Lagophthalmos is an ophthalmological pathology in which a person cannot completely close his eyelids. In common parlance it is also called “rabbit eye”. In addition to the fact that the palpebral fissure always remains open, dryness and lacrimation appear. Against the background of all the changes, vision decreases, the risk of conjunctivitis, keratitis and other eye diseases increases. Treatment of lagophthalmos is the only way to avoid severe consequences. Sometimes medications and occlusive dressings are enough, but more often you still cannot do without surgery.
Classification of lagophthalmos
Depending on the degree of intensity of the symptoms of the disorder, the following classification of lagophthalmos is found:
- weak degree - this disorder is characterized by a slight widening of the palpebral fissure. In this case, the extreme part of the lower eyelid often droops. In the medial third, it is clear that the dermis is smoothed. The patient manages to close his eyes almost completely. At the same time, during sleep the palpebral fissure is slightly open;
- moderate degree - symptoms of pathology appear more clearly than with a weak degree. As the disorder develops, the folding of the skin decreases. To close your eyes, a person has to make a lot of effort. Closing the palpebral fissure involves the orbital fragment of the orbicularis muscle. When a person sleeps, his eyes remain open;
- high degree - the eyes do not close at all. In this case, increased dryness of the conjunctiva and cornea is observed. As a result, inflammation and dystrophy of the visual organ develop.
Diagnostics
There are usually no difficulties in diagnosing “rabbit gas”. His clinic is very characteristic and rarely causes diagnostic difficulties. This diagnosis is indicated by the typical appearance of the patient and his complaints.
Typically, with lagophthalmos, patients note a feeling of sand in the eye and lacrimation. In this case, the specialist must conduct an instrumental neurological examination. This is necessary to identify the cause of the pathology.
In addition to physiological lagophthalmos, there are also 3 degrees of the disease with different anatomical manifestations:
- weak degree;
- average degree;
- strong degree.
Untreated lagophthalmos is a very dangerous thing, since if it lasts for a long time, it seriously damages the eye of patients.
With this disease, erosions and ulcers of the cornea, and then clouding of the eye, are common.
The treatment of this eye pathology should not be delayed.
Doctors often have to distinguish lagophthalmos from another eye pathology - ectropion of the eyes (eversion of the eyelids).
Causes of lagophthalmos
When lagophthalmos occurs, the closure of the eyelids is impaired. This is due to anatomical deviations, problems with innervation and the influence of external factors.
{banner_gorizontalnyy}
The key causes of lagophthalmos include the following:
- Paralysis and paresis of the facial nerve.
These pathologies cause problems with the innervation of the circular muscle of the optic organ. In normal condition, it is responsible for the motor activity of the eyelids. Such conditions are usually caused by the development of complex pathologies, traumatic injuries or surgical interventions. - Developmental deviations.
The pathology may be secondary. This disorder is typical for people with coloboma and symblepharon. In the first case, the conjunctiva in the splitting zone does not close. In the second, fusion of the orbital and palpebral conjunctiva is observed, as a result of which the eyes cannot close normally. - Pathology of the trigeminal nerve.
According to its structure, the fifth pair of cranial nerves belongs to the mixed category. Therefore, when it is damaged, not only motor function is disrupted. Sensitivity to pain, temperature, and touch also suffers. Trauma, complex diseases, and surgeries lead to pathologies of the trigeminal nerve. - Cicatricial eversion.
In such a situation, insufficient closure of the palpebral fissure is due to the fact that the lower eyelid sags. - Exophthalmos.
Displacement of the eyeball creates difficulties with closing the palpebral fissure. Moreover, they occur even with a normal structure of the organ of vision. - Retraction of the upper eyelid.
As the pathology develops, a shift of the skin fold towards the top of the orbit is observed. As the disorder develops, the sclera is exposed.
Treatment
Treatment of facial paralysis is carried out by a neurologist. To protect the eye from drying out and infection, drops or ointments containing sulfonamides and antibiotics are injected into the conjunctival cavity. When cicatricial eversion of the eyelids occurs, operations are performed to eliminate it. In the case of persistent L., partial suturing of the palpebral fissure is indicated (see Blepharorrhaphy). A significant distance of the lower eyelid from the eyeball is also corrected through surgery - a ligature made of synthetic materials or a strip of autofascia of the thigh is passed through the entire length of the eyelid (from the inner to the outer commissure).
Symptoms of lagophthalmos
At the first stage of development, the pathology is accompanied by incomplete closure of the palpebral fissure.
In this case, the person’s conjunctiva dries out. The following symptoms of lagophthalmos also occur:
- burning;
- severe tearing;
- conjunctival hyperemia.
As the disease progresses, the upper eyelid does not droop. As a result, the person cannot blink. Redness of the orbital conjunctiva is more pronounced in the morning, since the palpebral fissure remains open at night.
Patients complain of the appearance of a veil before their eyes. Excessive lacrimation in this pathology is complemented by photophobia. If there is loss of the corneal reflex, corneal irritation does not lead to eye closure.
Symptoms of the disease depend on the origin. When paralysis of the orbicularis muscle occurs, ectropion appears. If the lacrimal punctum is displaced, excessive tearing occurs. Signs of blepharitis appear quite early, and sluggish conjunctivitis develops.
If lagophthalmos of the eye is associated with pathology of the trigeminal nerve, the production of tear fluid is disrupted. Damage to the seventh pair of cranial nerves provokes dryness and a feeling of the presence of a foreign object. The prolonged presence of paralysis causes the development of atrophic changes, which manifest themselves as a decrease in eyelid turgor. They can move downwards or evert out.
What is lagophthalmos
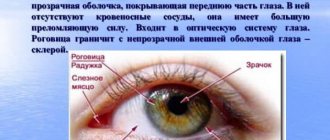
The diagnosis of “lagophthalmos” (from the Greek lagos - hare and ophthalmos - eye) is diagnosed when the eyelids of one or both eyes are not completely closed.
A healthy eye always retains protective mechanisms against environmental harm. It is the physiological hydration of the eye that allows it to retain all the most important qualities. To blink and moisturize the eye, the eyelids must close together. If this is not the case, then the organ of vision begins to dry out, which is unacceptable. Chronic eye dryness leads to a lot of troubles and ailments of the “apple of the eye.”
Why does this pathology occur? Often the eye cannot close completely due to strong protrusion of the eyeball. Such a pathological process can occur due to serious changes in the body. And the pathology may not necessarily concern the eye itself. It happens that lagophthalmos is caused by pathologies of other organs. Most often, non-closure of the eyelids can occur when:
- coloboma (congenital underdevelopment of the eyelids);
- paresis or paralysis of the facial nerve;
- Bell's palsy;
- cicatricial eversion of the eyelids (as a consequence of burns or operations);
- trachoma;
- protrusion of the eyeball (exophthalmos) due to pathology of the thyroid gland or orbital pathologies (tumors of the eyeball, etc.);
- consequences of unsuccessful facial plastic surgery;
- injuries to the face or middle ear;
- consequences of brain injuries with skull fracture;
- inflammation of the ear salivary glands;
- high myopia;
- accretion of the eyelid to the conjunctiva (symblepharon);
- blisters on the eyelids and conjunctiva (pemphigus);
- vitamin A deficiency.
It also happens that non-closed eyelids appear in people for no apparent reason. At the same time, a person may not know about this peculiarity of his. The patient does not feel any discomfort with this form of lagophthalmos. In this case, they speak of physiological lagophthalmos. Often this cosmetic defect is visible in infants already at birth.
Diagnosis of lagophthalmos
To make an accurate diagnosis, an external examination is performed. At the same time, the doctor asks the person to close his eyes. This needs to be done in different ways - as usual or by making additional efforts. This helps to establish the severity of the pathology.
A specific examination by an ophthalmologist is required for early detection of changes in the structure of the visual organ and selection of a treatment regimen.
Diagnosis of lagophthalmos is carried out by an ophthalmologist. It includes the following procedures:
- visometry - during the examination, visual acuity must be measured. With serious pathology, visual dysfunction often occurs;
- biomicroscopy - the procedure helps to identify symptoms of damage to the conjunctiva and cornea. If signs of inflammation or infection are detected, the operation is performed only after they have been eliminated;
- Ultrasound examination in B-mode - this procedure is required if there is a suspicion of pan- and endophthalmitis. If the transparency of the optical media of the visual organ is impaired, optical coherence tomography is performed instead of ultrasound.
To select the correct method of therapy, a differential examination is carried out. It is aimed at determining the etiology of lagophthalmos. With a paralytic origin of the disease, additional symptoms include smoothing of the folds on the forehead. The corner of the mouth also droops. In such a situation, it will not be possible to do without consulting a neurologist.
Pathologies in the structure of the eyelids are isolated. They are usually detected at an early age. Injuries or inflammatory processes lead to cicatricial eversion or development of retraction. Before performing surgery, a whole range of studies must be performed.
{banner_horizontalnyy2}
Photo
Ophthalmology classifies lagophthalmos by severity and degree of expression of symptoms. A few clear examples will help you better understand what patients are facing.
Low degree photography
Visual changes are not noticeable, the patient does not feel anxiety. The palpebral fissure is not very slightly open. The drooping of the lower eyelid is minimal. The medial third is defined by slight smoothing of the skin. So far there is no great difficulty in closing my eyes. The circulation of tear fluid is within normal limits. A small gap appears during deep sleep. Effective treatment will slow down the process and restore the functionality of the orbicularis muscles. There is no need to resort to radical means.
Photo of moderate lagophthalmos
The clinical manifestation of lagophthalmos is much more pronounced. A sharp reduction in skin folding. The patient needs to make a lot of effort to close both eyes tightly. You have to focus on blinking and use the orbital part of the circular muscles. There is a feeling of dryness and burning in the conjunctiva due to a lack of tear fluid and poor lubrication. During sleep, the eyes are completely open, which leads to dust and infection. Treatment must be carried out using comprehensively the entire available arsenal.
Photograph of severe lagophthalmos
The patient is unable to close his eyes. The complete absence of tear fluid leads to dryness of the conjunctiva and cornea. The result is inflammation of the membrane of the eye, leading to loss of vision. Therapeutic means cannot correct the situation. Lagophthalmos at this stage can be effectively combated exclusively by surgical methods.
To prevent the disease from becoming a big problem and becoming chronic, you need to immediately go to a specialist if you have the slightest doubt about the quality of the eye muscles. Even a small gap when closing and blinking requires consultation with a doctor. Unusual dryness, redness, burning, and the apparent presence of sand under the eyelid indicate the development of the disease. Therapeutic agents can easily slow down the progression of the disease in the first stage. This will prevent more serious changes in facial muscle tissue and nerve endings.
Without drawing the proper conclusions and ignoring minor inconveniences, the next stage will certainly develop. The eyelids stop participating in blinking, and the hyperemia of the orbital conjunctiva increases, since the palpebral fissure remains open at night. Patients often complain of decreased vision and the appearance of a cloudy veil. Lagophthalmos has dangerous consequences because it leads to complete loss of vision. Properly chosen treatment based on modern therapy, medication and surgery will restore the normal functioning of the orbicularis oculi muscles.
40% of patients suffering from lagophthalmos turn to ophthalmologists because of dryness, irritation of the cornea and a sharp deterioration in vision when the disease has entered the chronic stage. The appearance of catarrhal conjunctivitis indicates the last stage of the development of the disease. Lack of lubrication and protection of the eye causes the formation of numerous ulcers and a cataract develops. Severe forms lead to perforation and complete loss of vision.
Diagnosis begins with a visual examination of the eye. It is easy to determine the degree of lagophthalmos. We close our eyes. the presence of a gap between the eyelids indicates health problems. Special techniques and modern equipment help to choose means to combat the disease. Several types of eye exams will be needed.
Biomicroscopy. Identifies the symptoms and extent of damage to the cornea and conjunctiva. Having visually determined the onset of infectious inflammation, it is necessary to immediately begin treatment in order to prevent it from entering the acute phase.
Visometry. Visual acuity is measured using available means. The progressive disease is accompanied by severe dysfunction of visual perception.
Ultrasound. B-mode. Recommended for patients with suspected pan and endophthalmitis. If observed, severe opacities will require OCT.
Timely diagnosis will help overcome lagophthalmos. If you notice drooping corners of the lips or the absence of age-related folds on the forehead, you need to consult a neurologist in case of paralysis or stroke. Abnormal development of the eyelids is diagnosed in children at an early age. Cicatricial eversion or retraction is always the result of injury or complex tissue inflammation. If urgent surgical intervention is necessary, the patient is prescribed a detailed examination, requiring hospitalization and clinical conditions.
Treatment of lagophthalmos
When pathology develops, medications are often used that promote timely hydration of the orbital surface of the visual organ.
The key goal of therapy is to prevent the occurrence of xerophthalmia. At the same time, people with this diagnosis are prescribed the following medications:
- Antiseptic drugs.
The systematic use of such funds helps to avoid the development of infectious consequences and inflammation. - Artificial tear preparations.
These medications are indicated for the development of the disease against the background of damage to the trigeminal nerve. The need for such drugs is due to a violation of the production of tear fluid. - Humidifiers.
They are recommended to be used every day. This helps prevent complications and allows you to compensate for the key symptoms of lagophthalmos in the initial stages of its development. - Anti-inflammatory substances.
Such medications are prescribed when inflammation or infection is detected. They are indicated for keratitis, blepharitis, conjunctivitis.
Conservative methods for correcting the position of the eyelids include the use of adhesive dressings. This method is considered simple and economical. However, it does not achieve long-term effects.
To obtain a stable result, surgical intervention is performed in the treatment of lagophthalmos. The operation is aimed at restoring complete closure of the palpebral fissure. Its features depend on the cause of the development of lagophthalmos.
For facial paralysis, reconstructive interventions are indicated. Neurolysis helps to release the nerve from scar tissue that causes compression. Autotransplantation or reinnervation can also be performed. In this case, the distal part of the facial nerve is fastened to the central part of the accessory or hypoglossal nerve.
To correct the position of the palpebral fissure, tarso- or blepharorrhaphy is used. To avoid severe trauma, a special stretched thread must be passed through the eyelid. Gold or platinum implants are highly effective. If implantation cannot be performed, alternative methods of therapy are chosen. Thus, a recession of levators is often carried out. If the pathology is characterized by abnormal eversion, canthoplasty is performed.
To provide palliative care, a person is given injections in the upper eyelid. For this, hyaluronic acid or botulinum toxin is used. This substance helps lower the upper eyelid.
With proper treatment, the pathology usually has a favorable prognosis. Thanks to timely surgical correction, it is possible to restore normal operation of the eyelids. If treatment is not started in time, there is a risk of inflammation and degenerative complications. They can manifest themselves in the form of corneal perforation, panophthalmitis, and the formation of a cataract.
Causes
What contributes to the development of the disease leading to such consequences?
These include lesions of the facial nerve that innervates the orbicularis oculi muscle, or other mechanical effects that prevent the eyelids from closing completely, or their congenital underdevelopment, which does not allow the eye to close completely.
Other factors that have the potential to develop into this condition may include:
- otitis media, as well as other disorders of the hearing system;
- hypothermia;
- exophthalmos, inflammatory process in the parotid salivary gland;
- facial and skull injuries;
- previous flu with complications;
- various diseases of the central nervous system.
Lagophthalmos in children
The cause of lagophthalmos in children is the anatomical features of the eyelids, disruption of the innervation of the orbicularis oculi muscle, or traumatic injury.
Only a specialist can identify the disease. This is done by an ophthalmologist or neurologist. Parents should sound the alarm if their baby constantly sleeps with his eyes slightly open. If the eyelids do not close tightly only during the period of shallow sleep, this is not a deviation. This symptom indicates physical and nervous overexcitation that the child experienced while awake.
Physiological lagophthalmos, which is present in the first 12-18 months of life, is not a symptom of pathology. Usually, nervous overstrain leads to the child, in addition to manifestations of lagophthalmos, experiencing shuddering, muttering, babbling, and twitching of the limbs. Sometimes the baby may laugh or cry in his sleep.
Most often, lagophthalmos in children does not lead to negative consequences.
However, the presence of pathology during the daytime can lead to the following complications:
- drying of mucous membranes;
- infection and damage to the cornea;
- blurred vision.
In such a situation, you should immediately consult a doctor. The specialist will prescribe surgical intervention - blepharorrhaphy.
{banner_horizontalnyy3}
Prevention measures
There are no specific recommendations. It is necessary to avoid injuries and treat infectious diseases in a timely manner, not only ophthalmological, but also of the ENT organs. When working at a computer, you should use artificial tear drops, since the mucous membrane is not sufficiently moisturized.
The prognosis for lagophthalmos is favorable only if treatment is started on time. It is important to restore the functioning of the eyelids as quickly as possible. Moreover, this can only be done through surgery. But there is no need to be afraid of surgery. Because the consequences of untreated pathology are much worse.
Lagophthalmos can significantly reduce quality of life. Moreover, there is a high probability that pathology will deprive you of the most valuable thing - the ability to see the world. If you know for sure that you sleep with your eyes slightly open in your sleep, go to an ophthalmologist as soon as possible.
Express Your Reaction
Similar articles:
Macular degeneration is a cause of blindness in older people!
The process of aging also includes susceptibility to diseases that occur in old age...
Laser vision correction: arguments for and against
Some people see this world brightly and clearly, but for others everything around is unclear and blurry. Save your...
The retina of the eye - where it is thin, it tears...
I learned about this disease by chance, from a friend of mine, and decided to undergo fundus diagnostics. After…
Conjunctivitis
Every person has probably encountered conjunctivitis at least once in their life. Seemingly at first glance…
Retinal angiopathy - causes, symptoms, types and treatment
Retinal angiopathy is a change in the blood vessels of the fundus. They expand, contract, or their distortion arises...
Dacryocystitis of newborns - false conjunctivitis
Both pediatricians and parents, when there is discharge from a child’s eyes, first of all suspect conjunctivitis...
Complications of lagophthalmos
In 30-40% of cases, the disease leads to xerophthalmia. This condition provokes increased dryness of the cornea and conjunctiva. As lagophthalmos complicates, a person may develop catarrhal conjunctivitis and neurotrophic keratitis.
When ulcerative defects appear on the cornea, leukoma develops. It is characterized by blurred vision and the formation of a cataract. In difficult situations, corneal perforation is observed. The appearance of endophthalmitis can cause irreversible visual dysfunction and enucleation.
Complications
Lagophthalmos is accompanied by drying out of the cornea, which causes complications. Against this background, chronic and even catarrhal conjunctivitis, xerophthalmia, and neurotrophic keratitis develop. As a result, more serious problems arise.
The nutrition of the cornea is disrupted, its sensitivity decreases, and it begins to become cloudy. Ulcers do not heal well, so inflammation often occurs, infiltrates and a cataract (leukoma) form. As a result, visual acuity decreases. If treatment for lagophthalmos is not started at this stage, corneal perforation occurs. Then endophthalmitis develops - purulent inflammation that affects the inner membranes of the eyeball and the vitreous body. As a result, there is a risk of enucleation. This is an operation to remove the eyeball.
All these dangerous consequences can be avoided if the pathology is detected in a timely manner and treated.
Prevention of lagophthalmos
There is no specific prevention for lagophthalmos. Nonspecific methods are aimed at eliminating risk factors. They include timely treatment of infections and autoimmune pathologies, as well as lesions of the middle ear.
Lagophthalmos is a serious disorder that can lead to dangerous complications. To cope with the disease, you need to consult a doctor in time. To combat the symptoms of the pathology, the specialist prescribes medications. The pathology can be completely eliminated only through surgery.