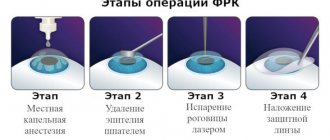
There are several types of myopia (myopia):
- axial myopia – the image is formed in front of the retina due to an increase in the length of the eye;
- refractive myopia - the image is formed in front of the retina due to the shortening of the focal length due to the high refractive power of the cornea;
- bivariate myopia - the image is formed in front of the retina both due to the elongation of the eye axis and due to the high refractive power of the cornea. With this form, there is a discrepancy between the change in eye length and the degree of myopia;
- lenticular myopia - the image is formed in front of the retina due to an increase in the refractive power of the lens, occurs in adulthood with cataracts, diabetes, nuclear lenticular sclerosis.
Myopic people see well up close and have difficulty seeing objects in the distance. With myopia, distant objects are perceived as blurry, blurry, and unsharp. Visual acuity becomes below 1.0.
Causes of myopia
Depending on the reasons, there are three main types of myopia:
- Axial. This type of myopia occurs when the anteroposterior size of the eyeball increases. Most often, the development of axial myopia is associated with heredity. If the structure of the connective tissue is disrupted, the posterior pole of the eye weakens, the eye increases in size, causing myopia.
- Refractive. Such myopia occurs when the eyeball is of normal size, when light rays passing through the anterior segment of the eye are refracted more strongly than necessary. This may occur with keratoconus, spasm of accommodation (spasm of intraocular muscles), and certain pathologies of the lens.
- Mixed. Combines both options.
Classification of myopia
- Low myopia – up to 3.0 D (diopter)
- Moderate myopia – up to 6.0 D (diopter)
- High myopia – above 6.0 D (diopter)
Myopia can be diagnosed at any age, but is most often first discovered in children aged 7 to 12 years. As a rule, myopia intensifies during adolescence, and after 18 years of age its progression usually stops. The causes of myopia are not fully understood. Currently, there are many theories, but none of them is the main one.
Contraindications to laser vision correction
Contraindications to surgery are conventionally divided into temporary, which can be eliminated, cured, etc., and absolute - with such contraindications, laser correction is either impossible or does not make sense, since the effectiveness of the intervention will be low.
Laser correction - contraindications:
- retinal dystrophy - people with moderate and high degrees of myopia often experience changes in the retina; some degenerations can be eliminated by laser coagulation;
- high degree of myopia - unfortunately, if myopia is above -15, then laser correction surgery will be ineffective, the person will still have to wear glasses;
- ophthalmological pathologies such as cataracts, glaucoma, nystagmus, keratoconus;
- systemic and chronic diseases;
- pregnancy and lactation are a temporary contraindication; six months after cessation of lactation, surgery is possible;
- thin cornea that does not allow correction.
Ophthalmologists recommend surgery after 18-20 years of age, even if myopia is slight, since the human eyeball is still developing. Also, in order for laser vision correction to be possible, vision must be stable, that is, myopia should not progress over a couple of years.
Risk factors
Heredity - it turns out that when both parents are myopic, half of the children develop myopia before the age of 18. If both parents have normal vision, myopia appears in only 8% of children. It is believed that hereditary factors determine a number of defects in the synthesis of connective tissue protein (collagen), necessary for the structure of the sclera, the lining of the eye. A lack of various microelements in the diet (such as Zn, Mn, Cu, Cr, etc.) necessary for the synthesis of the sclera can contribute to the progression of myopia, eye strain - prolonged and intense visual stress at close range, poor lighting of the workplace, incorrect sitting down when reading and writing, excessive exposure to TV and computer. As a rule, the onset of myopia coincides with the start of schooling.
Incorrect correction - the lack of vision correction at the first appearance of myopia leads to further overstrain of the visual organs and contributes to the progression of myopia, and sometimes the development of amblyopia (lazy eye syndrome), strabismus. If incorrectly selected (too “strong”) glasses or contact lenses are used to work at close range, this provokes overstrain of the eye muscles and contributes to an increase in myopia.
Important! At the first signs of myopia, you should immediately consult an ophthalmologist. Lack of myopia correction or correction with incorrectly selected glasses or lenses can lead to rapid deterioration of vision and the development of progressive myopia.
Progressive myopia - a condition in which the degree of myopia increases by one or more diopters per year - is considered progressive myopia. Myopia progresses most intensively in children during school years, during the period of the most intense visual stress. In parallel with this, there is active growth of the body (and the eyes, in particular). In some cases, elongation of the eyeball in the anteroposterior direction can take on a pathological character, causing deterioration in the nutrition of eye tissue, ruptures and detachment of the retina, and clouding of the vitreous body. Therefore, people with myopia are not recommended to work related to lifting heavy objects, with the body in a bent position with the head tilted down, as well as sports that require a sharp shaking of the body (jumping, boxing, wrestling, etc.), as this can lead to retinal detachment and even blindness. The progression of myopia gradually leads to irreversible changes in the central parts of the retina and a significant decrease in visual acuity. If peripheral retinal dystrophies are detected, leading to retinal detachment, retinal laser coagulation is performed in people with myopia for the purpose of a more dangerous complication - retinal detachment.
Types of myopia
There are stationary, progressive and complicated myopia. In the first case, the disease is characterized by a sluggish course and absence of complications. With a progressive form, a stable decline in vision occurs. Complicated myopia can lead to serious adverse effects on the fundus and optical media. Each person suffering from myopia can be diagnosed with a different degree and severity of this pathology. According to the nature of development, the disease is divided into three types:
- progressive;
- transient (occurs against the background of concomitant diseases);
- complicated (complications arise from the fundus, etc.);
- stationary.
The progressive form is dangerous because each year the patient’s vision drops by more than 1 diopter. When impairments become permanent, it can lead to visual impairment in the future. A milder form of myopia is considered to be transient, which bothers a person for a short time, usually during an exacerbation of any concomitant diseases or taking medications. Stationary myopia is easily corrected and does not progress. With weak myopia, the index of refractive error does not exceed 3 diopters (with a minus), with an average degree of myopia, deviations of up to 6 diopters are diagnosed. Values exceeding this threshold are characterized as high degree.
Modern types of correction for myopia:
Glasses are the most common method of correcting myopia, which remains the most in demand and popular nowadays, although it has a lot of inconveniences. Glasses for constant wear should be selected by an ophthalmologist based on the results and based on a complete ophthalmological examination. Visual acuity in them should not be less than 100 percent; this will ensure optimal vision, normal physiological functioning of the eye, and also prevent the progression of myopia.
Contact lenses – contact lenses have a number of advantages over glasses and today can provide a normal life for even a very active and athletic young man.
Laser vision correction - for adults (over 18 years old) with a stable form of myopia, modern ophthalmology offers the most progressive method of correction. The best laser vision correction technology today is REIK, LASIK or FEMTO - operations that guarantee a patient with myopia good vision, without any restrictions .
Modern correction methods
Despite extensive clinical experience, the treatment of myopia continues to remain one of the most difficult areas in ophthalmology. Modern medicine offers a wide range of possibilities and methods for correcting vision for myopia: from glasses known since the 18th century to the latest technologies. But, for their most effective use, it is important to determine the causes and type of myopia, as well as take into account many other associated factors.
Treatment methods for myopia include:
- wearing glasses;
- wearing contact lenses of various types;
- drug therapy;
- hardware therapy;
- therapeutic exercises for the eyes;
- laser correction;
- keratoplasty;
- eye lens replacement;
- radial keratotomy.
Each method has its pros and cons, indications and contraindications, almost all have the possibility of various complications. But they have the same goal - to correct vision, that is, to change the optical system so that the image is focused correctly.
Just three simple steps to good vision:
CALL THE CLINIC
Call +7 (495) 781-93-33 to make an appointment with a specialist Call me
VISION DIAGNOSTICS
We guarantee accurate diagnosis and selection of optimal treatment for myopia. Sign up
VISION CORRECTION
Drug or surgical treatment, selection of glasses and contact lenses. Prices
See also:
- Online tests for self-examination of vision
- Treatment of myopia in children
Myopia in adults
A decrease in visual acuity is caused by various refractive errors, but myopia occupies one of the leading positions in the list of eye pathologies faced by modern ophthalmologists.
In this article
- Myopia in adults
- General characteristics of the disease
- Main symptoms of myopia
- Types of myopia
- True and false myopia - what is the difference?
- Why does myopia develop?
- Modern methods of treating myopia in adults
- Physiotherapeutic method for treating myopia
- Surgical treatment of adult myopia
- Methods for correcting myopia
- What happens if myopia is not treated and corrected?
This disease of the visual system is diagnosed in children and adults. It can be either congenital or acquired. Myopic people experience great discomfort because with this disease the ability to see what is at a far distance is weakened: the image appears blurry and indistinct. Modern methods of treating myopia make it possible to stop the disease or stop its progression, even without resorting to surgery. There are effective methods of correction and treatment, alternatives to surgery, that allow you to restore one hundred percent vision. Let’s take a closer look at what modern techniques help get rid of visual discomfort with myopia, and also figure out how effective they are.
Cost of myopia treatment
| Primary appointment (examination, consultation) with an ophthalmologist (examination for teenagers) | 7 190₽ |
| Service code | Service name | Number of services | Price |
| A02.26.004 | Visometry, 2 eyes Code: A02.26.004 | 1 | 350 ₽ |
| A02.26.013 | Determination of refraction using a set of trial lenses, 2 eyes Code: A02.26.013 | 1 | 550 ₽ |
| А02.26.013.001 | Determination of refraction using a set of trial lenses in conditions of cycloplegia, 2 eyes Code: A02.26.013.001 | 1 | 800 ₽ |
| A02.26.015 | Ophthalmotonometry, 2 eyes Code: A02.26.015 | 1 | 400 ₽ |
| А03.26.001 | Biomicroscopy, 2 eyes Code: A03.26.001 | 1 | 990 ₽ |
| A03.26.003.001 | Examination of the periphery of the fundus using a lens, 2 eyes Code: A03.26.003.001 | 1 | 1 950 ₽ |
| А04.26.004.001 | Ultrasound biometry of the eye (A-method), 2 eyes Code: A04.26.004.001 | 1 | 900 ₽ |
| A12.26.016 | Autorefractometry with a narrow pupil, 2 eyes Code: A12.26.016 | 1 | 350 ₽ |
| B01.029.001.009 | Consultation with an ophthalmologist Code: B01.029.001.009 | 1 | 900 ₽ |
| SERVICE PACKAGE В01.029.001.002 | Promotion! Price for the package of services under the promotion ( Discount: 33% ): | 4 850₽ |
| Visual stimulation |
| Service code | Service name | Number of services | Price |
| А17.26.002 | Low-frequency magnetic therapy for the organ of vision Code: A17.26.002 | 1 | 450 ₽ |
| A19.26.001.001 | Exercises to restore and strengthen binocular vision using the Synoptophore device (Inami, Japan) 1 session Code: A19.26.001.001 | 1 | 900 ₽ |
| A19.26.001.002 | Exercises to restore and strengthen binocular vision using the Synoptophore device (Inami, Japan) 10 sessions Code: A19.26.001.002 | 1 | 8 500 ₽ |
| A19.26.001.003 | Exercises to restore and strengthen binocular vision using the Synoptophore device (Inami, Japan) 15 sessions Code: A19.26.001.003 | 1 | 12 000 ₽ |
| A19.26.002 | Exercises for training the ciliary muscle of the eye 1 session Code: A19.26.002 | 1 | 1 400 ₽ |
| A19.26.002.001 | Exercises for training the ciliary muscle of the eye 20 sessions Code: A19.26.002.001 | 1 | 18 000 ₽ |
| A19.26.002.002 | Exercises for training the ciliary muscle of the eye 15 sessions Code: A19.26.002.002 | 1 | 15 000 ₽ |
| A19.26.002.003 | Exercises for training the ciliary muscle of the eye 10 sessions Code: A19.26.002.003 | 1 | 11 000 ₽ |
Notes:
- The cost of all operations is indicated for 1 eye.
- When performing operations by Professor, Doctor of Medical Sciences V.V. Kurenkov, the cost increases by 30%.
Surgical treatment of adult myopia
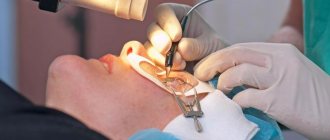
Surgical intervention for myopia is indicated for severe cases of the disease and its tendency to progress. In addition, this method is used by patients who, for some reason, do not want or cannot constantly use correction means. In most cases, modern surgical methods for treating progressive myopia guarantee a successful result: preventing further decline in visual function and returning clear vision without the need for correction. There are two types of eye surgeries: refractive and sclero-strengthening. In the first case, the purpose of the intervention is to correct the optical functions of the eye, in the second - the introduction of a substance into the back of the eyeball (it blocks the process of its further expansion).
Often in surgery, lens extraction, keratophakia, keratotomy, keratomileusis, etc. are practiced. In some modern clinics, innovative technologies are used that make it possible to successfully treat even a high degree of myopia.
Prevention of myopia
- Lighting mode – visual stress only in good lighting, using overhead light, a 60-100 W table lamp, do not use fluorescent lamps
- Regime of visual and physical activity - it is recommended to alternate visual stress with active, mobile rest - with myopia up to 3 diopters, as a rule, physical activity is not limited, over 3 diopters - lifting weights, jumping and some types of competitions are prohibited.
- Gymnastics for the eyes - after 20-30 minutes of exercise, it is recommended to do gymnastics for the eyes
- Correct vision correction - using glasses or contact lenses selected by an ophthalmologist.
- Training of muscles - the tension of which leads to an increase in myopia (laser stimulation, video-computer vision correction) - under the supervision of an ophthalmologist.
- Ophthalmological diagnostics - examination of the fundus of the eye on a wide pupil to monitor the condition of the retina and ultrasound measurement of the longitudinal size of the eye - at least once every six months.
- General strengthening activities - swimming, massage of the collar area, contrast shower, etc. on the recommendation of an ophthalmologist.
- Complete nutrition – balanced in protein, vitamins and microelements such as Zn, Mn, Cu, Cr, etc.
Types of operations for myopia and their implementation
The choice of a specific method of surgical intervention depends on the wishes of the patient, the availability of indications and the condition of the patient’s optical system.
- Radical anterior keratotomy. For pathological deviations in vision from 0.5 to 6 diopters.
- Myopic keratomyelosis. For pathological deviations in vision from 6 diopters and above.
- Extreme laser surgery. Laser vision correction for pathological deviations of vision up to 6 diopters.
- Excision of the lens (the operation is technically complex and is used in cases where the patient has contraindications to other methods of correcting myopia).
Anterior radial keratomy
The patient is under local anesthesia.
- The working area is prepared with anesthetic and antiseptic drugs.
- Then the specialist marks the locations of the planned incisions (the thickness should not exceed 90% of the total volume of the cornea).
- The surgeon then creates up to 12 incisions using a diamond knife. Pressure inside the eyeball provokes swelling of the cornea in the area of dissection and its further thinning.
The duration of the operation is 20–30 minutes.
Contraindications for surgery:
- pregnancy;
- diabetes;
- progressive myopia;
- thinned cornea;
- mental disorders;
- inflammatory processes in the eye area.
Myopic keratomileusis
The patient is under local anesthesia.
- An anesthetic drug and 7% polyglucin, which has a blood replacement effect, are injected into the eyeball.
- The eyelids are fixed with a blepharostat to provide free access to the working area.
- When the pupil dilates, the specialist performs manipulations to measure intraocular pressure.
- Then marking lines are applied.
- A flap is excised from the corneal tissue and folded back, after which another layer of the cornea is removed. Tissue dissection is performed with a laser or other device with a similar operating principle.
- The formed flap is returned to the anatomically correct position (along the marking lines) and a continuous suture is applied.
After this, a control measurement of intraocular pressure is carried out. An antibiotic is injected into the conjunctiva. As a result, the cornea becomes flatter.
The duration of the operation is 10–20 minutes.
ATTENTION! The method has contraindications similar to those for anterior radial keratotomy.
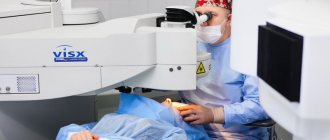
Laser eye surgery
Extreme laser correction
The operation follows the same scenario as for myopic keratomileusis. But the tissue to be removed is vaporized with a laser. The area of the removed cornea is calculated using computer programs.
The laser destroys bonds in tissues at the intermolecular level, without affecting the lens and other elements of the optical system. The accuracy of the laser is very high, thereby minimizing the risk of complications resulting from injury.
The duration of the operation is 15–60 minutes.
Lens excision (removal of the clear lens)
The operation is associated with great risk and is prohibited if:
- the presence of inflammation in the eyeball;
- retinopathy and retinal detachment processes;
- insufficiently large size of the eyeball (or anterior chamber of the eye).
Eye surgery consists of two stages: removing the patient's tissue and replacing it with a prosthesis. The intervention is performed under local anesthesia.
During the operation, the patient follows the surgeon’s instructions (focuses his vision and does not blink for a certain time).
The doctor creates a tunnel incision on the membrane of the eye. Through this access, an ultrasonic rod is inserted inside, destroying the lens. The breakdown product of the lens is sucked out.
A prosthesis (artificial lens) is inserted into the empty lens capsule. The lens body unfolds, after which the position of the prosthesis is adjusted by the surgeon. The puncture does not require stitches.
The eye is treated with a medical solution and a bandage is applied.
Maybe
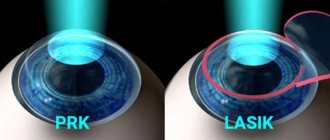
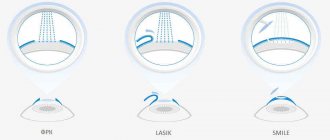
Laser keratomileusis (excimer laser keratectomy) - LASIK
Laser keratomileusis (excimer laser keratectomy) is a combined laser correction of myopia, named after the English abbreviation “Laser in Situ Keratomileusis” (LASIK). Nowadays, correction of myopia using the LASIK method is considered the most high-tech and most comfortable operation for the patient, as it allows you to quickly and painlessly restore the maximum possible vision without glasses and contact lenses. Today, LASIK surgery is the most popular surgery to get rid of glasses and contact lenses. Myopia correction using the LASIK method accounts for up to 90% of all types of refractive surgery in developed countries.
The uniqueness of the “laser keratomileusis” technology is that it allows you to accurately dose the refractive effect of the operation, while eliminating such unfavorable features of excimer laser keratectomy as damage to the surface layers of the cornea (epithelium and Bowman’s membrane). The main advantages of these operations are absolute painlessness and the highest precision of impact.
Key Benefits of LASIK
- rapid restoration of visual functions (within 1 - 2 days after surgery),
- minimal restrictions in visual load after surgery,
- preservation of the anatomical structure of the cornea,
- absence of an open healing wound,
- minimal pain (2 - 3 hours after surgery),
- stable results - durability of the refractive effect,
- the possibility of performing surgery on both eyes at once, without applying bandages,
- absence of corneal opacification in the postoperative period,
- the ability to correct myopia up to 25 diopters (including astigmatism).
Progress of excimer laser keratectomy surgery
Myopia correction is usually performed on both eyes at once. Before the operation, anesthetic drops are instilled. LASIK surgery does not require any general anesthesia. The patient is placed on the operating table, the skin around the eyes is treated with a special germ-cleaning solution and covered with a sterile delimiting bandage. Painkiller drops are instilled once again. Next, the following stages of the LASIK operation are carried out:
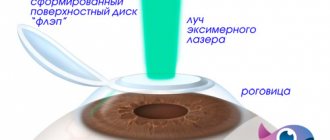
| To provide access to the middle layers of the cornea, using a special “microkeratome” device, a flap (“lid”) is cut out from the surface layers of the cornea and turned to the side. To achieve optimal results in forming corneal flaps of the required size, a computer method is used to calculate the operating parameters of the device. | |
| The laser then vaporizes the cornea, changing its curvature. | |
| At the end of the operation, the “lid” is placed in its original place. The flap is fixed without suturing, due to the adhesive properties of the cornea's own collagen. |
Install Flash Player to watch the movie.
Postoperative period
- It is better to spend the first day after LASIK in a hospital under the supervision of experienced staff. It is not recommended to touch the operated eye or rub the eyelids to prevent displacement of the corneal flap. It is also not recommended to wash your face at this time. During these days, eye drops are instilled.
- The next day after examination by a specialist, eye drops (antibacterial and anti-inflammatory) are prescribed for a period of 2 - 3 weeks, and if there are no problems, the patient is sent home.
- In the first two weeks after LASIK, it is not recommended to rub the eyes or put pressure on them; it is advisable for women not to use makeup on the eyelids and eyelashes, sprays or hairspray. It is not recommended to visit the sauna or swimming pool for 2 - 3 months.
- Visits to your doctor after LASIK surgery typically occur the next day, 2 weeks, one month, 3 months, and 6 months after surgery.
- Vision after surgery begins to recover within a few hours and reaches a sufficient level the next morning. In the next 2 to 4 weeks, vision reaches its maximum.
The operations listed above are not abdominal operations, since during them the surgeon’s knife does not penetrate the eye cavity. In cases where there are contraindications to excimer laser operations on the cornea (PRK, LASIK), the possibility of correcting myopia through intraocular operations (implantation of a phakic IOL or lens replacement for refractive purposes) is considered.
Our services in ophthalmology
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| Appointment with an ophthalmologist (primary) | 3 500 |
| Orthokeratological treatment (primary selection, both eyes) | 22 000 |
| Scleroplasty for progressive myopia in one eye | 35 000 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Myopia correction using Femto-LASIK method
Laser vision correction using the Femto-LASIK method is by far the most progressive. It provides an individual approach to each clinical case of myopia, provides wide possibilities for correction with a guaranteed lasting result. This technology can rightfully be considered unique. The Moscow Ophthalmological Center is one of the clinics offering femto-laser vision correction.
Three quarters of the world's leading ophthalmology clinics prefer this method of treating myopia. More than two million successful operations using the Femto-LASIK method have already been performed worldwide.
The key difference of the method is that it combines preservation of the upper corneal flap with absolute non-contact. Previous generation technologies allowed the corneal surface to be separated mechanically using a microkeratome (or epikeratome). During femto-laser correction surgery, even the separation of the flap occurs non-contactly with the help of another laser - a femtosecond beam. This technology eliminates not only the risk of complications, but also postoperative distortions, which previously often required additional correction (in particular, acquired corneal astigmatism).