Retinal dystrophy resembling a “snail trail” is one of the peripheral diseases of the visual organs.
The main reason for the appearance of pathology is the rapid development of myopia against the background of changes in the vascular structure. The trace of a snail on the retina indicates that serious degenerative changes have occurred in the organ. If left untreated, they can lead to complete loss of vision. The causes of these disorders are not entirely clear, but possible factors include: inflammatory eye diseases; diabetes mellitus and atherosclerosis. This disease can occur at any age, so no one is immune from it.
Peripheral dystrophy - what is it?
The root cause of this pathology is vascular damage, resulting in the formation of whitish stripes in the periphery of the retina. This is clearly visible in the photo posted above.
This type of dystrophy got its name due to the fact that the damage to the retina is very similar to the mark left by the snail. As the disease progresses, the lesions connect, forming a ribbon-like pattern.
Typically, the “snail track” is localized in the upper outer region of the fundus, and a distinctive feature is the appearance of extensive round-shaped tears. Due to this, the risk of retinal detachment increases, which is much lower with other types of dystrophy.
Laser coagulation of the retina - operation PPLC
Laser coagulation of the retina is used for peripheral and central retinal dystrophies, vascular lesions, and some types of tumors. Also, laser coagulation of the retina prevents the development of dystrophies and prevents retinal detachment, and is effective in preventing the progression of changes in the fundus.
This type of treatment is the only one and has no alternative for changes in the retina, “lattice” retinal degeneration, dystrophy (“snail track”), for vascular diseases of the eyes, for example, diabetic changes in the retina associated with diabetes mellitus, thrombosis of the central retinal vein, angiomatosis , age-related macular degeneration, vascular pathology of veins (DRP, thrombosis).
Laser coagulation of the retina is an outpatient procedure. During treatment, local drip anesthesia is used. It is easily tolerated by patients of all ages and does not put stress on the heart, blood vessels and other organs. Laser coagulation of the retina takes about 15-20 minutes. After a short rest and examination by a doctor, the patient returns home, continuing to lead his normal lifestyle.
The principle of treatment using laser coagulation is based on the fact that laser exposure leads to a sharp increase in temperature, which causes coagulation (clotting) of the tissue. Thanks to this, the operation is bloodless.
The laser has very high precision and is used to create fusions between the retina and the choroid of the eye. During laser coagulation, a special lens is placed on the patient's eye. It allows radiation to completely penetrate the inside of the eye.
The surgeon has the ability to monitor the progress of the operation through a microscope.
- Strengthening the retina with a laser avoids opening the eyeball and occurs without contact, which eliminates the possibility of infection.
- Thanks to the peculiarities of laser treatment, the intervention is bloodless.
- This treatment does not require general anesthesia, which means the body avoids unnecessary stress.
- Laser treatment takes place in a “one day” mode; there is no recovery period as such.
Peripheral preventive laser coagulation of the retina
Peripheral preventive laser coagulation of the retina is a procedure for strengthening the peripheral zone of the retina, aimed at preventing the occurrence of retinal detachment.
Retinal dystrophy often leads to microtears in these areas and the appearance of retinal detachment, which is difficult to treat and can lead to irreversible vision loss.
PPLC helps prevent retinal detachment, thus preserving vision.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aIPQTq0j35U
The method of peripheral preventive laser coagulation is based on laser treatment of thinned areas of the retina. Using laser radiation, the so-called “pairing” of the retina is performed in weak spots, and adhesions of the retina with the underlying tissues are formed around the breaks.
The main goal of PPLC is prevention - reducing the risk of complications, and not improving vision. What kind of vision will be after surgery largely depends on whether there are concomitant eye diseases that affect the ability to see well.
This procedure is performed in 1 session, without hospitalization and in a “one day” mode, under local drip anesthesia. On the same day, the patient returns home, continuing to lead his usual lifestyle.
Indications for PPLC
As statistics from ophthalmic surgeons show, before undergoing laser vision correction, about 60% of patients need to strengthen the retina. The PPLC method has been used in medicine for more than 40 years, and currently ophthalmologists cannot imagine how they can do without this unique method.
Peripheral retinal dystrophy is one of the main reasons for denying pregnant women a natural birth and recommending a cesarean section. With moderate and high degrees of myopia, the retina becomes thinner and stretches. This increases the risk of retinal rupture and detachment during childbirth.
However, this problem is now being solved by strengthening the retina before birth using the PPLC method. After this procedure, the retina is strengthened and its stretching and detachment are prevented.
A timely PPLC procedure gives women with problematic retinas the opportunity to undergo independent retinal resolution.
Doctors recommend performing peripheral preventive laser coagulation before the 35th week of pregnancy.
Article rating: 4.6/5 (150 ratings)
Causes
According to statistics, in 40% of cases, retinal dystrophy is diagnosed in people suffering from myopia (myopia). With farsightedness, such a pathology occurs in only 8%, and with ametropia, the incidence rate is less than 5%.
Risk factors for the development of retinal dystrophy of the “snail track” type include:
myopia;- eye injuries;
- hereditary predisposition;
- inflammatory processes of the organs of vision;
- infectious lesions;
- diabetes;
- changes associated with cardiovascular diseases;
- general diseases of the body;
- intoxication;
IMPORTANT! A person with at least one of these risk factors should visit an ophthalmologist at least twice a year. The slightest symptoms of dystrophic disorders are a reason to sound the alarm.
If the patient says that he sees everything in a fog, it means that dystrophy has reached the central region of the retina. In this case, vision can only be saved through surgery. But even after it, the risk of developing blindness is quite possible.
Symptoms
Retinal dystrophy of the “snail track” type is peripheral in nature. It can be asymptomatic for a long time. However, over time, vision deterioration progresses, and it becomes difficult for a person to navigate in space. The narrowing of visibility occurs in a concentric manner and it is difficult for the patient to read. However, in the absence of refractive errors, central vision functions are preserved.
In isolated cases, the symptoms of a “snail trail” appear as:
- flying spots before the eyes;
- defects in visual perception in the form of scotomas.
If a person sees flashes of bright light spots, urgent surgical intervention is required. This symptom is dangerous and is the main sign of a retinal tear. This type of PVCRD is characterized by a unilateral course, whereas with lattice dystrophy both eyes are affected.
ARTICLES ON THE TOPIC:
- What causes a retinal tear? Consequences, symptoms and treatment of the disease
- What causes a macular hole in the retina: all about the symptoms and treatment of the pathology
- How dangerous is the disease peripheral retinal dystrophy of the fundus?
Types of disease and characteristic symptoms
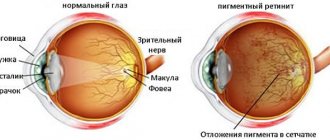
Depending on the location of the retinal lesion, the types of disease are distinguished: central and peripheral.
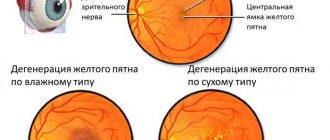
Central retinal dystrophy or macular degeneration
A disease accompanied by damage to central vision. As a rule, it develops in people whose age exceeds 55 years .
There are two forms of macular degeneration:
- dry form . Corresponds to the initial stage of the disease. During this period , visual acuity decreases , however, the patient does not feel this.
- wet form . If the disease was not diagnosed in time, then the dry form of dystrophy is transformed into a wet one. This indicates the development of the disease, the new stage of which is characterized by the fragility of the blood vessels of the eye and their predisposition to fragility. As a result, hemorrhages occur in the eye.
The main symptoms of central retinal dystrophy include:
- decreased central vision (distortion of the contours of objects and lines occurs);
- sensitivity to bright light;
- the formation of a dark spot, making it difficult to read, drive a vehicle and work with small objects;
- distorted perception of colors.
If you often spend time in front of a computer monitor, this can cause red eyes. Rest your eyes often.
Remedies for stye on the eye can be purchased at your nearest pharmacy. Read how to properly treat stye here.
Controlling eye pressure can save your vision https://help-eyes.ru/zabolevanie/glaukoma/glk-lechenie-glaznogo-davleniya.html
Peripheral retinal dystrophy
In this situation, destruction of retinal tissue . In this case, disturbances occur in the vascular system of the eye. As a result, the patient's visual acuity gradually decreases.
The early stages of the disease are very difficult to diagnose due to the lack of symptoms. The danger of the disease lies in the fact that it is not always detected during a routine examination by an ophthalmologist. , retinal detachment may occur over time .
Often the disease does not manifest itself in any way and is asymptomatic . Pathology can only be detected through a thorough examination by an ophthalmologist. Among the main symptoms of the disease are retinal breaks, dark “spots” in front of the eyes and flashes of light.
Despite the fact that there are many classifications of peripheral dystrophy, however, the main ones are distinguished.
Depending on the extent of the disease:
- chorioretinal - the retina and membrane vessels are damaged;
- vitreochorioretinal - the retina, membrane vessels and vitreous body are damaged.
Based on the nature of the damage:
- ethmoid - has a hereditary nature, the disease affects mainly men . The pattern of the disease resembles a grid and develops in both eyes. As a result, it may cause a retinal tear;
- “snail trail” - lesions form ribbons that resemble a snail trail. May lead to retinal rupture;
- frost-like - inherited, formed in both eyes. Yellowish-white spots are observed in the retina;
- “cobblestone pavement”—foci of the disease are located in distant areas of the retina. The pigment comes off in pieces;
- small cystic – a feature of the disease in the presence of small cysts. Formed as a result of eye injury;
- retinoschisis – separation of the retina. Typically typical for older people.
Diagnosis of pathology
The main danger of the “snail trail” is that in the absence of symptoms, the disease actively progresses. It is often discovered by chance during a routine examination. Patients with a history of risk factors are prescribed a detailed examination.
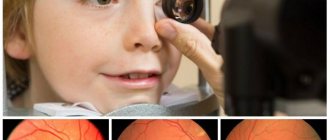
A complete diagnosis of retinal dystrophy is carried out using a three-mirror Goldmann lens. Before the examination, the ophthalmologist instills a drug into the patient's eyes that dilates the pupils as much as possible. This allows you to view the most distant areas of the retina.
Sometimes sclerocompression (a method of pressing the sclera) is used, which consists of the following: the retina moves from the periphery to the center; those areas that were previously invisible are visible.
Detailed diagnostic methods include:
Ophthalmoscopy. Dystrophy of the “snail track” type is formed in the upper outer quadrant of the central part of the eye. The affected areas of the retinal vessels form intermittent white streaks.- Perimetry. This method helps to determine the concentric narrowing of the patient’s field of vision.
- Visometry. This method is indispensable for diagnosing decreased peripheral vision against the background of normal central vision.
- Refractometry. Used to identify patients at risk.
- Ultrasound. Ultrasound radiation makes it possible to notice the first manifestations of retinal dystrophy. Changes in the vitreous body, the presence of tractions and adhesions are diagnosed. The size of the longitudinal axis of the eyeball is visible.
REFERENCE. the peripheral region of the retina is practically not visible during a standard fundus examination. However, it is there that degenerative processes appear, causing retinal detachment and rupture.
In the international classification of diseases ICD-10, retinal diseases are defined by code H35.
Diagnostics
To diagnose retinal dystrophy, the following examinations are necessary:
- Visual field examination;
- Study of color perception;
- Visual acuity testing;
- Fundus examination using a Goldmann lens;
- Fluorescein angiography (examination of eye vessels);
- Ultrasound and electrophysiological examination of the eyes;
- Tests to determine the state of the body's metabolism.
Read about where optic nerve atrophy can be cured.
Treatment
Dystrophy of the “snail track” type can only be eliminated with a laser, especially if there is retinal detachment. In order to stop the progression of the disease in time, you need to regularly visit the ophthalmologist’s office. This will help the doctor timely identify the initial signs of degenerative disorders and monitor their dynamics.
In most cases, laser coagulation provides a lasting positive effect, and the risk of postoperative complications is low. It is performed in a clinical setting using local anesthesia.
This procedure isolates damaged areas of the retina to prevent them from spreading to healthy tissue. In some cases, repeated laser coagulation is prescribed in order to consolidate the result.
Prevention of complications
Prevention of undesirable consequences significantly reduces the risks of retinal detachment and rupture. Prevention includes timely detection of possible occurrence factors. If they are present, then you should be regularly examined by an ophthalmologist in order to determine the onset of peripheral dystrophy if something happens.
To avoid serious complications, patients must be extremely attentive to their health. It is advisable to check the condition of the retina at least twice a year. This is especially true for expectant mothers who are indicated for fundus examination at the beginning and end of pregnancy. A postpartum examination by an ophthalmologist is necessary.
Also at risk are children born as a result of a difficult pregnancy. Therefore, even in a child, degenerative changes in the retina are corrected with a laser to reduce the risk of developing blindness.
Patients with a history of prerequisites for the development of snail-trace dystrophy are prescribed special courses of vitamin and vascular therapy. This is done to improve eye blood circulation.