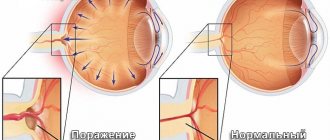
What is ophthalmotonus
Ophthalmotonus is the pressure exerted by the internal contents of the eyeball on the membrane of the eye. The characteristics of ophthalmotonus are determined by the following parameters:
- hydrodynamics of the internal environment of the eyeball,
- filling level of orbital vessels,
- parameters of the vitreous body and lens,
- level of rigidity of the outer membranes of the eyeball.
Over the course of the day, the degree of elasticity of the eyeball changes.
Increased intraocular pressure
What is tonometry, and why is it necessary to regularly check the pressure inside the eyes? Increased pressure leads to the death of the optic nerve, that is, to blindness. The structure of the eyeball includes fluid, which is in constant motion - inflow and outflow. Correct hydrodynamics ensure stable ophthalmotonus. Fluid retention inside the eyeball leads to increased pressure.
Every person can experience increased blood pressure: this happens during eye strain, an attack of hypertension, or during a stressful situation. However, this is a short-term phenomenon that subsequently passes.
Constantly increased ophthalmotonus disrupts the functioning of the optic nerve, putting additional stress on it. This leads to disruption of the blood supply to the visual organ and to the development of pathology - glaucoma.
Symptoms of high blood pressure are the following deviations: blurred image of objects, feeling tired when reading, redness of the eyeballs, pressure radiates to the temporal region.
With the initial degree of glaucoma, the patient notes a slight decrease in visual acuity. The danger of the disease lies in irreversible changes leading to loss of visual function. In addition to loss of vision, the patient experiences severe pain, so the affected eye must be removed.
Decreased ophthalmotonus
This pathology is less common than high blood pressure. The reasons may be the following factors:
- eye injury,
- dehydration,
- eye surgery,
- inflammation of the eyelids, eyeball,
- renal failure,
- low blood pressure,
- anatomical deviations in the structure of the eyeball.
Characteristic symptoms of decreased ophthalmotonus are: a feeling of dryness in the eyes and loss of shine, eyeballs sinking into the orbit. Reduced ophthalmotonus can lead to atrophy of the eyeball.
Tonometry procedure
Intraocular pressure provides the visual organs with density and elasticity, which is of paramount importance for the proper functioning of the eyes. Ophthalmotonus coordinates the dynamics of the waxing and waning of the fluid medium in the cavity of the eye chambers. It is this characteristic that the tonometry procedure evaluates. The examination is carried out using an ophthalmological instrument - a tonometer. The measuring unit for intraocular pressure is the millimeter of mercury.
Indications for examination:
- patients over 40 years old,
- detection of glaucoma,
- retinal detachment,
- postoperative examination,
- anatomical defects of the eye.
Tonometry is also prescribed for other diseases, namely: neurological pathologies, disorders of the cardiovascular system, endocrine pathologies.
Methods of conducting the examination:
- palpable,
- contact,
- contactless.
The palpation method is measuring pressure using your fingers. Contact and non-contact methods are carried out using hardware technology.
Contactless method
Non-contact tonometry is based on diagnosing pressure using a pneumotonometer. A stream of air is directed onto the eyeballs, under the influence of which the corneal layer bends. The characteristic of the resistance of the eyeball shows the level of ophthalmotonus. This is one of the most gentle diagnostic methods, which is used for continuous examination of patients, including children. No anesthetic is required for pneumotonometry.
Advantages:
- no contraindications to the procedure,
- no need for anesthetic,
- comfortable state of health of the patient,
- accuracy of the results obtained.
Flaws:
- readings are often underestimated,
- not used to evaluate patients with glaucoma.
The non-contact method eliminates infection in the eye sockets. The patient opens his eyes wide, focusing his gaze on the luminous point. At this moment, the device directs intermittent air currents that act on the cornea. Indicators of corneal changes are displayed on the monitor in numbers.
Contact method
The contact diagnostic method is carried out using different methods:
- palpable,
- applanation,
- dynamic contour,
- impressive.
Palpation
Palpation tonometry is an old diagnostic method that gives fairly accurate results. The method is used in the absence of special equipment, for example, in extreme conditions at the scene of an incident or in the postoperative period. The patient sits on a chair, closes his eyelids and lowers his eyeballs down. The determination of eye pressure is carried out literally by touch - the ophthalmologist lightly presses on the eyeballs, determining the density according to his sensations.
The result is determined by the following sensations:
- soft eyeball - hypotension,
- very soft eyeball - pathology,
- dense eyeball - moderate pressure,
- very dense eyeball - high blood pressure,
- stone eye - pathology.
Such diagnostics can only be carried out by an experienced ophthalmologist.
Applanation
Applanation tonometry can be performed using Maklakov cylinders or a Goldmann tonometer. Tonometry according to Maklakov is a widely used method for diagnosing intraocular pressure in our country. For children, an Icare or Schiotz tonometer is more often used, with the help of which a painless and quick examination is carried out.
Note! Each diagnostic type has its own values, so comparison of results is not correct.
Maklakov method
How is an examination performed using Maklakov cylinders? Before the procedure, a special anesthetic liquid is instilled into the eyes. Next, a weight with a dye is placed on the eye and an imprint is made on paper. The smaller the print on the paper, the more elasticity there is in the eyeball. This has a direct dependence on the degree of ophthalmotonus of the eyeball: the harder it is, the less susceptible it is to the pressure of the weight. The dye does not need to be washed off; it will flow out along with the tears.
Note! Since pressure readings vary throughout the day, examinations are carried out in the morning, afternoon and evening hours. Daily tonometry provides the most accurate diagnostic result and is able to detect glaucoma at the initial stage of formation.
Advantages:
- accuracy and reliability of the results,
- used everywhere.
Flaws:
- discomfort when touching the corneal cylinders,
- painful procedure,
- requires certain medical skills,
- allergy to anesthetic or dye.
Also inconvenient is the need to keep your eyes wide open. The technique has been used in ophthalmology since 1884.
According to Goldman
Goldmann tonometry is performed using a slit lamp and probe. Before the procedure, an anesthetic is instilled, then an application of paint-soaked paper is applied to the eyes or colored drops are instilled. Next, a stream of bright light is directed using a slit lamp. The pressure is checked using a probe that applies pressure to the eyeballs.
Impression tonometry
Impression electron tonometry is based on scanning the corneal layer. The ophthalmologist touches the cornea of the eye with the apparatus, and the characteristics of the eyeball are displayed on the monitor.
Electronic scanning is carried out as follows. The ophthalmologist holds the scanner to the eye, and the person must read the text written on the device. After this, the device displays the scanning result on the panel.
Methods for measuring intraocular pressure
Non-contact tonometry is a computer measurement, the principle of which is based on the reaction of the cornea under the influence of air flow. This takes into account the degree and rate of change in the cornea. The non-contact method is the most gentle and non-traumatic, there is no direct contact with the eye and no painful effect for the patient, and there is no risk of infection. The procedure takes a few seconds, no preparation of the patient is required, and he does not feel any discomfort.
Applanation tonometry is a measurement of intraocular pressure based on the Amber-Fick law. According to this law, internal pressure is defined as the ratio of external force and the size of the area of influence.
Impression tonometry - indentation of the cornea with a rod with a rounded end. The method is mainly used for increased V.D. and for measuring pressure when the surface of the cornea is curved, when it is impossible to capture a large area.
Dynamic contour tonometry is a contact tonometry method based on measuring intraocular pressure along the contour of the cornea. A probe with an integrated pressure sensor based on integral sensitive elements made of single crystals is placed in the central part of the cornea. The force of pressure of the probe on the cornea is constant. The sensor records eye resistance and receives up to 100 results/sec. Based on these data, the measurement result is displayed.
Non-contact tonometry
Contact tonometry
Preparing for the examination
First of all, it is worth recalling that not all patients undergo eye tonometry.
Contraindications include:
- bacterial/viral infections,
- violation of the integrity of the eyeball,
- pathology of the corneal layer,
- severe myopia,
- performed laser correction,
- psychical deviations.
Before diagnosis, you should not drink a lot of fluids, drink alcohol on the eve of a visit to the ophthalmologist, or consume any drugs containing drugs. Patients should wear glasses instead of contact lenses, since after the procedure they should not touch the cornea of the eyes for several hours.
Clothes should be spacious so that the neck does not compress the jugular vein. Any disturbances in blood circulation will negatively affect the diagnostic results. In addition to the recommendations listed, eye tonometry does not require special preparation. Accordingly, women are not recommended to dye their eyelashes and eyelids.
Measuring intraocular pressure - which method is better?
Intraocular pressure (IOP) is the pressure of the fluid inside the eye. The procedure for measuring IOP is called eye tonometry and is included in the mandatory set of vision tests for people over forty years of age. It is from this age that a person is at risk of developing glaucoma. In this case, the danger is increased IOP. In order to timely monitor the development of the disease, it is necessary to conduct tonometry of the eye at least once a year. Today, several methods are presented, but we will consider in the article whether there is the most effective one among them.
Measuring intraocular pressure
Bottom line
Ophthalmological diseases have become the norm of modern society. Poor lifestyle and nutrition, prolonged exposure to a monitor screen and lack of proper rest negatively affect eye health. The situation is aggravated by the uncontrolled use of medications; the use of various dietary supplements from unknown manufacturers has a detrimental effect on the visual organs.
Iphthalmotonus is measured by the degree of resistance of the cornea to pressure, studying the degree of compliance and the rate of restoration of shape. To do this, use weights or a jet of compressed air. These methods provide the most accurate characterization of intraocular pressure, compared to electronic scanning and palpation method.
What should be the normal level of intraocular pressure? The maximum result occurs in the morning after waking up. The pressure index changes with age and tends to increase. Normal pressure shows 10-21 mm of mercury; exceeding the value indicates a deviation.
Regular preventative examinations with an ophthalmologist will help avoid the development of serious eye diseases. However, it should be remembered that glaucoma can only be detected using a hardware method that allows determining the state of ophthalmotonus. The most reliable results are obtained using daily tonometry, which takes into account pressure parameters at different times of the day.