Description and history of the origin of the onion
Onion is a genus of perennial and biennial plants of the Amaryllidaceae family , which includes more than 900 different species. Among them, about 25 species are used for food, each of which includes up to 20 different varieties. There are also types of decorative onions, for example, giant onions and Christoph's onions.
Onions are used not only for food and decorative purposes, but also for the production of medicines and dyes. There are wild poisonous species of this plant.
The first historical evidence of onion cultivation dates back to 4000 BC . This fragrant plant was popular in Ancient Greece, Ancient Rome, Egypt, India, and Ancient China. Hippocrates, Aristotle, Paracelsus and other scientists and doctors of the past mentioned onions in their writings as a medicinal plant. The feathers and bulbs of the plant were used in religious rites; it was believed that their pungent odor warded off evil spirits. The ancient Romans believed that tears from onions would remove bad spirits from the body.
Onions came to the territory of Russia in the 12th-13th centuries thanks to trade with the Byzantine state. Then the fragrant vegetable was used as a folk medicine; it was also used to make protective amulets and amulets against damage, the evil eye and evil spirits. From the banks of the Danube River, different types of onions spread throughout the territory of the ancient Russian state.
The common species of onion (Allium cepa) in Russia is used as a spicy seasoning for soups, side dishes, salads, meat and fish dishes.
It can be useful:
Onion hair masks for the treatment of baldness
How to eat onions for weight loss: recipes for dietary dishes
Useful properties of leeks and their cultivation
Why onions sting children's eyes. Abstract of the educational activity “Let's plant onions for seven ailments”
Nina Kuznetsova Abstract of the NOD “Let's plant onions for seven ailments”
Summary of GCD in the middle group
"Let's plant onions for seven ailments"
Goals: Teach children to plant onions; to consolidate children's knowledge about the structure of the bulb, about the conditions necessary for plant growth (soil, moisture, light, heat); strengthen the skills of watering plants; learn to set a goal, prepare and clean the workplace.
Foster a desire to achieve results, participate in a common cause, and develop work skills. Arouse in children a cognitive interest in growing onions and a desire to care for them.
Preliminary work: examining the bulb; reading chapters from the fairy tale “The Adventures of Cipollino” by Gianni Rodari; conversation about the medicinal properties of onions.
Materials: magic bag, medium-sized bulbs, a box of soil, jars and cups for onions, gardener’s kits, watering cans, aprons; bulbs of different colors: white, brown, red, purple; colour pencils; Coloring pages with characters from the fairy tale “Cipollino”.
GCD move:
1. Organizational moment.
— Guys, a fabulous guest has come to us. Guess who it is?
Long unknown to many,
He became everyone's friend.
Chemical composition of bulbs
It was not without reason that ancient scientists considered onions to be valuable medicinal raw materials. The juicy pulp of onions contains a number of useful vitamins and minerals .
| Biologically active nutrient | Amount per 100 g of fresh onion pulp | % of recommended daily intake |
| Vitamin E | 0.2 mg | 1% |
| Vitamin C | 10 mg | 11% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.05 mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.02 mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.1 mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.12 mg | 6% |
| Vitamins N | 0.9 mcg | 2% |
| Vitamin PP | 0.7 mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B9 | 9 mcg | 2% |
| Potassium | 175 mg | 7% |
| Calcium | 31 mg | 3% |
| Magnesium | 14 mg | 4% |
| Sodium | 4 mg | 0% |
| Sulfur | 65 mg | — |
| Phosphorus | 58 mg | 7% |
| Chlorine | 25 mg | 1% |
| Bor | 200 mcg | — |
| Iron | 0.8 mg | 4% |
| Iodine | 3 mcg | 2% |
| Cobalt | 5 mcg | 50% |
| Manganese | 0.23 mg | 12% |
| Copper | 0.09 mg | 9% |
| Fluorine | 31 mcg | 1% |
| Chromium | 2 mcg | 4% |
| Zinc | 0.85 mg | 7% |
In addition to biologically active components, onion pulp contains 3 g of dietary fiber, 8.2 g of carbohydrates, 0.2 g of fat and 1.4 g of protein.
Cause of tearing when cutting onions
Protein is the reason why we cry when we cut onions . The structural components of proteins - amino acids - are always present in cell sap, of which cysteine and methionine contain sulfur in their chemical structure.
When the integrity of the cell membrane is violated, a series of intracellular enzymatic reactions are triggered , as a result of which 1-propenesulfenic acid is formed from sulfur-containing amino acids. This acid is converted to 1-sulfinylpropane, a volatile, unstable compound called a lachrymator. When lachrymator reacts with water on the surface of the mucous membrane of the eyes, nose or mouth, sulfur-containing acids and disulfides are formed, which cause irritation and burning.
The paradox of “onion grief” is that, when the mucous membrane of the eyes is reflexively irritated, tear fluid is released, but the more tears, the more fluid and the more disulfides are formed from 1-sulfinylpropane, and the more the eyes water. This biochemical mechanism was developed by the plant during evolution to protect itself from being eaten by animals.
Small amounts of disulfides formed in the oral cavity when eating fresh onions give this vegetable its pungency and pungency , which stimulates appetite and the secretion of gastric juice.
Possible dangers and precautions when cutting onions
When the lachrymator acts on the mucous membranes, an insufficient amount of sulfur-containing acids and disulfides is released to cause harm to human health. The amount of acid produced is negligible (less than 0.01%), while the tear fluid contains neutralizing substances that protect the eyes from aggressive environments.
A few minutes after contact with the volatile substances of onion juice, the normal pH of the tear fluid is restored, but the eyes hurt for some time even after rinsing. The severity of pain is individual and depends on the degree of sensitivity. The eye membranes and mucous membranes cannot be harmed by onions unless there is an individual intolerance or allergy.
In case of allergies, intolerances or hypersensitivities, you should take precautions when cutting onions :
- Use safety glasses and gauze moistened with water to protect the mucous membranes of the eyes, nose and mouth from volatile substances.
- Ventilate the room.
- After slicing, thoroughly wash your hands, knife and cutting board.
If drops of onion juice get on the sensitive mucous membranes of the nasal cavity , it is washed with a 1% solution of baking soda.
In case of contact with eyes, wash them with regular running water. If an immediate allergic reaction develops - anaphylactic shock, swelling of the larynx with obstruction of the airways, call an ambulance immediately.
What to do for oily skin:
1. Use as little makeup as possible.
The fact is that cosmetics are mixed with vinyl cutter and sebum produced in large quantities. This mixture is very difficult to cleanse and, as a result, clogs the skin pores, causing various inflammations. This happens especially often in hot weather, when sebum production increases significantly. In addition, makeup does not apply well to oily skin and looks unpleasant and sloppy.
Scientific research on “onion grief”
The chemical composition of the tear substance released when cutting onions was studied by an American chemist from Texas, Eric Block, who wondered why onions make people cry. During the experiments, Block encountered the difficulty of determining the chemical composition of the lachrymator , since 1-sulfinylpropane is unstable and instantly decomposes in water.
Eric Block also determined which acid is formed in onions as a precursor to 1-sulfinylpropane. Scientists from Case Western University in Ohio have determined the structure of the enzyme that triggers the synthesis of lachrymator in onion cells. Thanks to this research, Japanese breeders, together with colleagues from New Zealand, have developed an onion variety without a lacrimal enzyme, which can be cut without shedding tears. It is noteworthy that such onions not only do not cause tearing, but also do not have the characteristic pungent odor and bitterness.
The mechanism of lachrymator formation and the complete chain of chemical transformations occurring in onion cells during damage to the membranes was studied by Dwayne Mellor, a senior lecturer at Coventry University in the UK. The scientist notes that not all types of onions cause lacrimation during cutting, and the pungency of the onions depends on the amount of sulfur absorbed by the vegetable from the soil. Therefore, on soils rich in salts of sulfur-containing compounds, the most pungent and “evil” onions grow.
Duane Mellor, in his study of different varieties of onions, concluded that sweet, red salad varieties contain less sulfur compounds than classic white onions, and, accordingly, are less irritating to the eyes when cut.
The benefits of onions
No wonder the Egyptians idolized the onion because it had the power to scare away spirits. In a sense, it really protects us from evil - from harmful viruses and bacteria. Onions contain a huge amount of useful substances that help the body fight pathogenic microbes and also strengthen the immune system: vitamins B, C, PP, E, H, minerals and fiber.
In addition to its excellent composition, onions also have a high content of essential oils - these are phytoncides and allocins, which, in turn, have unique antioxidant properties. They protect not only the person who is cutting the onions from the harmful environment, but also other people in the room.
Sensitivity to onion lachrymator
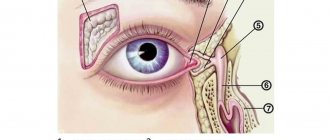
Why don't onions sting everyone's eyes? The reason lies in the individual structural features of the visual apparatus . Statistically, men have fewer receptors on the surface of the skin and mucous membranes, so they can more easily endure irritation when cutting onions. The older a person is, the thicker the surface of the epithelium of the mucous membranes and the lower the sensitivity to irritating factors.
The response to onion lachrymator varies with various eye diseases . With keratoconjunctivitis sicca, called dry eye syndrome, sensitivity to sulfur compounds in onion juice is sharply reduced until it disappears completely. In inflammatory and infectious processes, on the contrary, there is an increased secretion of tear fluid in response to lachrymatory substances.
Why do onions sting your eyes? The main reasons why the eyes sting
Know!
Many patients describe the tingling in the eyes as a burning sensation and . Often with such a symptom, you can notice other accompanying signs in the form
uncontrolled tearing
Sometimes a person has a tingling sensation accompanied by photophobia and redness of the conjunctival membrane.
In this case, there may be an irresistible urge to scratch or rub the eyes, but as a rule, this only leads to an increase in the symptom.
Depending on the disease, this sensation may be strong and constant, but may occur for short periods and go away on its own.
There can be many reasons for the appearance of such an unpleasant symptom as pinching eyes. The main factors provoking such unpleasant manifestations are the following.
- Cosmetic products and household chemicals.
In most cases, this is what causes the eyes to sting. Inappropriate or low-quality cosmetics and household chemicals, when they come into contact with the mucous membrane of the eye, become, albeit the smallest, a foreign object that the body tries to eliminate. This is why lacrimation and a pinching feeling occur. In most cases, you can get rid of this feeling by washing with clean water. In some cases, the compositions of decorative cosmetics cause not only a stinging feeling, but also redness, which can be relieved with the help of medications. As a rule, a few hours are enough for the eyes to fully recover. - Diseases of the visual organs.
Many pathological conditions lead to stinging of the eyes. Quite often, the first symptom of many diseases is stinging of the eyes. Subsequently, redness, itching and other unpleasant symptoms may appear, but this is not at all necessary. In most cases, this manifestation is characteristic of infectious conjunctivitis. But there are also many other pathologies with similar symptoms. - Allergic manifestations. Quite often, various allergic manifestations are expressed by itching or tingling. Unlike household chemicals, washing your face won't help. Unpleasant symptoms will be guarded until the allergen is eliminated.
- Spending a long time at the computer. Unpleasant symptoms can also occur from prolonged use of a computer. In this state, a person blinks less often, the mucous membrane dries out, and the eyes become overtired, and this becomes the cause. To eliminate this unpleasant manifestation, it is necessary to reduce the time you use the PC and systematically exercise your eyes.
- Use of corrective lenses. If you wear lenses for a long time, use them incorrectly, or neglect the terms of use, unpleasant consequences can occur. A pinching feeling is the most harmless of possible manifestations. To prevent this, you should not get carried away with lenses and, if possible, wear glasses.
How to cut onions without tears
In addition to using safety glasses and a gauze bandage, experienced chefs recommend using the following simple life hacks for chopping onions :
- Use a sharp knife. If the knife is not sharpened enough, the onion cells are crushed, releasing more onion juice and more lachrymator.
- Soak the bulbs for half an hour in cold water. Water decomposes the sulfur-containing lachrymator, so less of it is released when cutting.
- Wet the knife with water while slicing. The principle of operation of this life hack is the same as in the previous paragraph: water decomposes 1-sulfinylpropane. The more contact the bulb has with water, the fewer tears.
- Chop onions under a hood or fan. Directed air flow will reduce the concentration of volatile compounds in the air.
- Do not cut the onion to the spine. More sulfur compounds accumulate at the base of the bulb, so this part causes more tearing.
Practice shows that some folk methods of reducing lacrimation when cutting onions are ineffective :
- take water into your mouth while slicing;
- grease the board with lemon juice or sprinkle with salt;
- light a candle next to the cutting board;
- plug your nostrils with cotton wool;
- talking or singing while cutting.
Using a scientific approach, rather than old superstitions, you can minimize the discomfort when cooking your favorite dishes with onions.
Reviews
Housewives deal with tearing while cutting onions in different ways..
Irina, 27 years old : “I’m sharing a great way to cut onions without tears. You will need a hood, the bow itself and a board with a knife. Turn the hood on high, place a cutting board directly underneath it on the stove, and start cutting. Beauty!".
Ekaterina, 43 years old : “It’s very simple: peel the onion, cut it in half under running cold water (if the onion is vigorous or large, then into 4 parts) and put it in the freezer for 3-5 minutes. That's all! I’ve long forgotten the last time I cried from an onion.”
Tasha, 30 years old : “I read online that you need to put a lit candle next to the board. I checked it, it works! You can peel tons of onions this way – no tears! I hope someone finds this advice useful.”