet color blindness).
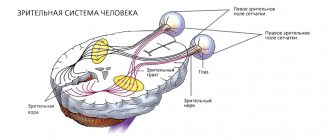
Color perception
The human eye is the most complex and advanced visual system of all mammals. It is capable of perceiving more than 150 thousand different colors and their shades. Color perception is possible thanks to cones - specialized photoreceptors located in the macula. An auxiliary role is played by rods - cells responsible for twilight and night vision. It is possible to perceive the entire color spectrum with the help of only three types of cones, each of which is sensitive to a specific part of the color gamut (green, blue and red) due to the content of iodopsin. A person with full vision has 6-7 million cones, and if their number is less or there are pathologies in their composition, various color vision disorders occur.
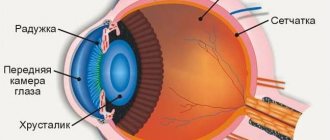
Structure of the eye
The vision of men and women is significantly different. It has been proven that women are able to recognize more different shades of colors, while representatives of the stronger sex have a better ability to recognize moving objects and maintain concentration on a specific object longer.
Treatment
It is impossible to completely cure impaired color vision. Treatment of color anomalies is aimed at reducing the severity of symptoms and correcting visual acuity. Treatment is also carried out with the aim of stopping the pathological process. In the absence of adequate therapy, a person can completely lose vision.
To normalize visual acuity, contact lenses or glasses are used. They are recommended to be worn by all patients with impaired color perception. In order to correct the perception of colors, there are tinted glasses and lenses with pigments. Patients are advised to go out in the sun only with sunglasses.
In the case of acquired color vision anomaly, when the cause of this condition is established, the issue of surgical correction can be decided. The operation can be performed on the affected area of the eye or on the part of the nervous system that is responsible for sensitivity to colors. If cataracts are present, surgery to remove them is indicated.
Complex therapy for impaired color vision includes vitamins. All patients are advised to take vitamin complexes with a high content of vitamins A and E.
If the disease occurs as a complication of diabetes mellitus, the patient is recommended to receive appropriate treatment from an endocrinologist.
Incidence (per 100,000 people)
| Men | Women | |||||||||||||
| Age, years | 0-1 | 1-3 | 3-14 | 14-25 | 25-40 | 40-60 | 60 + | 0-1 | 1-3 | 3-14 | 14-25 | 25-40 | 40-60 | 60 + |
| Number of sick people | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
Trichromasia - causes, varieties and symptoms
The content of the article:
Trichromasia is normal human vision in which the organ of vision recognizes shades of all three primary colors. Such people are called trichromats.
Kinds
We can highlight:
- normal;
- abnormal trichromasia.
Normal trichromatic vision
Special photoreceptors (cones), which are located on the retina, are responsible for color perception. Moreover, there are several groups of receptors that have different sensitivity to radiation with different wavelengths.
Thus, the cones, which are responsible for the perception of red color, react most strongly to light with a wavelength of more than 550 nm. (long-wave radiation), green cones - from 520 to 540 nm. (medium wavelength), blue cones - from 430 to 470 nm. (shortwave).
Thus, when light rays strike the retina, they excite all three groups of cones, but to varying degrees.
Anomalous trichromasia
Trichromasia reduces the patient's ability (but does not completely disappear) to perceive one of the three primary colors. If the red color is partially lost, this condition is called protanopia, if the green color is deuteranopia, and if the blue color is tritanopia. Such pathologies are congenital in nature and are associated with damage or absence of one of the groups of cones.
Diagnostics
With a slight impairment of color vision, a person may not even be aware of it. He often learns about the pathology as a result of a medical examination with an ophthalmologist.
To test vision for the perception of colors, special Rabkin tables are used, which depict numbers consisting of circles of a certain color, while the background of the picture has a different color. A healthy person (trichromat) can recognize a number without any problems, while a person with a pathology can find it quite difficult to see the symbol.
It is worth noting that the examination must be carried out in daylight, the distance from the patient’s eyes to the table is about 1 meter.
We advise you to read about another pathology of color perception, or rather about tritanopia.
To learn more about eye diseases and their treatment, use the convenient site search or ask a specialist a question.
ofthalm.ru
Interesting facts about color vision
Interestingly, color vision does not begin to develop immediately after birth, but only in the sixth month of life. It has been scientifically proven that all children are born with color blindness. This is not a pathology if color perception returns to normal after six months. Moreover, according to statistics, every 255 girls and every 12th boy have color blindness (the inability to distinguish colors).
From a physics point of view, only three colors are primary: red, green and blue, and the rest are the result of their combination in one order or another. It is believed that the human eye perceives only seven primary colors: blue, red, orange, green, yellow, violet and cyan. At the same time, we see up to 10 million different shades, including only 500 variations of gray.
Scientists have proven that our retina is not able to distinguish red, despite the presence of cones responsible for the perception of this spectrum. These receptors only detect yellow-green and blue-green colors. The brain then combines these signals and turns them into red.
Vision differs significantly between women and men. It has been proven that the fair half of humanity is able to recognize many more different shades, while representatives of the stronger sex can concentrate on a specific object for a longer time and recognize moving objects better. There is a rare genetic mutation that causes an extra cone cell to be present on the retina of women. Thanks to this, they perceive up to 100 million colors.
In addition to humans, reptiles and birds have good color vision. When conducting research, not three, but four types of cones were discovered in their retinas, so most of these animals are tetrachromats, capable of distinguishing millions of shades. Unlike us, birds perceive ultraviolet color. However, the vision of dogs and cats is limited to only two color spectrums: blue and red. Sea creatures see the world primarily in red hues.
Since childhood, we are accustomed to thinking that the sun is yellow. However, during the research process it was proven that it is a black space object. The thing is that a person distinguishes not only the wave spectrum, but also the temperature of light: the lighter the object, the warmer its emission spectrum. We see the sun as yellow because this star absorbs surrounding light without reflecting it off its surface.
Scientists have proven that with age, the human world partially dims and turns yellow, which is associated with a change in the optical properties of the eye, due to which the cones begin to perceive blue color worse. This phenomenon can be easily noticed if you study the paintings of artists that were painted in their youth and at a more mature age.
Interesting facts about the vision of a person of color:
- Children are born with color blindness. Color perception is normalized only after six months;
- Every 255 girls and every 12th boy are color blind;
- Color vision differs significantly between women and men (women perceive more shades);
- The retina of the human eye is unable to distinguish the color red;
- From a physical point of view, only 3 shades are basic: red, green, blue;
- In addition to humans, reptiles and birds have good color vision;
- The sun is a black cosmic object. We see it yellow because the star absorbs surrounding light rays;
- With age, the human world partially dims and turns yellow due to changes in the optical properties of the eye.
Symptoms
| Occurrence (how often a symptom occurs in a given disease) | |
| Color perception disorder | 100% |
| Poor vision at dusk | 90% |
| Rapid eye fatigue when performing visual work (eye fatigue, visual fatigue, eye strain, asthenopia) | 80% |
| Decreased visual acuity (deterioration of vision, poor vision) | 80% |
| Intolerance to bright light (photophobia, light sensitivity) | 60% |
| Double vision (diplopia) | 50% |
Diagnosis of color vision
Color blindness is detected during a vision test using Rabkin tables. The method is a test that uses 27 cards with numbers, numbers, geometric shapes and other symbols depicted on them. They are made of a large number of multi-colored circles. The ophthalmologist shows the card to the patient, and he must name the symbol within 5 seconds. 27 pictures allow you to determine the cause and form of color blindness. Several dozen auxiliary tables are used to identify the degree of the disease and its other features.
The results of diagnosing color vision anomalies will be accurate if the following conditions are met:
- the test is carried out in natural light;
- the sun's rays fall directly on the picture;
- the light does not blind the subject;
- the patient feels well;
- the pictures are located at eye level at a distance of no more than 1 meter from the person being tested.
If 90% of the answers are correct, then there are no problems with color perception. When the patient makes mistakes in 75% of cases, color blindness is diagnosed.
Structure and functions of the eye
How we see the image depends entirely on how accurate the signal is received in the brain cells and how accurately the received information is processed.
The correct structure of the eyeball plays a primary role in this. In adults, this organ in its normal state is a ball with a diameter of 24-25 mm. It consists of various tissues and structures that are involved in projecting the image and transmitting it to the desired area of the brain.
The outer part of the eye is protected by the cornea, which in its normal state is a transparent cover that is uniform in structure. The cornea transmits light rays through itself, as a result of which a person gets the opportunity to contemplate the world in a three-dimensional image.
The cornea does not contain a single blood vessel and is practically bloodless. The cornea consists of 6 layers:
- The epithelial layer is located on the outer surface of the eye and regulates the moisture of the eyes. This layer has a remarkable ability to quickly recover. For this reason, a speck or small particles that enter the eye cannot cause much harm to visual health, except in cases where the foreign body enters the deeper layers of the eye.
- Bowman's membrane is located immediately behind the epithelial layer; this organ is involved in the metabolic processes of cells and controls the nutrition of the cornea. This layer does not have the ability to self-heal, so damage to it will inevitably affect the quality of vision.
- Stroma is a collagen layer that fills the space.
- Descementum's membrane is a very thin element that delimits the stroma and the endothelial mass.
- The endothelial layer is responsible for removing excess fluid from the corneal layer and provides the permeability of the cornea.
- The tear film washes away dust microparticles and improves oxygen permeability into the eyes. The tear fluid coming from the tear film moisturizes and softens the eyes.
Cones and rods
Whether we are looking at magnificent paintings in a museum or enjoying the bright colors of tropical countries somewhere on the coast of a warm sea, the thought does not even occur to us that all this visible splendor is the result of the painstaking work of small photoreceptors - the rods and cones of the retina.
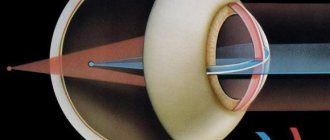
The human eye is an optical system, thanks to which people have the opportunity to fully see pictures of the world around them. This happens as follows: a photon, passing through the lens, is focused on the retina of the eye.
Next, light-sensitive cells are activated, the peripheral processes of which are cones and rods. Irritation from light is translated into a nerve impulse, which, in turn, is redirected for further processing to the brain.
These tireless workers received the name “cones” and “rods” due to their shape. Photoreceptors are extremely small in size:
- the sticks have a length of 0.06 mm, a diameter of 0.02 mm;
- cones are approximately 50 µm in diameter and only 2-4 µm in length.
Microscopic dimensions are more than compensated by quantity, which allows them to successfully implement their functions. There are more than a hundred million rods in the retina, and about 7 million cones.
The rods are highly sensitive to photons and their main mission is to provide vision in the dark. A light-sensitive pigment, rhodopsin, located in the membranes of the rods makes it possible to see in black and white.
In light, the pigment disintegrates into a blue region, and then, in interaction with the cones, color perception appears. Substances formed after the breakdown of the pigment act as an irritant on the optic nerve, which is how the impulse is transmitted.
Anomalies of the rod apparatus
The occurrence of defects in the rod apparatus leads to a decrease in the function of adaptation to twilight lighting. In ophthalmology, this phenomenon is called nyctalopia or hemeralopia. And among the people, such a pathology is called “night blindness.” It develops against the background of insufficient intake of vitamin A into the body. Moreover, it is vitamin A that is the basis for the production of retinol, which is essential for normal vision.
Anomalies of color perception in society
People with color vision impairments (except monochromats) have the same visual acuity as all other people. In this regard, they are not handicapped and do not need social protection. However, there are a number of restrictions for them when choosing a profession and type of employment.
Thus, if color vision is impaired, people are not allowed to work in transport; they cannot be railway workers, pilots, sailors, doctors, chemists, etc.
In Romania and Turkey, persons with diagnosed color vision anomalies are prohibited from being issued a driver's license. According to Russian law, colorblind people with dichromasia (protanopia, deuteranopia) have the right to obtain a driver's license only category A or category B, but do not have the right to work for hire. And in many countries of the European Union there are no such restrictions. Drivers' licenses are freely issued to colorblind people, and traffic lights that are convenient for them have even been developed.
By contacting the Moscow Eye Clinic, each patient can be sure that some of the best Russian specialists will be responsible for the results of treatment. The high reputation of the clinic and thousands of grateful patients will certainly add to your confidence in the right choice. The most modern equipment for the diagnosis and treatment of eye diseases and an individual approach to the problems of each patient are a guarantee of high treatment results at the Moscow Eye Clinic. We provide diagnostics and treatment for children over 4 years of age and adults.
Diagnostics
Currently, the assessment of color vision receives undeservedly little attention. Most often in our country, verification is limited to a demonstration of the most common Rabkin or Yustova tables and an expert assessment of suitability for a particular activity.
Indeed, color vision impairment often has no specificity for any disease. However, it can indicate the presence of such at a stage when there are no other signs. At the same time, the ease of use of the tests allows them to be easily used in everyday practice.
Color comparison tests can be considered the simplest. To carry them out, you only need uniform lighting. The most accessible: alternate demonstration of a red color source to the right and left eyes. At the onset of the inflammatory process in the optic nerve, the examinee will notice a decrease in tone saturation and brightness on the affected side. Also, the Kolling table can be used to diagnose pre- and retrochiasmal lesions. With pathology, patients will notice discoloration of images on one side or another, depending on the location of the lesion.
Other methods that help in diagnosing color vision disorders are pseudo-isochromatic tables and color ranking tests. The essence of their construction is similar, and is based on the concept of a color triangle.
The color triangle on a plane reflects the colors that the human eye can distinguish.
The most saturated (spectral) are located on the periphery, while the degree of saturation decreases towards the center, approaching white. The white color in the center of the triangle represents the result of balanced stimulation of all types of cones.
Depending on which type of cone cell is not functioning properly, a person may not be able to distinguish certain colors. They are located on the so-called lines of non-distinction, converging to the corresponding angle of the triangle.
To create pseudo-isochromatic tables, the colors of optotypes and their surrounding background (“masking”) are obtained from different segments of the same line of non-discrimination. Depending on the type of color anomaly, the examinee is not able to distinguish certain optotypes on the displayed cards. This makes it possible to identify not only the type, but also, in some cases, the severity of the existing violation.
Many versions of such tables have been developed
: Rabkina, Yustova, Velhagen-Broschmann-Kuchenbecker, Ishihara. Due to the fact that their parameters are static, these tests are better suited for diagnosing congenital anomalies of color perception than acquired ones, since the latter are characterized by variability.
Color ranking tests are a set of tiles whose colors correspond to colors in a color triangle around a white center. A normal trichromat is able to arrange them in the required order, while a patient with impaired color vision is only able to arrange them in accordance with the lines of non-discrimination.
Currently used: the 15-shade Farnsworth panel test (saturated colors) and its modification Lanthony with desaturated colors, the 28-shade Roth test, as well as the 100-shade Farnsworth-Munsell test for more detailed diagnostics. These methods are more suitable for identifying acquired color vision disorders, as they help to more accurately assess them, especially over time.
A certain disadvantage in the use of pseudo-isochromatic tables and color ranking tests is the strict requirements for illumination, the quality of the demonstrated samples, storage conditions (fading must be avoided, etc.).
Another method that helps in the quantitative diagnosis of color vision disorders is the anomaloscope. The principle of its operation is based on the composition of the Rayleigh equation (for the red-green spectrum) and Moreland (for the blue spectrum): selection of pairs of colors, giving a color indistinguishable from a monochromatic (color of the same wavelength) sample. Mixing green (549 nm) and red (666 nm) produces an equivalent yellow (589 nm), with the differences being balanced by changing the brightness of yellow (Rayleigh's equation).
A Pitt chart is used to record the results. The colors obtained by mixing red and green are placed on the x-axis depending on the amount of each of them in the mixture (0 - pure green, 73 - pure red), and brightness - on the ordinate. Normally, the resulting color is equal to the control color and is 40/15, respectively.
In case of violations of the “green” color receiver, more green is needed to obtain such equality, and in case of a defect in the “red” one, add red and reduce the brightness of yellow. In cerebral achromatopsia, virtually any ratio of red to green can be equated with yellow.
The disadvantage of the technique may be the need for special, expensive equipment.
Colorblindness. Interesting Facts.
- John Dalton was unaware of his color blindness for almost half of his life.
- The palette of the famous Vrubel is explained by the artist’s color blindness.
- Most animals, for example dogs, do not distinguish colors at all.
- Colorblind people, unlike people with normal vision, are able to see many shades of other colors, for example, khaki.
- In EU countries there are no restrictions for colorblind people when issuing driving licenses. With the exception of Romania.
- To correct color blindness, glasses with multilayer lenses based on neodymium oxide are used. They improve color perception in mild forms of color blindness.
Forecast and prevention of color vision anomalies
Prevention of the development of color vision anomalies has not been developed. All patients with color blindness, achromatopsia and acquired color vision deficiency should be registered with an ophthalmologist. It is recommended to undergo examination 2 times a year with additional ophthalmoscopy, visometry and perimetry. You should take multivitamin complexes containing vitamins A and E, and adjust your diet with the obligatory inclusion of foods rich in vitamins and microelements. The prognosis for life and work ability with color vision anomalies is favorable. In this case, patients often experience a decrease in visual acuity, and it is impossible to restore normal color perception.
Drivers, namely: in addition to the updated form that the candidate driver receives after passing the commission, the procedure itself and the list of doctors who give the go-ahead for the right to drive a vehicle have changed somewhat. So, today, the conclusion of doctors such as ENT and neurologist will be mandatory only for truck drivers. A visit to an ophthalmologist remains unchanged, mandatory for everyone, regardless of the category received. Testing color perception and vision testing are an integral test for everyone who wants to drive a vehicle. If everything is clear with visual acuity, then let’s figure out what a color perception test is for drivers and whether it is possible to prepare for this test.
Possible reasons
Different types of color vision disorders are determined by the structure and relationship of the cones of the retina.
Accordingly, the causes of diseases can be associated both with the inherited state of the receptor apparatus of the eye, and with various pathologies affecting the retina.
The hereditary form is much more common among men, although the pathological genes are located on the X chromosome. Other reasons:
- Parkinson's disease is a severe neurological disorder characterized by a progressive course.
- The neurological nature of the disease determines the possible damage to the nerve cells responsible for color processing.
- Cataract is a change in the structure of the lens that affects vision functions. The clouding of the lens that occurs with this disease also affects color perception. For people with this disease, colors appear less vibrant and distinct.
- Side effects of medications. An antiepileptic drug known as tiagabine has been shown to impair color vision in 40% of cases. However, this side effect goes away over time.
- Hereditary optic neuropathy is a common hereditary disease among men that affects the condition of the optic nerve. There is a disturbance in the perception of the red-green spectrum of colors.
- Kallmann syndrome is a hereditary disease associated with damage to the pituitary gland. The pathology primarily affects the development of sexual functions, but can also cause disturbances in color perception.
- Other diseases: Alzheimer's disease, glaucoma, chronic alcoholism, leukemia, sickle cell anemia, diabetes mellitus and macular degeneration.
- Aging. The retina can also wear out with age.
- Exposure to chemicals. Some chemicals, including carbon disulfide and fertilizers, can attack the retina and cause color vision problems.
Causes of color blindness
The most important cause of impaired color perception is a hereditary factor. The pathological gene is inherited from parents to offspring. If the cause of the disease is color blindness, the pathological gene is associated with the X chromosome, which manifests itself only when interacting with the Y chromosome. This means that women can be carriers, but only boys will be affected.
In a healthy person, cones are located on the retina of the eye. They perceive colors: blue, yellow, red. A hereditary disease can cause the absence of one of them, or several at once. In the latter case, the person will have black and white vision with the appearance of some color shades.
A person may be exposed to damaging factors that result in acquired color vision impairments:
- infectious and inflammatory diseases of the brain that affect the center of vision;
- mechanical damage to the brain or skull, which leads to damage to the center of vision;
- the growth of benign and malignant tumors, which with their edges compress the center of vision;
- inflammatory diseases of the optic nerve;
- infectious and inflammatory eye diseases that spread throughout the internal structure and spread to the retina;
- retinal hemorrhage;
- a complication of diabetes mellitus, as a result of which conglomerates of carbohydrates and fats form in the blood, which clog the microcirculation vessels of the eyes;
- narrowing and damage to the blood vessels of the eye microcirculation, resulting in reduced nutrition of the retina;
- mechanical damage to the eyes, as a result of which the retina, lens, and vitreous body suffer;
- increased intraocular pressure, which occurs due to an increased volume of intraocular fluid, as a result of which the chambers of the eyes increase in size, compressing the retina and optic nerve;
- increased exposure to ultraviolet radiation, which damages the retina;
- clouding of the lens, as a result of which the light beam passes insufficiently to the retina, reducing the perception of surrounding objects.
The acquired condition is characterized by the fact that when the damaging factor is eliminated, the color perception function is completely restored. That is why the doctor must identify the root cause in order to tell the patient about the prognosis of the disease and possible methods of therapy.
Trichromasia - impaired color vision
In the case of normal trichromasia, all rays of light that fall on the retina of the eyeball excite three types of receptor apparatus, but the degree of this excitation is different.
It is known that color perception is based on the excitation of special photoreceptors, which are located in the sensitive area of the eye. Moreover, different groups of photoreceptors have different sensitivity to light waves in a certain wavelength range.
For example, those cones that are responsible for recognizing red color are most sensitive to light with a wavelength in the range of more than 550 nm, green cones are mid-wavelength and perceive waves in the range of 520-540 nm, and blue receptors perceive short-wavelength range (430-540 nm). 470 nm).
With anomalous trichromasia, the patient experiences a decline in the ability to perceive one of the colors, but the color recognition function is not completely lost. If the perception of red color is reduced, then protanopia occurs, if the recognition of green color is reduced, deuteranopia occurs, and blue color is tritanopia. These changes are usually congenital and are associated with a decrease in the concentration of certain cones, that is, a violation of the structure of the receptor apparatus.
With anomalous trichromasia, the patient experiences a decline in the ability to perceive one of the colors, but the color recognition function is not completely lost.
Diagnostics
In case of minor anomalies in color perception, a person does not experience any discomfort. In this case, the patient learns about the presence of pathology only during a special study.
For diagnostics, various color tables are used, for example, Rabkin tables. In this case, the figure shows numbers that consist of circles of different colors. The background also consists of circles, but in a different color range. A patient with normal vision can easily read all the symbols. If there is a pathology of color perception, the signs become indistinguishable.
For the accuracy of the result, it is important to comply with the experimental conditions: the lighting should be daylight and uniform, and the table should be placed at a distance of a meter from the subject.
- Interesting
MonochromacyHuman color perception is formed on the principle of the presence of three main color pairs, which are called color-opponent pairs. These include…
proglaza.ru
Physiology of color vision. Impaired color vision in humans.
Color vision is color vision, color perception, the sleep of the eyes of h-ka and many species of animals with daytime activity to distinguish colors, that is, to sense differences in the spectral composition of visible radiation and in the color of objects. Visible part of the spectrum on. radiation of different wavelengths perceived by the eye as different colors. Color vision is due to joint the work of several light receptors, i.e. retinal photoreceptors of different types, differing in spectral sensitivity. Photoreceptors convert radiation energy into physiological energy. excitation, which is perceived by the nerve. s-my like different colors, because... radiation excites receivers differently. degrees. The spectral sensitivity of different types of photoreceptors is different and is determined by the absorption spectrum of the eye. pigments. Each light receiver individually is not capable of distinguishing colors: all radiation for it differs in only one parameter - apparent brightness, or lightness, because light of any spectral composition has a qualitatively identical physiological effect. impact on each of the photopigments. In this regard, any radiation with a certain ratio of their intensities can be completely indistinguishable from each other by one receiver. If there are several receivers in the retina, then the equality conditions for each of them will be different. Therefore, for a combination of several receivers, many radiations cannot be equalized by any selection of their intensities. Let's modernize the basics. ideas about color vision were developed in the 19th century. T. Jung and G. Helmholtz. According to this theory, there are 3 types of photoreceptors in the retina of the eye, sensitive to varying degrees to red, green and blue light. However, physiological The mechanism of color perception does not allow us to distinguish all radiation. Some people hereditarily lack one or two light receptors out of three; in the latter case, there is no color vision. Basic biological The meaning of color vision for humans and animals existing in the world of non-self-luminous objects is the correct recognition of their color, and not just the discrimination of radiation. The spectral composition of reflected light depends on both the color of the object and the incident light and is therefore subject to significant changes when lighting conditions change. Sleep is seeing. The device to recognize the color of objects by their reflective properties in changing lighting conditions is called constancy of color perception.
Color vision impairment is a feature of vision. functions that are endowed from birth. The phenomenon is caused by the X chromosome and, as a rule, is transmitted at the genetic level from mother to male child. For this reason, colorblindness often plagues the stronger sex. People suffering from color vision deficiency are unable to distinguish between three colors - green, blue and red. However, disturbances in color vision may also be observed, which a person acquires along the path of life. The causes of such disorders may be diseases of the eye retina, damage to the nerves of vision or vision. centers within the central nervous system. Acquired color vision disorders can occur in one eye or in both eyes, and are usually characterized by a disorder in the selection of all primary colors at once. With this disease, a colorblind person can see everything around him only in blue, red or green. When the underlying pathology is cured, color blindness is also cured, and the person’s vision returns to normal.
Types of color vision impairment
People's vision patterns are determined by the type of color vision impairment. The first type of color vision disorder is trichromasia
- assumes that h-k distinguishes all the basics.
colors, but sees them very dimly. The second type of color vision disorder is called dichromasia
, when a color blind person sees any two colors, with the exception of the third, any of the three.
This type of color blindness is more severe than the first type. In absence If you are unable to distinguish red, protanopia occurs; if you are unable to distinguish green, deuteranopia occurs; if you are unable to distinguish blue, tritanopia occurs. The last type of color vision impairment is called monochromasia
, in which there is a complete absence of color perception, complete color blindness. In other words, a person suffering from monochromasia is able to see his surroundings. the world is only black and white. Trichromasia is more common than other color perception disorders. The presence of this deviation in a person is detected after specific studies and tests.
Tactics for Chronomatic Anomaly
Since combat is almost entirely scripted, players have little control over its course.
- The Speed: Normal, Speed: Low and Speed: High phases alternate each other, affecting the speed of cooldown recovery, movement, attack and spell casting.
- Tanks must constantly change without gaining 10 charges
Anomalies of color vision are a violation of color perception by the visual analyzer.
Color vision is provided by cones. There are three types of cones: those that absorb the blue-violet part of the spectrum, green, and the yellow-red part of the spectrum. According to the principle of color mixing, any color is obtained by mixing the three above. According to the three-color theory, the natural sensation of color is called normal trichromasia.
A Brief Theory of Color and Light
Light is electromagnetic radiation, and the human eye can react to it and distinguish between frequencies. The eye perceives different frequencies as different colors. Electromagnetic radiation includes all frequencies, but the human eye reacts only to the so-called “window”, which lies in the range of 380-780 nm. As the wavelength increases, the color gradually changes from violet to blue, from blue to green, then to yellow, orange, red.
The eye is more sensitive to the perception of green color, and frequencies above the violet wave and below the red wave are not perceived by the “average” eye. The "average" eye is a statistical value, there are people with "color blindness" and their spectral sensitivity is narrower. But the trained eye of a photographer or artist can distinguish shades of colors that seem the same to people with “average” eyes.
Reference! According to the theory of evolutionary biology, it is believed that the human eye is more susceptible to the color green because, most likely, our distant ancestors had to distinguish this particular color well for a long time.
How to correct color vision?
Doctors have not yet learned to treat hereditary color vision disorders. If the problem is associated with a primary disease of the visual system, then appropriate treatment will restore color perception.
- Wearing colored contact lenses. With the help of such lenses, a person can begin to see differences between colors even in the absence of specific retinal cones.
- Wearing special glasses. Lenses may have anti-reflective coating.
Not all people with this problem require correction, since in many cases the color vision disorder is almost invisible. In addition, patients with color perception pathology often adapt to distinguish shades using a subjective perception of brightness.
Thus, color blindness and other types of color vision impairment are predominantly hereditary conditions. A quick color vision test will help make the correct diagnosis.
The video will show how color vision testing is carried out:
This happens due to the radiation of the visible spectrum of vibrations, to which the cones of the retina in the eyes are sensitive.
With the help of color perception, the informative capabilities of the visual organs are significantly expanded.
Opponent color theory
If a bright green ring surrounds a gray circle, then the latter, as a result of simultaneous color contrast, acquires a red color. The phenomena of simultaneous color contrast and sequential color contrast served as the basis for the theory of opponent colors, proposed in the 19th century. Goering. Hering proposed that there were four primary colors—red, yellow, green, and blue—and that they were coupled in pairs by two antagonistic mechanisms—the green-red mechanism and the yellow-blue mechanism. A third opponent mechanism has also been postulated for the achromatic complementary colors white and black. Because of the polar nature of the perception of these colors, Hering called these color pairs “opponent colors.” From his theory it follows that there cannot be such colors as “greenish-red” and “bluish-yellow”.
Thus, the opponent color theory postulates the presence of antagonistic color-specific neural mechanisms. For example, if such a neuron is excited by a green light stimulus, then a red stimulus should cause its inhibition. The opponent mechanisms proposed by Hering received partial support after they learned to record the activity of nerve cells directly associated with receptors. Thus, in some vertebrates with color vision, “red-green” and “yellow-blue” horizontal cells were discovered. In the cells of the “red-green” channel, the resting membrane potential changes and the cell hyperpolarizes if light of a spectrum of 400-600 nm falls on its receptive field, and depolarizes when a stimulus with a wavelength greater than 600 nm is applied. Cells of the “yellow-blue” channel hyperpolarize when exposed to light with a wavelength less than 530 nm and depolarize in the range of 530-620 nm.
Based on such neurophysiological data, simple neural networks can be constructed that explain how to communicate between three independent cone systems to produce color-specific responses among neurons at higher levels of the visual system.
Anomalous trichromasia: why it occurs, treatment
Distortion of color perception is not a life-threatening pathology, but it is a limitation for some professions. Anomalous trichromasia is a congenital, genetically determined vision defect. It lies in the incorrect perception of all 3 primary colors - red, green and blue. Diagnosis of the disease is carried out using a special test - a selection of color pictures with numbers and images on a non-uniform background. It is impossible to cure the disease, but the patient is given advice on lifestyle and safety measures.
Why does it happen?
Trichromatic vision is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. This is a genetic disease that does not depend on the influence of external and internal factors on the embryo or environmental influences on an already born child.
Normal trichromasia is present in humans without genetic pathologies of retinal nerve cells. The disease appears as a result of defects in the pigment saturation of rods and cones located in the retina. Based on differences in the loss of one or another receptor, pathology is divided into 3 groups:
- Protanomaly. With it, the receptors for the perception of red color are affected. A person is not able to distinguish even its spectral shades.
- Deuteranomaly. In this case, there is a deficiency of cells that capture green color and its spectrum.
- Tritanomaly. This is a pathological condition in which the entire blue spectral range falls out. This type of color vision disorder is considered the most favorable, since there are few blue shades in nature.
Return to contents
Symptoms of pathology
Severe disease requires vision only in black and white. Abnormal trichromat is manifested by the following clinical symptoms:
- Inability to distinguish between shades of the cold and warm spectrum. If a person has a more aggressive form of the disease, he sees everything in black and white and gray tones. If the disease is mild, the patient is able to distinguish muted red, green and blue shades.
- Color insanity. A classic example of this is the inability to distinguish between red and green traffic lights.
- Hemeralopia. The synonymous name for this symptom is “night blindness.” The term reflects the patient's inability to see normally at dusk and at night.
Return to contents
Diagnostic measures
Trichromasia pathologies are diagnosed using standard laboratory and instrumental examination methods:
To identify this pathology, perimetry may be prescribed.
- Changes in visual acuity. This is done using special tables.
- Perimetry. This technique uses perimetric data to help determine visual angle pathologies.
- Ophthalmoscopy. The method is performed using a slit lamp. It allows you to determine pathologies of the fundus, optic nerve, conjunctiva, cornea, vitreous body, lens and other ophthalmic structures.
- Color testing. For this purpose, a number of pictures have been developed that are shown to patients with color vision pathology. There are “false colors” among the tables. These are inclusions of different shades, among which you need to determine the hidden letter or number.
- Techniques using pigments. Here a set of colored threads, pencils or skeins of wool is used.
- Use of spectral devices. They, like a kaleidoscope, mix different colors and shapes.
- Determination of the color perception threshold.
- Study of the pupillary reflex in response to a colored stimulus.
Return to contents
Is treatment necessary?
It is impossible to cure a genetic predisposition. The only way to prevent it is chromosomal karyotyping of parents before planning pregnancy. If a child has already been diagnosed with color vision disorders, he can only be helped symptomatically. To correct the perception of colors and shades, special glasses are used. The little patient is also taught how to behave on the roadway, where children with this pathology often get into accidents at traffic lights. For patients with this diagnosis, there is a limitation in choosing a profession. They are not accepted into the army, they are not allowed to be drivers of civil and public transport, or operators of cranes.
Share with your friends:
Please rate:
etoglaza.ru
Theories of color vision
In the history of science, there have been many theories that have tried in different ways to explain the mechanisms of color vision. At the moment, scientists adhere to three concepts to understand this complex mechanism.
Trichromatic theory
This theory was developed at the end of the 19th century and is based on the works of Maxwell, Young and Helmholtz. These scientists guessed the existence of special eye receptors that are sensitive to the red, green and blue regions of the spectrum. According to this theory, it was assumed that these three types of receptors form three images of the world, which are transmitted to the brain, where they are compared.
As a result of these processes, a color sensation arises. The nature of color vision according to this theory was not in doubt, but there were objections to the three images that are sent to the brain - there is no explanation for a number of visual phenomena.
Opponent
At about the same time, Goering proposed another theory, which he called opponent. It is based on a large number of subjective observations - the perception of color tone and simultaneous contrast.
Hering stated that color tones are not perceived all at once, for example, a color sensation is never described as yellow-blue or green-red, but a combination of red and yellow, or yellow and green, is easily perceived by the eye. In this regard, the scientist had the idea that there must be a fundamental reason that opposes colors to each other.
These observations of Hering did not exclude the presence of three types of receptors, but he believed that they work on the principle of a bipolar response. Since this statement at that time seemed absurd from a physiological point of view, this theory did not take root.
In the middle of the 20th century, the opponent theory was revived again, as data began to appear that confirmed it. Signals were discovered in the retina of a goldfish, opponent physiological responses in macaque cells, and psychophysical data were obtained.
Prevention
In order to prevent the development of color blindness in a child, parents are recommended to undergo a medical genetic consultation before pregnancy. If a person already has an anomaly in color perception, he should be registered at a dispensary and regularly visit an ophthalmologist to monitor and correct treatment.
Color perception is the ability of the human visual system to distinguish the colors of objects falling into the field of view. Full perception of colors is possible only with coordinated operation of the visual system.
Chronomatic Anomaly Abilities
This section contains tips and tactics to defeat the Chronomatic Anomaly in normal mode. Features of the Raid Finder mode, as well as Heroic and Mythic mode, including new advanced combat mechanics, are discussed in the following sections.
When fighting the Chronomatic Anomaly, players must quickly kill priority targets, as well as groups of smaller targets that spawn approximately once per minute. In addition, the raid will have to move a lot, as well as often use abilities to interrupt spells and control.
Time flow
Fading Time Particles and Time Particle Fragments
From time to time, a Fading Piece of Time will appear from the Night Well. Particles are the main priority for fighters, i.e. you need to switch to them as quickly as possible.
- The fading particles of time are motionless. If you divide the area around the well into quarters, relative to the boss, particles will appear in the previous quarter (in a clockwise direction).
- The location where particles appear is indicated by white clouds. Look for these clouds and get closer to them.
- Fading Motes of Time apply Chronomat to a target with the highest threat level and deal moderate Arcane damage.
- They also use Nightwell Warp frequently and deal moderate damage to all players. During Speed: normal Distortion of the Nightwell occurs once every 5-7 sec.
- During Speed: low Nightwell distortion occurs every 10-11 sec.
- During Speed: high Nightwell distortion occurs every 1.5 sec.
- Each successful Nightwell Distortion increases the power of the next distortion by 20%, the effect is cumulative.
- Players must interrupt the Nightwell's Warp to avoid fatal damage.
- Fragments also cast Chronomat on the highest threat target and attempt to cast Nightwell Warp.
- The Nightwell's Particle Warp deals less damage and is increased by 5% per charge, but is just as threatening due to the large number of particles.
- Use AoE stun spells to prevent particles from casting Distortion.
- Kill them as quickly as possible.
Overwhelming Power and Temporal Slam
One minute into the first four phases and then in random order, the Chronomatic Anomaly turns to the Nightwell and begins casting Overwhelming Power.
- On a successful cast, Overwhelming Power begins to deal damage to the entire raid. The effect triggers once every 5 seconds. and gradually intensifies.
- Each proc of Overwhelming Power increases the damage of the next proc by 15%.
- Overwhelming Power casts infinitely and eventually kills the entire raid.
- The overwhelming power cannot be interrupted by conventional means; to do this, you must use a Temporal Rift.
In some phases, particles appear late, and Overwhelming Power manages to deal heavy damage to the raid. In this case, healers should use healing cooldowns while waiting for Temporal Strike.
- The bomb can be applied to everyone except tanks.
- At first, the Time Bomb does no damage.
- When dispelled, it deals damage to the entire raid.
- The Time Bomb deals less damage to those further away from it.
- During Speed: A regular Time Bomb explodes after 20 seconds. after appearance.
- During Speed: low The time bomb explodes after 60-90 seconds.
- During Speed: high The time bomb explodes in just 4-8 seconds.
Players with the bomb should run out of the raid in about 8 seconds. before the explosion. In the Speed: High phase, you should run out immediately. Before exploding, the Time Bomb begins to pulsate, reminding the player to run as far as possible.
Temporal explosion
- In the Speed phase: normal: The time delay is used once every 20-30 seconds, 2-3 times per phase.
- The effect applies to 4 targets.
- Targets require moderate healing.
- The effect lasts 20 seconds.
- The time delay is used once every 43 seconds, 2 times per phase.
- The time delay is used once every 13 seconds, approximately 4 times per phase.
Chronometric particles
Once every 5-6 seconds. Chronomatic Anomaly applies Chronometric Particles to the current target. This mechanic requires changing tanks.
- Chronometric particles stack and deal more and more damage.
- At 10 charges of Chronometric Particles, Chronometric Overload is triggered.
- Chronometric Overload deals heavy damage to the entire raid and instantly kills the target (tank).
- Tanks should change with 9 or less charges (depending on the battle phase).
The duration and speed of the Chronometric Particles depends on the Passage of Time.
- During the Speed phase: normal, the Chronometric Particles effect lasts 20 seconds. and fires once every 2 seconds.
- During the Speed phase: low, the effect of Chronometric Particles lasts 60 seconds. and fires once every 6 seconds.
- During the Speed phase: high, the effect of Chronometric Particles lasts 10 seconds. and fires once every second.