Pressing headaches in the eyes and temples are a common companion for office workers. During the next attack, it is difficult for them to read, especially if the text is written in small print, and in general any attempts to focus their vision on the flickering monitor screen seem unbearable. The easiest way to explain this condition is by banal fatigue, but not everything is as simple as it seems at first glance. The cause may be increased intraocular pressure, and if this diagnosis is confirmed at an appointment with an ophthalmologist, then neither rest nor eye exercises will solve the problem. You need to take measures and drops, and do it as soon as possible - the risk of developing glaucoma at this stage is already very high.
What's pressing on your eye?
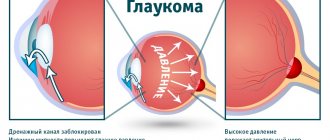
The structure of the eye has a complex structure, but it is not necessary to study it all in detail to understand what intraocular pressure is and why it suddenly deviates from the norm. It is enough to imagine the eye as a liquid surrounded by multiple membranes. The outer one is the sclera, behind it is a network of blood vessels, and even deeper is the ciliary body. When the muscles contract, the shape of the lens changes and the person can see something up close. But this is not the only function of the ciliary body.
Another important task assigned to it is the secretion of intraocular fluid. By circulating between the various chambers of the eye, it ensures normal metabolism and maintains a certain level of intraocular pressure (IOP). In other words, the fluid secreted by the ciliary body constantly puts pressure on the eye, setting the parameters of its normal size and shape. As soon as the amount of this fluid increases excessively or there are problems with its outflow, the pressure will jump. This will entail distortion of the shape, and, consequently, of the entire optical system of the eye.
Important! Intraocular pressure directly affects the quality and acuity of vision. When it deviates from the norm, the shape of the eyeball changes and the mechanisms of accommodation that allow close vision are disrupted.
Normal blood pressure and pathology
Intraocular pressure may fluctuate slightly depending on what time of day the test is performed, but in general it is a constant value. In the morning, intraocular pressure may jump by 2-3 marks. Most likely, the reason lies in the horizontal position of the body, slowing of the pulse and breathing, as well as the predominance of the parasympathetic nervous system during sleep. By evening the pressure gradually drops.
Normal intraocular pressure ranges between 10 and 21 mm. Hg column, although much depends on how the measurement is carried out. These numbers are the limit of true pressure, but if you try to determine it using a tonometric method, the norm will be different - from 12 to 25 mm. Hg Art. That is, it is simply not correct to compare indicators obtained by different methods.
Important! In domestic ophthalmological clinics, the method of the Russian researcher Maklakov is used to measure intraocular pressure. According to it, normal intraocular pressure is that which is below 26 mm Hg, from 27 to 32 mm Hg. Art. – moderately elevated, more than 33 mm Hg. - a reason to take action.
Treatment of high eye pressure
Treatment of eye pressure requires careful diagnosis. To normalize the situation, eye drops are mainly used.
Modern pharmacology offers several types of such drugs, depending on the principle of their action and the complexity of the disease.
- Drops to reduce eye pressure in glaucoma.
- Drops for localizing inflammatory processes (conjunctivitis, blepharitis) - antibacterial drugs;
- Moisturizing eye drops after a long stay at the computer.
In addition to drops, drug treatment is prescribed using tablets, a special set of exercises, vitamin preparations, and Sidorenko glasses. Along with medication and physiotherapeutic treatments, doctors suggest the use of traditional medicine.
Measurement according to Maklakov
- The patient lies down on the couch, and the doctor administers anesthesia by instilling several drops of dicaine into each eye in turn.
- Then the head is fixed and asked to look at one point.
- A small weight treated with special marking paint is carefully lowered onto the open eye, under the pressure of which the eyeball should be slightly deformed.
- Now the weight is lowered onto a sheet of paper to see how much paint is left on it. Intraocular pressure is determined by the intensity of the imprint.
- The procedure is repeated again in both eyes to avoid the possibility of misinterpretation.
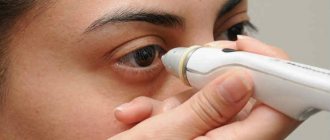
Naturally, some amount of paint from the load will remain on the surface of the eyeball, but it will quickly be washed away with tears. Instead of weights, ophthalmologists sometimes use a portable device that looks like a ballpoint pen. They also apply pressure on the eye, having previously treated the eyeball with an anesthetic.
This method also has an alternative – non-contact tonometry. No weights are placed on the eye, but instead a controlled air flow is used. Many patients find this method more acceptable, but in reality it is rarely used - it is not as accurate.
Important! In patients with glaucoma, eye pressure fluctuates much more noticeably throughout the day than in healthy people. Having such suspicions, the doctor may ask the patient to come to the clinic several times throughout the day. To ensure the accuracy of the diagnosis, you need to measure your blood pressure at least three times before lunch, and the same number in the evening.
How to measure the pressure inside the eye yourself?
Without the help of a doctor and special equipment, it is impossible to determine with what force the fluid secreted by the ciliary body presses on the eye. Nevertheless, it is possible to understand that blood pressure is greatly increased, and ophthalmologists recommend that everyone master this simple technique.
Close your eyes and relax. Now gently press your index finger on the eyeball. You should feel an elastic ball that gives in to your pressure - this is normal. If the eye is very hard and practically does not deform, most likely the IOP level is elevated and it is better to consult a specialist to make sure that its value is not critical.
Types of home measuring instruments
At home, the following types of devices are commonly used to determine intraocular pressure:
- Semi-automatic.
- Mechanical.
- Automatic.
Important! Mechanical models are considered the most accurate. They are easy to use and show the most accurate data.
Structurally, a mechanical tonometer consists of a balloon with which air is pumped, a rubber cuff, a phonendoscope and a pressure gauge.
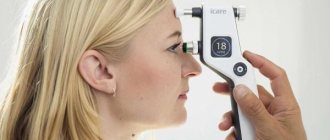
Portable blood pressure monitors are popular and are ideal for home use. In a short period of time, it is possible to determine accurate pressure readings. To do this, a person will not have to take anesthetics, without which measurements cannot be carried out in medical institutions.
Such devices are equipped with lightweight tips, which, striking the central part of the cornea, provide information about IOP. Before and after use, the part in contact with the eye shell must be thoroughly sterilized. Otherwise, the risk of infection in the eyes increases.
Features of the portable tonometer include:
- Simple controls.
- Automatic saving of past indicators.
- Absence of the slightest negative effect on the human body.
- The information of interest is displayed on the monitor.
- When used correctly, the portable blood pressure monitor will produce a single signal indicating that eye pressure is being measured correctly.
- Such devices are often used by people diagnosed with glaucoma, and continuous monitoring of their vision is necessary. The convenience is that the obtained measurements are saved along with the time and date of the manipulation.
On the good side, portable non-contact devices have proven themselves, with which it is not at all difficult to independently monitor the condition of your eyes. There is no direct contact with the eyelid, which is very convenient and comfortable for a person. It is not surprising that such tonometers are allowed to be used by young children at home. There is no need to use painkillers.
Advantages of contactless models:
- The measuring process is controlled electronically, the risk of injury to the cornea is prevented, and the accuracy of the indicators is maximum.
- Prevention of infection due to the non-contact action of the tonometer.
- Possibility of repeated use for patients with overly sensitive eyes.
- The external parting panel is made of materials resistant to chemical disinfection.
- There is no need for anesthesia.
- The eyelid, which is compressed by the rod during the measuring process, does not affect the correctness of the result obtained.
- Possibility of performing the procedure in a sitting or lying position.
- Permitted for use if there are contraindications for corneal tonometry.
Why does intraocular pressure increase?
Two parts are responsible for the regulation of intraocular pressure - the nervous system and some hormones. That is why most often a temporary increase in IOP is associated with increased mental work, stress and the experience of violent emotions. In women, the risk of glaucoma can develop during menopause, when large-scale hormonal changes occur in the body.
So, the true cause of IOP most often needs to be looked for in one of the following directions.
- Chronic stressful situations, prolonged mental or physical stress.
- Problems with the cardiovascular system that provoke surges in blood pressure.
- Some kidney diseases, due to which a lot of fluid is retained in the body.
- Endocrine pathologies, in particular increased levels of adrenal hormones in the blood, hypothyroidism.
- Anatomical pathology in the structure of the eyeball. People suffering from atherosclerosis should be especially careful in this regard.
In any case, it is important to understand that intraocular pressure does not suddenly increase on its own, it is always a consequence. Sometimes - hidden pathological processes occurring in the body, and sometimes - diseases associated directly with the eyes. So, a jump in IOP can be provoked by:
- an eye tumor that puts pressure on the inner membranes and chambers of the eye, thereby interfering with the normal outflow of fluid;
- inflammatory disease of the iris (iritis), ciliary body (cyclitis), choroid (uveitis);
- severe eye injury, after which inflammation, swelling and stagnation of blood in the vessels inevitably appears.
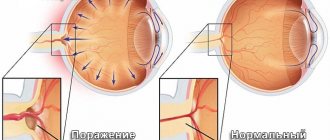
Important! Under any of the above circumstances, IOP cannot be critically high all the time. It increases periodically, in jumps, which depend on the characteristics of the course of the disease that provokes it. But if the pathology is not found and treated, then with age, increased IOP can transform into glaucoma. Gradually, due to strong pressure, the retinal cells will be destroyed, the optic nerve will atrophy, and eventually the person will completely lose vision.
Symptoms of eye hypotony
If a person is healthy, he may show signs of eye hypotony. The course of the disease does not manifest itself, the pathology is characterized by development if the cause is not an injury to the eyeball. If eye hypotony lasts several weeks, symptoms begin to appear:
- discomfort in the eyes and a feeling of squeezing;
- fatigue of the visual organs from the usual load;
- a man walks with red eyes;
- the pupil reacts sluggishly to light;
- the field of view decreases - the image is clear in the center, but begins to blur towards the periphery;
- dry cornea.
The presence of symptoms is a signal that you need to visit an ophthalmologist. You can stay healthy in the early stages. Over time, low intraocular pressure can lead to complications:
- loss of eyeball function;
- swelling of the optic nerve;
- identification of folds in the retina, while the vitreous body becomes cloudy;
- the size of the eyeball is reduced;
- the eye is deformed.
With such manifestations, it will not be possible to restore the lost health of the visual organs; the deformation of the structures cannot be restored.
How to relieve intraocular pressure?
Trying to deal with the consequences without eliminating the cause is useless. That is why, if you notice that your eyes are constantly tired, red and very tense, you need to look for a reason that provokes periodic jumps in intraocular pressure. Further, the method of eye restoration will depend on how neglected everything is.
If we are talking about the initial stages and barely noticeable symptoms, then, most likely, preventive measures alone will be sufficient:
- master a set of eye exercises and devote a few minutes a day to it;
- choose safety glasses for reading and standing in front of a monitor;
- As far as possible, limit any eye strain - TV, computer, working with small parts;
- give up contact and strength sports;
- Spend free time outdoors, giving your eyes a chance to rest and look into the distance.
Treatment of intraocular pressure with drops
When high IOP ceases to be episodic and develops into ocular hypertension or hypotension, preventive measures alone are not enough - timely local treatment is needed. With such diagnoses, the easiest way to regulate the pressure in the eye is with eye drops. They come in several types.
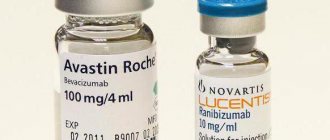
- Those that act directly on the ciliary body and reduce fluid production are carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. The most popular of this group are Azopt and Trusopt. By reducing the amount of intraocular fluid, the pressure also decreases, but this process can be accompanied by burning, severe redness of the eyes and even a bitter taste in the mouth.
- The second category is prostaglandins. They operate on a different principle: they affect not the amount of fluid, but its intensive outflow. If this is the problem, Travatan, Taflotan and Xalatan are most often prescribed. But they also have side effects - the iris of the eye may darken.
- Beta blockers - for example, Timolol, Okumol, Okupress, Arutimol, Okumed and the more modern Betoptik. They also reduce the amount of fluid formed in the eye, but have one significant nuance - together with eye pressure, they reduce the heart rate, which is strictly contraindicated for heart patients.
There are also combination drugs that act in two directions: on the one hand, they inhibit the process of fluid production, and on the other, they increase its outflow. This category includes “Xalacom”, “Fotil”, “Kosopt”.
Important! On average, drops are used twice a day, but the exact dosage and frequency of instillation can only be determined by a doctor, having an accurate description of the clinical picture. By self-medicating, you can not only further damage your vision, but also damage your cardiovascular system, lungs and kidneys.
Relieving intraocular pressure at home
If you feel pressure in your eyes, but cannot immediately get an appointment with an ophthalmologist, then instead of drops you can try to relieve painful symptoms using traditional methods. Helps normalize eye pressure:
- meadow clover decoction (brew with boiling water, leave for 2 hours and drink 100 g before bedtime);
- tincture of golden mustache (pour about 20 purple inflorescences with 500 grams of vodka and leave in a dark place for 12 days, then take one teaspoon before breakfast);
- a glass of kefir with cinnamon.
No matter how tempting such treatment may seem, ophthalmologists do not recommend relying too much on it. Such recipes can be used only if the pressure jumps rarely and not greatly. Trying to get rid of serious symptoms that indicate progressive blindness in this way is simply dangerous.
Most of these arrogant patients, when they finally get to the ophthalmologist’s office, hear one thing: “an operation is necessary.” A laser is used to relieve high intraocular pressure. Depending on where the problem is located, they can either excise the iris or stretch the trabecula to increase the flow of fluid.
If you don't want to end up in the operating room, take the advice of ophthalmologists seriously and constantly engage in prevention. A five-minute break every hour of working near the computer, a simple set of gymnastic exercises for the eyes, a dinner of sea fish and blueberry-carrot snacks - and you will maintain sharp vision for many years!
Sources used:
- Volkov, V.V. Glaucoma at pseudonormal pressure / V.V. Volkov. - M.: Medicine, 2001.
- Lusine, Levonovna Harutyunyan Determination of target pressure in primary open-angle glaucoma: monograph. / Lusine Levonovna Harutyunyan. - M.: LAP Lambert Academic Publishing, 2013.
- D. Hubel. Eye, brain, vision. — ed. A. L. Byzova. - M.: Mir, 1990.
- American Optometric Association - Ocular Hypertension
Symptoms of eye pressure
In the initial stage, eye diseases do not have pronounced symptoms. The only thing that should cause concern is rapid eye fatigue and a feeling of heaviness. But the situation is aggravated by the fact that most people do not pay attention to these symptoms, mistaking them for ordinary fatigue. Meanwhile, the disease progresses, complicating future treatment.
As time passes, the symptoms become more pronounced, and these may include the following signs:
- fatigue in the eyes is felt not only in the evening, but also in the morning;
- noticeable redness of the whites;
- with the onset of twilight, visual acuity decreases;
- there is increased blood pressure;
- heaviness and pressure in the eyeball;
- spots before the eyes;
- pain in the eyes.
Any discomfort may indicate the progression of eye diseases. All of the above symptoms worsen if a person works in front of a computer monitor. If your main activity is computer-related, then you need to pay attention to the condition of your eyes more often.
Older people are more likely to develop eye diseases. That is why ophthalmologists recommend checking eye pressure more often at home or seeking help from specialists.