Many people have experienced pain in the eyes and watery eyes - these are symptoms of conjunctivitis. But its complication is often encountered - blepharoconjunctivitis. Every person values their vision, so timely identified and treated eye diseases make it possible to preserve it in its original form. What is blepharoconjunctivitis? Let's figure it out.
Forms of the disease
With conjunctivitis, there is a burning sensation and pain in the eyes, lacrimation, but when the eyelids are included in this process, blepharoconjunctivitis is formed. The clinical picture is a set of symptoms characterizing blepharitis (eyelid hyperemia) and conjunctivitis. When these symptoms come together, treatment becomes quite difficult. The risk zone includes both children and adults.
The disease has several forms:
- Acute, characterized by the appearance in a short time.
- Subacute. It mainly affects children. Appears gradually, in the initial period in the corners of the eye sockets.
- Chronic . The infection is of a sluggish nature, aggravated by periods. Sometimes without symptoms.
Varieties
- Allergic blepharoconjunctivitis. Caused by individual increased sensitivity of the body to a specific allergen.
- Bacterial (epidemic). It is provoked by staphylococcus.
- Seborrheic (dermatic). The background for development is severe seborrheic dermatitis or rosacea.
- Demodectic blepharoconjunctivitis. It is caused by the parasitic demodex mite.
In hot climates, a person can become infected with the Koch-Wicks bacillus. Blepharoconjunctivitis, provoked by the Koch-Wicks bacillus, is of an acute epidemic nature. It spreads through the unwashed hands of a sick person, infected things and objects. It is characterized by outbreaks of the disease in hot climates, especially among children. Blenorrheal blepharoconjunctivitis occurs in infants infected with gonococcus during childbirth by a mother with untreated gonorrhea. Blepharoconjunctivitis, caused by the Morax-Axenfeld bacillus, is subacute in nature, chronic and localized in the corners of the eyes.
Causes
According to statistics, inflammatory (infectious, allergenic) eye diseases account for up to 40-50% of the outpatient flow of patients to see an ophthalmologist, and the bulk of them are patients with red eye syndrome. Among possible inflammatory diseases of the organs of vision, conjunctivitis is more common - up to 67% and blepharitis - about 23%.
According to the total number of cases of diseases, demodectic blepharitis and blepharoconjunctivitis make up, according to various sources, 39-88%, which indicates a fairly high incidence rate. Typically, infection of the conjunctiva occurs from the outside; autogenous infections are possible.
Also predisposing factors are microtrauma of the conjunctiva, previous infections, myopia, astigmatism, as well as a general weakening of the body due to hypothermia/overheating.
As a rule, blepharoconjunctivitis is contagious because it has a viral (adenoviral) nature of infection, less often - allergenic. The causative agents of blepharoconjunctivitis can be microorganisms of pathogenic coccal nature (pneumococci, streptococci, gonococci, staphylococci, Koch-Wicks and Morax-Axenfeld bacilli), as well as microscopic Demodex mites.
Causes and types
Blepharoconjunctivitis has several types:
- Bacterial. The causative agent is Staphylococcus aureus. A large amount of purulent discharge appears from the eyes. When one organ is affected, most often the second is involved in the disease process if the infection cannot be eliminated immediately.
- Scaly (seborrheic). Scales similar to dandruff appear on the edges of the eyelids.
- Allergic . Reaction to interaction with any allergens.
- Meibomian blepharoconjunctivitis. Characteristically, there is a secretion from the meibomian glands that glues the eyelids together and has an opaque appearance.
- Demodectic. It is a consequence of infection with demodectic mites.
- Viral. The main cause is the presence of herpes or adenovirus infection. It may appear after or during a viral illness. It can be observed in childhood.
Factors that contribute to the appearance and development of blepharoconjunctivitis:
- weakened immune system;
- unbalanced diet (consumption of foods low in vitamins);
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, ENT organs;
- allergy;
- anemia;
- myopia, eye injuries;
- the presence of worms;
- recurring viral infections;
- long-term use of antibacterial drugs.
Etiology of the disease
Blepharitis in children.
Source: o-krohe.ru In the vast majority of cases, pathology occurs due to excess sebum, which accumulates on the edges of the eyelids. This phenomenon provokes bacteria to actively reproduce, resulting in inflammation.
Blepharitis may be accompanied by seborrheic dermatitis, in which case dry skin patches on the face or scalp begin to peel. An allergic reaction may occur, which is accompanied by redness of the skin.
Blepharitis in children occurs when basic hygiene standards are not observed, if the child has been exposed to the wind for a long time, if vision is impaired, or if there are parasites or infections in the body.
Numerous microorganisms can cause blepharitis in a child - molluscum contagiosum, herpes virus, fungi, mites, staphylococcus and others. Sometimes the cause may be chronic anemia, vitamin deficiency, diseases of the oral cavity and nasopharynx, and problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
Risk factors
The most common provocateurs of blepharoconjunctivitis are:
- weakened immunity;
- poor nutrition;
- vitamin deficiency;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- myopia, other pathologies;
- anemia;
- eye injuries;
- neglect of personal hygiene rules;
- viruses, such as ARVI, influenza;
- fungi;
- infection with worms;
- caries;
- proximity of allergens;
- diseases of the ear, nose and throat, such as tonsillitis;
- long-term use of antibiotics.
Rarely does any single cause lead to the development of the disease; as a rule, blepharoconjunctivitis requires a combination of a whole range of factors. Blepharoconjunctivitis is an acquired disease from which even a newborn baby is not immune: during childbirth there is a risk of eye infection.
Symptoms
Manifestations of the disease vary so much that a person cannot independently determine what type of illness he has. Therefore, if you have the slightest concern in the eye area that lasts for more than three days, you need to seek qualified help from a specialist (ophthalmologist). Symptoms of blepharoconjunctivitis are determined depending on its type. The common signs that unite each type of disease are:
- swelling of the eyelids;
- lacrimation;
- reduced eye shape;
- red eyes, photophobia;
- thickening of blood vessels;
- eye fatigue.
Each blephoroconjunctivitis has its own characteristics, regardless of the general symptoms:
- The bacterial species is characterized by the appearance of ulcers at the base of the eyelids and abundant discharge of pus, with slight redness.
- Seborrheic – characterized by constant strong burning and redness (of the whites and conjunctiva) in the eyes, the edges of the eyelids peel.
- Allergic – manifests itself in the presence of an allergen. Patients experience severe watery eyes, swollen eyelids, and itching.
- Viral - accompanied by severe redness, lacrimation, and body hyperthermia may be observed.
- With meibovian blepharoconjunctivitis, an accumulation of secreted opaque secretion is added in the corners of the eyes, with demodectic blepharoconjunctivitis - scales located between the eyelashes.
Read in a separate article: Is it possible to wash with conjunctivitis, swim in a sauna and pool?
Drug therapy
Depending on the degree of the disease and the age of the patient, the following groups of drugs for treatment can be prescribed for the treatment of demodectic blepharitis of the eyelids.
- Antibiotics in the form of drops: “Tafazol”, “Kolbiotsin”, “Eubetal”, “Prenacid”, “Carbachol”, “Acular”, “Okumetil”.
- Antibiotics in the form of ointments for blepharitis: Metronidazole, ichthyol and zinc ointments, Tobrex, Tsipromed.
- Antimicrobial agents, for example, Metronidazole.
- Antiseptics “Vitabakt”, “Okomistin” as a prevention of secondary infection.
The course of treatment usually ranges from two weeks to a month. After a few days, the first noticeable results should already appear. If this does not happen, then you need to contact an ophthalmologist, he will select another remedy. Long-term use of antibiotics is dangerous - there is a danger of developing superinfection and the growth of microorganisms that are immune to them, including fungi. Do not make your own diagnosis and treatment.
Only a specialist will select medications that will effectively cope with the disease. Inappropriate ointments or drops will only worsen the development of the infection and delay recovery.
What is the result?
You will strengthen your immunity. The inflammatory process is localized. The pain, itching and burning that tormented you will disappear. Redness and swelling will disappear. Metabolism in tissues, muscles and the cornea of the eyes will improve. Your body will begin a powerful process of regeneration and restoration. Immunity will increase. The risk of vision-threatening complications will be eliminated.
Powerful and effective treatment with the Vizulon device will quickly eliminate the clinical manifestations of the disease, localize the foci of pathology, and reduce the dosage of medications. This will allow you to live a full life and forget about your illness forever.
Your body will quickly cope with the inflammatory process and return to its normal functioning. Unpleasant symptoms of inflammation will disappear, appearance will improve and cosmetic defects will be eliminated. And most importantly, you do not have to worry about the serious consequences of the disease associated with deterioration or loss of visual functions.
Symptoms of the disease
What are the symptoms of blepharoconjunctivitis? Patients often complain of itching and burning in the orbital area. Sometimes a person develops a fear of light, a feeling of sand in the eyes. Tearing immediately begins if the patient looks at the rays of the sun or a bright lamp.
Redness and swelling appear around the eyes. Visual acuity decreases if part of the cornea is inflamed. In the presence of a bacterial pathology, patients suffer due to the periodic formation of pus with an unpleasant odor.
Watery discharge is present when the pathology is of viral origin. Patients complain of severe pain in the eyes. Nearby lymph nodes often become inflamed.
The allergic type is accompanied by bilateral damage to the eyeball. A viscous secretion is also released. But the lymph nodes do not become inflamed. You cannot wear contact lenses if you have this condition. This intensifies the described manifestations and increases irritability of the mucous membrane of the visual organ.
Treatment
Treatment of blepharoconjunctivitis is carried out locally. For viral blepharoconjunctivitis, drugs are prescribed in the form of Actipol, Poludan drops, Acyclovir tablets, which have an antiviral effect. The dosage and duration of use is determined by the patient's condition. The bacterial species requires treatment with antibiotics (Tetracycline, Ciprofloxacin), Metronidazole ointment and drops containing Dexamethosone. Treatment of eyelashes and eyelids with alcohol-based solutions is used for demodectic disease. Eye protection medications (Oftagel) are instilled in advance. To prevent infection from affecting your face, you should consult a dermatologist.
For all blepharoconjunctivitis, anti-inflammatory drugs are used. Drops have proven themselves to be effective in restoring damaged eye tissues. (Taufon, Taurine) The drug Systane Ultra can relieve dry eyes.
In combination with drug therapy, it is possible to use traditional medicine recipes, among which we can particularly highlight the use of herbal infusions (yarrow, calendula, and chamomile) for washing the eyes. You can use regular tea leaves for this purpose. A new gauze pad should be used to rinse each eye.
Treatment of blepharitis in children
Treatment Source: okulist.com.ua
Treatment of blepharitis in children depends on the clinical variant of the disease. In the treatment of a simple form of the disease, physiotherapeutic methods are used, for example, electrophoresis with solutions of antibacterial drugs or irradiation with UV rays. Systemic vitamin therapy and a hypoallergenic diet are prescribed.
Several times a day, the edges of the eyelids are treated with brilliant green or chamomile decoction, and then an antibacterial ointment (for example, tetracycline) is applied. In cases where ulcerative blepharitis occurs, before applying the ointment, the crusts are softened with sterile petroleum jelly or lanolin and removed.
For demodectic blepharitis, in addition to the above remedies, zinc-ichthyol ointment, alkaline drops, and also treatment of the facial skin with tar soap are used.
Treatment of chronic forms is difficult. It is recommended to continue therapy for a month after symptoms disappear. Local and internal treatment is carried out, including the fight against concomitant infections.
Meibomian blepharitis is treated with the methods described above. In addition, the eyelids are massaged (a glass rod is used for this) followed by smearing them with brilliant green.
Treatment of blepharitis in children is aimed, first of all, at eliminating the cause that led to the occurrence of blepharitis. Secondly, much attention is paid to the hygiene of diseased eyelids. The eyelids should be treated with an antiseptic solution; furatsilin solution is very suitable for this procedure.
All crusts that have formed on the eyelids are carefully soaked and removed with cotton swabs. You cannot treat two eyes with the same swab. Ulcers with blepharitis must be carefully treated with brilliant green.
During treatment of any form of blepharitis, systemic vitamin therapy is mandatory. It is necessary to review the child’s diet and balance it. In addition, you need to strengthen the child’s immunity through hardening and outdoor sports.
Important:
If necessary, treatment of blepharitis involves the prescription of immunostimulating agents.
To cure chronic blepharitis in a child, you need to be patient. After all, even if the clinical manifestations of the disease are eliminated, relapses may appear again soon if the disease is not fully treated.
Traditional recipes for the treatment of blepharitis
Treatment with folk remedies Source: poglazam.ru
Despite the fact that folk recipes are considered safe, they should not be used without consulting a doctor. Many medicinal herbs are poisonous and, if they get into the eye, can greatly aggravate the course of the disease. They are quite suitable for enhancing the effectiveness of drug therapy.
- You can use eucalyptus leaves, sage, calendula or chamomile to wash your eyes. Both infusions and decoctions can be made from these herbs. It is recommended to do 3-5 washes per day.
- Rose oil will help get rid of scaly blepharitis. They lubricate the child's eyelids to make it easier to remove scales. You can also brew rose petals and wash your eyes with this infusion.
- For the treatment of demodectic blepharitis, clover inflorescences are used; they relieve inflammation well. Collect, wash and chop the clover flowers, then squeeze the juice out of them. 3 drops should be instilled into each eye of the child once a day. It is recommended to make eyelid lotions from the remaining pulp.
- If blepharitis is of an allergic nature, then the first thing, of course, is to exclude the allergen that affects the child. If, after eliminating the allergen, there is still discomfort in the eyes, then they can be washed with a solution of boric acid; Lotions made from fresh cottage cheese help relieve inflammation from the eyes. To do this, you need to put a spoonful of cottage cheese in gauze and apply it to your eyelids.
- To cure meibomian blepharitis, traditional medicine recommends the following recipe: take a medium onion, boil it in half a liter of water, add 1 tbsp. l. honey and mix well. Rinse your eyes with this solution at least 5 times a day.
- To cope with chronic blepharitis, you will need thyme. You need to prepare a decoction from this plant and wash your eyes. For 1 tbsp. l. herbs you need to take a glass of boiling water.
- Burdock oil helps with seborrheic form. They need to remove crusts from their eyelids and lubricate them before going to bed.
- If you mix half a glass of black and green tea and add a dessert spoon of dry grape wine, you will get a solution that is very useful for washing your eyes with blepharitis.
Massage is also very useful for blepharitis. Buy a special stick at the pharmacy. There is a spatula at one end and a ball at the other. The end with the spatula massages the eyelid, and the side with the ball is convenient for applying ointment. You need to massage the eyelid from the outer edge to the inner.
Therapy for blepharoconjunctivitis
It is necessary to treat the disease in accordance with the etiology and characteristics of its course. An effective treatment regimen for blepharoconjunctivitis is prescribed by a qualified ophthalmologist. If necessary, consultation with an infectious disease specialist, dermatologist, or allergist is carried out. Self-medication is unacceptable. During therapy, it is important to eat properly and follow a daily routine.
Removal of secretions from the conjunctival cavity is carried out by washing the eyes with antiseptic and disinfectant liquids.
For bacterial forms of pathology, erythromycin ointment can be effective. Basically, the treatment of blepharoconjunctivitis is carried out using drip solutions and liniments for local action. The table shows drops and ointments used for blepharoconjunctivitis of various etiologies:
| View | Group of drugs | Name of drugs |
| Bacterial | Antibacterial | "Tobrex" |
| Dibiomycin ointment | ||
| Erythromycin ointment | ||
| "Sintomycin" | ||
| Tetracycline ointment | ||
| Sulfanilamide | "Albucid" | |
| "Sodium sulfate" | ||
| Viral | Antiviral | "Poludan" |
| "Aktipol" | ||
| "Oftan" | ||
| "Trifluridine" | ||
| Seborrheic | Antifungal | "Fluconazole" |
| "Ketoconazole" | ||
| "Metrogil" | ||
| Allergic | Antihistamine | "Allergodil" |
| "Fenistil" | ||
| "Eden" | ||
| "Sodium cromoglycate" | ||
| "Olopatadine hydrochloride" |
Solcoseryl will help restore damaged corneas. For any type of blepharoconjunctivitis, patients are recommended to take vitamins A, B, C. If the cornea is damaged, medications are prescribed that stimulate its regeneration, including: Solcoseryl, methyluracil ointment. It is contraindicated to apply an aseptic dressing, as secondary keratitis may result.
Treatment with folk remedies
You can supplement the main therapy with traditional medicine. Herbal decoctions that have bactericidal and antiseptic effects are used. Treatment with folk remedies should be carried out with the permission of the treating specialist. Effective recipes for infusions that can be used to wash your eyes:
- Mix chamomile, calendula, sage, eucalyptus leaves (1 tbsp each).
- Brew the mixture with boiling water (200 ml).
- Leave for 10-15 minutes.
- Cool the liquid.
- Filter.
Another way:
Rose petals can be infused in boiling water and the resulting solution can be used to wash the visual organs.
- Collect 1 tbsp. l. red tea rose petals.
- Pour boiling water (1 cup) overnight.
- Rinse your eyes with the resulting infusion in the morning.
For those suffering from chronic blepharoconjunctivitis, thyme infusion is recommended:
- Dry grass (1 tbsp) pour water (200 ml).
- Let it sit for a day.
Treatment of acute and chronic forms of the disease
Etiopathogenetic therapy is focused on eliminating the pathogenic factor as completely as possible. For viral infections, the basis of treatment is measures to strengthen the immune system (drugs containing interferon or stimulating its secretion); for bacterial infections, antibiotics of various spectrums of action are used, in various pharmaceutical forms and dosages (determined by the specificity and sensitivity of the pathogen, prescribed exclusively by a doctor, taken and discontinued only under medical supervision); for fungal infections - antimycotic ointments, drops, etc.
Allergic inflammation requires suppression of sensitivity to the allergen (if it cannot be radically excluded from the living space), i.e. prescribing a desensitizing and antihistamine regimen, often with the inclusion of hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Additionally, according to indications, various moisturizing, soothing, anti-inflammatory drugs can be prescribed, incl. decoctions of chamomile, calendula, sage, tea.
Blepharoconjunctivitis of dermatitis, fungal, demodectic, rosacea origin are, as already emphasized, therapeutically resistant and easily chronic diseases. Of primary importance in therapy are local antiseptic and antiparasitic procedures - washing, wiping, ointments (for example, based on ether, zinc, dimexide, etc.). For each specific case, the therapeutic strategy, usually combined (including immunostimulation and elimination of secondary infectious factors), is selected individually; treatment is usually long-term, with variable therapeutic success, i.e. the likelihood of relapses and exacerbations is very high.
Taking into account the above, the most effective treatment for blepharoconjunctivitis is its prevention: timely elimination of foci of infection and exacerbations of somatic or endocrine pathology, compliance with sanitary, hygienic and ergonomic standards, improving the diet, giving up destructive habits and self-medication. At the first signs of inflammation of the eyelids or conjunctiva, you should urgently see a qualified ophthalmologist, because even quite reasonable advice from a pharmacist from the nearest pharmacy or the use of folk remedies in practice often results in serious consequences.
Prevention
Methods for preventing the disease come down to following simple hygiene rules:
- do not touch your eyes with dirty hands, wash them often and thoroughly;
- do not use other people’s personal hygiene items;
- carry out timely replacement and treatment of contact lenses;
- avoid injury to the organs of vision;
- If infectious diseases occur, treat them promptly;
- Maintain cleanliness and order in the living area.
Blepharoconjunctivitis is an insidious disease which frequent relapses are possible, therefore, at the first symptoms, you must immediately consult a doctor and strictly follow his recommendations. The disease can only be defeated through the combined efforts of the patient and the doctor.
Causes
Causes of occurrence Source: zreniemed.ru
Most often, the causative agent of blepharitis in children is Staphylococcus aureus, which is activated in the body under certain conditions. However, the nature of the disease can also be parasitic or caused by various other factors.
The causes of childhood blepharitis can be:
- past infectious diseases;
- severe fatigue (both physical and mental);
- hypothermia;
- demodex mite, which gets into the eyelash bulbs when the baby comes into contact with birds, down and feather pillows, as well as in case of chronic gastrointestinal problems, diabetes, various types of allergies, focal points of infection;
- weakened immune system;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract (colitis, gastritis, cholecystitis);
- constant visual tension;
- diabetes;
- worms;
- dirt getting under the eyelids;
- sensitivity to various irritants (pollen, cosmetics, dust);
- metabolic disorders in the body;
- bleeding from a diseased tooth, tonsils in chronic tonsillitis;
- refusal to wear glasses if you are farsighted, as the eye muscles suffer from tension and fatigue;
- avitaminosis;
- rubbing the eyes with dirty hands;
- anemia;
- external atmospheric phenomena: exposure to wind, smoke, dust.
If parents know exactly what causes can cause such an unpleasant disease in a child as blepharitis, they can somehow protect the eyes from infection. First, teach him to follow basic hygiene rules. Secondly, introduce him to a healthy lifestyle from an early age.
Thirdly, treat any internal diseases in a timely manner. If it was not possible to protect the baby, you need to see the first signs of blepharitis in a timely manner. This will allow treatment to begin as early as possible.
What will happen if left untreated?
In most cases, the development of blepharoconjunctivitis leads to severe complications that pose a real threat to your health and visual acuity, up to and including complete loss of visual function. Among these complications:
- Trichiasis (abnormal eyelash growth)
- Scar deformation of the eyelids
- Chalazion (chronic inflammation of the periciliary gland)
- Keratitis
- Loss of vision
If you do not take urgent measures or use ineffective treatment, then powerful pathological processes will inevitably start in your body, which will lead to serious disorders of visual function. The progressive inflammatory process will not only cause discomfort and pain, but will also jeopardize your vision.
Complications of blepharoconjunctivitis can cause partial or complete loss of visual functions, lead to irreversible consequences and forever deprive you of the usual joys of life. Timely treatment will help the body quickly cope with inflammation and begin the recovery process.
General information
Blepharoconjunctivitis is an infectious or allergic inflammatory process of the mucous membrane of the eye (conjunctivitis), leading to disease of the eyelid margins (blepharitis). Both diseases occur simultaneously.
Blepharoconjunctivitis often develops into a chronic form and is difficult to treat. It is dangerous due to complications such as inflammation of the cornea, leading to deterioration or loss of vision. Contagious.
Classification
There are blepharoconjunctivitis:
- Epidemic, divided into acute and chronic. It is characterized by:
- redness of the eyes without any significant changes in the eyelids;
- purulent mucous “collars” at the base of the eyelashes;
With epidemic blepharoconjunctivitis, pus appears on the eyelashes
- small erosions along the ciliary edge;
- eyelash loss.
If the pathogen is viral in nature, then blepharoconjunctivitis begins acutely with lacrimation and a rash of small blisters on the inner fold of the conjunctiva.
- Seborrheic blepharoconjunctivitis develops as a consequence of seborrhea (increased production of sebum by the sebaceous glands with the formation of dandruff) or rosacea (small pink acne with purulent heads). Its symptoms:
- hyperemia of the conjunctiva and sclera of the eyes;
- an unpleasant burning sensation and “sand in the eyes.”
Seborrheic blepharoconjunctivitis can be recognized by the hyperemic sclera of the eyes
- The allergic type of disease has various manifestations, its main symptom is its occurrence in connection with the action of some allergen. Symptoms may become more intense after eating spicy, spicy foods.
- Demodectic. Its characteristic symptoms:
- severe itching of the eyes, especially painful in the morning;
- sticky discharge with epithelial scales accumulating on the eyelashes.
Pathogenic factors (causes)
To date, there is no single, statistically reliable idea of the role and correlation of the main causes of blepharoconjunctivitis. In most sources, blepharoconjunctivitis is divided according to etiopathogenetic criteria into three types.
Infectious, in which different classes of pathogens are characterized by specific features of the clinical picture:
- viral inflammations, as a rule, begin acutely, against the background of the general symptoms of ARVI, and are manifested by photophobia, burning, foreign body sensation, hyperemia, pain, lacrimation;
- The distinctive features of bacterial infections are abundant mucopurulent discharge, beginning in one eye with possible involvement of the other, swelling, redness, and in severe cases, ulceration of the eyelids, conjunctiva, and cornea;
- similar in nature, but, as a rule, less pronounced and much more persistent symptoms are inherent in fungal infections; typical is the formation of various kinds of films, “gluing” mucous accumulations, nodules and erosions on the skin of the eyelids.
Allergic reactions usually develop as part of a more general, systemic reaction, and are characterized by irresistible itching (especially along the edge of the eyelids), lacrimation, severe swelling of the eyelids, and violent accompanying symptoms from the nasopharynx.
Seborrheic (dermatic) are caused by functional disorders in the eyelash follicles and sebaceous glands; manifested by peeling, accumulation of dandruff flakes and scales on the eyelids and eyelashes, itching, a feeling of rough dryness, and a tendency to secondary infection when scratching.
A number of provoking and potentiating factors are also described:
- ametropia (refractive errors) to a strong degree in case of refusal of optical correction, which causes constant eye strain;
- exhaustion of the body, weakened immune system, anemia, hypovitaminosis;
- endocrine and other disorders in which the biochemical composition of the secretion of the eye glands may change;
- “pink” acne (a common cause and companion of the so-called “blepharitis rosacea”);
- the presence of multiple microtraumas and damage to the conjunctiva, which creates conditions for secondary infection. Such trauma can be associated with constant mechanical, physical or chemical irritation (dust, ultraviolet burns, aggressive fumes, etc.), as well as with the activity of a microscopic skin parasite - the Demodex mite.
The last factor should be discussed in more detail.
Complications
Blepharoconjunctivitis is not a harmless pathology.
In some cases, the disease can lead to adverse consequences.
Possible complications:
- secondary ectropion of the century,
- development of keratitis, chorioretinitis,
- dacryocystitis,
- dry eye syndrome,
- cicatricial entropion,
- orbital phlegmon,
- extremely rarely - thrombosis of the sigmoid sinus.
Remember! To prevent such diseases, it is necessary to take a responsible approach to the treatment of the disease and strictly adhere to medical recommendations.
Diagnostics
To make a correct diagnosis, an ophthalmologist conducts laboratory and instrumental research methods .
First, the doctor collects a thorough medical history, trying to find out the cause of the disease, and conducts a visual examination. Then he proceeds to diagnose:
- Visometry. With blepharoconjunctivitis, most often visual acuity is slightly or not at all impaired.
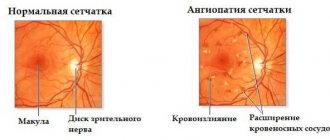
- Biomicroscopy. The doctor detects swelling and redness of the conjunctival vessels and skin of the eyelids. Pathological discharge accumulates along the peripheral edge.
- Fluorescein instillation test. This method allows you to detect violations of the integrity of the tear film.
- A swab-scraping from the conjunctiva followed by bacterial culture. With the help of diagnostics it is possible to identify the etiology of the disease.
Reference! If necessary, the ophthalmologist can prescribe a consultation with specialized specialists - an allergist, a dermatologist, an ENT doctor.
With their help, therapy is selected aimed at completely eliminating the cause of the disease.