Causes
This disease mainly occurs in people who have white skin color. This is a unique fact. People who lead an unhealthy lifestyle and are overweight have an increased risk of encountering pathology. The main reasons that lead to thinning of the retina include:
- diabetes;
- impaired renal and liver function;
- hypertension;
- complications after ARVI, influenza;
- infectious eye diseases;
- the presence of myopia and farsightedness;
- hereditary predisposition.
Each patient has individual reasons for the development of the disease. Their presence and method of treatment can only be determined after a comprehensive examination. If there are representatives in the family who are faced with such a pathology, everyone needs to undergo examinations with a doctor more often. This will help to identify thinning in time and take the necessary measures.
Types of pathology
Retinal dystrophy can be central or peripheral. In order to begin treatment, it is important to determine the type of pathology.
- Central - vision decreases and it is difficult for a person to read, write, or drive a car.
- Peripheral - there are no symptoms, the disease is difficult to diagnose. Peripheral vision is affected. Then “floaters before the eyes” and “sparks in the eyes” appear.
If we are talking about hereditary pathology, pigmentation or a dotted white form of the disease may be observed at birth. Destruction of the retina in this case is diagnosed in childhood.
Risk group
Every person has no protection from such a pathology. It usually appears as a consequence of age-related changes, but can also affect people of different age categories. The risk group includes:
- young children;
- patients with blue eyes;
- aged people;
- premature babies;
- people with hypertension;
- patients with diabetes mellitus;
- high degree of myopia;
- myopia;
- presence of cardiovascular diseases.
Given this information, people who have an increased risk of encountering this pathology should consult an ophthalmologist more often.
Factors provoking the development of pathology
The main cause of retinal dystrophy is natural wear and tear of the organs of vision and age-related changes in the body. But this phenomenon is not at all necessary in old age; not all older people develop dystrophy of the visual organs. The risk group includes:
- those suffering from diabetes mellitus, kidney and adrenal dysfunction;
- hypertensive patients;
- patients diagnosed with high and moderate myopia - in this case, the retina overstretches, becomes thinner in certain areas and ultimately ruptures;
- people prone to vascular diseases;
- victims of severe intoxication.
It has already been proven that dystrophic changes in the retina are caused by genetic predisposition and can be inherited. For this reason, children of parents who have been diagnosed with such a pathology should especially carefully monitor the condition of their visual organs.
This is interesting: according to research, atrophic changes in the retina are more common in females with fair skin and blue irises. Moreover, the symptoms of dystrophy often begin to express themselves clearly during pregnancy in women.
Classification
The disease is acquired and hereditary in nature. Ophthalmologists divide the extreme into two types: pigmented (occurs due to dysfunction of certain receptors), dotted white (usually occurs in childhood and is characterized by slow development).
The acquired form is often associated with age-related changes in the body. It is mainly diagnosed in older people. The disease is accompanied by the development of cataracts. This type of disease is divided into:
- Peripheral – leads to a decrease in visual acuity and quality. This type of thinning occurs as a result of injury or an inflammatory process.
- Central - the lesion leads to disruption of central vision. Significantly affects daily lifestyle.
The central view has two distinct forms, which have certain differences:
- wet - leads to disruption of the vascular system in the visual organs, as a result, fluid begins to accumulate under the retina, which circulates in the vessels;
- dry – a disorder of the vascular system, which leads to the accumulation of foods and the breakdown of nutrients.
Only an ophthalmologist can determine the type of retinal thinning after a thorough examination. For this purpose special equipment is used. First of all, the presence of a genetic predisposition should be excluded. This type of pathology can be detected in young children.
Other symptoms of retinal detachment due to myopia
In this article
Myopia is not only changes in the fundus of the eye, it is also the thinning of the retinal pigment epithelium and the accompanying degenerative changes. Among the first changes are redistribution of pigment and blanching of the optic nerve head. Atrophy then occurs either around the disc or on one side of it.
Further changes appear on the temporal side of the disc in the shape of a crescent. The size of these changes corresponds to the area of thinning of the retina. Moreover, the progression of myopia is accompanied by further stretching of the fundus, a decrease in blood supply to the choroid and an increase in chorioretinal degeneration.
There are many types of diseases, as well as the causes of their occurrence. One of them is myopia.
Retinal detachment can occur in anyone, and patients with high myopia are at particular risk. With high myopia, a large eyeball provokes stretching of the retina and disruption of its nutrition. The latter causes a deterioration in metabolic processes in tissues and blood circulation, which causes hypoxia and retinal dystrophy.
There is peripheral and central chorioretinal dystrophy. In the most serious case, a “dry” or “wet” lesion of the macular region of the retina occurs. This significantly impairs vision and even leads to blindness. If the adverse changes in the retina are severe, the patient is diagnosed with myopic disease.
Myopic disease occurs quite rarely. As a rule, high myopia remains a harmless pathological change in refraction.
Timely preventive measures significantly reduce the risk of retinal detachment due to myopia or any other disease.
As mentioned above, the main preventive measure is laser coagulation. This is a fairly simple and not painful procedure, but if the eyes are very sensitive, pain may still occur. In this case, factors such as:
- volume of coagulation and zones of its implementation;
- model of laser equipment;
- features of the anatomy of the palpebral fissure;
- correct choice of contact lens;
- surgeon experience.
If the patient knows that the pain threshold is low or that he is uncomfortable during the procedure, it is better to warn the doctor about this in advance. The pain can be reduced with the help of special medications and then the procedure will take place without any difficulties.
Another symptom of retinal detachment is “morning improvement” - a sign in which a person, after a long period of inactivity, becomes able to see well: the veil fades or decreases. By lunchtime the patient's condition worsens, and by evening everything reaches its peak.
If the retinal tear is in the upper parts of the eye, then due to the descending fluid, retinal detachment occurs very quickly in myopia. If the gap is at the bottom, then the detachment slowly rises and occurs less rapidly, but the scars will be more pronounced, since there will be much more time for their occurrence.
To prevent retinal detachment due to myopia and other diseases of the visual organs, you need to regularly visit an ophthalmologist and carefully follow all his recommendations.
Symptoms
Each type of this disease is accompanied by severe symptoms. In the peripheral form, the initial stage does not cause pain. There are also no visual defects observed. The first symptoms begin to appear when the retina ruptures. Often patients who are faced with this form of the disease begin to complain of the appearance of black spots before their eyes. This makes it difficult to lead a normal lifestyle.
When the form is wet, visual distortion of objects begins. A narrowing of the visual fields may also occur. Sometimes this causes the visual fields to begin to fall out. The main symptoms of retinal thinning include:
- decreased visual acuity;
- disorientation in a dimly lit room;
- dysfunction of the receptors that are responsible for twilight vision;
- color vision impairment;
- the appearance of a film and blurred vision.
Each patient experiences symptoms differently. If the disease appeared in childhood, it may develop slowly and not cause suspicion among parents. A small child will not be able to talk about what is bothering him on his own. Therefore, in order to avoid such consequences, it is necessary to undergo a scheduled examination by a doctor in a timely manner.
Main symptoms
If a person has a thinned retina, then he experiences the following clinical signs:
Redness of the organs of vision and dryness of the mucous membrane may be symptoms of the development of pathology.
- presence of black spots before the eyes;
- photophobia;
- lacrimation;
- headache;
- pressing sensations in the eye sockets;
- disturbance of general well-being;
- difficulty working with small objects and reading;
- inability to distinguish colors;
- sharp deterioration of vision in the dark;
- distortion of the shape of objects;
- redness and dryness of the eye mucosa.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis is carried out by an ophthalmologist. Initially, it is necessary to study the patient's medical history to exclude the presence of predisposing factors. After this, you should listen to the patient's complaints and conduct a visual examination. Often a person can talk about the presence of spots or films before the eyes. They can be located in different areas, depending on the location of the thinning. To establish an accurate diagnosis, the doctor uses the following diagnostic methods:
- ophthalmoscopy – allows you to study the condition of the fundus of the eye;
- measurement of intraocular pressure;
- visual acuity test;
- determination of the state of visual fields;
- tests for the perception and discrimination of colors and shades;
- Ultrasound;
- MRI and CT.
After a thorough diagnosis, the doctor can determine the cause and type of disease. This is very important, because the method and success of therapy will depend on it. It is also important to consult a doctor in a timely manner and not try to get rid of unpleasant symptoms on your own. Lack of treatment can lead to severe consequences. Doctors especially do not recommend self-medication with folk remedies.
Retinal diseases
According to etiology and pathogenesis, all retinal diseases are divided into several large groups:
- vascular disorders;
- inflammatory;
- dystrophic lesions;
- injuries;
- benign and malignant neoplasms.
The treatment of each retinal disease has its own characteristics.
To combat pathological changes in the retina, the following can be used:
- anticoagulants - Heparin, Fraxiparin;
- retinoprotectors - Emoxipin;
- angioprotectors - Ditsinon, Troxevasin;
- vasodilators - Sermion, Cavinton;
- B vitamins, nicotinic acid.
The drugs are administered parabulbarly (eye injections); eye drops are used less frequently. For ruptures, detachments, and severe retinopathy, laser coagulation, cerclage, episcleral filling, and cryopexy can be performed.
Inflammatory diseases are retinitis of various etiologies. Inflammation of the retina develops due to microbes entering it. If everything is simple here, then other groups of diseases should be described in more detail.
Vascular pathology
One of the most common vascular diseases of the retina is angiopathy - damage to vessels of different sizes. The cause of its development may be hypertension, diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis, trauma, vasculitis, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
Initially, patients may experience dystonia or vasospasm of the retina, later hypertrophy, fibrosis or thinning of the vessels develops. This leads to retinal ischemia, which causes the patient to develop angioretinopathy. In persons with hypertension, arteriovenous chiasm and copper and silver wire symptoms appear. Diabetic retinopathy is characterized by intense neovascularization—pathological proliferation of blood vessels.
Retinal angiodystonia is manifested by decreased visual acuity, flickering of spots before the eyes and visual fatigue. Arteriospasm can occur with high or low blood pressure and certain neurological disorders. In parallel with damage to arterial vessels, the patient may develop phlebopathy.
A common vascular pathology is central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO). The disease is characterized by blockage of this vessel or one of its branches, leading to severe ischemia. Central artery embolism most often occurs in individuals with atherosclerosis, hypertension, arrhythmia, neurocirculatory dystonia and some other diseases. Treatment of pathology should begin as early as possible. If medical care is not provided promptly, occlusion of the central retinal artery can lead to complete loss of vision.
Dystrophies, injuries, developmental defects
One of the most common malformations is coloboma - the absence of part of the retina. Macular (mainly in older people), central, and peripheral dystrophies are often encountered. The latter are divided into different types: ethmoid, fine cystic, frost-like, “snail trail”, “cobblestone”. With these diseases, defects resembling holes of different sizes can be seen in the fundus of the eye. Pigmentary degeneration of the retina also occurs (its cause is redistribution of pigment).
After blunt trauma and contusions, Prussian opacities often appear on the retina. Treatment of the pathology consists of the use of antihypoxants and vitamin complexes. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy sessions are often prescribed. Unfortunately, treatment does not always have the expected effect.
Neoplasms
A retinal tumor is a relatively common ophthalmological pathology – it accounts for 1/3 of all neoplasms of the eyeball. Patients are usually diagnosed with retinoblastoma. Nevus, angioma, astrocytic hamartoma and other benign neoplasms are less common. Angiomatosis is most often combined with various malformations. Treatment tactics for tumors are determined on an individual basis.
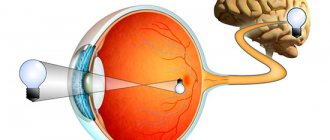
The retina is the peripheral part of the visual analyzer. It carries out photoreception - the perception of light waves of different lengths, their transformation into a nerve impulse and its conduction to the optic nerve. With lesions of the retina, people experience a wide variety of visual disorders. The most dangerous consequence of retinal damage is blindness.
Treatment
Treatment depends entirely on the type and degree of development of the pathological process. If a doctor diagnoses an advanced form of the disease, then it is impossible to restore vision and its quality. This is a difficult and irreversible process. In the initial stage of development, you can get by with taking medications. Basically, doctors prescribe drugs that tend to dilate blood vessels. Additionally, it is necessary to prescribe vitamin complexes and drugs to strengthen the vascular system of the whole body.
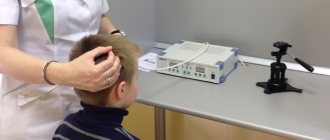
Doctors often prescribe the use of physiotherapeutic methods for treating such pathology. The following are considered effective:
- microwave and ultrasound therapy;
- laser coagulation;
- influence of electrical impulses.
In modern ophthalmology, laser treatment is mainly used. In addition, this type of therapy prevents the development of complications and other ophthalmological diseases. This type of treatment is also used by patients who have contraindications to surgery.
Treatment for thinning retina
Treatment of retinal dystrophy is carried out using various methods: drug treatment, physiotherapy, surgery. Often people turn to alternative medicine.
The main purposes of using drugs for thinning of the retina:
- prevent thrombosis;
- prevent the development of hypoxia;
- reduce the growth of blood vessels (abnormal);
- reduce vascular permeability.
For these purposes, drugs such as antiplatelet agents, angioprotectors, polypeptides, vitamin complexes (vitamins A, B and E are effective), vasodilators, etc. can be prescribed.
Treatment of such a complex and dangerous disease should be carried out exclusively by a specialist. Self-medication and ignoring the disease can lead to serious consequences.
At the initial stage of the disease, in addition to drug therapy, a therapeutic effect can also be obtained from the following types of physiotherapy:
- retinal stimulation (electrical and photo);
- magnetic therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- irradiation of blood with laser (intravenously).
The most effective method today is laser coagulation of the retina. The operation is performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia. Has a number of significant advantages:
- short duration of the procedure;
- short recovery period;
- efficiency;
- relative safety.
In some cases, other types of surgical intervention (including vitrectomy) are prescribed.
Treatment of retinal dystrophy with traditional methods at the initial stage is also possible, but as an auxiliary therapy and only with the prescription (permission) of a specialist.
Various decoctions are used for this:
- from goat milk and water;
- from pine needles, rose hips and onion peels;
- from celandine and water (purified).
It is also believed that hirudotherapy (treatment with leeches) has a certain effect. Their bite helps relieve inflammation, eliminate pain, increase immunity, cleanse toxins, and lower blood sugar and cholesterol levels.
Complications
The main complication is irreversible processes in the retina. This leads to impaired visual acuity. Sometimes images and objects may become distorted. Typically, such complications occur in the absence of proper and timely treatment. With proper treatment, retinal thinning rarely has serious consequences. With the help of laser coagulation you can get rid of this pathology.
It is important to consider that in old age, ophthalmological diseases are difficult to treat. Therefore, often against such a background, irreversible processes occur in the form of a decrease in the quality of vision. The congenital form of the disease is also difficult to treat. A person always has to take vitamin complexes and supporting medications for the visual organs. During prolonged exercise, it is recommended to use drops to prevent the development of dry eye syndrome.
How to treat thinning
Various methods are used to treat thinning.
Drug therapy
If necessary, the patient is hospitalized and treated in a hospital for 10 days. At this time, he receives a course of treatment with drugs that restore blood flow and improve blood properties. During treatment, patients, in addition to the ophthalmologist, are under the supervision of a cardiologist and a therapist. After treatment in a hospital, the patient undergoes a new examination.
Vitamins
For the treatment of retinal pathologies, vitamin complexes and mineral supplements are recommended. These supplements are necessary to improve retinal nutrition and curb the spread of pathology. The main preventative measures are taking vitamin complexes and mineral supplements (BAA).
Vitamin complexes that are used for retinal dystrophy
- The drug Napravit is used to treat inflammation of the vitreous body, lens and retina. This drug improves vision in the dark, reduces inflammation in the retina, strengthens blood vessels, improves eye nutrition, and reduces eye fatigue. The substances that make up Napravita are vitamins B2, B1, B6, A, C and P, zinc, eyebright and blueberry extract.
- Blueberry-Forte has a good strengthening effect. The drug is used for all eye diseases. The drug Blueberry-Forte contains large quantities of blueberries and zinc oxide.
- A general complex that significantly improves the functioning of all parts of the eye is Lutein. It has a very effective effect on the organ of vision during the recovery period after surgery, with severe myopia, age-related changes and with retinal dystrophy. Consists of beta-carotene, selenium, zinc, taurine, copper. It also contains blueberry extract, calendula petals, vitamins E, C and A.
- Another complex that contains lutein in large dosages. It is used for preventive purposes against diseases of cataracts and retinal degeneration with heavy eye strain. In addition to lutein, it contains zinc, zeaxanine, copper, tocopherol and vitamin C.
Vitamin complexes and vitamin supplements help improve the health of the eyes and the entire body as a whole. It should be used only as prescribed by a doctor, in order to avoid surprises caused by the specific characteristics of the body in the perception of certain components of the drug.
Forecast
The dry form of the pathology has a favorable prognosis. Wet can cause vision loss, especially if not treated promptly. It is also necessary to visit an ophthalmologist several times a year. Timely therapy always gives hope for a successful result.
If you ignore such manifestations, the prognosis may be disappointing.
In case of such diseases, it is strictly forbidden to put excessive strain on the eyes, especially in old age, when age-related changes occur in the body. Any stress in this case negatively affects the patient’s well-being and can provoke the development of unpleasant symptoms.
Forms of the disease
Macular degeneration (central retinal degeneration) is one of the most serious eye diseases, leading to complete loss of central vision. With this disease, a gray transparent spot first appears in front of the eye, which darkens over time and loses transparency, as a result of which the person cannot see the objects he is looking at. One of the reasons for the development of macular degeneration is high myopia.
Peripheral dystrophy is diagnosed during an examination of the fundus with special lenses. According to statistics, this disease in the vast majority of cases (40%) develops in people with myopia. Its main danger lies in the absence of symptoms at the development stage, so it is usually diagnosed by chance.
However, if the patient does not regularly visit the ophthalmologist’s office, and pathological processes begin to develop in the periphery of the retina, then due to retinal detachment, visual acuity will occur unexpectedly for the patient. Often people come to the ophthalmologist only when the retinal detachment has reached the central zone and there is an accompanying feeling of a veil before the eyes.
Depending on the location, peripheral and central retinal dystrophy are distinguished. With the first, the macula is thin and sparse closer to the edge of the eye, and the person experiences a narrowing of the visual fields. This condition occurs more often with myopia and traumatic injuries to the fundus. Central dystrophy is characterized by the appearance of scotomas or dark spots when looking at objects.
In the ophthalmologist's office, the patient can learn the causes and treatment of this disease. The type and degree of its development depends on the specific treatment option for retinal thinning. In advanced cases, it will not be possible to restore good vision. If the disease has just arisen, then medications and vitamins are prescribed, with the help of which you can strengthen the blood vessels. Also, physical treatment methods such as:
- Application of microwaves and ultrasound. Intravital measurements in the eyeball and its anatomical and optical elements are diagnosed. Ultrasound is prescribed as a complement to generally accepted clinical methods for diagnostic measures in ophthalmology. Sometimes an ultrasound is preceded by an x-ray of the eye.
- Use of laser, magnet. This method is considered relatively new in ophthalmology. Thanks to this method, you can get rid of the problem of poor vision once and for all and restore your vision to 100%.
- Effect of electrical impulse. Galvanization is effective; the method is used to increase or decrease the functions of eye tissues. The pain-relieving method is especially suitable after a person has suffered injuries related to the organs of the visual system.
As for preventive measures, these include special exercises for the eyes, a healthy diet, as well as an annual examination at the clinic. At the initial stage of the disease, it is necessary to drink a vitamin complex. Vitamins A, E and B can normalize vision, improve blood flow and fill the body with useful substances.
Medicines that are recommended for the treatment of thinning of the retina are prescribed exclusively by a doctor: No-spa, Retinalamin, Ascorutin, Methionine, Pentoxifylline, Lucentis. During pregnancy, many medications are prohibited, so you should not self-medicate.
Comprehensive treatment, which includes taking vitamins, medications, exercises, etc. It is recommended to use at least 2 times a year. Therefore, if the disease is severe or you were diagnosed too late, you may even be prescribed surgical intervention - be prepared for such an outcome.
You may be interested in: Which drops are best to choose to strengthen the retina?
Prevention
Preventive measures help prevent the development of various diseases. Because in any case, it is easier to prevent the development of pathology than to treat it. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is especially important. Doctors strongly recommend avoiding eating fried, fatty and unhealthy foods. You should also follow simple rules:
- stop smoking, drinking alcohol and drugs;
- sleep should be complete, loads should be alternated with proper rest;
- exercise;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- do not self-medicate;
- undergo a preventive examination by an ophthalmologist in a timely manner;
- do not spend long periods of time reading, using the computer, or watching TV;
- comply with industrial safety rules;
- Wear safety glasses in sunny weather.
If you constantly follow the rules of prevention, you can reduce the risk of developing ophthalmic diseases. It is also important to consider that as you age, you need to consume more vitamins and healthy foods to support visual acuity.
General symptoms of pathology
Regardless of the causes and classification, general signs and symptoms of the disease are identified. Among the most pronounced and widespread of them are the following:
- Narrowing of the visual field. The patient is able to distinguish objects located only in the central region of his visual field. At the same time, to determine the periphery, he has to turn his head. In the later stages, this symptom of retinal dystrophy transforms into so-called tunnel vision.
- Nyctalopia. With peripheral dystrophy, damage to the so-called rods is most likely, due to which night blindness or a significant deterioration in the quality of vision in the dark or at night progresses.
- The appearance of scotomas (colored and black spots). These defects may not be noticeable in the early stages, so their presence can only be determined with the help of specialized professional tools. In severe cases, severe image distortion is usually observed.
- Metamorphopsia. This sign is characterized by a change in the perception of the size of surrounding objects and their contours.
- Decreased visual acuity and quality (can occur symmetrically and asymmetrically);
- The appearance and progression of a veil, fog before the eyes;
- Optical effects, “flies”, flickering, “lightning”;
- Increased fatigue, rapid fatigue (eye fatigue is often observed constantly);
- Distortion of visual perception of objects and surroundings;
- Distortion of the perception of the color spectrum.
It is rarely possible to detect the disease in the early stages. As a rule, this practice is observed during routine examinations and accidental detection of retinal damage. As the symptoms of dystrophy progress, they become more pronounced and painful, the quality of vision and visual perception rapidly decreases without the possibility of full recovery. The chances of reversing the pathology without serious consequences become less when it is detected at later stages of development.
Laser method of treatment
Laser treatment is used for almost every eye ailment. The energy contained in the laser beam has a very effective effect on the affected areas. Considering the form of the disease, there are several laser treatment options.
A popular technique is laser beam stimulation of damaged areas. At the same time, the healthy retina area is not affected. As a result, the metabolic process is activated. The progress of the disease is slowed down for several years.
The second example of an operation using a laser is vascular coagulation. It consists of the following: the beam acts on the affected areas in such a way that the vessels whose structure is disturbed are separated from the healthy ones. As a result of the operation, a special insulator of the vascular system is formed, where nutrients do not enter. This method can stop the progressive pathology.
Laser treatment, reviews of which you can learn from those who have had such a diagnosis, is the most effective and popular method of improving vision. So, I liked one of the following reviews, which cannot be ignored:
Leah, 39 years old: “Hello everyone, I had a problem - thinning of the retina. I thought and pondered for a very long time how to overcome the problem. And after visiting an ophthalmologist, he suggested a laser method. Thanks to this intervention, I reduced the risk of retinal detachment. Fortunately, I came in at the first stage of the disease, so I did not lose my vision.”
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of chorioretinal dystrophy include the appearance of spots before the eyes, distortion of straight lines, the appearance of blind spots in the field of view, flashes of light, loss of clarity of vision, the ability to write and read.
At initial manifestations, fog may appear before the eyes, often in the form of a light or dark spot. Objects lose their brightness, letters in the book break and it is impossible to write and read. Curvature of surrounding objects; when walking, there is a feeling of a rising road towards you.
People usually discover that they are sick by noticing a loss of peripheral vision and the ability to navigate in dimly lit spaces. For some, vision is very weak; for others, the disease gradually leads to blindness.
Definition and classification of degenerative eye diseases
Various lesions of the lining of the eyeball are combined into a common type - degenerative-dystrophic cell damage. All types of dystrophy require different methods of diagnosis and treatment and are prescribed by an ophthalmologist after examination and diagnosis.
Surgical treatment methods are often used to treat dystrophy. This disease is still under research and for some types of eye diseases no effective treatment has yet been found.
There is congenital and acquired dystrophy. There are many reasons for this disease. People with diabetes and older people are at risk of degenerative eye disease.
The deposition of cholesterol plaques in the vessels increases the chance of getting retinal dystrophy in addition to other concomitant diseases. Therefore, to prevent diseases of the eye shell, you need a proper balanced diet.
There are three types of disease depending on the area of retinal damage.
- In case of damage to the retina in the central part, macular degeneration occurs.
- If only the outer parts of the retina are affected, then dystrophy has formed in the periphery of the eye.
- Generalized dystrophy affecting the entire visual apparatus.
Central
If central vision is affected, but peripheral vision remains unchanged, then the patient suffers from the disease of central retinal dystrophy. Objects that are directly in front of your eyes lose clarity, color and shape. Even in light twilight, the visibility of objects is completely lost. Sometimes dark or glowing spots appear before the eyes.
The appearance of these symptoms is an urgent reason to visit a doctor to determine the type of eye disease and prescribe treatment.
Central chorioretinal retinal dystrophy
REFERENCE. With chorioretinal dystrophy of the retina, the lesion concerns the pigment layer of the retina and the vitreous plate. In this case, the capillary layer of the vessels of the eye is affected.
Symptoms of chorioretinal dystrophy - bright glare flashes before the eyes, the shapes of objects are distorted, and blind spots appear in the field of vision. Vision noticeably deteriorates; unclear images of objects make it impossible to write and read.
For chorioretinal dystrophy, only an ophthalmologist prescribes concomitant treatment. Based on the examination, the doctor decides whether this will be drug treatment or, in advanced cases, laser or surgical intervention.
Macular (age-related) retinal degeneration
All older people undergo known age-related changes in the retina, which depend on the general physical condition of the patient. In this progressive eye disease, the central part of the retina is affected. Visual acuity invariably and gradually decreases. The process of loss of central vision is irreversible, but vision is preserved in the peripheral zones. There are two forms of this disease - wet (wet) and dry.
Dry form
The accumulation of cell breakdown products causes improper metabolism between the retina and the blood vessels of the eye. They accumulate under the retina and are deposited in microscopic piles. The most common form of the disease is dry and accounts for 90% of all cases of dystrophy. Vision deteriorates gradually and partial or complete blindness occurs.
Wet form
The most dangerous cases are when the dry form turns into a wet form. When new vessels grow, they penetrate under the retina. Fluid can pass through their walls under the retina. It is the wet form of dystrophy that has serious consequences for vision. Typically, vision deterioration occurs over several weeks or even several days. The process progresses quickly, and if left untreated, it can lead to complete loss of vision.
Peripheral dystrophy
The most dangerous group for peripheral dystrophy is people who have been myopic since childhood. With myopia, ocular blood circulation decreases, as the supply of oxygen and necessary substances to the eye deteriorates. For a long time, this pathology does not manifest itself with obvious symptoms.
The appearance of sparkling dots before the eyes serves as the first signal of dystrophy and impaired vision function. For early symptoms of peripheral dystrophy, conservative therapy is used. Severe degenerative changes require correction of the affected tissue areas with laser coagulation.
Lattice retinal dystrophy
Another type of peripheral dystrophy is lattice dystrophy. Reduced blood flow in the vessels of the eyes causes the progression of myopia. Retinal detachment is the most severe result in advanced lattice dystrophy.
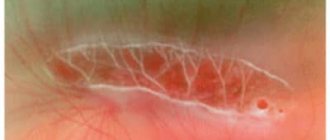
When examining a patient, a doctor may see signs of lattice dystrophy in the fundus. These are whitish-yellow fleecy stripes in the form of a lattice. Often the retina at the intersection of the vessels turns red due to thinning of the vessels. Pigmentation may change - reddish or pinkish stripes. Retinal cysts or tears may appear. Light or dark areas appear around the vessels.
Expert opinion
Kim Oksana Alexandrovna
Head of the ophthalmology clinic. Ophthalmologist with more than 10 years of experience.
As dystrophy progresses, the retina becomes thinner, and the resulting tension between the vitreous body and the retina deforms the membrane. This can lead to rupture and peeling of the retina if fluid gets under the retina. This type of dystrophy accounts for 65% of the total number of degenerative diseases. If the pathology begins in childhood or young age, then it progresses over time.
Peripheral retinal dystrophy of the “snail traces” type
“Snail trail” is a type of peripheral dystrophy that occurs with increasing myopia. Dystrophy is localized in the upper quadrant of the eye. Zones of liquefaction of the vitreous eye appear as whitish spots. The streak-like changes in the retina have a slight shine with numerous pinpoint thinning and defects in the form of holes. The name of the disease was received precisely because of its resemblance to the trail left by a crawling snail.