Classification of eye asthenopia
Eye asthenopia is classified into the following types:
- Accommodative asthenopia.
The most common type of pathology, in which the development of the disease occurs due to weakening of the muscles associated with the movement of the lens. Deterioration in muscle function occurs due to a spasm of accommodation due to astigmatism, farsightedness and other diseases that cause decreased vision. - Muscular asthenopia.
This type of disease occurs due to overstrain of the muscles responsible for the functioning of the eyeball. Often the development of pathology is provoked by the presence of myopia and strabismus. The most serious complication that is possible with improper treatment or its absence is loss of binocular vision. - Combined asthenopia.
With this type of asthenopia, symptoms and disturbances in the functioning of the visual apparatus appear that relate to the two previous types of the disease. A common sign of combined asthenopia is the patient’s complaints of decreased visual acuity due to blurriness or double appearance of objects. - Asthenic asthenopia.
It often occurs due to general fatigue of the body, against the background of various infectious diseases, and due to poor lifestyle choices. Intoxication can also provoke the occurrence of asthenopia of this type. - Neurogenic asthenopia.
With this type of asthenopia, the onset of the disease is provoked by deviations in the functioning of the central nervous system. In this case, neurologists or psychiatrists are involved in prescribing a treatment regimen. - Symptomatic asthenopia.
In this case, the development of asthenopia provokes pathologies of internal organs and inflammatory processes of various types. Elimination of unpleasant symptoms will largely depend on the success of treatment of the disease that caused the development of asthenopia.
{banner_horizontalnyy}
Asthenopia (visual fatigue)
“Our eyes are tired,” we say when we read for too long, or work at the computer, or repair our watches, or sew. This is usually followed by a gesture that, again, is familiar to everyone: rub the inner corners of the eyes with the tips of the index and thumb (the physiological meaning of this instinctive gesture is to stimulate blood circulation and eliminate mechanical stagnation). However, the eyes can get tired after four hours of continuous concentration, or after ten minutes. In the latter case, they talk about rapid fatigue of the visual system, or asthenopia (the well-known cognate word “asthenia” translated from Greek means “lack of strength”; asthenopia, accordingly, is “powerlessness of the eyes”).
Causes of eye asthenopia
The development of eye asthenopia can be caused by many reasons, among the main ones:
- driving transport in weather conditions that create insufficient visibility;
- work involving examining small or merging-colored parts (embroidery, knitting, sewing);
- nervous shocks of various nature;
- reading books in dim or too bright lighting;
- incorrect selection of frames or lenses;
- frequent work at a computer monitor;
- various diseases of the visual organs (myopia, astigmatism, farsightedness);
- watching TV from too close a distance.
Symptoms of eye asthenopia
Eye asthenopia has the following clinical symptoms:
- painful sensations in the eye area - cutting, burning, having varying intensity and duration;
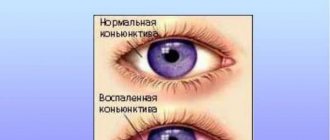
- pronounced redness of the organs of vision;
- lacrimation, varying strength;
- photophobia;
- difficulty in determining the shade and dimensions of surrounding objects;
- problems focusing on objects;
- the appearance of a “veil” effect before the eyes or “fog”;
- manifestation of the “jumping letters” syndrome, due to which reading will be difficult;
- objects blur before the eyes or appear double.
In addition to the listed symptoms, patients often experience headaches. They vary in strength and duration depending on the stage diagnosed. Moreover, the pain is migrating in nature, it can move to the neck and shoulders.
A frequently diagnosed sign of pathology is attacks of nausea. In addition, patients complain of a feeling of foreign objects in the eye area. Although the doctor does not detect them during examination. These complaints indicate the presence of “sand in the eyes” syndrome; it is a frequent accompaniment of the development of pathology.
At the compensation stage, all symptoms of the disease are short-lived; they can disappear within 10-15 minutes after their onset. Most patients may not even register their occurrence as they go away after a short time. The next stage is characterized by an increase in the duration of the manifestation of negative symptoms.
Signs of the disease appear a short time after rest. Clinical symptoms occur even with small amounts of exercise. At this stage, with proper treatment, all pathological processes are reversible. At the stage of decompensation, pathologies that are characterized by an irreversible nature arise.
What are the symptoms of this condition
When our arms or legs get tired, we feel weakness in them and difficulty in performing some actions. The same thing happens with the eyes. Their visual function is impaired or not fully performed. It is important to understand that such a violation can be temporary (for example, during the performance of some work) or persistent (changes in accommodation and refraction are long-term.)
Symptoms of asthenopia are subjective and objective.
Subjective feelings:
- Tired eyes “put pressure on the consciousness” - a person loses concentration and performance, feels a headache, weakness, absent-mindedness, and general malaise.
- Visual disturbances include blurred vision, loss of clarity of vision, and double vision.
- Eye sensations – dryness and tension of the eyeballs, a feeling of sand, a desire to close the eyelids, photophobia.
When examining such patients, it is possible to identify objective disorders:
- Presence of symptoms of refractive error.
- Deterioration of accommodation.
- Symptom of "dry eye".
- On examination, redness, frequent blinking, and lacrimation are noticeable.
Asthenopia in children
Asthenopia in children often occurs in connection with other diseases of the eye area. In addition, in the absence of proper correction of emerging vision problems, pathology may also appear. Children diagnosed with astigmatism and myopia are at particular risk.
Schoolchildren most often develop an accommodative type of disease. Asthenopia of this type when diagnosed in a child does not require special therapeutic measures. Healing occurs with age due to the natural enlargement of the organs of vision, as the previously relaxed ciliary muscle begins to grip the lens of the eye more tightly.
Today, due to the high prevalence of gadgets, the disease often occurs in preschool children. The main symptoms include redness, tearing and disruption of sleep. In this case, it is necessary to limit the child’s interaction with the source that causes negative symptoms. {banner_horizontalnyy2}
Smartphones, tablets and computers must be kept away from children. Rest and sleep will allow the child's body to recover from eye fatigue. Among the main therapeutic measures of the initial stage are gymnastics and nutrition enriched with vitamins.
If you have any unpleasant symptoms, you should consult an ophthalmologist. Only with the help of qualified therapy can the development of complications be prevented. A complete examination can make it possible to make the correct diagnosis and, if necessary, prescribe treatment.
Diagnosis of eye asthenopia
To identify the presence of asthenopia in a patient, the ophthalmologist prescribes a series of diagnostic tests.
These include:
, with its help determine the degree of myopia and astigmatism, identify refractive errors;
, prescribed for examining the eyeball, in particular its anterior sections;
, its implementation makes it possible to establish the visual acuity of the subject and identify possible deviations;
, using this examination to assess the refractive ability of the visual apparatus;
, determines the point of clear vision, reveals the syndrome of splitting or blurriness of objects;
, allows you to assess the state of binocular vision;
is carried out if such a diagnosis was made to the patient during the examination.
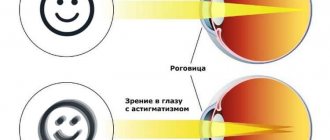
Accommodative asthenopia
The cause of this type of asthenopia is uncorrected farsightedness, presbyopia (age-related weakening of near vision) and astigmatism, which results in strong tension in the ciliary muscle (an intraocular muscle, the contraction and relaxation of which changes the shape of the lens of the eye and thereby allows a person to see well at different distances) .
Asthenopia can develop already at school age, but go away over time due to the continued growth of the eyeball and increased efficiency of the ciliary muscle.
In adults, the appearance of asthenopia with good vision most often occurs after 40 years with the development of age-related weakening of near vision (presbyopia), and in this case, the symptoms of asthenopia will intensify with its progression.
If there are complaints of visual fatigue, the ophthalmologist conducts a study of visual acuity of the eyes with and without correction and a mandatory study with maximum relaxation of the ciliary muscle (state of cycloplegia), using special eye drops.
If the result is farsightedness, presbyopia, or astigmatism, then subsequent treatment of asthenopia will be based on the correction of these disorders using glasses and contact lenses.
Means for correcting such disorders with concomitant asthenopia are prescribed as early as possible; in parallel, the issue of a rational regime of visual stress, proper organization of the workplace, regular breaks during visual work, and general strengthening measures are resolved.
Children are given glasses to wear all the time. Adults with high, sufficient distance visual acuity select glasses for working and reading at close range.
Treatment of eye asthenopia
Therapeutic measures will depend on the stage of the disease and its type.
Treatment of various types of eye asthenopia occurs as follows:
- With the accommodative type of asthenopia, the use of glasses or contact lenses is prescribed. The prescription is written by an ophthalmologist.
- The muscular form is eliminated using a synoptophore. This device allows you to train weakened muscles of the visual apparatus.
- With the combined type, both wearing glasses and treatment with a synoptophore are combined.
- With the asthenic type, treatment should include identifying the cause of the disease. Only its elimination can ensure the effectiveness of therapeutic measures. As a rule, the patient should focus on maintaining a healthy lifestyle, improving the quality of nutrition, and changing the work schedule.
- Symptomatic therapy cannot be done without treating the disease that causes asthenopia.
- The neurogenic form involves undergoing treatment by a neurologist and visiting a consultation with a psychiatrist.
Depending on the stage of asthenopia, the following measures are distinguished:
- At the initial stage, more rest and proper nutrition are often prescribed. It is recommended to isolate the organs of vision from work requiring excessive stress.
- At the subcompensation stage, hardware techniques are prescribed. An accomodo trainer and Sidorenko glasses have an effective therapeutic effect.
- The stage of decompensation is not complete without corrective optics and prescription of contact lenses. Additionally, the ophthalmologist prescribes the use of special eye drops. Their use stimulates the contractility of the muscles that affect the diameter of the pupil. For example, Tropicamide or Mydriacyl.
Mydriatics can also help in milder stages of the disease. To quickly eliminate the symptoms of eye fatigue, Visine or Systane drops are prescribed.
Types of asthenopia
Despite the apparent “simplicity” of such a phenomenon as eye fatigue, it is by no means, firstly, harmless, and secondly, simple. Asthenopia (like any other local “powerlessness” in the body) can be based on various, including quite serious, reasons. Thus, according to the etiological, causal principle, several variants of asthenopia are distinguished.
Accommodative asthenopia
An increased load on the eyes is any refractive error, be it myopia, farsightedness, astigmatism, presbyopia, which a person does not consider necessary to correct with glasses or lenses. In such cases, the visual system reflexively, regardless of consciousness, overstrains itself in an attempt to ensure the maximum possible visual adaptation to the environment. This evolutionary mechanism was formed in those times when the life of a given individual literally depended on the vigilance, attentiveness and “resolving power” of the eyes. Therefore, the ciliary (“ciliary”) body, which performs several functions in the eyeball, including accommodation, will in any case be excessively strained or, conversely, stretched in order to give the lens the necessary curvature of the surface, i.e. the refractive power required for a given case.
If the focal point, despite all efforts, still ends up behind, in front of or to the side of the macular region of the retina (or there is no single focus at all, as happens with astigmatism), the ciliary muscle still does not give up its attempts to accommodate and adjust vision at the required distance. Obviously, such a regime is completely anomalous for the delicate ocular biomechanics; overload will increasingly deplete muscle fibers, leading to increased concentrations of lactic acid (“fatigue hormone”) and the development of asthenopic symptoms.
Accommodative asthenopia often manifests itself at school age, which is due to a combination of a number of unfavorable factors for the eyes: rapid growth of the body, hormonal instability and endocrine changes, traditional school overload, passion (sometimes manic) for TV or computer games, lack of sleep, etc. This pathogenic combination is well known, but is not always taken into account by parents when organizing the child’s study, recreation, physical and mental activity regime. In fact, have all parents tried to at least approximately track how many hours a day the child spends almost motionless, peering at the small screen of a smartphone?
The most favorable, but, unfortunately, far from guaranteed outcome may be a spontaneous reduction of asthenopia with further growth and formation of the eyeball, as well as strengthening of the accommodating muscles.
In adulthood (usually after 40 years), even against the background of normative visual acuity, ocular weakness and fatigue may be accompanied by the initial stage of presbyopia, i.e. farsightedness due to age-related weakening of the ciliary muscle. In such cases, asthenopia progresses in parallel with the worsening of farsightedness.
A person may not immediately notice rapid visual fatigue, but gradually the problem becomes too obvious to ignore. Needless to say, this kind of symptom complex requires, at a minimum, an examination and consultation with an ophthalmologist, and you should contact it as early as possible.
Patients with suspected accommodative asthenopia must undergo visimetry - a thorough measurement of visual acuity and refractive parameters of the eye. For this purpose, special diagnostic glasses with a set of replaceable lenses are used, and mydriatic drops are instilled into the eyes, providing cyclopegia (essentially artificial paralysis of the accommodating muscle in its extremely relaxed state) and pupil dilation.
If the doctor establishes a clear connection between asthenopic symptoms and existing ametropia (refractive error), i.e. the accommodative nature of asthenopia will be confirmed, the first and most important therapeutic step is the appointment of optical correction - glasses or contact lenses - without which any further steps will be meaningless. As a rule, constant wearing of glasses is prescribed in childhood or adolescence; for adults, provided the acuity of “distant” vision is relatively preserved, glasses can be selected for reading or for working with small objects at a short distance.
In addition, a patient with this type of visual fatigue is strongly advised to pay attention to how his usual working day is organized; how long do intensive loads on the visual system alternate and with what? how the workplace is lit; how many hours a day are devoted to rest and how much, in particular, to sleep; whether there is activity in his life that can be considered generally strengthening (amateur sports, tourism, summer cottage, etc.). It is impossible to imagine a situation where all these factors cannot be optimized in principle: even basic eye gymnastics, taking just a few minutes, can radically relieve eyes that have become petrified in constant tension.
Any doctor knows the latent (and sometimes openly manifested) irritation that such “banal” and “primitive” recommendations cause in many patients: unfortunately, we often prefer to believe in expensive imported tablets or drops, although much better and longer lasting ( and most importantly, an effect that is natural for the eyes) could be achieved by overcoming elementary laziness and thinking about what our vision will be like in three, five or ten years.
Muscular asthenopia
The muscular variant of asthenopia, as the name suggests, is associated with dysfunction of the muscular system of the eyeball; in this case we mean not internal accommodating, but external oculomotor muscles, which ensure rotation of the eye in all planes.
If a myopic person does not resort to optical correction, relatively successful functioning of the visual system at close distances can be achieved at the cost of excess convergence: the eyes, when the oculomotor frame is tense, are reduced to the bridge of the nose. With normal vision, focusing is achieved by the effort of the ciliary muscle and an increase in the curvature of the lens; with myopia, the accommodating muscle is relaxed, and stereoscopic (3D) vision is ensured precisely by convergence. This is especially true for those cases where the degree of myopia in the right and left eyes is different: to form a binocular image, the brain “requires” an equally clear signal from both retinas. The development of the asthenopic symptom complex is thus caused by a discrepancy between the degree of tension of the accommodative and oculomotor muscle systems.
It is also possible to develop heterophoria, or latent (hidden, implicit) strabismus. This variant of strabismus is not noticeable with open eyes, but if one of them is closed, it turns out that the axis of the open eye is still directed straight, while the axis of the closed eye deviates, i.e. leans to the side. This ophthalmopathological phenomenon is due to the uneven development and different functional state of the oculomotor muscles. The fact is that the “rotary” system, fused with the outer surface of the eyeball, consists of six separate muscles, and if some of them are more developed than others, the rest have to overexert themselves to compensate for this difference in strength. Accordingly, constant excess tension inevitably depletes muscle tissue and leads to asthenopic symptoms.
Closing the eye relieves excess tension, the extraocular muscles (including the weaker and, therefore, more tired ones) relax, and the rotation of the closed eye may be inconsistent with the movement or gaze of the open one. It should be noted that heterophoria is not a condition that can be dismissed with disdain; with long-term existence of hidden strabismus, true strabismus easily develops.
The therapeutic strategy for muscular (as well as for accommodative) asthenopia includes, as a first-priority measure, optical correction of myopia. If latent strabismus is detected, the best and most effective remedy is a system of eye training exercises. For these purposes, special devices have been developed and used. Often, for example, synoptophore training is prescribed; the principle of its operation is the separate presentation of two images to the right and left eyes - a person, observing these images through the eyepieces, must, through an effort of will, merge them into a single visual image, which can only be ensured by coordinated tension (and therefore training) of the oculomotor muscular system . Such trainings are prescribed in the form of a more or less long series; if necessary, a repeated course can be prescribed, which in most cases makes it possible to achieve pronounced and stable therapeutic success: strabismus is gradually reduced. If the desired result is not achieved, the ophthalmologist calculates and prescribes special glasses with prismatic curvature, which, even with deviation of one of the eyes, allow you to see quite well without overworking the eye muscles.
Asthenic asthenopia
Eye fatigue can be a consequence and one of the manifestations of systemic asthenia - general exhaustion, weakening, "weakening" of the body - which manifests itself in a wide range of mental and physiological disorders. Asthenopia as part of a general asthenic symptom complex occurs, as a rule, after suffering systemic diseases, severe infections, various intoxications, as well as due to chronic physical or intellectual fatigue or an unhealthy regime of workload and rest. From here the necessary response measures naturally follow: massive restorative therapy, rationalization and normalization of the daily routine, vitamin therapy, and, if possible, long-term rehabilitation and restorative rest (for example, sanatorium treatment). But the first and mandatory step is to treat the underlying asthenic pathology, if any.
Symptomatic asthenopia
Asthenopia of the symptomatic type is a local reaction to infectious and inflammatory diseases of the eye and adjacent organs (ear, nasopharynx, oral cavity, etc.). Often, visual fatigue is one of the earliest symptoms of incipient inflammation of the intraocular structures, which also involves the ciliary body. With symptomatic asthenopia, high-quality diagnosis (if necessary, with the involvement of related specialists), localization of the inflammatory focus and its adequate treatment are crucial.
Nervous asthenopia
If all the reasons described above are reliably and reliably excluded, all that remains is to assume the psychogenic origin of eye fatigue. Indeed, in certain forms of neurotic disorders and personality anomalies (primarily neurasthenic and hysterical types), asthenopia is one of the components of the general neurotic syndrome. Obviously, in such cases, etiopathogenetic (aimed at eliminating the causes) therapy should be provided by a neuropsychiatric specialist.
If you notice signs of visual fatigue (asthenopia), contact the specialists of our ophthalmology center: modern equipment and extensive practical experience of doctors will help you quickly determine the cause and effectively eliminate the problem.
Complications of eye asthenopia
If treatment was carried out on time in the early stages of the disease, then recovery occurs in a short time and without complications.
However, the lack of qualified assistance for eye asthenopia leads to a number of negative complications:
- blepharitis;
- conjunctivitis;
- strabismus;
- decreased visual acuity due to the development of complications;
- the appearance of neuroses due to frequent attacks of migrating pain.
{banner_horizontalnyy3}
Prevention of eye asthenopia
The main preventive measures for eye asthenopia are as follows:
- First, you need to work on proper workplace lighting. The light should not be too dim or too bright, and sudden changes in lighting are not allowed. For example, you should not look at a glowing monitor in complete darkness. Natural light has the most gentle effect on the organs of vision. In rooms isolated from sunlight, incandescent lamps up to 60 W can be used as lighting. More indicators are not welcome, as they can harm the eyes.
- Changing your usual diet towards increasing the consumption of fruits and vegetables.
- If you are busy at work that puts unnecessary strain on the visual system, it is necessary to take rest breaks.
- It is necessary to perform eye exercises on an ongoing basis. One of the easiest exercises to perform is focusing your gaze on objects at different distances.
- If the bulk of the working day is spent behind a computer monitor or is associated with another type of activity that has a negative impact on visual acuity, then the use of vitamin complexes is indicated.
- The text font should be large enough and easy to read.
- Massage of the collar area can also help prevent the development of asthenopia. After all, eye health depends on the timely flow of blood to the organs of vision.