What is laser vision correction
Human vision is the means by which we receive information from the environment.
Moreover, more than 80% of information perception occurs through the eyes, so any even slight visual impairment causes significant discomfort. The human eye is a complex mechanism. Light rays passing through the cornea, lens and vitreous body are naturally refracted and reach the retina. Afterwards, the signals are transmitted via the optic nerve to the brain, processed in its corresponding zone - and the person receives a clear image. With myopia and farsightedness, light rays are focused not on the retina, but behind or in front of it, and the picture turns out blurry.
The goal of any vision correction is to change the refractive power of the eye so as to “collect” the rays precisely on the retina. It is for this purpose that people wear glasses and contact lenses. However, these correction methods provide good vision only for the time they are used and do not relieve a person from the problem of poor vision.
Laser vision correction or refractive surgery is a medical procedure using modern laser technologies to correct the following diagnoses:
- myopia (nearsightedness);
- hypermetropia (farsightedness);
- astigmatism.
Unlike glasses or contact lenses, laser correction radically solves the problem of poor vision, and no additional devices will ever be needed to see perfectly.
Hygiene procedures
It is important to prevent water from getting into your eyes for the first week. In the shower, you should turn your back to the pressure and stand one step further than usual. In this position, you need to lean back, and then less water gets on your face, and the shampoo will flow past your eyes. If shampoo or other hygiene product gets on the mucous membrane, do not rub your eyes. For rinsing, you need to use refreshing drops to relieve the burning sensation and prevent burns.
Do not allow tap water to get into your eyes, as this can cause inflammation and affect the results of the operation. Water from swimming pools and natural bodies of water is also dangerous.
Vision correction methods
In general, the following types of visual acuity correction are used in medicine:
- Spectacle correction is all types of glasses that can increase the acuity or improve the quality of a patient’s vision. Nowadays, there are many materials and filters used to make spectacle glasses.
- Contact correction - contact correction is the correction of vision using contact lenses that are placed directly on the surface of the eyes.
- Surgical correction - surgical vision correction includes all surgical interventions that will ultimately help the patient see better. Most often, such manipulations are necessary for various diseases.
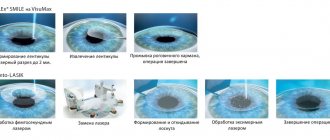
- Laser vision correction differs from conventional surgery in that there is no direct contact of any instruments with the eye. All manipulations are performed using a directed laser beam. The three most common types of laser vision correction are photorefractive keratectomy (PRK), LASIK and ReLEx SMILE. Their main difference is in the methodology and scope of application of the tools:
1. PRK (PRK) - the effect is performed directly on the outer surface of the cornea;
2. LASIK (Laser keratomileusis) - influence on the internal layers, which are previously exposed by a tangential cut of a surgical instrument and bending the resulting valve; 3. ReLExSMIL on the inner layers, but without forming a valve. The principles of PRK and LASIK, in fact, are not competing, they even complement each other. It is customary and more expedient to perform operations to correct myopia and complex astigmatism associated with myopia using superficial methods such as PRK; the correction of other refractive errors is more effective when using valve technologies, that is, LASIK.
Limitations on physical activity
Laser vision correction is a reason to avoid intense physical activity during the period of complete restoration of the visual system. As a rule, this process takes a month, but it is better to consult a doctor on this issue. During the rehabilitation period, you cannot go to the gym, dance, yoga, fitness, Pilates or jogging. To be completely safe, it is best to give up football, tennis, boxing, wrestling, scuba diving, diving and team sports for a year.
Restrictions on various types of activities:
- Running – 2 weeks.
- Aerobics – 1 week.
- Yoga and Pilates – 1 week.
- Strength exercises – 2 weeks.
- Swimming – 1 month.
- Football – 1 month.
- Non-contact martial arts – 1 month.
- Sauna, steam room – 1 month.
- Snowboarding and skiing – 1 month.
- Squash, cricket, tennis – 1 month.
- Rugby, contact martial arts – 1.5-3 months.
- Scuba diving – 3 months.
When playing sports, you need to protect your eyes from sweat. To do this, you should wear a bandage. After laser correction, it is not recommended to throw back your head, bend over sharply, or lift heavy objects.
It is better to plan a pregnancy six months after laser correction. Hormonal imbalance and subsequent childbirth can affect the results of vision correction.
Laser correction for various visual impairments
Hyperopia, also known as farsightedness, is a condition of the organs of vision in which the image is focused in the plane behind the retina, and not on it. As a result, all objects become blurry. Hypermetropia can occur at any age.
What unites age-related and normal farsightedness is the fact that it is difficult for a person to focus vision on an object nearby: the image “floats”.
Laser correction is an effective way to restore vision in mild to moderate farsightedness, which will allow you to forget about glasses or contact lenses for many years.
Advantages of laser surgery:
- rapid recovery - 1 - 2 days after surgery;
- minimal restrictions after surgery;
- preservation of the corneal structure;
- no wounds;
- minimum pain - 2 - 3 hours after surgery;
- laser correction of farsightedness provides stable results and a lasting refractive effect;
- It is recommended to treat farsightedness in both eyes at once;
- absence of corneal opacification in the postoperative period;
- the ability to correct high degrees of farsightedness, including astigmatism.
Myopia or simply myopia
- This is a violation of refraction - the refraction of light in the eye. As a result of the disease, an image is formed in front of the retina; in order to focus on an object, a person needs to hold it directly in front of his eyes. Myopia can be congenital or acquired, and usually worsens with age.
Surgeries for myopia are classified as cosmetic. This means that there are no absolute indications for their implementation; it all depends on the patient’s desire, his desire for comfort and refusal to use glasses and contact lenses.
Advantages of laser surgery:
1. Safety—observations of patients have shown that this type of intervention is safe and very effective. 2. Possibility of use for various eye diseases - if patients have no contraindications, laser treatment will help restore good vision in many eye diseases. 3. Speed of the operation—the duration of the procedure is no more than 15 minutes. 4. Painlessness—the patient only feels touch during the operation. 5. Stable results - provided the patient does not have progressive myopia, the correct shape of the cornea after laser correction will remain for many years.
Astigmatism
- a common visual impairment caused by congenital changes in the shape of the cornea. Astigmatism occurs due to deformation of the two main meridians of the eye - vertical and horizontal. The refractive power along the main corneal axes determines the type of astigmatism:
- Direct astigmatism - the maximum refractive power is observed at the vertical meridian.
- Reverse - occurs when the greatest refraction occurs in the region of the horizontal axis.
- Astigmatism with oblique axes - due to deformation of the cornea, the main meridians do not coincide with the horizontal and vertical axes of the eyeball.
Surgeries for astigmatism using laser energy have now become popular. Such methods allow treatment to be carried out as quickly as possible and with the least likelihood of side effects. The benefits of laser intervention are the same as for myopia and farsightedness.
Possible complications after surgery
Despite the detailed study of all stages of the operation and the predictability of the results, risks of complications of laser vision correction exist, although they are minimized. Many years of application experience serves as proof of this.
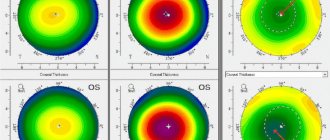
It is important to understand that different modifications of laser treatment for refractive errors have certain indications - specific numbers of myopia, farsightedness or astigmatism for which the operation will be effective. Serious impairments in visual acuity can cause insufficient correction as a result of manipulation - ophthalmologists always warn patients about this at the stages of preoperative consultation.
Also, if there is a significant deviation of the patient’s vision before surgery from normal refraction and the thickness of the cornea is insufficient for full correction, the laser ophthalmic surgeon will warn about residual myopia or farsightedness after surgery. In this case, the patient will have to additionally wear glasses. However, they will require thinner lenses; in some cases, doctors may allow you to do without them altogether and use them for distance viewing and, for example, for driving a car, in cases where maximum vision is required. In any case, this is better than complete dependence on corrective glasses and limited choice of frames due to the thickness of the lenses.
It is important to know that the optimal age for laser correction is considered to be 18-45 years old. It has been proven that until adulthood, the human visual system is imperfect, and indicators of visual acuity impairment may change. After 40-45 years, age-related changes in the eye begin - presbyopia occurs, vision problems when working at close range, the development of which is not affected by eye surgery.
The main negative consequences of laser vision correction that are feared after surgery are:
- Unpredictable changes in visual acuity.
The state of the visual system after correction is predictable - vision subjectively improves immediately, and after a few weeks it fully reaches the expected levels, and the result is permanent. Regression is often associated with non-compliance with the postoperative regimen by the patients themselves. An important factor in maintaining the result for many years is the stability of vision before surgery. The patient must be sure of this and provide data to the surgeon for at least the last year. This could be an ophthalmology report or a prescription for glasses or contact lenses. - Dry eye syndrome.
Changes in the integrity of the cornea, damage to nerve endings or tear ducts can lead to temporary unpleasant symptoms - burning, stinging, and a feeling of dryness in the eyes. Treatment involves the use of drugs - artificial tears. However, these recommendations apply to almost everyone who works for a long time at a computer or in an office with “dry” air. - Photophobia.
Discomfort when looking at brightly lit objects during the rehabilitation period is a normal reaction, but after some time the symptom should stop bothering you. Long-term persistence of such unpleasant sensations is considered a complication of laser vision correction. With such complaints, you should definitely contact an ophthalmologist for advice. - Edema.
Surgical intervention disrupts the constancy of the internal environment of the organ of vision and can cause the development of swelling, redness and other subjective unpleasant sensations. - Increased intraocular pressure.
Any violation of the integrity of the eye tissues can lead to disruption of the normal processes of formation of intraocular fluid, its outflow and is a slight stress for the eye. - Retinal damage is completely excluded.
The laser beam affects only the cornea and does not reach the retina and does not cause damage. - Excessive thinning of the cornea.
In some cases, when the surgeon takes a certain risk, taking on a patient with too much myopia for surgery or an insufficiently accurate diagnosis was carried out, keratoconus may occur. The use of a modern femtosecond laser and precise keratotopograph virtually eliminates this possibility. - Infectious processes.
Keratitis, conjunctivitis, intraocular inflammatory processes are possible complications of laser vision correction, to prevent which special anti-inflammatory drops and medications are prescribed immediately after correction. - Impaired twilight vision
– deterioration in the perception of surrounding objects in low light conditions, halos around light sources, “halo” effect. Characteristic in cases of correction of high degree refractive errors, in the vast majority of cases they disappear within 6 months after surgery.
Indications and contraindications for laser vision correction
Surgery for deviations from normal vision is prescribed in the following cases:
- degree of pathology from 3 diopters;
- mixed astigmatism with farsightedness;
- inability to wear contact lenses and glasses.
Surgical intervention is not prescribed:
- children under 18 years of age and adults over 45 years of age;
- patients with only one visual organ;
- for infectious and psychological diseases;
- in case of oncological pathologies;
- during breastfeeding and childbearing;
- for diseases of the cardiac and endocrine systems;
- with diabetes mellitus.
Important! For patients who are not eligible for laser surgery, alternatives are offered, such as lens implantation, tangential and arcuate keratomy, refractive lens replacement, and other surgical options.
Contraindications for surgery
There are several contraindications in which surgical intervention using a laser is prohibited or not recommended:
- certain working specialties (pilots are sometimes prohibited from such operations);
- engaging in extreme and traumatic sports that can cause head injuries (martial arts, football, hockey and others);
- diseases and conditions that affect the operation process;
- reduced immunity (increases the risk of complications);
- pregnancy (affects vision clarity);
- diabetes mellitus (affects vision clarity)
- taking steroids;
- eye diseases (glaucoma, inflammatory processes, keratoconus, herpes infection)
- previous eye surgery.
Laser surgery and patient age
The permissible minimum age at which laser vision correction can be performed is 18 years. If the procedure is carried out earlier, the result will not be final, since in children the eye tissues go through a developmental stage and the refractive properties of the corresponding elements of the eye gradually change, reaching a stable position by about 18 years.
After 45 years, people experience age-related hardening of the lens, which becomes increasingly difficult to adapt to optical conditions, and the muscles that hold it weaken, and the eye loses the ability to focus. This means that, starting from the age of 45, all interventions are performed after a thorough diagnosis and for serious indications. Doctors generally do not recommend any surgery to improve vision for people over 55 years of age.
Permissible eye strain
It is important to dose visual stress. You should not overwork yourself with reading, rub your eyes, put pressure on them or squint too much. Depending on the extent of laser correction, the patient may have difficulty reading small print. This phenomenon should not be a cause for concern as it will disappear within a few weeks.
Patients over 45 years of age may need glasses for presbyopia. Additional correction for age-related changes in vision is needed only for certain types of activities. These are usually activities that require good near vision.
You can watch TV on the first day, but it’s better to focus on your feelings. For complete comfort, you can close your eyes. When using technology with displays, you should take breaks every 45 minutes. After surgery, prolonged concentration of vision greatly tires the eyes for the first 3 weeks, which can cause various disorders.