What is ZhKL
Modern LCDs are gas permeable. The optical device is breathable and made of silicone. Such contact products allow you to see perfectly all day long and there is no need to frequently use artificial tears.
Corrects ophthalmological defects associated with changes in the shape of the cornea. They can be daytime or nighttime, and are allowed for children over a certain age and adults. The effect on the cornea is minimal and gentle, which has a positive effect on eye health.
Indications for use:
- scarring;
- consequences of injuries and eye surgeries;
- astigmatism;
- keratoconus;
- age-related farsightedness and myopia.
Rigid contact products are prescribed to people who need the highest possible visual acuity and improved peripheral vision. They are used by pilots, jewelers, surgeons and gynecologists.
It is recommended to be worn by people with myopia and for corneal refractive treatment.
Night lenses
Designed specifically for use at night, as they do not come into contact with the corneal layer. Night lenses have only a passive effect on the cornea, excluding direct pressure. Therefore, the risk of material sticking to the mucous membrane is completely eliminated.
However, one should not hope to completely correct vision defects with night lenses: the effect lasts no more than a day.
Indications for use:
- athletes;
- working in smoky rooms;
- school age children;
- treatment of farsightedness/myopia.
Athletes, due to the specific nature of their activities, cannot use glasses during training. Therefore, the only way to correct vision is to wear night silicone lenses. The same applies to people working in smoky rooms. Constant dust and smoke damage the optics, so there is no point in wearing them during the day. Night correction replaces the use of daily patterns.
Patients who are prohibited from surgery on the visual organs can use night lenses to correct farsightedness/myopia. The same applies to schoolchildren. The use of glasses and daytime lenses during an active lifestyle is impossible, so the only way out is hard lenses at night to correct myopia/farsightedness. In children, visual organs are formed before the age of 17 and can be easily corrected with the help of night-time LCDs.
Advantages
Hard contact lenses are an excellent option for people who cannot achieve ideal vision with soft contact lenses. Gas-permeable ones are better than soft ones. In addition to the ability to pass a high amount of oxygen, they have a lot of other positive properties.
Advantages of housing and communal services:
- Strength. Rigid optical devices hold their shape well due to the high density of the material. Less susceptible to deformation due to mechanical impact and blinking.
- The image remains stable and stable. The picture of the world is not distorted when blinking.
- Rigidity increases wear life. With proper care they will last for years.
- Resistant to protein deposits. This significantly saves processing time and increases the duration of use.
- Vision is better than with soft CLs.
- The LCL base does not contain water, so they rarely dry out, unlike hydrogel ones. You need to moisturize, but not as often as soft and hydrogel products.
- LCDs are more economical despite their high cost. They do not need to be changed monthly. A change is carried out if changes relate to deterioration of vision.
- The diameter is smaller than the cornea. This allows oxygen to flow to the peripheral zone and be washed with tears.
- Silicone-based LCDs provide better vision quality than soft ones. This advantage is especially noticeable when correcting astigmatism and high degrees of presbyopia.
LCDs are easier to handle because they do not tear or break. Such optical devices are easy to maintain and clean.
Gas permeable contact lenses are considered superior to regular hard ones. They provide the same vision correction, are durable and easy to maintain. However, there is one difference - they are safer. There is an exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Gas-permeable LCLs allow you to wash the surface of the eye, which significantly improves heat transfer. Doesn't dry out or cause irritation.
What is special about gas permeable lenses?
This type of lens provides oxygen access to the cornea of the eye due to the material from which it is made, which has a smaller diameter compared to other lenses. They do not contain water and are resistant to deposits on the surface of the lenses. Ophthalmologists recommend gas-permeable hard lenses to patients when signs of corneal starvation—limbal hyperemia, neovascularization, etc.—appear.
Differences from soft
Hard lenses are made from a special type of silicone and hydrogel. Thanks to this, lenses have good breathability, while soft lenses transmit oxygen less well.
Unlike soft lenses, hard lenses solve the problem of visual impairment.
This type has high density and strength. They are difficult to scratch and tear, but they are easier to crush.
They are smaller in diameter than the cornea, while the soft ones cover it completely. Rigid lenses not only allow the cornea to breathe, but also moisturize and wash away dust particles from the tear fluid.
Thanks to the hydrogel, the lenses have a plastic texture without water content. They neither dry out nor irritate the eye, and do not require constant moisturizing with drops.
Lenses do not have an expiration date.
Specifics of wearing
Rigid night lenses are put on 10-15 minutes before bedtime and removed in the morning. To achieve the effect, the lenses must be worn for 8 hours in a row.
The mode of wearing lenses depends not on the time of day, but on the time of sleep. If the patient works at night and sleeps during the day, then the lenses are worn during the eight-hour daytime sleep.
Attention! It is necessary to monitor the condition of the lenses; if cracks or chips appear, they must be replaced immediately. Cracks and chips may occur due to frequent falls of lenses onto a table or floor.
Important! After a year and a half, it is necessary to replace the lenses with new ones.
Flaws
Rigid contact products, despite a large list of advantages, have disadvantages.
These include:
- Comfort. It will take some time to adapt to wearing it. For some it takes 4 days, others get used to it up to 3 weeks. Adaptation is not painful, a person just feels a slight discomfort in the eyes. If you take a break from wearing it, you will have to get used to it again.
- If one or two LCLs are lost, the patient will suffer significant material damage. Since the manufacture of a new optical device costs from 2 to 5 thousand rubles per piece. This is due to individual selection to achieve the correct fit and stability on the outer shell of the eye.
- Glasses after them do not always help. The picture is blurry, vision is blurred. It will be restored if you put on glasses a few days after removing the GCL. They change the shape of the cornea, which is what causes poor vision if you immediately put on glasses.
TCL has more positive criteria than disadvantages. Therefore, they are recommended by ophthalmologists for vision correction.
Oxygen access: why are they so cool and safe
There are a lot of good Russian models that are cheaper, but we use American ones - they are approximately twice as thin.
This immediately eliminates all other lenses from the selection options. Yes, there are cheaper options, but we use hard contact lenses when the patient needs comfortable vision without glasses and without surgery, or when it is necessary to stop progressive myopia in a child. If you want something cheaper, go with glasses, it’s more justified in terms of safety. So, despite the rigidity of the material, fluoro-silicone acrylate has a structure that does not interfere with the flow of oxygen to the eye (almost mythical 100 percent oxygen permeability), that is, night lenses are significantly safer than soft ones in this regard. Given the almost guaranteed limited wearing time (I know very few people who can regularly sleep 12 hours), safety requirements will be met almost automatically. This is a direct consequence: we do not have patients with complications from such lenses. But, really, it must be said that we are somewhat disingenuous when we talk about long-term wear: usually by the end of the year the patient gets so used to the fact that he can run, jump and swim freely that he really wants to get such vision, but is too lazy to put on lenses, and keep the schedule too.
Therefore, the patient usually comes for laser correction, having enjoyed life and counting the costs for the coming years. As a result, there are only a few hundred long-term cases of wearing hard night contact lenses in Russia - as a rule, these are those who use them due to the impossibility of other correction and unwillingness to wear glasses. Usually - female models and athletes, mainly boxers and hockey players.
Features of use
The duration of use of LCDs depends not only on storage and cleaning, but also on proper donning and removal.
We recommend reading: How to properly put on and remove lenses
Step by step donning procedure:
- Wash your hands thoroughly with neutral soap. Dry with a paper towel or a regular one, but without lint. Hygiene is important to prevent infections and reduces the likelihood of infection.
- Wipe both sides with soapy water and rinse with saline solution.
- Place on the tip of your index finger and add a drop of artificial tears. It is important to watch which side you are putting on to see if it is turned inside out. Some manufacturers indicate an indicator on the right side to make it easier to determine the position of the corrector.
- Use the middle finger of your second hand to push back the lower eyelid. Look up. Use your index finger to fix the upper eyelid in the desired position.
- Place on the cornea. Carry out the donning procedure in front of a mirror.
Discomfort or itching when starting to use contact lenses is considered normal. To prevent their appearance, after putting it on, it is recommended to look down with your eyes closed and not blink often.
It is important to follow these guidelines when wearing contact lenses:
- Do not use immediately after waking up. Wait 20 minutes. Remove 20–30 minutes before going to bed.
- Do not rinse with tap water. Use distilled.
- Don't sleep with your lenses on. The cornea needs rest.
- Moisten with artificial tears before removing. This way there is no risk of damaging the cornea.
- There is no need to use artificial tears during the day. But if you stay in a heated room for a long time or in a too cold room, using the solution will not hurt.
- Do not shower while wearing and remove before using the hot tub.
- Do not wear if there is prolonged discomfort, redness or redness of the eyelids, severe watery eyes, or if you are taking anti-allergy medications.
- Paste before applying makeup and do not use broken or cracked product.
- Sleeping with hard contact lenses is not recommended. This increases the risk of developing a corneal infection by 4 to 7 times. Sticks to the cornea.
- Remove if you have increased photosensitivity or blurred vision as a result of pathological processes or taking medications that cause this side effect. Such signs indicate oxygen starvation of the eye tissues; rest is required.
When you need to remove, wash your hands again with neutral soap and dry with a paper towel. Drop artificial tears and carefully remove from the cornea.
Rigid and night (orthokeratology) lenses
Rigid contact lenses, also known as rigid gas permeable lenses (including Ortho-K, OK lenses, and night lenses), are made of hard plastic that allows oxygen to pass through them to your eyes. Hard contact lenses (not just nighttime ones) are better at correcting some vision problems than soft lenses. When you first put in hard lenses, you need to practice putting them in and taking them out until you feel comfortable.
With some skill, putting on and removing night lenses is even easier than soft ones. Here are some tips to help you.
The best way to remove hard contact lenses
Place your left hand under your right eye. Tilt your head, place your palm.
Look at your palm. Place your right index finger next to your eye.
Pull the outer corner of the eye outward by applying pressure with your index finger. Blink. Hard contact lenses should pop right into your hand.
Repeat this procedure with your left eye, pressing with your right hand under the eye and pulling up the corner of the eye with the index finger of your left hand.
Night lenses: how to remove them easily?
Night lenses are small in size
and can be difficult to remove—
they are not flexible
like soft lenses.
From left to right: soft contact lens, hard orthokeratology lens, and hard scleral contact lens.
For those who wear night lenses, the doctor gives them a special rubber suction cup to remove them.
But in order to shoot lenses with it, you need to know some tricks.
Hold the upper eyelid with your non-dominant hand. Grasp the suction cup between your thumb and index finger, but you can still hold the lower eyelid using your middle finger.
The suction cup creates a gentle suction pressure; it must be pressed (like a pipette) and placed on the lens in the center of the eye. The lens can now be removed from the eye. It helps to wet the end of the suction cup in the solution first.
Your lenses may have shifted to the white part of your eye. Then first use a mirror to find the contact lens. Then, if possible, try using gentle pressure through your eyelids to move the lens toward the center of your eye. After which it is easy to remove.
What if the lens stuck in the morning?
It's not uncommon to find that your OK lens seems stuck to your eyeball when you wake up in the morning.
In this case, you must first relieve the feeling of the lens sticking before removing it. Try placing your finger on your lower eyelid and lightly pressing upward on your eyeball. If the contact lens remains stuck, try adding a drop of solution (drop into the eye) and repeat the procedure described above.
How to remove night lenses without a suction cup?
- Open your eyes wider (this is important!).
- Place your finger on the outer edge of your eye.
- Place your palm under your eye.
- Press your finger at the edge of your eye and pull your finger towards your ear, while blinking.
- The lens will pop out of your eye and into your palm.
It's just a skill. The trick is that you open your eyes wider
than the diameter of the lens, and then pull it to the side (toward your ear). Since there is no room for the lens to go down, it always bends a little, overcoming surface tension. That is, you need to apply a little pressure to one edge to break the surface tension on the opposite edge, changing the geometry. And the lens is easily removed.
Open your eyes wider, even wider
, pull, catch, clean. All!
It just takes a little practice.
In the first month, you store night lenses alternately in two different solutions (two days in each), and after a month there is only one left - peroxide, it lasts for about a month, and a new bottle always comes with a new storage jar, as in the photo below . Always change the jar when starting a new bottle, because its catalyst located at the bottom is designed just for the volume of the bottle (about 35 days):
Tricks for easier removal of night lenses:
1. Dry hands and face (small detail, but a huge difference).
2. Look down (this is why with night lenses the mirror is placed on the table, lying down, and not in front of you).
3. You need to blink with more force than usual.
What
not to do:
LCD for children
Ophthalmologists do not recommend wearing them in children. This is due to the fact that the muscles stop tensing, and vision deteriorates. Ophthalmologists recommend wearing it in exceptional situations.
GCLs do not cause irritation, dryness or burning. Children are allowed to wear them, but only those who are able to care for them themselves, clean them properly and store the optical device in a container. LCDs are recommended for children aged 7 years and older, who are taught how to properly put on, take off and care for.
Wearing lenses cannot be avoided if you have keratoconus. These changes are more common among teenagers, but can occur in children and adults. In this case, LCLs correct the abnormal shape of the outer shell and return it to its previous shape.
Children are recommended to buy one-day ones, which do not require careful care and are less likely to scratch the cornea. Children are selected for lenses with a high oxygen permeability coefficient, since they have lower corneal sensitivity than adults.
How to shoot?
Putting on contact lenses seems to be the most difficult task. But removing them is also not always easy. The moment you decide it’s time to take the lenses out of your eyes, remember the rules of hygiene. Again, thoroughly wash your hands, wipe them dry, and only then touch the lenses. Use a mirror to see where the contact lens is on your eye. Hold your upper eyelid with one hand and lift your eyes up. Push your lower eyelid down with the finger of your other hand. Using your index finger and thumb, carefully remove the lens in a pinch-like motion. Ready!
There is another way to remove lenses from your eyes: you simply slide the lens down a little, and it ends up on your finger. You can use any of the contact lens removal methods. You will definitely find one of them comfortable, and then the question of how to remove the lenses will no longer worry you.
How to learn to remove and put on lenses for the first time?
We strongly recommend that you select contact lenses from an ophthalmologist who specializes in contact vision correction.
In this case, you can be sure that the lenses will be selected correctly and, therefore, will not cause discomfort. In addition, when selecting lenses, each contact correction specialist provides detailed instructions on putting on and taking off. Rarely does a patient cope with this task right away. Therefore, do not be upset if you do not understand from the first minute how to put on or remove lenses. This will take some practice and patience. And the ophthalmologist understands this very well.
Night hard contact lenses
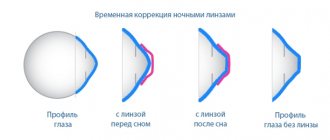
This is a new method of vision correction that involves refractive treatment. Such lenses are also called orthokeratological lenses. They are worn before bed and are flatter in shape than the cornea.
Orthokeratology lenses work while you sleep, and during the day they allow you to see the world without glasses. They are gas permeable.
Orthokeratological CLs (OCLs) affect the upper, superficial layer of the outer layer of the eye. They thicken it at the edges, making it slightly flat in the center. The result is a change in the refraction of light rays.
OKL will be in effect and worn for at least 8 hours. The effect is cumulative. After the first use, vision improves up to 70%, after a week it reaches 100%. It is allowed to be worn during the daytime. Then the maximum effect will occur at night.
During the day, the outer shell of the eye gradually returns to its previous position, so it is recommended to wear eye lenses every night.
Don't get confused
One more moment.
Everything that is written in the post regarding the safety of hard contact lenses applies only and exclusively to special lenses for night use during sleep. There are also hard contact lenses that are used for routine corrections, and those that are used after operations to create an additional exogenous frame of the eye. Almost none of the above applies to them; they are most often worn out of forced necessity. And one more important point: yes, there are hard lenses that are milled individually to fit the curve of the cornea (most often after transplantation or major operations) and provide ideal vision. Such corneoscreaal lenses have a mechanism for creating a liquid medium (tears) between the tissues of the cornea and the lens - they sit not on the cornea, but on the conjunctiva. They are done by only one clinic in Russia, as a “last chance” solution, the indications are extremely specific. If you're interested, I'll give you a tip in a private message.
Proper storage
To avoid infection in your eyes and to avoid throwing away your lenses a month after use, you must store them properly.
Place in a special container with a solution that should completely cover the lenses. The liquid contained in it cannot be used a second time. The optical device is always placed in a new solution.
Clean every evening with a multi-functional product for gas-permeable rigid cables. Cleaning is done with your index finger. Pour 2-3 drops of solution and carefully clean. You can't make an effort. Then rinse with distilled water and place in a designated storage container, adding a new disinfectant solution.
For proper disinfection, each lens must remain in the container for at least 6 hours.
Never use expired products for cleaning or storage. Always check the expiration date.
Make sure your lenses do not come into contact with water or saliva, as both contain germs and can cause eye infections.
What are hard lenses
There are many parameters in which contact lenses can differ, but one of the main ones is the material from which they are made. That’s why there are soft and hard models. Rigid models are distinguished by the fact that they are gas permeable. The ability to pass gases is measured in special points. A more detailed difference between hard and soft lenses is described in this material.
Hard contact lenses typically range between 70 and 170 points, while soft lenses very rarely achieve readings greater than 30 points. Even the most modern and technologically advanced soft models are noticeably inferior in this regard.
There are several characteristic features that distinguish hard lenses from softer ones:
- Higher final clarity of vision due to the fact that optical characteristics are better preserved.
- The shape of the lens is maintained much better due to higher rigidity.
- It is much more convenient to put on lenses of this type, as well as more convenient to remove them.
- Much less protein deposits accumulate on the surface, making it much easier to keep the lenses in good, clean condition.
- There is no need to use extra drops to moisturize your eyes.
- The diameter providing access to oxygen and tear fluid to the periphery of the eye is much smaller.
- The period of use increases noticeably, but the adaptation period also increases; it is necessary to adapt for some time after any long break in wearing.
- Selecting such lenses is more difficult, but when you finally select them, the result will be even better than with soft lenses.
- If you wear these lenses for a long time, then the effect of wearing glasses, if you also have them, will decrease for some time.
Read more about how to remove lenses correctly.
Hard lenses are selected in several stages, which should take place in the following order:
- It all starts with a visit to the doctor. When you visit him, you must provide the doctor with all the information about your general health, about all diseases, both affecting the eyes and not affecting them at all. It is necessary to talk about your previous experience with vision correction, and you also need to check with your ophthalmologist whether he considers this vision correction option suitable for you, taking into account your individual characteristics. It is necessary to find out whether there are contraindications or not.
- Next comes the examination procedure, which is especially important in this situation. It is necessary to collect the most detailed information about the structure of the patient’s eyes, the diameter of the pupil, the condition of the cornea, it is necessary to determine the functions of the lacrimal canals and examine the abundance of other parameters in order to ultimately select the necessary lenses. During the examination, a vision test, visometry and an autorefractometer are used. Specialized diagnostic lens samples are also used for accuracy of selection, but it is still not always possible to select them the first time. Sometimes a return visit is required.
- The selected sample is carefully checked, for example how well it fits after a few minutes. Various methods are used for this, including slit lamp analysis.
- After this, the order is placed, and the hard lens begins to be manufactured.
If hard lenses are not suitable for you, then at one stage the ophthalmologist will certainly inform you about this.