Visual impairment is a significant disability that creates learning problems that can only be solved with the help of specialized knowledge. Most blind and partially sighted children are born with visual impairment. Approximately two thirds of children with visual impairments are educated in regular schools. About a third of them attend special schools for students with learning or physical disabilities. Two percent of students attend special schools for blind and partially sighted students.
Why vision tests are so important
The sooner any vision problem is detected, the sooner you and your child can get the treatment and support they need.
Children may not realize they have a vision problem, so without routine tests there is a risk that the problem will not be noticed.
If you have any concerns about your child's vision, contact your GP or optician.
When should a child's vision be checked?
A newborn baby's vision is checked several times during the first hours, weeks and years of his life.
Examination by an ophthalmologist at 6 to 8 weeks of age
This is a follow-up examination to check for any obvious problems that were not picked up soon after birth.
At the age of 1 year, or from 2-2.5 years
You may be asked if you have any concerns about your baby's vision. If necessary, a visit to an ophthalmologist can be scheduled.
At the age of 4 or 5 years
A child's vision is tested after he or she starts going to school. The goal is to identify any problems early.
Vision screening is usually done at school.
Schedule for checking a child with an ophthalmologist
The baby undergoes the first examination by an ophthalmologist almost immediately after birth. At the same time, the greatest attention is paid to children with congenital pathologies, birth injuries and premature babies. If there are indications, it is necessary to see a specialist when the child is one month old.
A healthy baby needs to make an appointment with an ophthalmologist at the age of three months, after which a check-up with a specialist is scheduled for 6 and 12 months. When checking a newborn's vision, the doctor does not use any special instruments.
Despite the fact that it is difficult to call such an examination complete, an experienced specialist can easily identify congenital pathologies.
You can conduct a vision test for children and at home; such a test does not require specific knowledge and skills. It is enough to observe the baby’s reaction to various objects - already at the age of 2 months he is able to follow moving objects. At 3 months, a child is already able to fix his gaze on an object that interests him, and at six months he can easily recognize a familiar thing located at a short distance.
At one year old, a baby can distinguish even relatively small objects at a distance of 1 meter, at 2 years old - at an even greater distance.
Classification of violations
The classification of all deviations from normal visual function is based on determining the type of disorder and the degree of its development. First of all, the doctor prescribes all the necessary diagnostic measures to find out what disease the child has. He will then set the stage.
According to the stage of the disorder, all patients are divided into:
- blind (with complete loss of vision, as well as with loss of the ability to see, but maintaining the ability to sense bright light or darkness);
- partially blind (with light perception and residual vision);
- totally blind (in the absence of vision in general and all light perception capabilities in particular);
- visually impaired (with vision from 0.05 to 0.3).
The ability to see two luminous points with a minimum distance between them is the criterion for assessing visual acuity. The degree of violation is determined in relation to the deviation from the norm, which is 1.0. Based on this criterion, it becomes clear that the popular definition of “minus 3” is nothing more than mild myopia, and “plus two” is slight farsightedness.
The social adaptation of children with minor disabilities is not difficult, because children with indicators of 0.3 and above can attend regular schools, then study at universities and even serve in the army. If the degree of impairment is determined to be from 0.05 to 0.3, the child will have to study in a special school for the visually impaired. If vision is less than 0.05, the child will be able to attend only specialized schools for the blind and be taught using a special method.
Checking the vision of a preschool child
There are a fairly large number of ways to test a child’s vision at home if he does not yet know the letters. According to many ophthalmologists, the most effective and accurate method is to use the Orlova table, in which pictures are used instead of the usual letters to test vision in children.
Orlova's table By clicking on the picture you can download it and print it
The table contains 12 rows of images, with the top row having the largest size, and each subsequent row having a smaller size. On the left side there is information about what distance the child should be in order to obtain the most accurate result. On the right are the visual acuity values.
Before you start testing the vision of a child over the age of 3, it is necessary to ensure good lighting in the room where the testing will be carried out. The table should be printed on high-quality paper and placed at the baby’s eye level.
When checking vision, you need to close 1 eye, but the child should not squint. There are several important points that should not be forgotten during an eye exam:
- Before starting the test, you need to make sure that the child understands the essence of the task. To do this, you need to ask him to name all the symbols present in the table. This approach will allow parents to know exactly what their child names each picture.
- Children get tired during an eye test much earlier than their parents. Therefore, so that the child does not lose interest in this procedure, you need to start from the top row and ask him to name 1 image from each line. If at any point you notice a problem with image identification, you should go through the rest of the pictures from the same row.
Causes of vision problems in infants and children
There are a number of different vision problems that can be detected during eye tests, including:
- childhood cataracts are cloudy spots in the lens of the eye that are present from birth
- lazy eye (amblyopia) – where vision in one eye does not develop properly
- strabismus - when the eyes look in different directions
- myopia - when distant objects appear blurry while near objects are seen clearly
- farsightedness - when you can see distant objects clearly, but near objects are out of focus
- astigmatism - where the clear layer at the front of the eye (cornea) is not perfectly curved
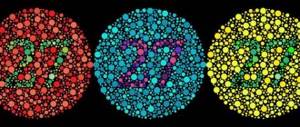
- color vision deficiency (color blindness)—difficulty seeing colors or distinguishing between different colors; it is more common in boys than girls
Checking a schoolchild's vision
For children who already know the alphabet, another method is recommended, which involves the use of Sivtsev’s table, which allows one to obtain very accurate results. It is in many ways similar to Orlova’s table, however, it does not use pictures to test vision, but ordinary letters.
Sivtsev’s table By clicking on the picture you can download it and print it
You should start, as in the previous case, from the top line, indicating the letters from left to right. The algorithm of actions in this case is as follows:
- The child should move 5 meters away from the table and cover one eye with a hand, cardboard or other object.
- Name the letters in the tenth line.
- It should take no more than 2-3 seconds to recognize each character.
- Repeat this procedure for the second eye.
If you follow these recommendations, such a vision test for children will not take much time, and the child will not get tired. If there are no errors in the names of the letters, vision is normal and there is no cause for concern. If any difficulties arise, you should contact an ophthalmologist who will conduct an examination, make an accurate diagnosis and, if necessary, prescribe the optimal treatment.
Thus, if parents know how to test their child's vision at home, they can identify possible problems at an early stage, preventing them from developing.
Symptoms and signs of disorders
- a baby who is more than 2 months old does not focus his gaze on objects when they move, does not react to the appearance of his mother in the field of view;
- there is involuntary trembling of the eyeballs (the medical term is nystagmus);
- strabismus was noticed in one or both eyes;
- the eyeballs seem swollen, this may indicate cancer, high intracranial pressure, damage to the thyroid gland;
- the pupil has changed its dark color to a lighter one and it seems that it is illuminated, this indicates oncological damage to the visual apparatus;
- the child squints, rubs his eyes, complains of discomfort, objects splitting in two, pain;
- a schoolchild or kindergartener gets tired quickly, complains of a headache or dizziness, constantly wants to sleep;
- It has been noticed that the child blinks more often than he should.
If a child has two or more symptoms on an ongoing basis, then examination by a doctor is mandatory.
conclusions
The occurrence of ophthalmological diseases in young children should not be ignored. It is at a tender age that various anomalies and slight deviations from the norm often first appear; over time, they can develop into more serious problems.
Because of them, vision impairment or blindness may begin. This causes absolute harm to children's development.
Currently, many different tables have been developed that can be used to test vision. Using them, you can accurately determine not only visual acuity, but also other required indicators.
Timely detection of vision problems helps prevent their development or provide treatment without waiting for irreversible deterioration.
Contraindications
There are practically none. Visometry is absolutely safe and can be performed on both adults and children.
However, you need to understand that the organ of vision is sensitive to any changes in the body, so the results may be inaccurate in the following cases:
during colds and infectious diseases, especially with the presence of conjunctivitis, lacrimation, irritation of the eyelids and cornea, the crisis course of hypertension - due to spasm of blood vessels in the fundus, blurred vision and the appearance of “floaters” before the eyes are possible. In this case, it is better to wait until the pressure stabilizes after a recent injury or concussion, as well as after a stroke
In these diseases, it is very important to immediately examine the fundus of the eye and retinal vessels, but it is better to postpone the determination of acuity for 1-2 months due to alcohol and other types of intoxication, which may prevent you from strictly following the doctor’s instructions.
No special preparation is required for the examination; the procedure is performed without restrictions at any examination by an ophthalmologist.
Visual acuity: treatment and prevention
Keeping your eyes healthy and strong until old age is the desire of every person; for this, doctors recommend adhering to basic hygiene measures:
There is some danger in girls’ desire to borrow someone else’s decorative cosmetics that come into contact with the eyes
But it is also better to give preference to higher quality brands with safe ingredients; Towels, sponges for washing and other hygiene products must be for individual use; Makeup should be applied carefully, without injuring the mucous membrane. Be sure to remove makeup before going to bed; When working at a computer for a long time, do not forget to do relaxing exercises for your eyes and shoulder girdle.
This will help prevent muscle fatigue and pinched nerves, which sometimes lead to decreased vision; Good lighting is required. The work area does not need too bright or, conversely, dim light. Under no circumstances should it irritate the nervous system by blinking and flickering; You should also not use sunglasses in accordance with the season, time of day and place; Try to adhere to a sleep schedule so that your eyes and the whole body rest; Do not touch your face or straighten your eyelashes with dirty hands; Stop drinking alcohol and tobacco. This will help avoid surges in intraocular pressure and circulatory problems in the eyes; Include healthy foods rich in vitamins and minerals in your diet. So, keep not only your eyes healthy, but your entire body; Stay hydrated. Liquid is necessary for the normal functioning of systems and organs, and helps get rid of harmful substances.
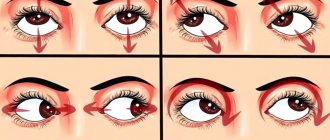
Eye exercises will help minimize the negative impact of working in front of monitors. You can get acquainted with them in this video:
Symptoms and signs of disorders
The most common symptoms and signs of disorders:
- a baby who is more than 2 months old does not focus his gaze on objects when they move, does not react to the appearance of his mother in the field of view;
- there is involuntary trembling of the eyeballs (the medical term is nystagmus);
- strabismus was noticed in one or both eyes;
- the eyeballs seem swollen, this may indicate cancer, high intracranial pressure, damage to the thyroid gland;
- the pupil has changed its dark color to a lighter one and it seems that it is illuminated, this indicates oncological damage to the visual apparatus;
- the child squints, rubs his eyes, complains of discomfort, objects splitting in two, pain;
- a schoolchild or kindergartener gets tired quickly, complains of a headache or dizziness, constantly wants to sleep;
- It has been noticed that the child blinks more often than he should.
If a child has two or more symptoms on an ongoing basis, then examination by a doctor is mandatory.